Key Takeaways
- Mining is not energy-efficient; staking is.
- Staking doesn’t require a significant hardware investment, but mining does.
- Compared to mining, staking provides a more steady and predictable income stream.
- Mining requires more technical expertise and has more outstanding entrance fees.
- Network security is supported by both systems, although by distinct means.
- If staking is not designed correctly, it could result in centralization.
- Mining’s enormous energy usage has a significant influence on the environment.
The world of cryptocurrency can be exciting, but also a little intimidating. If you’re thinking about diving in, you’ll likely come across two terms: staking and mining. Both play a crucial role in the world of crypto, by securing blockchain networks and verifying transactions.
Staking vs Mining are two essential methods you’ll probably encounter if you’ve ever pondered how to get involved in the cryptocurrency market. While staking provides a more energy-efficient option, mining uses sophisticated computer capability. Which, though, is best for you?
We’ll delve further into the differences between staking vs mining in this article, assisting you in comprehending the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Prepare to learn which approach can work best for you on your cryptocurrency adventure!
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Staking?
- How Does It Work?
- Advantages of Staking
- Disadvantages of Staking
- What is Mining?
- How Does It Work?
- Advantages of Mining
- Disadvantages of Mining
- Key Differences between Staking vs Mining
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Staking?
Credits: Freepik
Staking is crucial in cryptocurrencies and blockchain. This is especially true for networks that use the Proof of Stake (PoS) process. In contrast to the usual Proof of Work (PoW), it needs lots of processing power for coin mining. Proof of Stake is a more energy-efficient option. Here, the number of coins a user is prepared to “stake” as collateral—that is, hold—determines their ability to validate or mine transaction blocks.
Some call them validators. They take part in a proof-of-work (PoS) system. They commit some of their cryptocurrency holdings to the network. Staking shows the validators’ dedication to the network. It helps its integrity and health. Staking adds to network security. Staker awards come as extra coins or fees. They get them for their commitment and as a motivation to behave well. The procedure is similar to generating interest in a conventional banking sense in that the size and duration of your stake determine how much your investment grows over time.
When a user locks up a portion of their assets in a wallet that allows staking, the process starts. As a security deposit, this locked-up money ensures the validator honors network policies and reliably validates transactions. A validator may face consequences if they suggest or approve of fraudulent transactions. This is sometimes called “slashing,” when a validator loses some of their stake. The possibility of punishment deters dishonest behavior and contributes to the security and dependability of the network.
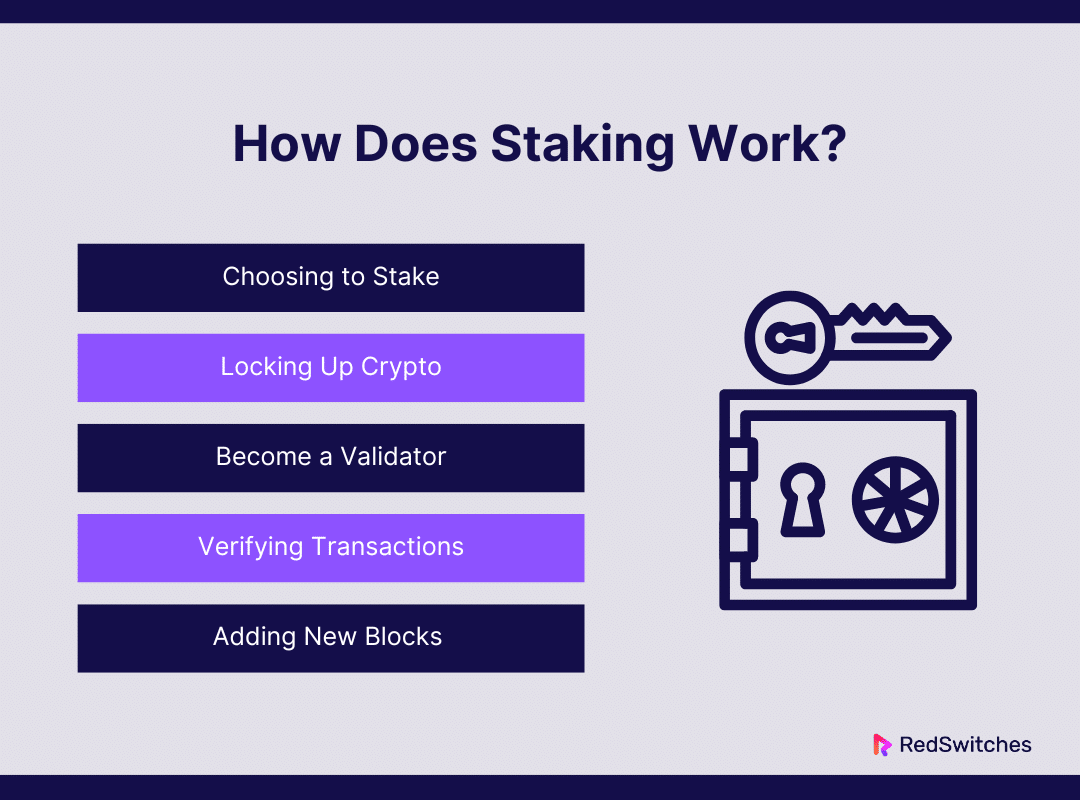
How Does It Work?
The Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus model, which underpins staking as a blockchain technology mechanism, differs significantly from networks such as Bitcoin’s conventional Proof of Work (PoW) approach. This is a thorough explanation of how staking operates:
Choosing to Stake
In a Proof of Stake (PoS) system, every cryptocurrency holder who satisfies the minimum needed balance can engage in staking. This cutoff point, also known as the “staking minimum,” changes depending on the network and is intended to weed out participants. The only active people are those with a significant commitment and a stake in the network’s success. Because their significant holdings are at risk, this criterion helps to maintain a trustworthy and committed group of validators who are less likely to act maliciously.
Locking Up Crypto
Users must deposit a certain quantity of their cryptocurrency into a digital wallet made explicitly for staking to engage in staking. This wallet has to stay connected to the blockchain at all times, either directly or via a staking pool, which is a service that pools the stakes of several users to make them more likely to be selected as validators. Since the staker has a financial stake in the outcome, the locked coins serve as a security deposit that encourages the upkeep of network integrity and truthful involvement in consensus processes.
Become a Validator
A staker can become a validator by locking up their cryptocurrency. At the same time, the actual selection process is based on several criteria set by the PoS protocol unique to that blockchain. A rotating mechanism, a certain amount of randomness, or even a weighted influence based on the quantity of cryptocurrency invested, the length of the stake, and past reliability could all be used in the selection process. This encourages decentralization and lowers the possibility of any validator having excessive influence by ensuring a secure and equitable process of validator selection.
Verifying Transactions
By guaranteeing the integrity of transactions, validators are essential to the blockchain. They confirm each transaction’s legitimacy by ensuring that all prerequisites are satisfied: the sender needs to have a sufficient balance, the transaction needs to be correctly signed to prevent fraud, and it needs to abide by network rules. Validators safeguard the network from erroneous transactions and potential intrusions by carrying out these checks, enabling safe and efficient blockchain operations.
Adding New Blocks
After a validator has confirmed a set of transactions, they put the verified transactions together in a new block. The network is then asked to validate this block. After several validators examine the proposed block and agree it is valid (i.e., it complies with protocol guidelines and doesn’t include any fraudulent transactions), the block is formally added to the blockchain. This procedure is essential for disseminating and synchronizing the ledger’s updated state among all network users, in addition to aiding in the blockchain’s expansion.
Advantages of Staking
Credits: Freepik
Comparing staking in blockchain networks to mining or other types of participation, particularly those that employ a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus process, reveals some noteworthy benefits. Here is a thorough analysis of the advantages of staking:
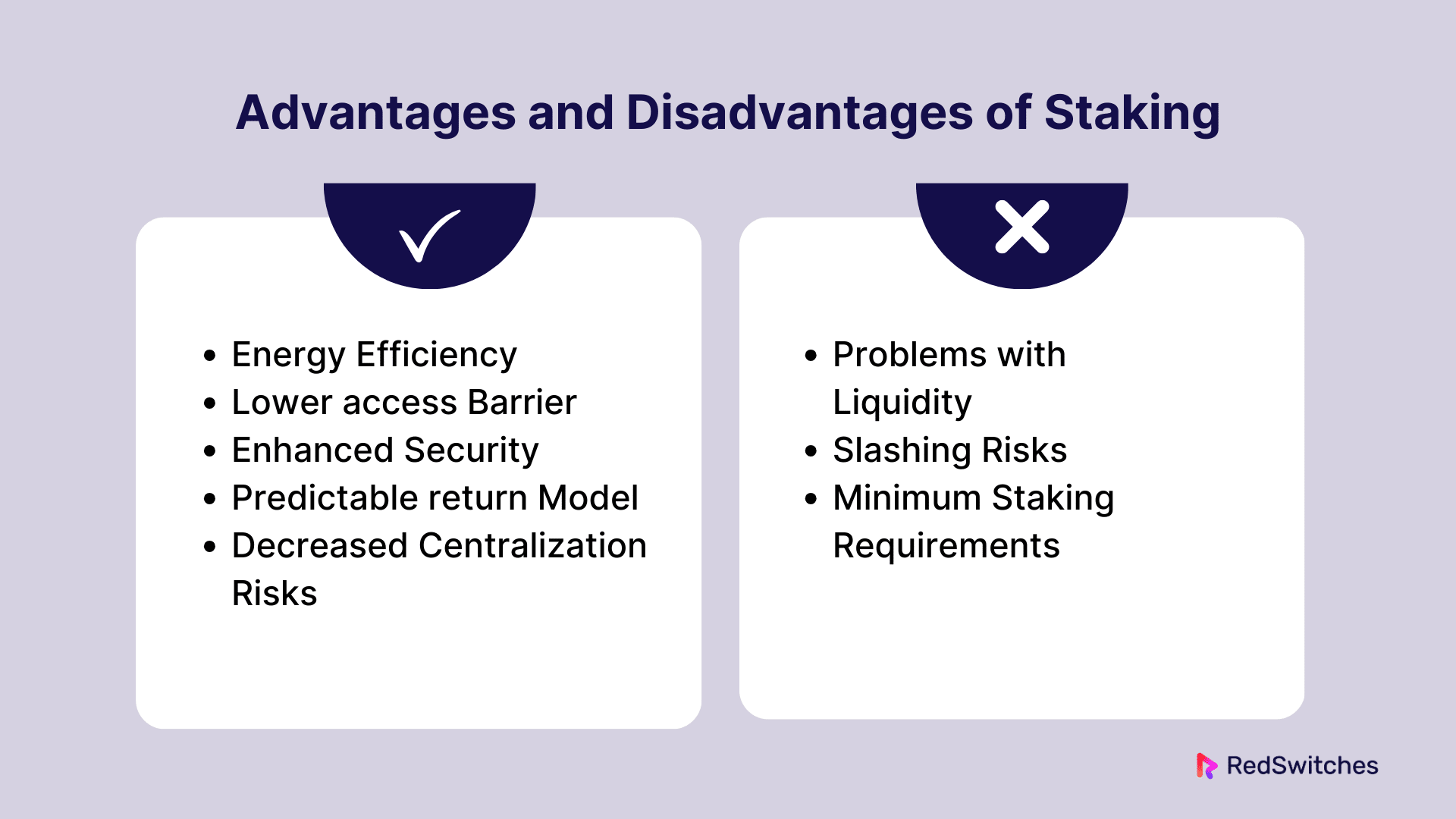
Energy Efficiency
Staking’s energy efficiency is one of its most lauded advantages. Proof of Work (PoS) systems demand validators to keep and lock up a specific amount of bitcoin as a stake. This is in contrast to PoW systems. They, as seen in networks like Bitcoin, need much processing power and electricity to mine blocks. This procedure does not need to solve complex math problems. So, it uses much less electricity. Because of this, staking is a greener and more sustainable option than mining. It fits better with global efforts to cut energy use and carbon emissions.
Lower access Barrier
Compared to mining, staking usually has a lower access barrier. Expensive hardware, such as high-performance CPUs, GPUs, or specialized ASIC devices, and ongoing electricity costs are frequently needed for mining. On the other hand, staking typically just needs minimal coins and a simple computer that can stay online. Because of this, staking is now more widely available to people who might not have the financial or technical know-how to start a mining company.
Enhanced Security
Staking helps to keep the blockchain more secure. Validators are motivated to uphold network security and integrity because their coins are at risk; any activities that comprise the network could result in severe fines known as “slashing,” which could result in significant personal financial losses. Because each validator’s incentives align with the network’s objectives, attacks are less likely to occur, strengthening PoS networks’ defenses against malicious activity.
Predictable return Model
Staking offers a more predictable return model than mining, which depends on solving blocks first and can be somewhat unexpected owing to competition and varying difficulty levels. Depending on the particular staking rules of the network, validators are usually selected based on some criteria, such as the amount staked, the length of the stake, and the general dependability of the node. This can frequently result in a more consistent and predictable flow of rewards.
Decreased Centralization Risks
PoS systems can aid in lowering the risk of centralization, which is particularly important in PoW systems since big mining pools have the potential to control the mining process. Staking makes it more difficult for a single party to control a sizable chunk of the network’s overall stake because it requires less physical hardware and offers large-scale operations less of an edge. This encourages a blockchain network that is healthier and more decentralized.
Disadvantages of Staking
Staking has several benefits, especially regarding accessibility and energy efficiency, but there are also apparent drawbacks that users need to be aware of. The following is a thorough analysis of the possible disadvantages of staking on a blockchain network:
Problems with Liquidity
When you stake your Bitcoin, you temporarily lock up your money. You can’t use these coins for any other reasons during this time. This includes selling or trading them in reaction to market conditions. This can be especially problematic in erratic markets where moving money rapidly is critical. Also, stakers may have to hold an item. The item is much less valuable than when they staked it. This happens if the value of the cryptocurrency they staked drops.
Slashing Risks
Staked coins in Proof of Stake systems may be “slashed” or permanently destroyed as a punishment for validators who do not carry out their responsibilities correctly or try to compromise the network. This poses a serious concern, especially in networks where bugs or other technical problems could unfairly penalize trustworthy validators. Due to the intricacy of maintaining a node, errors may occur and cause stakers to lose money.
Minimum Staking Requirements
To engage in staking, a minimum quantity of coins is often required by many PoS networks. Setting this threshold too high may prevent smaller investors from becoming validators if they lack the funds to meet the minimum staking criteria. This may restrict involvement to wealthy people or institutions, which would go against the decentralization that blockchain technology seeks to accomplish.
What is Mining?
Credits: Freepik
Mining is a key part of many cryptocurrency networks. This is especially true for networks like Bitcoin that rely on Proof of Work (PoW). Completing intricate mathematical puzzles is necessary to verify transactions and safeguard the network. In order to maintain a blockchain’s integrity and the chronological order of transactions, this procedure is essential to its operation.
Miners in PoW-based systems solve cryptographic problems. They use specialized computer gear to participate in mining. The privilege to append a new block of transactions to the blockchain belongs to the first miner to answer the riddle. This accomplishment is called “block finding.” Miners get block rewards, which are new bitcoin. They also get transaction fees from the block’s transactions.
The security and decentralization of the blockchain network are vitally dependent on miners. They need to use a lot of electricity and processing power to process transactions and create new blocks. By doing this, the issue of double-spending—the possibility of spending a single digital token more than once—is mitigated. It would take a lot of computation and a 51% attack for one party to change the blockchain. They would need over 50% of the network’s total processing power.
Network-to-network variations exist in the hardware requirements for mining. Yet, specialized mining rigs have more efficiency and power. They cost a lot. They use graphics processing units (GPUs) or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). These tools improve the miner’s odds of cracking the cryptographic riddles and making money.
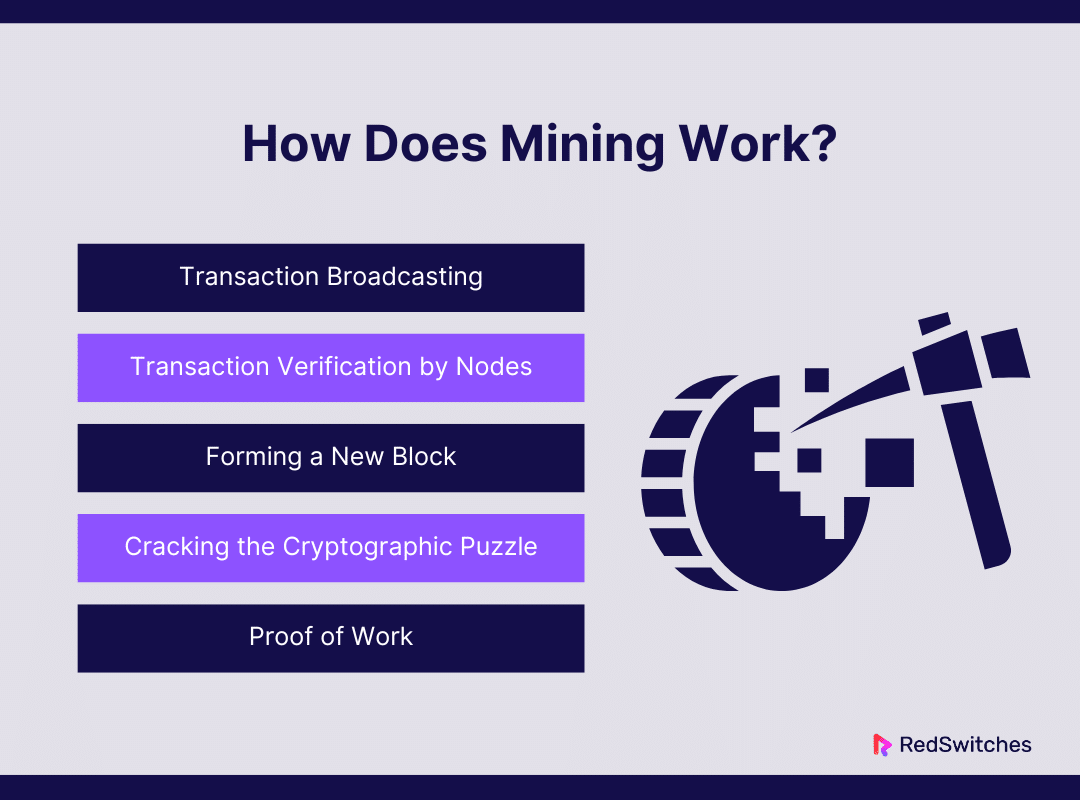
How Does It Work?
Transaction Broadcasting
Mining begins when a transaction is completed and sent out to the network. During each transaction, cryptocurrency is transferred between addresses. Until these transactions are verified through mining, they are not instantly regarded as legitimate and are not added to the blockchain ledger.
Transaction Verification by Nodes
Network nodes confirm the transaction data before mining commences. They verify the legitimacy of the transaction signatures and the sender’s financial stability. This verification helps ensure that the transaction complies with network regulations and that the same coins haven’t been spent twice.
Forming a New Block
Miners group transactions together into a data block after they have been verified. This block also includes a reference to the blockchain’s prior block to ensure the chain’s continuity. However, this block must be cryptographically sealed before it can be put into the blockchain, which requires mining labor.
Cracking the Cryptographic Puzzle
The key to mining is cracking the intricate code that protects the network. In this challenge, the task is finding a hash—a distinct digital fingerprint of the data—that satisfies specific network-defined requirements. For Bitcoin, for instance, the hash is required to fall short of a specific value. Until the prerequisites are satisfied, this method necessitates continuously producing hashes by changing a nonce, a changeable portion of the block header.
Proof of Work
The cryptographic puzzle’s solution shows how much processing power the miner has used. Proof of work (PoW) secures the network by making it computationally costly and time-consuming to add new blocks. It also discourages fraud and assaults like double spending and trying to change previous transactions.
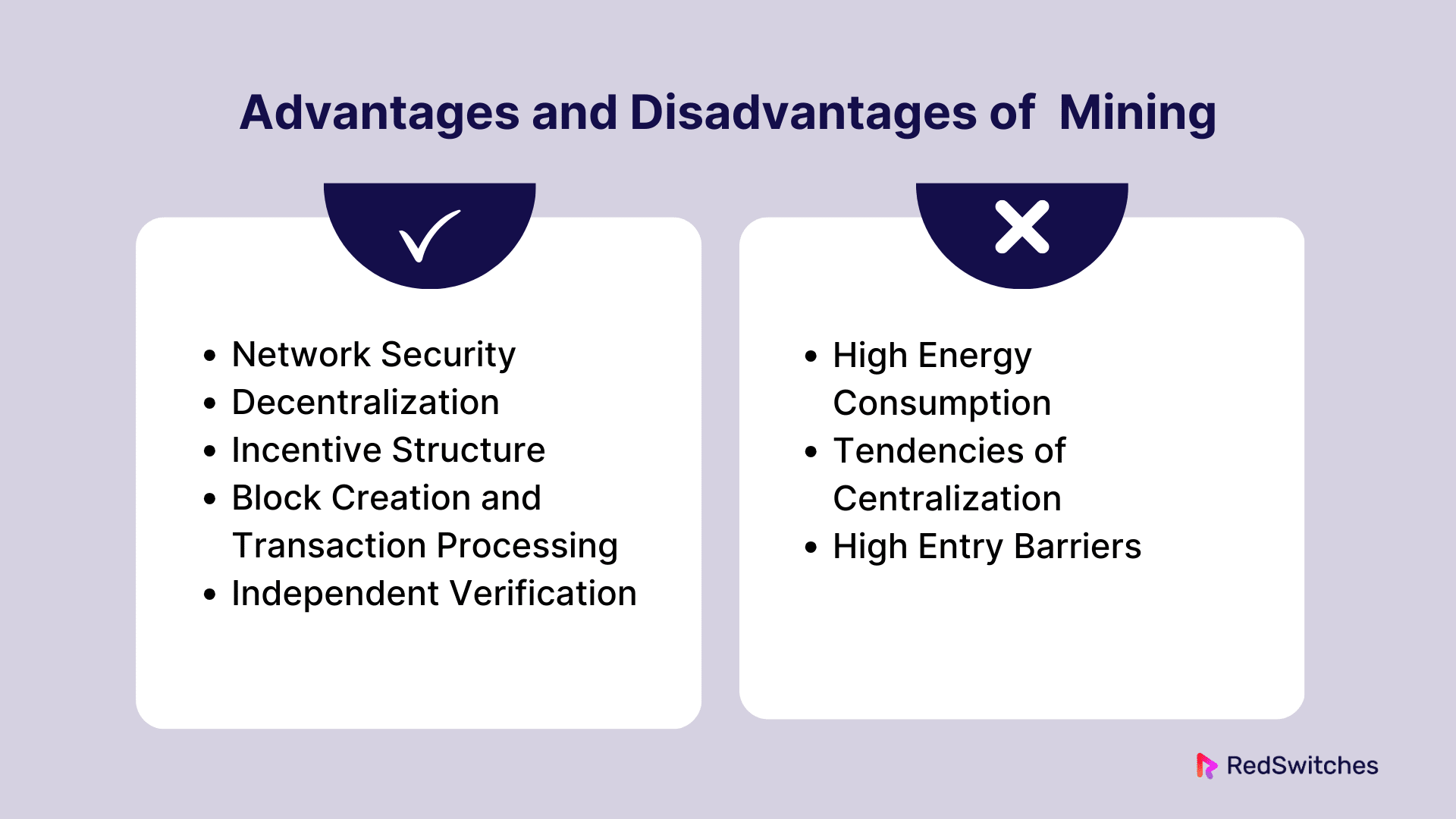
Advantages of Mining
Credits: Freepik
Mining has several clear benefits as a crucial part of Proof of Work (PoW) blockchain networks. These advantages give members incentives in addition to enhancing the blockchain’s security and integrity. This is a thorough analysis of mining’s benefits:
Network Security
One of the blockchain’s main benefits is the security it offers. Mining involves deciphering challenging cryptographic riddles, which require a lot of processing power. Due to this high resource need, it would be tough for any lousy actor to change any transaction on the blockchain, as they would need to own at least 51% of the network’s total processing power. This security mechanism, Proof of Work, keeps the blockchain unchangeable and impenetrable while preventing double-spending.
Decentralization
The blockchain network’s decentralization is facilitated by mining. Anyone with the required hardware and electricity access can participate in the mining process in blockchain technology, unlike traditional banking systems where transactions are regulated and verified by a central authority. This promotes a more robust and resilient network since control and verification of transactions are dispersed across multiple independent miners rather than concentrated in a single entity.
Also read Maximize Transaction Security: The Essential Role of Dedicated Servers
Incentive Structure
Mining gives users a clear financial incentive to keep the network safe and secure. New Bitcoin coins and user-paid transaction fees are given to miners as rewards. Due to this incentive structure, more people will mine, enhancing network security. The money made from mining can also partially offset the expenses of purchasing and running heavy mining machinery.
Block Creation and Transaction Processing
New blocks are made, and transactions are handled through mining. This is essential to any cryptocurrency network’s operation. When miners crack a cryptographic riddle, they add a new block to the blockchain. A collection of transactions that are thereby formally documented and validated are contained in this block. Through block rewards, this procedure makes it possible to transfer digital assets safely and increases the amount of cryptocurrency in circulation.
Independent Verification
Using mining, transactions may be independently verified without the assistance of outside parties. Every miner independently confirms the integrity of the proposed blocks and the transactions. As a result, there is less dependency on the outside, potentially unreliable validators, maintaining the blockchain’s status as a genuine peer-to-peer network where trust is established internally rather than imposed.
Disadvantages of Mining
Mining, which is essential to Proof of Work (PoW) blockchain networks, has a number of severe drawbacks and difficulties that may have an impact on miners as well as the ecosystem as a whole. Among them are:
High Energy Consumption
One main complaint against mining is the amount of energy it uses. Powerful computer technology that uses a lot of electricity is needed for mining to carry out intricate mathematical calculations. This raises more general environmental problems and drives up miners’ operating expenses. Mining enterprises’ carbon footprints have come under examination, mainly as people’s awareness of climate change has grown worldwide. Some have questioned the sustainability of proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains due to the energy-intensive nature of mining, particularly in areas where fossil fuels play a significant role in electricity generation.
Tendencies of Centralization
Blockchain is supposed to be decentralized, but because mining is so competitive, there is some centralization. Mining demands substantial financial and technological resources. Because of this, individuals and small organizations frequently find it challenging to compete with the massive mining farms and pools that dominate the mining industry, particularly in regions where energy is more affordable.
High Entry Barriers
High-performance mining devices, such as GPUs (Graphic Processing Units) and ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), might be unaffordable. The continuing expenses for maintenance and electricity also contribute to the financial strain. Entrance barriers are significant for new miners, particularly those from regions with more excellent electricity prices or less access to cash.
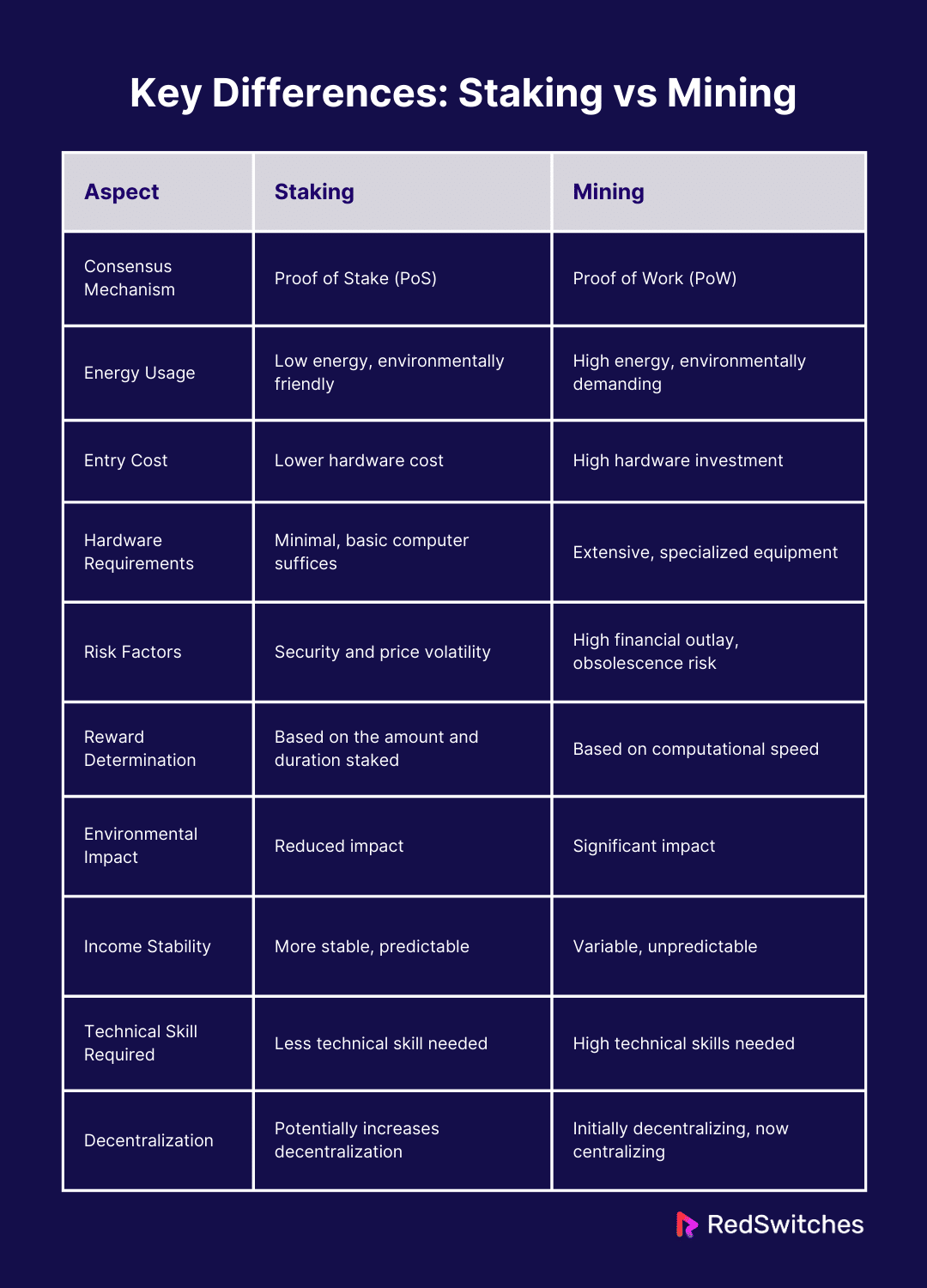
Key Differences between Staking vs Mining
Let’s break down the core differences in the staking vs mining debate to help you decide which approach aligns best with your goals and resources.
Consensus Mechanism
Staking
In the Proof of Stake (PoS) paradigm, staking generates new blocks and fortifies the network. In contrast to conventional Proof of Work systems, PoS eliminates the need for miners to work out challenging math problems. Instead, the quantity of bitcoin that validators are ready to “stake” as collateral determines which of them gets to make new blocks. A validator’s odds of being chosen to approve transactions and append a new block to the blockchain increase with the amount of coins they stake.
Mining
The initial consensus method used by several cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, is called Proof of Work (PoW). Miners must compete with each other. They use powerful computers to solve tricky riddles. The privilege to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain belongs to the first miner to answer the riddle. This procedure is costly and slow to change. It adds to network security and to the process of validating and recording transactions.
Energy Usage
Staking
Staking is considered more environmentally friendly than mining due to its low energy usage. The network software and a constant internet connection are the key energy-consuming tasks in the Proof of Stake (PoS) paradigm, which allows users to participate in the validation process. Staking eliminates the requirement for significant processing power and the correspondingly high electricity consumption because it does not require solving intricate cryptographic puzzles.
Mining
Mining is known for requiring a lot of energy, especially when using the Proof of Work (PoW) approach. Miners must solve cryptographic riddles using strong computer hardware, like GPUs or ASICs. The procedure necessitates ongoing, significant computing efforts, which draw a lot of electricity.
Entry Cost
Staking
Generally speaking, staking has a cheaper entry cost than mining because it requires much less hardware investment. The primary requirement for staking in a Proof of Stake (PoS) system possesses a specific quantity of the cryptocurrency that the staker intends to use. The minimal staking requirement, which varies based on the blockchain, is often available to a wide spectrum of investors.
Mining
On the other hand, mining can have a high entrance cost, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) systems. Proficient and potent computer gear, such as expensive ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) or top-tier GPUs, is necessary for mining operations to be successful. The substantial electricity consumption of these systems raises the overall operating expenses.
Hardware Requirements
Staking
Because staking usually takes little hardware, more people can participate in it. The essential gear is a dependable computer or server that can execute the staking software and keep an ongoing internet connection. The main purpose of this configuration is to guarantee that the participants can continue to be online and complete network validation activities when requested to act as validators. Since the process does not demand large amounts of processing power due to sophisticated computations, high-end hardware specs are not necessary.
Mining
On the other hand, mining demands large hardware investments, especially in networks where the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus process is employed. Strong and specialized computer systems, like high-performance GPUs or ASICs made just for mining, are essential for miners. These technologies are required to solve the cryptographic riddles that build new blocks and safeguard the network. In addition to being strong, the hardware must operate at high power and heat output levels for extended periods of time.
Risk Factors
Staking
The dangers associated with staking are mostly related to the network’s security and the volatility of cryptocurrency pricing. The possibility of “slashing,” in which a percentage of the cryptocurrency that has been staked is lost as punishment for any conduct deemed harmful to the integrity of the network, such as failing to stay online to carry out validation tasks or making an effort to validate fraudulent transactions, poses a serious risk.
Mining
Risks associated with mining in Proof of Work systems are numerous. One of the main issues is the large financial outlay needed for mining hardware, which can easily become outdated due to the speed at which technology is developing or changes in network complexity.
Reward Determination
Staking
Rewards from staking are usually based on several variables, including the quantity of cryptocurrency staked, how long it has been staked, and the total amount of cryptocurrency staked on the network. These variables influence the possibility of a participant being selected as a validator. After being selected, validators can propose or approve new blocks to be added to the blockchain and get rewarded for their efforts.
Mining
Determining rewards in mining, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) systems, is a highly competitive process that relies on the miner’s ability to solve cryptographic riddles first. The rewards comprise newly created coins and transaction fees from the transactions in the new block. However, the miner’s computational power and the total network mining power significantly impact the likelihood of receiving these rewards.
Environmental Impact
Staking
Staking is frequently commended for having less of an impact on the environment, particularly compared to conventional mining methods. Staking uses a lot less electricity because it doesn’t require a lot of processing power. Thanks to the Proof of Stake (PoS) approach, complex mathematical problems can be solved without the use of energy-intensive technology.
Mining
Because mining requires a lot of energy, especially when using the Proof of Work (PoW) concept, it is well known to have a significant negative environmental impact. The procedure entails deciphering cryptographic riddles, which necessitates large processing power and, thus, electrical power.
Income Stability
Staking
Regarding money, staking is usually more reliable and steady than mining. The structure of rewards in Proof of Stake (PoS) systems provides this stability. According to predetermined network regulations, participants receive rewards based on the quantity of cryptocurrency they have invested and the stake length.
Mining
On the other hand, mining revenue can be very erratic and unexpected. The competitive aspect of solving cryptographic puzzles, the riddles’ varying difficulty as more miners join the network, and the intrinsic volatility of cryptocurrency values, which impact the value of mining rewards, are the main causes of this instability.
Technical Skill Required
Staking
Compared to mining, staking usually requires less technical expertise. It is vital for participants to understand how to utilize a wallet that enables staking as well as how to buy and hold the required coin. If direct staking is not possible because of high minimum requirements, then learning how to join a staking pool is typically part of the technical requirements beyond these fundamentals.
Mining
Mining, on the other hand, demands a far higher degree of technical proficiency. ASICs, GPUs, and other complex hardware configurations must be understood and operated by miners. To optimize efficiency and profitability, they must also be able to adjust performance settings, control heat dissipation, and guarantee a steady power supply.
Decentralization
Staking
The purpose of staking in Proof of Stake (PoS) systems is to encourage decentralization, while it may or may not succeed. In theory, proof-of-stake (PoS) systems facilitate a wide distribution of the responsibility of transaction validation by enabling every cryptocurrency holder to stake and potentially become a validator.
Mining
Originally, mining encouraged decentralization by enabling anyone with the required computer power to participate in the process, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) systems. However, over time, a certain amount of centralization has resulted from the competitive nature of mining and the significant resources needed for hardware and electrical expenses.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mining and staking have their respective advantages and disadvantages and are essential components of the blockchain ecosystem. Given its Proof of Work process, mining provides strong security but requires high energy consumption and a technical skill set. However, under the Proof of Stake architecture, staking appears to be a more accessible and energy-efficient option, even though it also has drawbacks, including possible centralization and liquidity problems.
Staking vs mining will depend on investment capacity, technical proficiency, and environmental issues for companies and individuals wishing to utilize these technologies effectively. RedSwitches has a variety of reliable server options that are engineered to satisfy the demanding requirements of contemporary cryptocurrency mining operations, as well as the dependability required for staking if you’re looking for hosting options that can facilitate any of these activities.
FAQs
Q. What is staking vs mining vs minting?
Staking uses retained funds to support network operations, mining uses puzzle-solving to safeguard transactions, and minting produces new coins.
Q. Staking vs Mining: Is Crypto mining or Crypto staking more profitable?
Staking provides a more consistent stream of low-cost revenue than mining, which can deliver large returns at significant costs.
Q. Is it better to stake or earn crypto?
Regarding generating cryptocurrency, staking is typically simpler and more energy-efficient than active techniques.
Q. Staking vs Mining: What is the difference between crypto mining and crypto staking?
Crypto mining involves the process of using computational power to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions on a blockchain network and earn rewards, while crypto staking involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the network and earn rewards in the form of additional coins.
Q. How does crypto mining work?
Crypto mining is the process of using computing power to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions on a blockchain network. Miners compete to be the first to solve these problems and add a new block to the blockchain, earning rewards in the process.
Q. Staking vs Mining: What is crypto staking, and how does it differ from mining?
Crypto staking involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the network and validate transactions. Stakers are rewarded with additional coins for their participation, whereas miners earn rewards by solving complex mathematical problems through computational power.
Q. Staking vs Mining: Can you earn passive income through crypto mining and staking?
Yes, both crypto mining and staking offer opportunities to earn passive income. Mining rewards miners with newly minted coins for their computational efforts, while staking rewards stakers with additional coins for supporting the network and holding assets in their wallets.
Q. Staking vs Mining: Is there a difference in energy consumption between crypto mining and staking?
Yes, there is a significant difference in energy consumption between mining and staking. Mining typically requires a vast amount of energy to power the computational rigs, while staking generally consumes much less energy as it mainly involves holding coins in a wallet.
Q. What is liquidity mining in the context of cryptocurrencies?
Liquidity mining, also known as yield farming, is a process where users provide liquidity to a decentralized exchange or liquidity pool and earn rewards in return. It is a way to earn passive income by lending your crypto assets to support the liquidity of the platform.
Q. How does Bitcoin mining differ from Ethereum mining?
Bitcoin mining involves using specialized hardware to mine new bitcoins by solving complex mathematical problems, while Ethereum mining, especially with the upcoming transition to Proof of Stake (POS), requires users to validate transactions by staking their Ethereum holdings instead of solving algorithms like in Bitcoin mining.