Key Takeaways
- Validator nodes are essential for the security and integrity of PoS blockchains.
- They validate transactions, propose blocks, and participate in consensus processes.
- Validators stake cryptocurrency as collateral, incentivizing honest participation.
- Different types of validator nodes serve varied roles within blockchain ecosystems.
- Validator nodes must meet specific hardware, software, and staking requirements.
- The future of validator nodes includes enhanced security, increased decentralization, and improved sustainability.
- Ongoing technological developments and regulatory adaptations will shape validator nodes’ evolution.
Validator nodes are the unsung heroes of blockchain technology. They silently but firmly maintain the security and integrity of digital ledgers worldwide. They form the foundation of the staking process. They are critical to the reliability and efficiency of blockchain networks.
This blog takes the reader on a tour of validator nodes in staking. It shows their crucial function, the strict procedures they must follow, and their significant influence on the digital economy.
This in-depth guide promises to unlock the mysteries of validator nodes and reveal the opportunities they offer in the growing world of blockchain tech. It is for blockchain enthusiasts eager to learn more, aspiring validators, experienced investors looking to diversify, and others who want to explore the core of blockchain technology.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Validator Node?
- How do Validator Nodes Work?
- Types of Validator Nodes
- How Do Validator Nodes Differ from Full Nodes?
- Setting up Validator Node
- Validator Nodes in Staking: Best Practices for Security and Efficiency
- Empowering Blockchain Stability: The Role of Dedicated Servers in Validator Nodes
- Future of Validator Nodes in Staking
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Validator Node?
Credits: Freepik
A Validator Node is a vital part of a blockchain network’s design. This is especially true for Proof of Stake (PoS) systems. Traditional Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains rely on mining to reach consensus and uphold the network’s integrity. In contrast, Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains rely on validator nodes. They validate transactions and create new blocks using computational power. These nodes ensure the network runs safely and smoothly. They validate transactions and suggest new blocks to add to the blockchain.
A pool of potential validator nodes is chosen based on the cryptocurrency each is willing to “stake.” They stake it to act as collateral. This stake is a deposit. Validators are motivated to operate well. Misconduct or neglect on their part may lead to penalties, including loss of their investment. It discourages fraud. This protects the network’s security and integrity.
Running a validator node involves more than passive investment; it also calls for ongoing oversight and active involvement. Validators must stay online and perform various duties, including participating in consensus processes, validating transactions, and producing blocks when selected.
Although precise responsibilities and the method for becoming a validator can change significantly throughout blockchain protocols, the fundamental idea that validators are essential to the network’s dependability, security, and usefulness is always accurate.
Validators play a vital part in the PoS blockchain ecosystem by carrying out these duties. They speed up the transaction process, defend the network from intrusions, and enhance the blockchain’s general scalability and efficiency.
Validators are compensated for their efforts, usually with freshly created tokens or transaction fees. These incentives ensure that staking can be profitable even with the hardware and energy requirements of operating and maintaining a validator node.
How do Validator Nodes Work?
Credits: Freepik
The integrity, security, and continuity of Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain networks are crucially maintained by validator nodes, who play a critical role in their operation. Validator nodes can have intricate internal workings that involve numerous essential procedures and operations. Understanding these can help one understand how PoS blockchains function at their core.
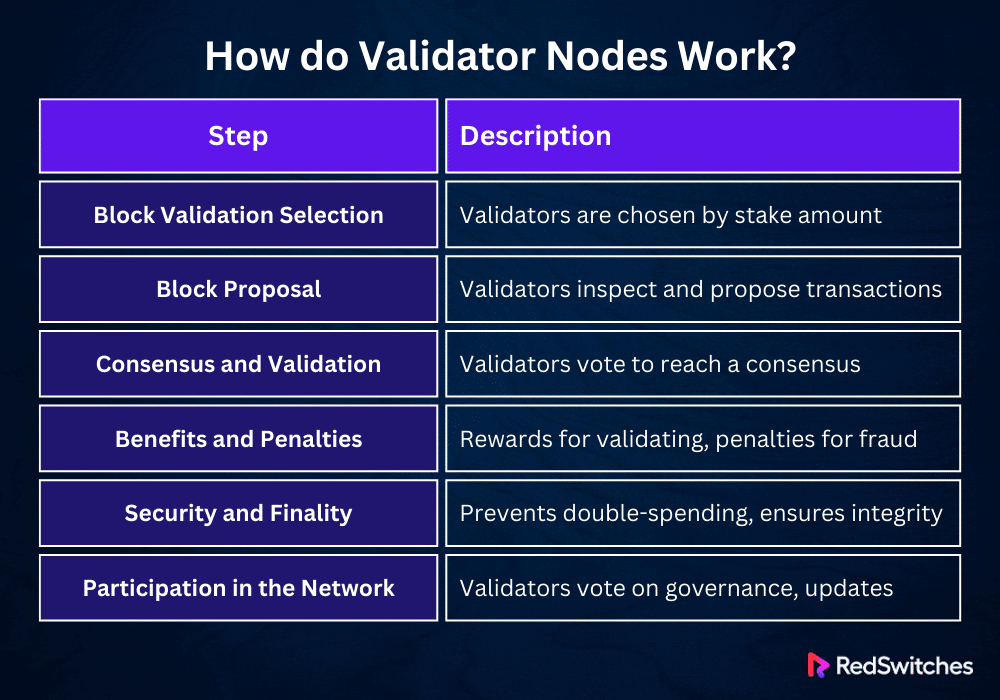
Block Validation Selection
This is a validator node’s initial action when proposing or validating a new block. In contrast to Proof of Work (PoW) systems, in which the privilege to submit a new block is obtained by computational work, Proof of Stake (PoS) systems choose validators according to the amount of their stake and occasionally additional criteria, including the duration of their stake.
Staking is how validators lock up a specific quantity of tokens as a security deposit. The reasoning for this is simple: people who have more invested in the network are less inclined to act maliciously because they stand to lose more.
Block Proposal
After being chosen for submitting a new block, a validator starts a crucial procedure that involves sorting through the network’s transaction pool, which is a collection of all outstanding transactions waiting to be added to the blockchain.
The validator carefully inspects every transaction, confirming its legitimacy and the sender’s identity by ensuring the sender has the required balance and that the digital signature is legitimate.
Also Read How To Use Blockchain as Database for Maximum Security
Consensus and Validation
Following a block proposal, more validators attempt to confirm its legitimacy. This could entail comparing the suggested block to the network’s policies to ensure that all of its transactions are legitimate and that the block is constructed correctly.
Although the intricacies of this procedure might change throughout PoS protocols, validators typically participate in some sort of voting mechanism or collective consensus. The block is appended to the blockchain whenever a consensus is obtained and considered legitimate.
Benefits and Penalties
Validators are rewarded for their involvement in the block proposal and validation process. Generally, transaction fees and occasionally freshly generated tokens fund these awards. The precise reward structure, which varies depending on the network, encourages validators to keep supporting the network’s operations.
On the other hand, malicious or negligent validators may be subject to sanctions, including partial loss of their staked tokens through cutting. This system of incentives and sanctions guarantees validators a financial incentive to behave in the network’s best interest.
Security and Finality
Using validator nodes, the PoS technique improves the blockchain’s security and finality. Validators are directly involved in countering attacks like double-spending, which is an attacker’s attempt to use the same digital asset twice. Due to the staking process, such attacks are economically impossible because they would need to obtain majority ownership of the staked tokens, which would be highly costly.
Participation in the Network
Validator nodes frequently participate in other network governance tasks, such as voting on protocol modifications or updates and block validation. This engagement guarantees the network maintains its dynamic nature, enabling it to adapt to novel problems and possibilities.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
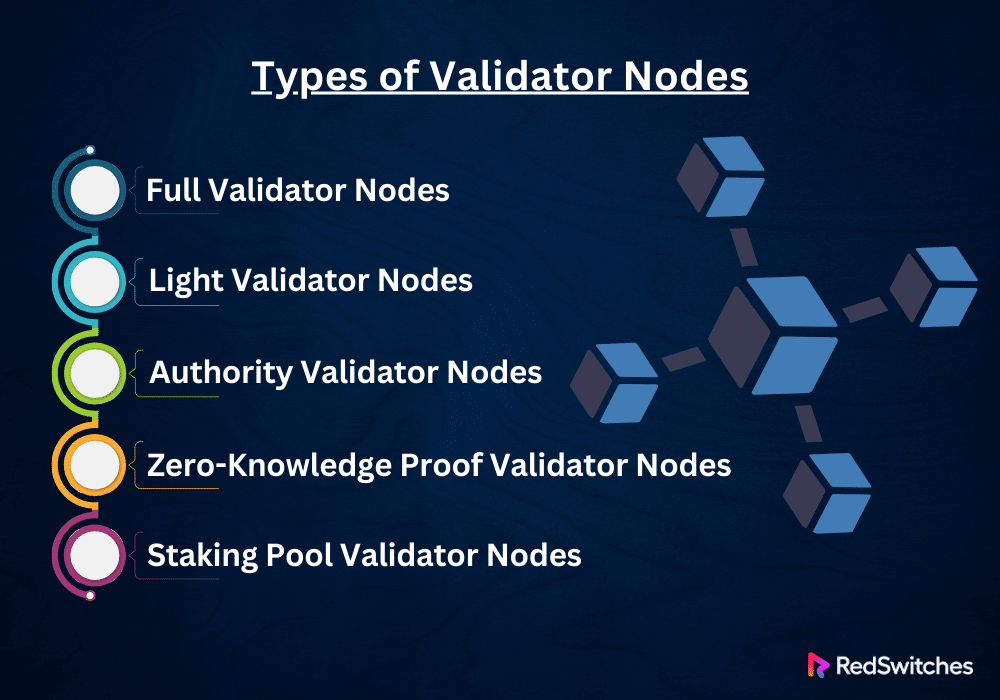
Types of Validator Nodes
In the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem, validator nodes are key. They maintain the network’s security, effectiveness, and integrity. But not every validator node is equal. Understanding these differences is critical. They explain how blockchains stay secure and work. The following are some of the main kinds of validator nodes that are present in different blockchain systems:
Full Validator Nodes
Full validator nodes keep a complete copy of the blockchain ledger. They can verify each transaction and block by the network’s rules. These nodes join in the consensus-building process. They do so by submitting new block proposals and voting on the acceptability of blocks from other validators. Full validator nodes must process the complete blockchain history. They need lots of storage, processing power, and network bandwidth. Their thorough validation procedure makes a significant contribution to the decentralization and security of the network.
Light Validator Nodes
Full validator nodes differ from light validator nodes. Light ones rely on a condensed version of the blockchain instead of the complete ledger. They validate transactions and blocks by asking other complete nodes. They also use tools like Simplified Payment Verification (SPV). Because light nodes are made to need fewer resources, they are appropriate for gadgets like laptops and smartphones that have limited processing and storage capabilities. They help the network scale and be accessed. But, they are not in the consensus process. They rely on full nodes to verify transactions.
Authority Validator Nodes
These nodes are found in Private or Permitted blockchain networks. They are chosen or elected by standards set by the protocol or governing body of the network. These nodes are typically well-known and reliable entities, like businesses or associations, permitted to approve transactions and suggest additional blocks.
Reputation, stake in the network, and tech capability are all critical. They are often considered in selection. Because they have more authority and trust, authority nodes can facilitate faster and more efficient transactions, but they may sacrifice decentralization in the process.
Zero-Knowledge Proof Validator Nodes
ZKP validator nodes are experts in verifying transactions utilizing zero-knowledge proofs. This cryptographic technique lets a party prove a statement’s truth to a third party. They do so while withholding extra information.
These nodes improve security and privacy by confirming the authenticity and accuracy of transactions without requiring access to the transaction’s content. ZKP validator nodes are essential components of blockchain networks where transaction confidentiality and privacy are prioritized.
Staking Pool Validator Nodes
Several stakeholders pool their resources to create staking pool validator nodes to improve their chances of being chosen as validators. While they function similarly to full validator nodes, these nodes represent a collective of people instead of a single person.
Staking pool members assign their stake to the pool’s validator node, which then uses it to approve transactions and suggest blocks on their behalf. The staking pool’s earnings are subsequently divided among its members according to the amount each contributed. By enabling smaller stakeholders to engage in and gain from the consensus process, staking pools democratize the validation process.
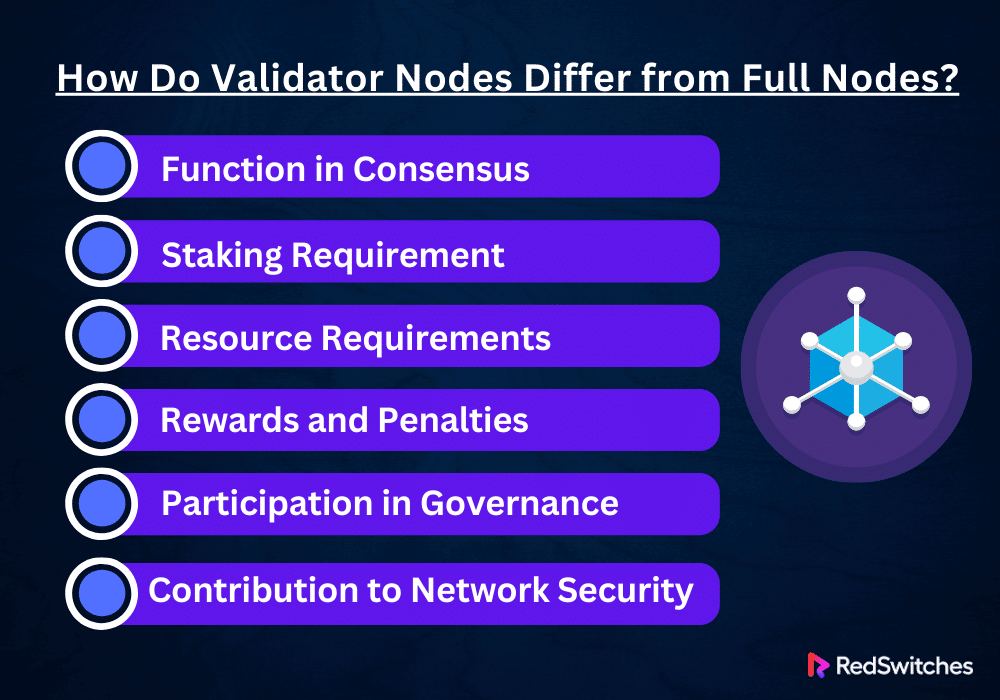
How Do Validator Nodes Differ from Full Nodes?
Credits: Freepik
Two critical parts of blockchain networks are validator nodes and full nodes. Each has a unique function. They preserve the integrity, security, and operation of the network. Understanding the differences between these two node categories is essential. They are vital to understanding blockchain technology and duty delegation in a network.
Key Differences
Function in Consensus
Full and validator nodes differ primarily in participating in the blockchain’s consensus mechanism. Validator nodes actively contribute to suggesting, approving, and confirming new blocks. Full nodes do not help choose which blocks to add to the blockchain. Instead, they check that blocks and transactions follow the blockchain’s rules.
Staking Requirement
Validator nodes do not need to run a full node to be required to stake a particular amount of cryptocurrency as a security deposit. This staking mechanism lets validator nodes participate in the consensus process. This is essential to the operation of PoS blockchains.
Resource Requirements
Full nodes need storage for the whole blockchain. But, both types of nodes may need lots of processing power to run. In addition to requiring storage for the entire ledger, validator nodes also need consistent, dependable internet access and, in certain situations, more powerful processing capacity to efficiently contribute to the consensus process and quickly validate transactions.
Rewards and Penalties
Validator nodes are rewarded with new coins or fees for participating in the consensus process. However, they may also be penalized for dishonest behavior or neglect of responsibilities. Full nodes are neither rewarded nor penalized in the same way as miners in a proof-of-work (PoW) system or validators in a proof-of-stake (PoS) system.
Participation in Governance
Validator nodes frequently have a voice in a blockchain network’s governance choices. They have a stake in the network’s future. This is due to their role in the consensus process and their network ownership. They can influence the path and development of the blockchain by casting votes on suggestions for enhancements or modifications to the network protocol.
Even though they are necessary for the network to function, full nodes usually do not directly influence governance choices unless they also serve as validator nodes or the network has unique features that let full node operators participate in governance.
Contribution to Network Security
Although in distinct ways, validators and complete nodes contribute to network security. By actively participating in the consensus process, validator nodes protect the network by ensuring that only legitimate transactions are uploaded to the blockchain and that consensus is reached without centralized management. Their financial interest in the network serves as a deterrent to malicious activity.
Setting up Validator Node
Anyone who wants to actively participate in the governance and consensus of a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain must first set up a validator node. Although the specifics can differ significantly amongst blockchains, the broad procedures listed below can serve as a solid starting point. For comprehensive instructions, you must refer to the documentation of the particular blockchain you are interested in.
Recognize the Requirements
Before setting up a validator node, it is essential to conduct in-depth research on the blockchain network you hope to support. This entails learning the network’s consensus mechanism, staking requirements, and other qualifying needs.
Furthermore, determining the hardware requirements is crucial since, to run a validator node, a server typically has to have a strong CPU, a lot of RAM, and enough storage space to hold the blockchain’s whole ledger. Being familiar with the required software, including the blockchain client and any additional tools the network recommends, is vital.
Also read DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM: Should You Consider the Upgrade?
Get the Required Tokens
Credits: Freepik
Turning into a validator begins with obtaining the required quantity of coins for staking, which differs significantly amongst blockchains. Typically, this stage involves buying or getting the required tokens via a cryptocurrency exchange. One of the most important requirements to become a validator is to meet the minimum staking requirement.
Configure Your Hardware
The following step involves configuring the hardware according to the given specifications. This could involve setting up a dedicated server at home or choosing to use server space from a cloud service provider. You must ensure your node’s integrity. This requires strong security measures, like setting up firewalls, updating software, and blocking unwanted access.
Install and Configure the Blockchain malware
To avoid malware, download the official blockchain software from a reliable source. After installation, the software must be carefully configured according to the blockchain’s requirements. This may involve configuring certain settings or options that are relevant to validators.
Stake Your Tokens
First, make a safe wallet for the cryptocurrency to begin staking by the blockchain’s rules. To demonstrate your commitment as a validator, you may be required to transmit a transaction to a specified address or carry out a particular command within the blockchain client.
Validator Nodes in Staking: Best Practices for Security and Efficiency
Credits: Freepik
A validator node’s security and effectiveness are critical to the integrity and reliability of the blockchain network as a whole and to its success. The best techniques for running a validator node in staking efficiently and securely are listed below.
Optimize Hardware Setup
To run a validator node in staking effectively, you must optimize your hardware setup. Choosing the right components is more important than having powerful hardware. They must meet the node’s needs. SSDs can access data faster than HDDs, so they are favored because they can process and validate transactions and blocks more quickly.
The node needs enough RAM to avoid stuttering, especially when network traffic is high. The CPU needs sufficient power to handle computational tasks effectively. The node’s scalability should also be taken into account; as the blockchain expands, your hardware should be able to meet the rising demands.
Network Optimization
The validator node’s speed and dependability are crucial regarding validator nodes in staking. They connect to the blockchain network. Brief outages can cause missed blocks or penalties. Your validator node can have the bandwidth it needs. Using a dedicated internet line reduces congestion on shared networks. You can ensure that your node stays connected by adding network redundancy measures, like failover systems or backup ISPs. It will stay connected even if one of the services is unavailable. You may need to use high-availability cloud services. Or, configure many network interfaces. Configurations for Quality of Service (QoS) can prioritize your node’s traffic, improving its performance even more.
Automate Updates and Maintenance
Automating updates and maintenance can greatly improve your validator nodes in staking. It will be more efficient and dependable. Although manual updates can be laborious and prone to human error, they are regularly essential for security and performance. Automation solutions can plan and deploy upgrades during off-peak hours to reduce downtime.
Likewise, regular upkeep duties might be automated, like cleaning the cache or checking security setups. This ensures they are done reliably and consistently. When implemented thoughtfully, automation can reduce the workload on node operators and mitigate the risk of vulnerabilities or inefficiencies affecting the node’s performance.
Join a Staking Pool
Regarding validator nodes in staking, Joining a staking pool offers an option for lone validators. They might not have the means or know-how to maximize their node alone. Staking pools combine the resources and stakes of many participants. This allows them to meet the requirements for validators together.
Through this partnership, you may have access to cutting-edge infrastructure and expert management, which could lead to increased operational efficiency and even bigger profits because of the increased consistency of block validation and proposal contributions.
Additionally, by distributing the risk across several validators, staking pools can offer a more robust and varied approach to staking.
Employ Energy-Efficient Techniques
Using energy-efficient techniques and tools can drastically lower a validator node in staking’s operating expenses and environmental impact. This may entail using highly rated power supply and CPUs, among other energy-efficient hardware components. Energy savings can also be achieved by configuring servers to go into low-power modes when not in use without sacrificing the availability or security of the node.
Additionally, you can lessen your node’s environmental impact by operating it using renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power. Energy efficiency can also be improved by using virtualization technologies to reduce the number of physical servers needed to handle server workloads without compromising performance.
Empowering Blockchain Stability: The Role of Dedicated Servers in Validator Nodes
Dedicated Servers are the Backbone of validator nodes, which are crucial for the integrity of blockchain networks. They are responsible for verifying, voting on, and maintaining the blockchain’s history. These servers provide these nodes with the necessary resources to perform their tasks efficiently.
Reliability Through Dedicated Resources
Dedicated servers offer validator nodes a stable and reliable environment. This is essential for nodes that must remain online and responsive to maintain the network’s continuity.
Enhanced Security for Trustworthy Transactions
Security is paramount in blockchain operations. Dedicated servers can be fortified with advanced security measures, ensuring that validator nodes are less vulnerable to attacks and unauthorized access.
Optimized Performance for Faster Consensus
The performance of validator nodes directly impacts the speed of transaction verification. Dedicated servers can be optimized for the specific needs of blockchain protocols, leading to quicker consensus times.
Scalability for Growing Networks
As blockchain networks grow, the demand for validator nodes increases. Dedicated servers allow for easy scalability, ensuring that nodes can handle increasing transactions without a drop in performance.
Dedicated servers play a pivotal role in supporting validator nodes. They provide a robust, secure, and scalable foundation essential for blockchain networks’ smooth operation. By ensuring that validator nodes have the resources they need, dedicated servers help maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of the blockchain.
Future of Validator Nodes in Staking
The future of Validator nodes in staking in the blockchain ecosystem looks bright. But it will likely change. This will be due to advancing tech, shifting laws, and changing public expectations. Validator nodes’ function and operation are expected to change a lot as blockchain tech advances and new consensus techniques arise. The new tech is made to meet current challenges and take new opportunities. The major trends and advancements listed below could shape the future of validator nodes in staking.
Enhanced Security Measures
The security of validator nodes in staking will become more important as blockchain networks expand in size and value. It is anticipated that increasingly advanced security protocols and countermeasures will be created to shield validator nodes from various cyber threats, such as DDoS attacks, Sybil attacks, and other nasty actions. HSMs, secure multi-party computation, and advanced cryptography may become the norm. They protect validators and guarantee the dependability and integrity of staking.
Decentralization and Fair Participation
In Validator Nodes in Staking, the foundation of blockchain technology is the decentralisation idea. Still, talks within the community have been sparked. They are about worries that power is concentrated in a few powerful validators. Later advancements might focus on methods that promote wider involvement in staking. They would reduce barriers to becoming a validator and create more inclusive staking algorithms. These algorithms would ensure a fairer reward distribution. This might involve better protocol design. It would allow more people to take part effectively. And, it would do so without risking security.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Regarding Validator Nodes in Staking, Energy consumption has been a major concern for the cryptocurrency industry for Proof of Work (PoW) networks, in particular. Even if PoS and staking use less energy, future validators might focus on cutting their environmental impact. This could result from using energy-efficient hardware and green technologies. It could also result from protocols aimed at lowering blockchain networks’ total energy use. Validators could also get incentives from community efforts or protocol mechanisms.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Validator nodes in staking will likely have to navigate a changing regulatory environment. This will happen as blockchain is used more in traditional finance and business. Validators may eventually have to follow laws. These laws will cover cross-border operations, financial transactions, and data privacy. Moreover, governance models might develop to include more complex processes. Validators would use them to settle disputes and make decisions. They might combine aspects of decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) structures and corporate governance.
Technological Developments and Interoperability
Blockchain technology is progressing. New ideas for validator nodes in staking operation and architecture will emerge. Improved zero-knowledge proofs will make staking safer. So will sharding for scalability and quantum-resistant cryptography. Furthermore, validator nodes may be essential in enabling cross-chain interactions and transactions. As blockchains progress, they will need to support many networks. This will require them to support many protocols and consensus methods.
Improved User Engagement and Education
Future validator nodes in staking will probably focus more on user engagement and education. It may be possible to increase participation by providing materials and tools. These would make becoming a validator easier for the public and create a more diverse validator community. The democratization of staking would let people directly participate in managing blockchain networks. It would also improve network security by making the networks decentralized.
Conclusion
Validator nodes are the backbone of Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain networks, serving as essential components for governance, consensus, and security. These nodes maintain the integrity of the network, approve transactions, and support a strong, decentralized digital economy via staking. Validator node progress is related to technology development, community involvement, and a dedication to sustainability and diversity. The importance of validator nodes in staking will only increase in the future, demonstrating their vital role in the development of blockchain technology.
Are you ready to play a pivotal role in blockchain technology? At RedSwitches, we equip you with top-tier dedicated servers designed explicitly for staking as validator nodes. Our robust infrastructure ensures unbeatable uptime, ironclad security, and the fastest connections, empowering you to validate transactions smoothly and effectively.
Join us to contribute to the decentralization and fortification of blockchain networks. Getting started is easy, and you’ll be making your mark on a safer, more connected digital world in no time. Dive in with RedSwitches today and be part of blockchain’s bright future!
FAQs
Q. What are validator nodes in staking?
A validator is a member of a blockchain network who stakes Bitcoin as collateral to verify transactions and suggest new blocks.
Q. Why do validators need staking?
Validators require staking as a security deposit to maintain network integrity, remunerate sincere involvement, and penalize dishonest behavior.
Q. What is the role of validators in crypto?
Validators approve transactions, add new blocks, and participate in the consensus process to ensure the security and accuracy of the blockchain.
Q. What are validator nodes in staking?
Validator nodes in staking are nodes that validate transactions on a blockchain network. They play a crucial role in ensuring the authenticity of transactions and are responsible for adding new blocks to the blockchain.
Q. How do I run a validator node?
To run a validator node, you need technical knowledge of the blockchain network you are participating in, set up the necessary infrastructure, and stake a certain amount of coins, such as 32 ETH in the case of Ethereum.
Q. What are the benefits of running a validator node?
You can earn rewards like staking rewards for securing the network by running a validator node. It also allows you to support the decentralization of the blockchain network and contribute to its overall security.
Q. Validator Nodes in Staking: How does liquid staking work for validator nodes?
Liquid staking allows you to stake your coins without locking them up for a specific period. This provides flexibility as you can still trade or use your staked assets while earning staking rewards as a validator.
Q. Why is it important to be a reliable validator?
Reliable validators act in the network’s best interest by validating transactions accurately and promptly. This helps maintain the security and integrity of the blockchain network.
Q. What is the best crypto for staking with validator nodes?
Ethereum is often recommended as one of the best cryptocurrencies for staking with the Best Validator Nodes due to its popularity, network security, and potential staking rewards.
Q. How can I start staking with a validator node on the Ethereum network?
To start staking on the Ethereum network, you must stake at least 32 ETH, set up and run your own validator node, and ensure you have the necessary technical knowledge to manage the node effectively.
Q. What are validator node rewards?
Validator node rewards are usually given in the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency and are given to those who validate transactions and safeguard the network.
Q. What is a validator node in blockchain?
A validator node is an essential part of a blockchain. It checks and validates new transactions and blocks to guarantee the security and integrity of the distributed ledger.