Key Takeaways
- Validator nodes are crucial for verifying transactions and maintaining blockchain integrity.
- Setting up a validator node requires careful attention to hardware and software specifications.
- Security practices, including robust access controls and key management, are essential for protecting nodes.
- Regular software updates and security patches are critical to keep validator nodes functioning efficiently.
- Monitoring tools and alert systems help maintain node health and quickly address potential issues.
- Effective troubleshooting relies on detailed documentation and responsive support mechanisms.
- Through database pruning and data retention policies, storage optimization enhances node performance.
- Disaster recovery plans, including regular backups and recovery testing, are crucial for node resilience.
- Staying informed and engaged with the blockchain community supports continuous learning and adaptation.
- Validator nodes require ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and network security.
In the world of blockchain, validator nodes are the backbone. They verify transactions and keep the network running smoothly. But like any machine, validator nodes need care and attention to work their best.
Setting them up right is only the start. You must also keep them updated, secure, and running without issues. This guide will walk you through how to keep your validator node in top shape.
Why is this important? Well, validator downtime can be caused by poor maintenance. Downtime means missed rewards and can even lead to penalties on some blockchains. Let’s avoid that!
We’ll cover everything from software updates to security tips. By the end, you’ll be a validator maintenance pro!
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Explanation of Blockchain Technology
- What are Validator Nodes?
- How do Validator Nodes Work?
- Validator Node Configuration
- Core Validator Nodes Maintenance Tasks
- Additional Considerations
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Explanation of Blockchain Technology
Credits: Freepik
Blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently. Each transaction is recorded as a “block” of data, which links together to form a “chain.” This structure makes it difficult to change or hack the data.
How Blockchain Works
The process starts when a transaction occurs. This could be any exchange of information or assets. This transaction is then verified by a network of computers known as nodes. Once verified, the transaction is combined with others to create a new block. This block is then permanently and unalterably added to the existing blockchain.
Security Features
One of the key features of blockchain is its security. The blocks are secured using cryptography. Each block contains a unique code, called a hash, which links it to the previous block. This and the fact that the network must approve every block change helps prevent fraud and unauthorized changes.
Decentralization
Unlike traditional ledgers, a blockchain does not have a central authority. This decentralization means no single person or group controls the entire blockchain. As a result, it promotes transparency and trust, as any user can independently verify the data.
Importance in Various Sectors
Blockchain technology is not limited to one sector. While it started with digital currencies like Bitcoin, it is now being explored for various applications. These include supply chain management, financial services, and even voting systems. Its ability to provide a secure and transparent record of transactions makes it valuable across many fields.
Blockchain technology offers a secure, transparent, decentralized way to record transactions. Its ability to ensure data integrity without needing a central authority is revolutionary. This technology has the potential to impact various aspects of society, making it an important area of study and application.
What are Validator Nodes?
Credits: Freepik
Validator nodes are the heart of blockchain networks. They check transactions to ensure everything is correct, keeping the blockchain safe and reliable. Validators are super important for the network to work correctly.
How do Validator Nodes Work?
Validator nodes operate by verifying transactions that occur within the network.
On the Ethereum Network, a transaction starts by checking for enough funds. It also checks the transaction’s legitimacy.
After verification, transactions enter a ‘mempool.’ Later, chosen validators group them into blocks. These validators are selected based on their cryptocurrency stake. This stake acts as a security deposit to promote honest behavior.
Validators update the blockchain’s state by confirming new blocks and transactions. They take part in the consensus process. This method confirms transaction validity, ensuring accuracy and preventing double-spending. Validators continually work to secure the blockchain and keep it updated.
How do Validator Nodes Differ from Full Nodes and Mining Nodes?
Let’s compare three types of nodes:
Validator Nodes vs. Full Nodes
Validator nodes validate transactions and join the consensus process. Full nodes store the entire blockchain and check transactions against consensus rules. They do not create new blocks, keeping the network secure and functioning correctly.
Validator Nodes vs. Mining Nodes
Mining nodes are in proof-of-work systems. They add transactions to the blockchain by solving cryptographic puzzles, which require a lot of computing power. Miners earn cryptocurrency for this work. In proof-of-work systems, all mining nodes are validators, but not all validators mine, especially in proof-of-stake systems.
Running a Validator Node: The Requirements & The Rewards
What are the main components of a validator node? Let’s Find out:
Requirements
Validator nodes need a lot of resources. For example, the Polygon Network recommends at least 16 CPU cores, 64 GB of RAM, and ample SSD storage. The operating system should be strong and safe, like Ubuntu or macOS. Validators must stake a significant amount of the network’s tokens as a security deposit.
Rewards
Validators earn rewards for helping secure the network. They get staking rewards in the network’s currency and commission rewards from delegators’ earnings. Validators also earn block rewards when they propose and validate blocks.
Validator nodes are vital for blockchain operations. They secure the network and validate transactions. Their roles differ from those of full and mining nodes but are crucial for blockchain functionality and security.
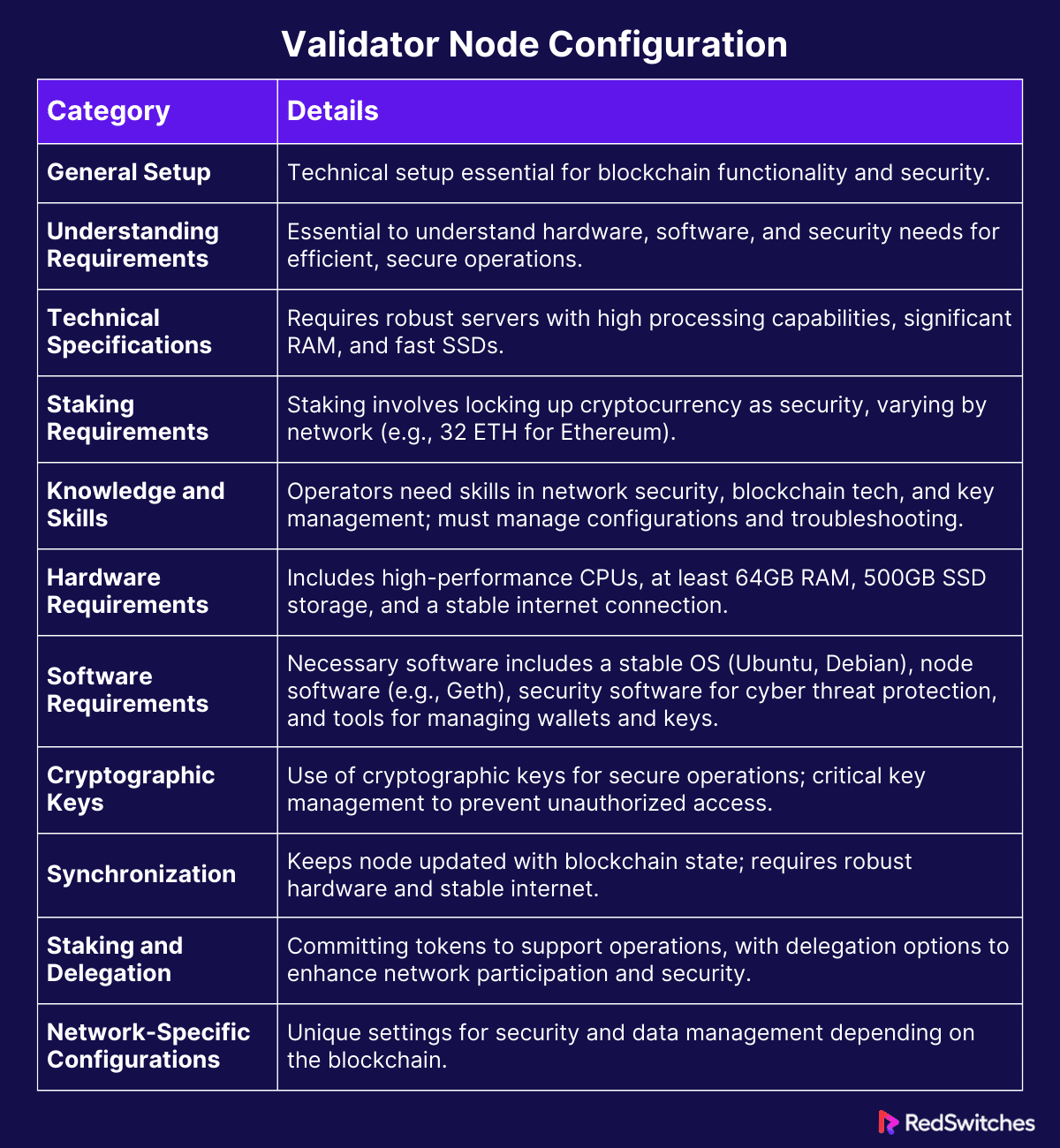
Validator Node Configuration
Credits: Freepik
Setting up a validator node is a technical process that requires careful configuration. This is to ensure its functionality and security within the blockchain network.
Understand Requirements
Understanding the requirements to ensure a validator node’s efficient and secure operation is crucial before initiating its configuration.
Technical Specifications
Technical requirements are essential for the smooth operation of a validator node. The node must run on a reliable and secure server. It should have adequate processing power, memory, and storage to handle the network’s demands. For example, some networks might require a multi-core processor, substantial RAM, and high-speed SSD storage to effectively manage the blockchain’s workload.
Staking Requirements
Staking is a critical component of running a validator node. It involves locking up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as a security deposit. The staking requirement varies depending on the blockchain network. For instance, Ethereum requires a minimum of 32 ETH to be staked by those wishing to operate a solo validator node. This requirement ensures that validators are vested in the network’s security and performance.
Knowledge and Skills
Running a validator node also demands a specific set of skills and knowledge. Operators must be proficient in network security, understand blockchain technology, and be capable of managing cryptographic keys. They need to know how to configure and maintain the node’s software, handle updates, and troubleshoot potential issues.
Important Note: The specifics of setting up a validator node vary significantly depending on the blockchain you’re interested in. I’ll outline the general process and crucial factors to keep in mind.
Hardware Requirements
Credits: Freepik
Setting up a validator node involves stringent hardware requirements to ensure the node functions optimally and maintains the integrity of the blockchain network. Here are the necessary hardware specifications:
CPU
A high-performance CPU is crucial for a validator node. It handles complex cryptographic operations that secure transactions and blocks within the blockchain. The CPU must be powerful enough to process these transactions efficiently and support the node’s continuous running without lag.
RAM
Sufficient RAM is essential for the smooth operation of validator nodes. Typically, a minimum of 64GB of RAM is recommended. This memory capacity allows for the efficient execution of smart contracts and speedy transaction processing, which is vital for maintaining the node’s high performance and reliability.
Storage
Another critical component is reliable and fast storage. Solid-state Drives (SSDs) are preferred due to their speed and durability. At least 500GB of SSD storage is advisable to effectively handle the large volume of blockchain data. This capacity supports the current blockchain size and accommodates its growth over time.
Internet Connection
Validator nodes require a robust and stable internet connection. This connection ensures that the node constantly communicates with the blockchain network. It facilitates quick data transmission and reliable participation in consensus mechanisms, vital for the network’s security and efficacy.
Individuals or organizations can effectively run validator nodes by ensuring these hardware specifications are met. These nodes then contribute significantly to blockchain networks’ security and operational efficiency.
Software Requirements
Credits: Freepik
Setting up a validator node requires a combination of critical software components to ensure efficient operation and robust security. Here are the essential software requirements:
Operating System
Choosing the right operating system is foundational for running validator nodes. Popular choices include Ubuntu, Debian, and CentOS. These Linux distributions are favored for their stability and security features, which are crucial for supporting the complex operations of blockchain nodes. Running a validator node on a dedicated server enhances system configuration control.
Node Software
Node software is the core application that allows the validator to interact with the blockchain. For instance, Geth is commonly used for Ethereum nodes. This software handles tasks such as processing transactions, creating blocks, and connecting with other nodes in the network. It is essential for maintaining the integrity of the blockchain ledger.
Security Software
Robust security software is necessary to protect the node from cyber threats. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption tools. Effective security software ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data by guarding against unauthorized access and potential vulnerabilities.
Wallets and Keys
Secure management of wallets and cryptographic keys is critical for any blockchain participant. Wallets store private keys securely, enabling users to access their digital assets. Public keys verify transactions, ensuring they are valid and authorized. Proper management of these keys is essential to prevent unauthorized access and potential loss of funds.
The right software makes all the difference. It helps your validator node stay secure and do its job on the blockchain. Setting everything up carefully is key to running a successful validator node.
Also Read Unlocking Crypto Rewards: How Long Does Crypto Staking Take?
Cryptographic Keys for Validator Nodes
Credits: Freepik
Cryptographic keys are crucial for the operation of validator nodes in blockchain networks. These keys authorize transactions and maintain network security and integrity.
Importance of Cryptographic Keys
Validator nodes use cryptographic keys to perform various network actions. These keys ensure that the node’s operations are secure and verifiable by other network participants.
Key Types and Usage
- Ethereum-Based Networks: Validator nodes on Ethereum-based networks often require two sets of key pairs. One is an Ethereum key pair for general interactions with the Ethereum blockchain. The other is a network-specific key pair, such as a Chainflip-native key pair for specific functionalities like State Chain interactions.
- Tendermint-Based Networks: The consensus key is vital for networks like Tendermint. This key is used primarily for voting on blocks. Since it must always be online to participate in consensus, it is critical to protect it using advanced security measures. Storing it simply in a JSON file is not safe. Instead, a Key Management Server (KMS) or Hardware Security Module (HSM) can provide the required security.
- Substrate-Based Networks: These networks utilize session keys. Session keys are online keys validators use to sign messages related to consensus. They are not involved in controlling funds directly but are critical for the consensus process. Regular updates or changes to these keys can help maintain security.
Secure Key Management
Managing these cryptographic keys safely is essential to prevent unauthorized access and potential network attacks. Key management practices may include:
- Using hardware security modules (HSM) to safeguard keys physically.
- Implementing key management servers that help securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys.
- Employing encryption methods like GPG for transferring keys securely to backup locations.
Cryptographic keys are fundamental for validator nodes. Proper management and security of these keys are imperative to ensure blockchain networks’ ongoing integrity and security. Validator nodes must adopt robust security practices to manage these keys effectively.
Synchronization
Credits: Freepik
Synchronization is vital in validator node setup. It keeps the node updated with the latest blockchain state. The process downloads and checks the entire blockchain history. This is necessary for the node to work well and safely.
Importance of Synchronization
Synchronization ensures validator nodes have a full and accurate copy of the blockchain data. This accuracy is crucial for verifying transactions and upholding the blockchain’s integrity.
Challenges in Synchronization
Even with strong hardware, nodes on networks like Solana often sync slowly. This slowdown can come from high server loads, insufficient hardware resources, or shaky internet connections. These problems can cause nodes to stay caught up on the blockchain, affecting their performance and the network’s security.
Addressing Synchronization Issues
Improving hardware setup is key to better synchronization. Ensure there’s enough CPU power, RAM, and storage. A stable and fast internet connection also helps speed up the process. Downloading an offline blockchain data package on networks like Neo can also reduce the syncing load.
Tools and Techniques
Different blockchains offer various tools and techniques to aid in synchronization. For example, the Waves blockchain effectively utilizes CPU frequency during block verification, a single-threaded process. The signature validation process, although multi-threaded, has a negligible effect on synchronization speed. Understanding these specifics can help users configure their systems to optimize synchronization times.
Staking and Delegation
Staking and delegation are critical mechanisms in blockchain networks that facilitate the operation of validator nodes. These processes play significant roles in ensuring network security and operability.
Staking
Staking involves committing a certain amount of cryptocurrency tokens to a validator node. This commitment signals the network that the node is ready to participate as a validator. The amount required for staking exceeds the “seat price,” which is dynamically determined based on the total tokens staked by all validators in the network.
Delegation
Delegation allows individuals who do not wish to operate a validator node to still participate in the staking process. By delegating their tokens to a validator, these token holders can earn rewards without managing the complexities of running a node. This process broadens participation and enhances network security by increasing the number of staked tokens.
Customization and Contracts
In some blockchain networks, staking and delegation are facilitated through customizable smart contracts. Validators may deploy their own staking pool contracts, which outline the terms for commission fees and the division of rewards. This allows validators to set terms that might attract more delegators.
Network-Specific Rules
Different blockchain networks have distinct rules for staking and delegation. For instance, on the Avalanche network, validators must stake a minimum of 2,000 AVAX tokens to participate, while delegators can start with as little as 25 AVAX. Both validators and delegators earn rewards, but the specific distribution depends on the validator’s delegation fee rate.
Network-Specific Configurations
Setting up a validator node requires precise configurations specific to each blockchain network. These settings are crucial for the node to function correctly and securely within the network.
Berachain Validator Node Configuration
For Berachain:
- Initialization: Begin by initializing your node following the guidelines for setting up a local validator node.
- Security Settings: It is vital to configure security settings such as disabling RPC ports. This prevents DDoS attacks and potential slashing.
- Data Management: Set pruning settings to effectively manage data storage. This limits the amount of blockchain history stored on the node, optimizing performance.
Oasis Validator Node Configuration
For Oasis:
- Entity Setup: Initialize your entity on the localhost and create an account using the Oasis CLI.
- Account Management: Add this entity account to the Oasis CLI and import the private key of the funding account.
- Network Registration: Include your node ID in the entity descriptor file and ensure your entity is registered on the network. Confirm that your node is connected and functioning as a validator.
Meter Validator Node Configuration
For Meter:
- Port Configuration: Configure network ports to facilitate communications, including P2P, API, and Ethereum-compatible interfaces.
- Node Election: Elect your node as a candidate for a delegate node using the Meter Wallet Staking portal.
- Token Staking: Stake MTRG tokens and submit the transaction to become a candidate. Ensure your node is among the top 500 candidates to participate in the consensus process.
General Recommendations
Validator nodes need better hardware than full nodes. This is because they do more processing for consensus and validation. Here are some tips:
- Public IP and Ports: Keep a public IP address and ensure the right ports are open for validator activities.
- Security Measures: Focus on security setups. Turn off password authentication over SSH. Avoid running non-validator services on the same IP. Enable only the essential EVM APIs.
These specific network setups are crucial for running and securing validator nodes in blockchain networks. Setting things up right and following these tips help keep the blockchain stable and efficient. A dedicated server provides the physical and network security needed for a validator node to prevent unauthorized access and potential attacks.
Core Validator Nodes Maintenance Tasks
Maintaining validator nodes is crucial for ensuring their security and optimal performance within the blockchain network. This involves regular software updates and diligent monitoring.
Software Updates
Credits: Freepik
It’s crucial to update the software of validator nodes. Updates bring new features, fix bugs, and enhance security. These changes keep the blockchain network stable and secure.
- Update Process: Typically, you pause the node, swap the old software with the latest version, and restart. This method keeps downtime short and can be done in one maintenance session.
- Planned Maintenance: For bigger updates that take longer, validators may need to stop their network activities temporarily. This step is called “chilling” the stash. After the update, validators rejoin the network to continue their duties.
- Security Considerations: Always follow the recommended procedures for updates. This prevents penalties for actions that could harm the network’s security.
Also read Maximizing Staking Rewards: Navigating the Choice Between Cloud and Dedicated Servers
Monitoring
Regular monitoring of validator nodes ensures they are functioning correctly and efficiently:
- Key Metrics: Validators should monitor network connectivity, resource usage (such as CPU, memory, and disk space), block production rates, and synchronization status with the blockchain.
- Tools and Alerts: Using monitoring tools allows validators to track the health of their nodes continuously. These tools can alert validators to any anomalies or issues that might arise, enabling quick resolution before they affect the network.
- Importance of Vigilance: Consistent monitoring is fundamental to maintaining a secure and reliable validator node. It helps detect potential problems early and keeps the node operating smoothly within the blockchain ecosystem.
Hardware Maintenance and Monitoring
Effective hardware maintenance and monitoring are crucial for continuously operating validator nodes in a blockchain network. These practices ensure that the hardware remains reliable and efficient.
Uptime
Maintaining high uptime is essential for validator nodes. Uptime refers to when the node remains operational and connected to the network without interruptions. High uptime is critical for validators as it affects their ability to participate in consensus and maintain their reputation within the network. To meet the rigorous uptime requirements of blockchain networks, a validator node should ideally be deployed on a dedicated server.
Redundancy
Implementing redundancy measures is another vital aspect of hardware maintenance. Redundancy involves setting up additional systems or components that can take over if the primary system fails. This can include having backup servers or duplicated network connections, ensuring the node can continue operating even if one part of the system breaks down.
Resource Monitoring
Monitoring the physical resources of the node—such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and disk space—is essential:
- CPU and Memory Usage: Keeping an eye on CPU and memory usage helps identify when the node is under strain, which could indicate a need for upgrades or optimizations to handle the increased workload.
- Disk Space: Monitoring disk space is crucial to ensure the node has enough room to store the blockchain’s growing data. Running out of disk space can cause the node to stop functioning properly.
Regularly checking these hardware metrics allows for proactive maintenance, helping to avoid downtime and ensuring the validator node runs smoothly and efficiently. This vigilance is key to maintaining the integrity and performance of blockchain networks. A dedicated server for a validator node allows for better resource allocation. It is crucial for processing transactions efficiently.
Security Practices
Credits: Freepik
Effective security practices are crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of validator nodes in blockchain networks. These practices encompass access control, key management, and regular audits.
Access Control
Access control is fundamental to securing a validator node. It ensures that only authorized users can access the node and its resources. This can be achieved through:
- User Authentication: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms such as two-factor authentication (2FA) to verify the identity of users accessing the node.
- Permissions Management: Assigning specific roles and permissions to users based on their job requirements limits access to critical system components and reduces the risk of accidental or malicious changes.
Key Management
Key management involves the safe handling and storage of cryptographic keys used by the blockchain node:
- Secure Storage: Storing keys in secure environments, such as hardware security modules (HSMs) or encrypted storage solutions, to protect them from unauthorized access and tampering.
- Regular Rotation: Regularly updating and rotating keys to minimize the risks associated with key theft or leakage.
Audits
Conducting regular security audits is a proactive measure to identify and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities:
- Internal Audits: Regularly review security policies and procedures to ensure they are current and effective.
- External Audits: Hiring external security experts to perform thorough assessments and penetration tests can help uncover hidden vulnerabilities and improve the security posture.
Monitoring and Alerts
Monitoring and alerts are critical to maintaining a validator node’s health and security. They ensure that potential issues are quickly identified and addressed.
Performance Metrics
Credits: Freepik
It’s crucial to monitor performance metrics to keep the validator node working well:
- Resource Utilization: Check CPU, memory, and disk usage regularly. This helps spot any bottlenecks or issues with performance.
- Network Performance: Keep an eye on bandwidth usage and latency. This ensures the node keeps a stable and fast connection to the blockchain network.
For optimal performance and reliability, it is advisable to use a dedicated server tailored explicitly for validator node operations.
Slashing Protection
Slashing protection helps prevent penalties for actions that might harm the network:
- Downtime Prevention: Use solutions that keep the node online to avoid penalties for being offline.
- Double Signing Protection: Ensure the node does not sign conflicting transactions or blocks. This could be viewed as trying to disrupt network consensus.
Logs
Keeping detailed logs is essential for both security and operational efficiency:
- Activity Logs: Recording all actions the node and its users takes to provide an audit trail that can be analyzed following a security incident.
- Error Logs: Monitoring for errors that may indicate operational problems or security concerns that require immediate attention.
Troubleshooting
Effective troubleshooting is essential for maintaining the operational health of validator nodes. It involves a systematic approach to diagnosing and resolving issues, supported by comprehensive documentation and responsive support systems.
Documentation
Having thorough and accessible documentation is vital for effective troubleshooting:
- User Manuals: Detailed guides and manuals provide step-by-step instructions on setting up, configuring, and maintaining validator nodes. They serve as a first reference point in troubleshooting.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Specific documentation focused on common problems and their solutions can help users quickly identify and resolve issues without external assistance.
Support
Strong support systems are essential for solving complex problems that a guide alone can’t fix.
- Technical Support: Access to expert and responsive support teams can greatly reduce downtime. They provide real-time help.
- Community Forums: Many blockchain projects have active forums and user groups. These are great places to share experiences and solutions. Forums help with collaborative problem-solving and offer insights beyond the official documentation.
Don’t Miss Out: Buy Your Dedicated Server with Bitcoin Today!
Additional Considerations
Maintaining a validator node involves more than regular updates and monitoring. Additional considerations can enhance the node’s efficiency and ensure its resilience.
Storage Optimization
Effective storage management is crucial for the smooth operation of validator nodes:
- Database Pruning: This involves removing unnecessary data from storage to free up space and improve system performance. Pruning helps maintain only the essential data, making the database leaner and faster.
- Data Retention: A clear data retention policy ensures that only relevant data is kept for necessary periods. This helps manage storage efficiently while complying with legal or operational requirements.
Blockchain-Specific Tasks
Validator nodes may require specific tasks that are unique to each blockchain:
- Custom Scripts: Writing and implementing custom scripts can automate specific blockchain tasks, reducing the manual workload and minimizing human error.
Disaster Recovery
Credits: Freepik
Preparation for potential disasters is key to the resilience of validator nodes:
- Backups: Regular backups of the node’s data and configuration settings are essential. These backups should be stored in secure, geographically diverse locations to protect against data loss from local hardware failures or natural disasters.
- Recovery Plan: A detailed recovery plan ensures that operations can be quickly restored after a disruption. This plan should outline steps for using backups to restore functionality.
- Automation: Automating recovery processes can speed up the return to normal operations and reduce the risk of mistakes during high-pressure situations.
- Test Environments: Regular testing of the disaster recovery plan in controlled environments is crucial. This ensures that the plan is effective and that staff are familiar with recovery procedures.
Stay Informed
It’s crucial to keep up with the latest in the blockchain world:
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with new blockchain research, updates, and security tips. This helps you get ready for changes and challenges. A validator node should be hosted on a dedicated server to ensure maximum uptime and security.
- Community Engagement: Join discussions in blockchain forums. These discussions offer insights into common problems and new solutions.
These steps are important for keeping your validator node strong, efficient, and secure. By focusing on these areas, node operators can ensure their systems are well-maintained and current with the latest blockchain trends.
Conclusion
Setting up and running a validator node isn’t just about getting it started—it’s about keeping it in top shape. You’ll need the right hardware and software, strong security measures, and sharp monitoring systems. Effective troubleshooting, storage optimization, and solid disaster recovery plans are also key to keeping your node efficient and resilient. Plus, staying active in the blockchain community helps you keep pace with the latest trends and best practices.
Looking to launch and maintain a top-notch validator node? Check out RedSwitches dedicated servers. We offer tailored solutions that provide the robust infrastructure and expert support necessary for optimal node operation. Dive into our services today and enhance your blockchain capabilities with RedSwitches.
FAQs
Q. What is a validator node?
A validator node is a server on a blockchain network that is responsible for validating transactions and blocks. By ensuring the accuracy and security of the blockchain, validator nodes help uphold the network’s integrity.
Q. Do validator nodes make money?
Yes, validator nodes can earn money through transaction fees and block rewards. The specific earnings depend on the blockchain protocol and the amount of work the node performs.
Q. How do I become a node validator?
To become a node validator, you typically need to run specific node software, meet hardware and software requirements, stake a certain amount of the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency, and follow the network’s protocol for becoming a validator.
Q. What is the difference between a validator node and a full node?
A validator node hosts a full copy of the blockchain (like a full node) and participates in the consensus process by validating transactions and blocks. Full nodes verify transactions against the blockchain’s consensus rules but do not create new blocks.
Q. How much does an Ethereum validator node make?
As of the latest updates in Ethereum 2.0, an Ethereum validator node can earn varying amounts based on network conditions and the amount staked. Rewards fluctuate with the number of validators and the total ETH staked, with potential annual returns typically ranging between 4% and 10%.
Q. What is the difference between PoS and PoW consensus algorithms?
PoS (Proof of Stake) and PoW (Proof of Work) are methods used to add new transactions to the blockchain. PoW requires solving complex problems and uses a lot of energy. PoS lets participants use their own coins as a security deposit. It uses less energy and helps keep the network safe.
Q. How can running your own validator on a PoS mainnet generate passive income?
When you run your own validator on a PoS mainnet, you help validate transactions. This means you are part of the network that checks and confirms new entries. Validators are rewarded with cryptocurrency, which can be a form of passive income. Your setup needs to stay online and meet certain requirements to keep working and earning.
Q. What is a nominator, and how do they contribute to the DeFi ecosystem?
A nominator in some blockchain networks chooses validators to support with their crypto assets. They help secure the network by picking reliable validators. This role is key in DeFi, or decentralized finance, which lets people participate in finance more democratically than traditional methods.
Q. What should one consider before installing a validator node on AWS (Amazon Web Services)?
Before setting up a validator node on AWS, make sure the server matches the blockchain’s needs. Consider CPU power, memory, storage, and internet speed. AWS lets you adjust these resources as needed, which is why many choose it for running validator nodes.
Q. Can you explain the process from testnet to mainnet in blockchain development?
Moving from testnet to mainnet is an important step in developing blockchain technology. First, updates and new features are tested on a testnet, where no real money is at risk. This helps find and fix problems. If the test goes well, the final version is moved to the mainnet, where real transactions happen and get recorded on the blockchain.