Key Takeaways
- Staking nodes enhance blockchain security and offer passive income opportunities.
- Dedicated servers for staking ensure improved performance, security, and control.
- Regular updates and secure server access are essential for maintaining node integrity.
- Integration with DeFi opens new avenues for liquidity and yield generation.
- Automation and AI technologies streamline node management and optimization.
- The future of staking nodes involves specialization, enhanced security, and AI-driven solutions.
- RedSwitches provides the infrastructure and support needed for successful staking on servers.
Many people have found staking in cryptocurrencies as a profitable alternative to energy-intensive mining. However, to fully realize the benefits of staking, one needs to go beyond simple involvement and operate a staking node on a server. Despite its intimidating appearance, this project offers a wealth of benefits, protection, and control over your digital assets.
Today, we set out to simplify this process, turning what seems like a complex undertaking at first glance into a rewarding and doable trip. Setting up your own staking node is a step towards financial empowerment and contributing to the blockchain ecosystem, regardless of your level of experience with cryptocurrencies or your curiosity as a novice.
Now that we’re in the realm of Node Staking, we can flip the key and start earning a consistent passive income from the comfort of your server.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Staking Node?
- How do Staking Nodes Differ from Traditional Staking?
- Benefits of Using a Dedicated Server for Staking
- Staking Node Installation on Dedicated Server
- Security Practices For Securing Your Staking Node
- Troubleshooting common issues
- Future of Staking Nodes on Dedicated Servers
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Staking Node?
Credits: Freepik
A crypto staking node is crucial for a proof-of-stake network. A computer or server that engages in the blockchain network by staking, holding, and locking a portion of the native coin is known as a staking node.
The node validates transactions, generates new blocks, and preserves the network’s integrity. This is in exchange for the opportunity. PoS systems use asset ownership to reach consensus and protect the network. This is different from PoW systems, which rely on computing power.
Staking nodes are for more than just keeping money in wallets. Nodes validate blocks and transactions per network rules. They improve blockchain security and allow node operators to suggest protocol changes. Node operators use them to vote on proposals. Collateralized stakes ensure node operators act in the network’s best interest. Malice or negligence may result in penalties, such as stake reduction.
Running a staking node has several benefits. Users receive rewards based on their stake, like transaction fees or extra coins from the network. This method promotes a secure network. It also offers stakeholders passive income.
Second, maintaining a staking node helps the network become more decentralized. The network grows more resistant to failures and attacks the more nodes that operate independently.
How do Staking Nodes Differ from Traditional Staking?
Credits: Freepik
Blockchain networks’ proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism relies on traditional staking and staking nodes. However, they have various functions and differ in terms of reward structures and levels of involvement. Anyone wishing to participate in the staking ecosystem must be aware of their subtle differences.
Traditional Staking
A more accessible way to participate in a PoS network is through traditional staking. To keep the network running, a certain quantity of bitcoin must be kept and locked in a wallet. In traditional staking, a stakeholder ” votes” with their tokens for the security and consensus of the network.
They receive staking rewards based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. Rewards are usually proportional. This method does not always require a full node. It is more straightforward and more user-friendly for cryptocurrency users. Conventional staking is typically accomplished through a staking pool or a blockchain wallet.
Staking Nodes
Conversely, operating a staking node signifies more extraordinary dedication and involvement inside the network. Staking nodes’ tasks are maintaining the blockchain, creating blocks, and verifying transactions. You need to control and operate a server or node that is always available. This involves performing essential network operations and staking a specific number of tokens. Staking nodes are vital for the network’s integrity. They boost security and consensus.
There is a corresponding disparity in remuneration for varying levels of responsibility. Operating a node requires extra expenses and work. Staking node operators can earn larger payouts than regular stakers. These incentives cover the cost of the electricity and processing power used to keep the node running and the return on the amount staked.
Also Read CMS Security: 4 Types of Threats and 9 Tips To Prevent It
Important Differences
Technical Knowledge: Since running a staking node entails configuring, protecting, and maintaining a server, technical knowledge is required. Traditional staking involves less technical expertise and is easier to understand and utilize.
Investment: Operating a staking node frequently necessitates additional investment in dependable hardware and continuous expenses like electricity and internet services on top of the initial staked token investment. On the other hand, traditional staking mainly entails investing in the stake.
Risk and Return: Because staking nodes provide value to the network, they frequently have a bigger potential payout. However, they also come with a higher risk, which includes the potential for penalties (slashing) for not meeting network requirements or experiencing outages. Conventional staking provides a safer, more passive source of revenue.
Contribution to Network: By actively taking part in consensus and validation procedures, staking nodes substantially contribute to the network’s security and well-being. By offering financial collateral, traditional staking contributes more passively to network security.
Benefits of Using a Dedicated Server for Staking
Using a server for staking has many advantages. This is especially true when operating a staking node. These advantages can significantly improve the staking procedure’s effectiveness, security, and financial gain. Dedicated servers offer more robust security, more control, and dedicated resources. Here’s a thorough examination of the main advantages:
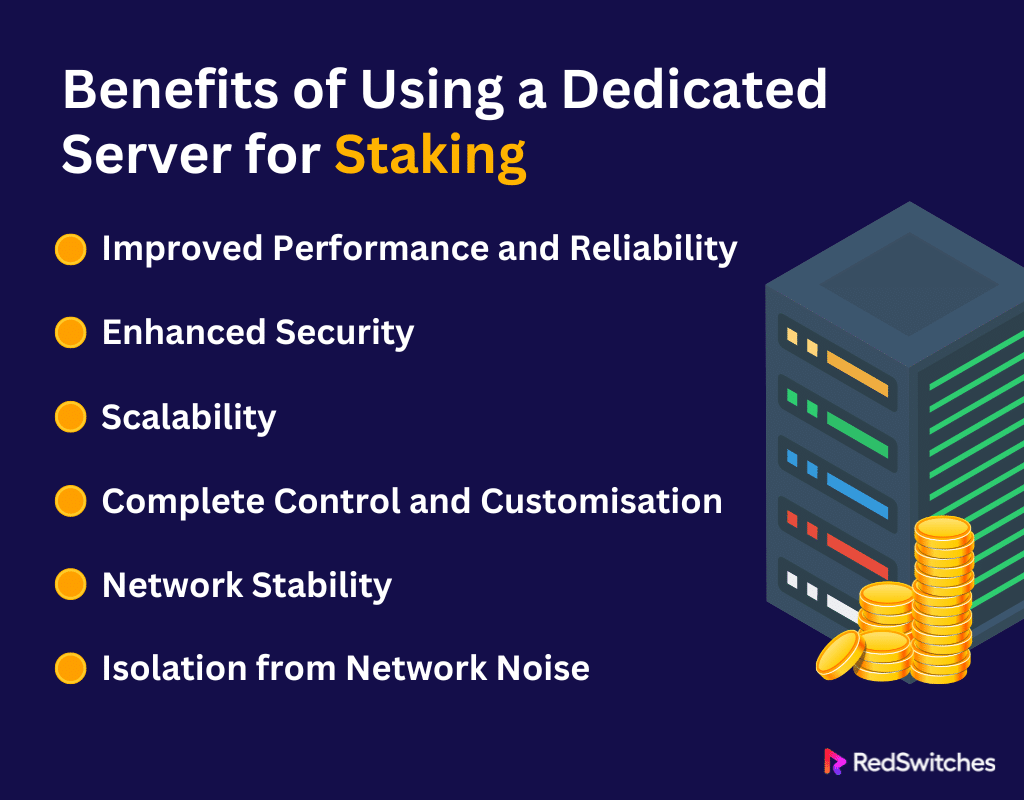
Improved Performance and Reliability
A server ensures your staking node runs smoothly without interference. It provides exclusive access to its CPU, memory, and storage resources. Downtime or performance issues may result in missed transactions or fines in some staking protocols. This is vital for keeping staking nodes running smoothly. Dedicated servers ensure network uptime and maximize returns with provider guarantees.
Enhanced Security
A strong security perimeter is crucial for your business in the digital world. Cryptocurrencies are involved. Dedicated servers provide an impregnable barrier against the constant attacks on the internet. You can customize your security protocols to meet the unique requirements of your staking node when you have a server. Customization goes beyond generic solutions. You can install security protocols, encryption, and firewalls to protect your node from attackers. Data centers with servers enhance security, protecting hardware from threats.
Scalability
Staking operations must grow. Dedicated servers support this development. Because staking activities and cryptocurrency markets are dynamic, you need a platform that can grow with you. The scalability of servers is exceptional; they allow for easy CPU, RAM, and storage capacity upgrades. Your staking node can handle more transactions and stake different cryptocurrencies. Save time, expand resources, and avoid moving servers. Your node will perform nicely and seize new opportunities.
Complete Control and Customization
Credits: Freepik
A server allows you to design the server environment according to your specifications. Its sovereignty is unmatched. You can adjust every server component to match your staking node’s needs. Fine-grained control optimizes performance, strengthens security, and ensures dependability. Customizing is crucial in cryptocurrencies and blockchain. Minute inefficiencies can lead to risks or lost opportunities.
Position your staking node within the blockchain network to thrive. Utilize a server for optimal performance.
Network Stability
Your network connection’s speed and stability are crucial in blockchain operations. Every millisecond matters. Modern data centers house servers, forming a reliable network foundation. Many power sources, backup generators, and several internet pathways are built into these data centers. Outside disturbances won’t affect your stake node. Your staking node must maintain essential capabilities. This includes processing transactions in real time and participating in the consensus process seamlessly. This depends on unwavering connectivity. Sturdy infrastructure ensures your activities flourish with unmatched network performance.
Isolation from Network Noise
The internet has interruptions and diversions, especially in shared hosting. Others’ behaviors may infringe on your privacy. Dedicated servers provide a protective barrier between your staking node and the din of “network noise.” This isolation means the resources for your server are only for you. Other users’ requests won’t affect them. This exclusivity is essential to sustaining the steady performance for successful staking operations. Your server’s processing power is focused solely on your staking node. This maximizes response times and processing speeds. This isolation strengthens your node’s defenses against outside threats while improving operating efficiency.
Also Read: Automated Staking Scripts and Tools for Server-based Nodes
Staking Node Installation on Dedicated Server
Credits: Freepik
Installing a staking node on a server demands technical expertise and a calculated strategy. To receive staking rewards, follow the blockchain network’s consensus process. This comprehensive guide will walk you through setting up your staking node on a server:
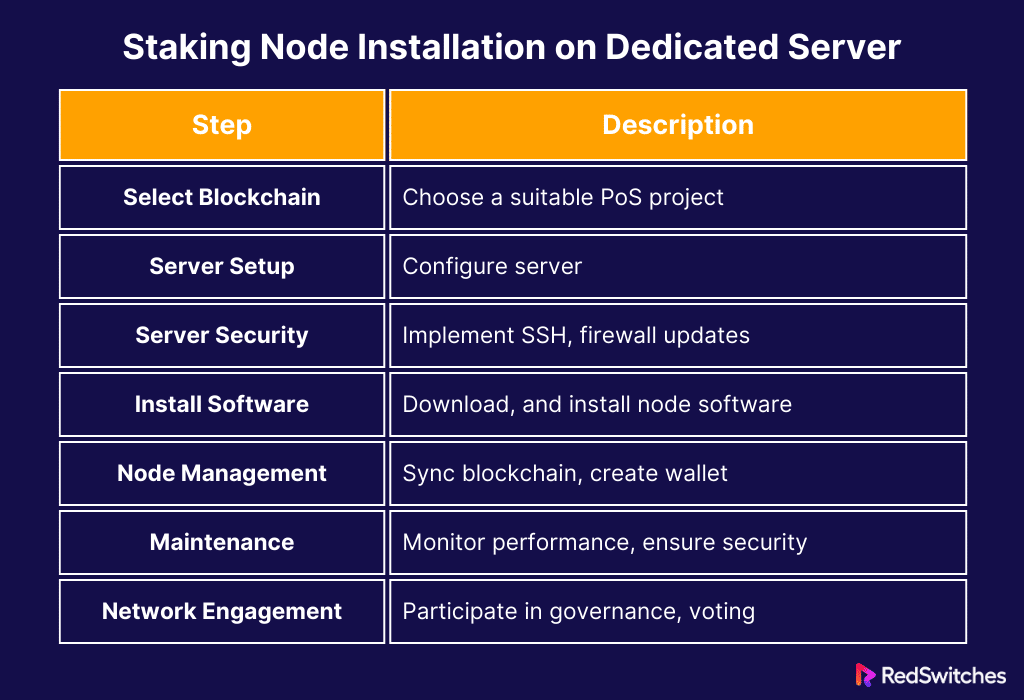
Selecting the Appropriate Blockchain and Staking Conditions
Explore blockchain projects using proof-of-stake before committing to a staking node. Search for projects with an active community and staking rewards that align with your goals and show growth potential. Fully understand the requirements of the selected blockchain. These requirements will determine the minimal stake and hardware/software needs for running a node. This first stage ensures a clear path and the knowledge you need to start your staking endeavor.
Setting Up Your Dedicated Server
Choosing the right server provider is essential. It depends on whether the provider meets your blockchain project’s hardware requirements. Consider the server’s geographic location, uptime, and customer support. Maximize latency and network connectivity. After choosing, you must configure your server to meet the unique needs of the blockchain. Choose a suitable operating system, like Linux, and set up your network. This is crucial in building a safe and solid base for your staking node.
Protecting Your Server
Protecting your server is the first line of defense against online threats for your staking node. Creating SSH keys removes risks from password logins. SSH keys provide secure, encrypted connections. Password logins are susceptible to brute-force attacks. This first action lays the groundwork for a secure server environment. Limit potential access points for attackers. Set the firewall to allow only necessary ports for your node’s operations. Strengthen your server’s defenses. Create a virtual moat around your staking node. Updating your server software regularly is essential. It protects from the latest exploits and vulnerabilities that can harm your node.
Installing Node Software
After securing your server, you can install the node software essential to operationalizing your node. Download the official software through the blockchain project’s approved channels to start securely. Avoid the risk of installing corrupted or harmful software. Follow project-specific instructions carefully. Extract files, run scripts, and modify parameters to fit the node’s functionality. Pay close attention to detail during the installation procedure to align with blockchain protocols. This phase may require installing additional dependencies like libraries supporting the node’s software. Databases holding blockchain data may also be necessary for smooth operation.
Setting Up and Managing Your Node
The next important step is to start the blockchain synchronization process when the node software has been deployed. Your node must validate each transaction on the blockchain from the beginning to accurately show the network. The procedure may take some time because of the blockchain’s size. It’s essential for your node to function correctly. After synchronization, creating a dedicated wallet for your node is critical. Your staking tokens, essential for using the network’s staking mechanism, are stored in this wallet. It stores your digital assets and rewards you for validating them.
Observation and Upkeep
A staking node’s vitality is found not just in its initial configuration but also in its continuous upkeep and observation. Implement advanced monitoring tools to measure your node’s performance and ensure efficient operation. These tools offer real-time insights into CPU usage, memory consumption, network latency, and bandwidth. Making proactive modifications is easier. Network connectivity is crucial for prompt transaction validation. A reliable and fast connection to the blockchain is essential. Security monitoring solutions protect the node and staked assets from hostile actors. They provide an extra defense by detecting weaknesses and potential breaches.
Engaging in the Network
Running a staking node entails a privilege that includes active network governance involvement. Numerous blockchain initiatives provide its node operators the capacity to shape the project’s course using vote and proposal submission processes. Decentralized networks are built on this foundation of governance involvement, which enables a democratic method of decision-making. By participating in governance, you can ensure that your interests as a node operator are reflected and that the network’s development is in line with the needs of its users, in addition to helping the blockchain evolve.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
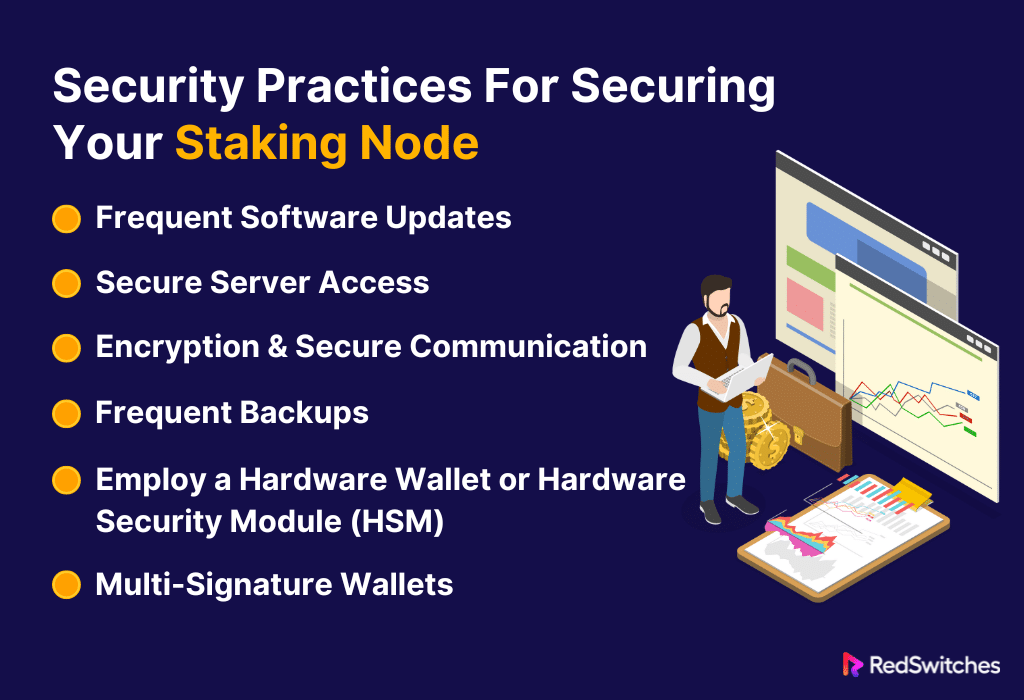
Security Practices For Securing Your Staking Node
Safeguarding a staking node is crucial in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Stakes are high, and threats constantly evolve. Implement robust security procedures to protect your staking earnings. Ensure the integrity of the blockchain and maintain your node’s operation. The following comprehensive security procedures are necessary to protect your staking node:
Frequent Software Updates
Regularly update your node’s software and dependencies to secure your staking activities. Upgrades fix vulnerabilities and boost performance. This increases your staking node’s effectiveness. Automate updates for security and performance to reduce vulnerability. However, it is imperative to proactively stay informed about upgrades that require manual involvement through official blockchain project channels.
Secure Server Access
Enhancing your server’s access control reduces the risk of unwanted access and sets the groundwork for a safe staking node. SSH keys improve security by preventing unauthorized access through guessing or brute-force attacks. A well-configured firewall limits access to essential ports and services. This deters potential invasions, increasing security. To protect your node, encrypt your internet traffic with VPNs or dedicated networks for staking. This adds extra security against external attacks.
Encryption & Secure Communication
Encryption methods like TLS should be used for all node communications to ensure data integrity and secrecy while in transit. By effectively thwarting attempts at data interception and eavesdropping, this encryption ensures that private information stays out of the hands of nefarious individuals. Ensuring a secure communication channel is crucial in staking.
Transactions and node communications can be targets for exploitation. It preserves your node’s reliability and trustworthiness. This promotes a secure environment for staking activities and protects against data tampering.
Frequent Backups
Credits: Freepik
The key to a successful staking operation is regularly backing up important node data. This includes wallet contents and configuration details. Encrypt and securely store backups off-site to quickly restore your node in case of data loss. Use trustworthy cloud services for additional security. Preventive action ensures steady stake contributions. It guards against hardware failures, cyberattacks, and disasters. It offers a quick recovery path.
Employ a Hardware Wallet or Hardware Security Module (HSM)
Hardware wallets or HSMs raise security for staking nodes with large asset values. These gadgets are designed to protect private keys from both physical and virtual dangers. Transaction signatures are done inside the device. Your keys stay safe from online exposure. High-stakes scenarios require secure private keys to ensure node security.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple approvals before executing transactions. This setup is crucial for minimizing compromised credentials. It ensures that all transactions, massive transfers, undergo a rigorous verification process. The multi-signature system divides authority among entities. This lowers unauthorized transactions, improving staking rewards security. This technique strengthens staking rewards against exploitation. It enhances security for your node.
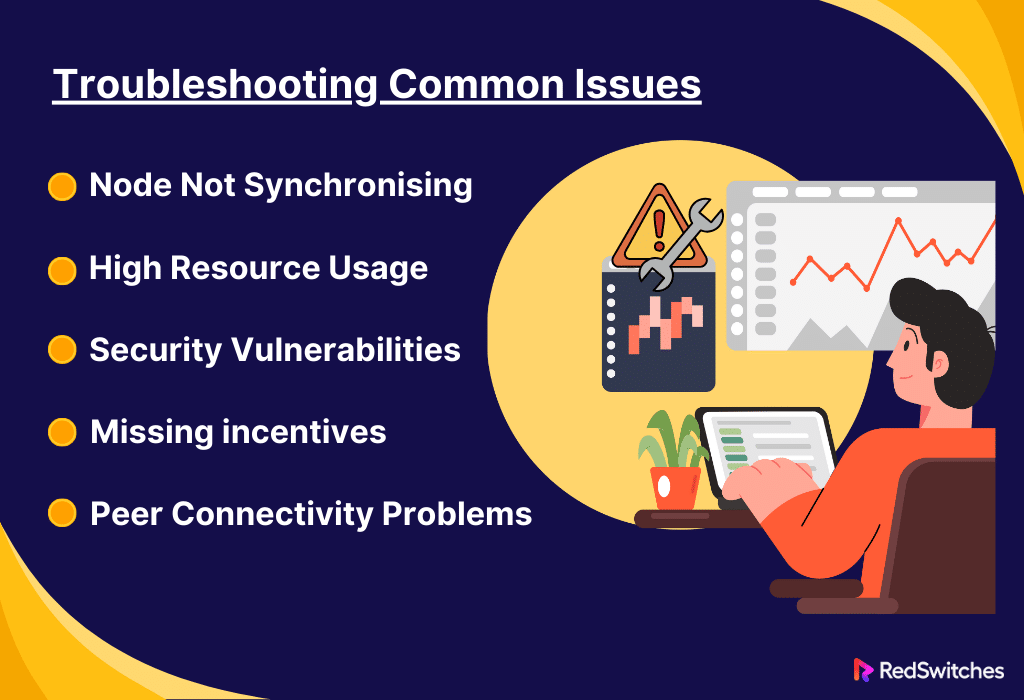
Troubleshooting common issues
Troubleshooting staking nodes involves finding and fixing issues that impact functionality, security, or communication. Here are thorough descriptions of how to handle some of the most typical problems that arise when staking nodes:
Node Not Synchronising
A staking node cannot create or validate blocks without syncing with the blockchain network. To solve this problem, ensure your node has a fast internet connection. A weak connection can negatively affect the node’s capacity to maintain network synchronization.
Check the node’s configuration for faults. Misconfigured settings can cause connection issues. Update your node’s software to the latest version for compatibility with modern network protocols.
Out-of-date software may not function properly. Check your firewall and port settings to ensure your node can connect without restriction. Verify that traffic on the blockchain ports is allowed.
High Resource Usage
A node may perform poorly or crash using too much CPU, memory, or disc space. Change the node software settings for better resource management. Adjust memory allocation, cache sizes, and database procedures to reduce excessive resource usage.
Upgrade your server’s hardware if resource use is too high for running a staking node. Additionally, look for any indications of malware or unauthorized access, as these can also result in higher resource usage. A thorough security audit can assist in locating and resolving such problems.
Also Read Clean YUM Cache in Linux, Red Hat, and CentOS [4 Easy Solutions]
Security Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities in security put your staking node’s integrity and the assets it contains at serious risk. Regularly update the software to fix potential vulnerabilities. Attackers could exploit them. Restrict access to the node’s administrative interfaces to trusted IP addresses.
This strengthens the defense against unauthorized access. Implement strong access controls, like using unique passwords and SSH keys. To quickly take action to secure the node, monitoring tools should be implemented to identify any unexpected behavior or changes in node configuration that might point to a security breach.
Missing incentives
Credits: Freepik
If you do not receive the anticipated staking incentives, it can be worrying. As several blockchains have particular reward requirements, it’s a good idea to confirm that your node is actively participating in the consensus process.
It’s also crucial to check the status of your staked tokens to ensure there are no problems, such as being in an unbinding period that keeps them from being eligible for awards. You can ascertain whether there is a problem with your awards by clearly understanding the blockchain’s reward distribution system, which will also assist you in understanding how rewards are computed and dispersed.
Peer Connectivity Problems
For a node to maintain blockchain synchronization, it must be able to establish peer connections. Make that your node’s peer list is filled with healthy peers if you’re having trouble connecting; manually add known good peers if needed.
Modifying firewall rules or NAT setups on the network might be necessary to enable peer-to-peer communication. Restarting the node can sometimes fix connectivity problems and renew its connections, allowing it to rejoin the network and continue functioning as an active node.
Future of Staking Nodes on Dedicated Servers
Credits: Freepik
Blockchain protocols, cryptocurrency use, and technological improvements will affect staking nodes. These nodes run on servers. Staking nodes on servers will change as the blockchain ecosystem evolves. This is a thorough analysis of potential developments for staking nodes on servers in the future:
Enhanced Specialisation and Professionalism
The blockchain ecosystem is evolving. This evolution creates a higher demand for specialized staking services. This leads to a more complex and professional staking environment. Operators will develop exclusive technologies and procedures for staking. They will also invest in advanced hardware and software.
This specialization will likely lead to developing custom staking protocols and creative tactics. These tactics will take advantage of untapped blockchain market prospects. Specialized consulting services that optimize staking operations may become more prevalent. These services cover technical setup, security, financial planning, and regulatory compliance.
Enhanced Security Measures
Staking nodes have a strategic role in blockchain networks. They are valuable targets for cyberattacks. Operators must use a multi-layered security strategy. Security measures will include advanced technology like quantum-resistant algorithms.
These will surpass traditional methods to counter threats from quantum computing. Developing and using Advanced HSMs and multi-signature wallets will enhance digital asset protection.
Integration with Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
Staking nodes and DeFi can create new opportunities for liquidity, yield, and financial innovation. Staking assets in DeFi could create new financial products using unique features. Platforms can combine staking payouts from multiple blockchains.
Investors can create diverse portfolios or derivatives based on staked assets’ future yield. This integration will enhance staking’s appeal as an investment strategy. It will also aid DeFi in maturing and becoming more sophisticated. This will foster innovation and cooperation among different blockchain networks.
Automation and AI-driven Management
Using automation and AI to improve operations and decision-making will be key to managing staking nodes in the future. AI will improve the analysis of blockchain data. It will also forecast market patterns and suggest staking plans. These plans will balance risk and profit. Machine learning algorithms can detect and react to security threats on their own.
They can also modify node configurations based on changing network conditions. Intelligent systems will automate routine maintenance tasks. This includes troubleshooting, health checks, and software upgrades. Staking nodes will be efficient systems. They can adapt to the blockchain environment using AI. This change makes them self-optimizing.
Conclusion
Configuring and managing a staking node on a server in blockchain technology is both a challenge and an opportunity. The road to successful staking includes investment, technology, and optimism. Choose the right hardware. Implement robust security. Connect to DeFi. Use AI for node management. Due to security, efficiency, and integration advancements, staking nodes will become more significant and profitable in the blockchain network.
RedSwitches offers dedicated server solutions for individuals ready to run their staking node. They are a reliable partner. We provide strong security, top service, and high performance for a successful staking business. You can depend on our infrastructure and expertise for blockchain technology. This will improve your staking returns.
FAQs
Q. What is staking in a blockchain?
Staking in blockchain is the process of holding funds in a cryptocurrency wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network, earning rewards in return.
Q. What is the difference between delegating and staking?
Staking involves directly participating in network operations by locking up tokens while delegating your staking power to another validator to participate on your behalf.
Q. What is the purpose of staking?
The purpose of staking is to secure the network and validate transactions. In return, stakers earn rewards for their contributions.
Q. What is node staking on servers?
Node staking on servers refers to participating in the Ethereum staking network by running a validator node on a server, which helps secure the network and earn staking rewards.
Q. How does staking on Ethereum work?
Staking on Ethereum involves locking up a certain amount of ETH as a stake to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. In return, validators receive rewards for their contribution to securing the network.
Q. What are the risks of staking ETH?
The risks of staking ETH include potential slashing penalties for malicious behavior, risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities, and fluctuations in the value of the staked ETH.
Q. How can I start staking my ETH?
To start staking your ETH, you need to have at least 32 ETH, set up a validator node on a server or use staking platforms like Rocket Pool, and participate in the Ethereum staking process.
Q. What are the considerations when choosing a staking method?
When choosing a staking method, consider factors such as the amount of ETH required, risks involved, rewards offered, ease of participation, and whether you prefer solo staking or pooled staking.
Q. What is liquid staking, and how does it work?
Liquid staking allows you to stake your ETH while maintaining liquidity to trade or use your tokens. It works by issuing tokenized representations of staked ETH, which can be transferred or traded.
Q. What are the different types of staking options available for Ethereum?
Ethereum staking options include solo staking, where you run a validator node independently, pooled staking, where multiple users combine their ETH to stake together, and staking as a platform service.