Did you know the worldwide Linux market will reach $15.64 billion by 2027? It is safe to say that the world of Linux is vast and varied, with distributions tailored to all the different types of users, from casual desktop enthusiasts to seasoned programmers.
When discussing Linux distributions, two names, Linux Mint or Ubuntu, take the lead. While both are based on Debian, they diverge in ways that can significantly impact the user experience. Choosing the proper distribution is much like selecting the right pair of shoes. It’s all about fit, comfort, and suitability for the journey ahead.
This blog will discuss the differences between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, exploring each distribution’s unique features, performance metrics, user interfaces, and more.
Table of Contents
- What is Linux Mint?
- What is Ubuntu?
- Similarities Between Linux Mint and Ubuntu
- Ubuntu vs. Linux Mint: Differences and Comparison
- Conclusion – Linux Mint vs Ubuntu
- FAQs
What is Linux Mint?
Credits: Linux Mint Website
Before we dive into the Linux Mint vs Ubuntu comparison, it is essential to explore their definitions.
Linux Mint is a modern operating system known for its remarkable features and ease of use. Based on the Ubuntu operating system (which is based on Debian), Linux Mint offers a stable and robust platform for desktop and laptop computers.
It comes with full multimedia support and is highly user-friendly, making it an excellent choice for individuals new to Linux and experienced users who prefer a more efficient and less cluttered desktop environment. Mint offers a more traditional desktop experience with a customizable start menu and desktop shortcuts, making it a popular alternative for those migrating from macOS or Windows.
Key Features of Linux Mint
When determining which to choose, Linux Mint versus Ubuntu, exploring the features of each can help streamline the decision-making process. Below are the key features of Linux Mint:
Cinnamon Desktop Environment
Linux Mint’s flagship edition comes with the Cinnamon desktop environment, known for its modern yet traditional interface, which feels familiar to users of other major operating systems.
Cinnamon offers a sleek layout with an intuitive menu, making navigation and system management straightforward and user-friendly. The environment is highly customizable, with various themes and extensions to tailor the desktop to your preferences.
Software Manager
Software management is a breeze on Linux Mint, thanks to its Software Manager. This feature provides users access to thousands of programs, all categorized and searchable for easy discovery.
The applications within are reviewed and rated by the community, ensuring you can make informed decisions about the software you install. The Software Manager in Linux Mint is also known for its speed and simplicity, allowing quick installations and hassle-free updates.
Update Manager
Keeping your system secure and up to date is crucial, and Linux Mint’s Update Manager simplifies this process. It categorizes updates based on their stability and security level, enabling users to choose how cutting-edge or stable they want their system to be.
The Update Manager is designed to be unobtrusive, providing notifications without interrupting the user’s workflow. It is also robust enough to handle kernel updates without needing a complete system upgrade.
Mint Tools
Linux Mint comes with an extensive suite of tools known as ‘Mint Tools.’ These include the Mint Install for software downloads, Mint Update for system updates, and Mint Menu, which provides an elegant, searchable menu to access your software and settings. These tools are developed with the end-user in mind, offering both ease of use and powerful functionality, distinguishing Linux Mint from other distributions.
Performance and System Requirements
One of Linux Mint’s most praised features is its performance, particularly on systems with limited resources. It’s optimized to run smoothly on new and older hardware, making it an ideal choice for users who do not have access to the latest technology. This accessibility factor is a significant benefit. It enables more people to use a modern and secure operating system without demanding expensive upgrades.
Community and Documentation
Linux Mint has a solid and welcoming community, an invaluable resource for new users. The community forums are active and friendly, making it easy to seek help and advice. The distribution boasts comprehensive documentation that covers everything from installation to advanced system management. This makes it easy for users to find the information they need to get the most out of their system.
Security and Privacy
Security is an important aspect of Linux Mint. The distribution comes with firewall tools and takes a conservative approach to automatic software updates, reducing the risk of regressions. On the privacy front, Linux Mint doesn’t collect personal data, and it provides users with significant control over their information, standing as a proponent of digital privacy rights.
Looking for the best browsers for Linux? Read our blog for our top 10 picks, ‘Penguin Picks: 10 Best Browsers Linux Tailored to Perfection.’
Pros and Cons of Using Linux Mint
Weighing the pros and cons of each Linux distribution when contemplating between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu can offer valuable information on the better option for you. Below are the pros and cons of using Linux Mint:
Pros
User-Friendly Interface
Linux Mint is renowned for its sleek, intuitive interface, which offers a smooth transition for Windows or macOS users. Cinnamon’s desktop environment strikes a familiar chord with its layout and functionality, making the switch less tedious. Mint comes with various customization options, allowing users to tweak their desktops to suit personal preferences while maintaining a clean and navigable user experience.
Robust Software Management
With its Software Manager, Mint provides users access to a vast repository of applications and tools. This feature simplifies the installation and management of software, boasting an extensive list of programs that can be installed with just a few clicks.
Whether you need productivity tools, programming software, or media applications, Mint’s Software Manager can streamline the process in a way that is accessible to users of all skill levels.
Solid Performance and Stability
One of Linux Mint’s most persuasive advantages is its performance. It’s known for running smoothly on various hardware, including older machines where other operating systems might struggle.
This reliable performance, coupled with a strong record of stability, makes Mint a safe choice for those who need a dependable system for daily use, whether for work, education, or personal projects.
Security and Privacy
Linux Mint has a robust security protocol, offering users peace of mind. The OS regularly receives updates and patches to address any vulnerabilities. Mint doesn’t collect much personal data compared to some of its competitors, which is a significant plus for users who prioritize privacy.
Helpful Community Support
The community around Linux Mint is a treasure trove of knowledge and assistance. For newcomers and experienced users, the forums and online resources are brimming with tips, tutorials, and guidance. This community-driven support can be invaluable when troubleshooting issues or seeking advice on system optimization.
Cons
Fewer Commercial Applications
While Mint’s Software Manager is robust, specific commercial software and games don’t support Linux. This can be a hurdle for users who rely on specific applications for their profession or who enjoy popular titles in gaming, often resulting in the need to find alternatives or use compatibility layers such as Wine, which might not always provide a smooth experience.
Hardware Driver Support
Although Mint performs well on various machines, hardware drivers can face challenges, particularly for new or specialized hardware. While the Mint team works diligently to support a broad range of devices, users may occasionally encounter issues with compatibility, which can affect the system’s usability.
Potential for Learning Curve
There might be an initial learning curve for individuals new to the world of Linux. Even with Mint’s dedication to user-friendliness, transitioning from another OS involves adapting to a different way of managing system settings and understanding the file structure. The extensive documentation and helpful user community mitigate this con.
Use Cases of Linux Mint
Narrowing down the use cases of each Linux distribution when deciding between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu can help offer valuable information on which is best suited for your individual needs. Below are the use cases of Linux Mint:
For Personal Computing
Linux Mint shines as a personal computing platform, offering an intuitive interface that newcomers to Linux can easily adapt to. Its similarity to traditional Windows in terms of layout lowers the learning curve for switching users. With a suite of free, open-source applications, Mint is an excellent choice for everyday tasks like web browsing, media consumption, and document editing.
As a Developer’s Workspace
Developers find Linux Mint a powerful workspace due to its compatibility with many programming tools and languages. Its terminal and package managers facilitate easy installation and management of development environments. The stability of Mint ensures that developers have a consistent platform for coding, testing, and deploying applications.
For Educational Purposes
Educational institutions increasingly adopt Linux Mint because of its cost-effectiveness and the rich repository of educational tools it provides. Its user-friendly design is suitable for students of all ages, encouraging learning and exploration in a computing environment. The software center in Mint allows easy access to a wide array of learning software, making it an ideal OS for educational establishments.
In Corporate Environments
Linux Mint’s reliability and security features have made it suitable for many corporate environments. It integrates well with various server technologies and databases, making it a solid workstation OS for enterprise users. Plus, the lack of licensing fees can lead to significant business cost savings.
For Older Hardware Revitalization
Linux Mint breathes new life into older hardware by requiring fewer resources than the latest versions of Windows or macOS. Its lightweight nature allows for smooth operation on systems that may struggle with more demanding operating systems. This makes Mint a popular choice for refurbishing older PCs for charitable causes or extending their usable life.
As a Home Theater PC
Mint can transform a standard computer into a capable Home Theater PC (HTPC). It supports various media formats and can run popular HTPC software like Kodi smoothly. With its low resource usage, even older machines can become effective media centers under Mint.
For Security and Privacy-Conscious Users,
Security-minded users appreciate Linux Mint for its robust privacy features and the fact that it’s less prone to viruses compared to other OSes. Mint regularly receives security updates, and users can access various encryption tools and VPN services. The operating system’s emphasis on user privacy makes it a strong choice for those looking to safeguard their data.
What is Ubuntu?
Credits: Ubuntu Website
Ubuntu is a free and open-source operating system based on Linux, which is itself derived from the Debian architecture. It is one of the most popular distributions of Linux available and is widely recognized for its user-friendliness and accessibility to newcomers. Developed by Canonical Ltd., Ubuntu aims to offer a secure, stable, and customizable computing experience for users on desktops, servers, and, more recently, on IoT devices.
The name ‘Ubuntu’ originates from an ancient African word meaning ‘humanity to others,’ the OS espouses the spirit of community collaboration and sharing, which is central to the open-source movement. Ubuntu has a wide range of pre-installed software programs, including a web browser, media apps, an office suite, and more, making it a ready-to-use solution straight after installation.
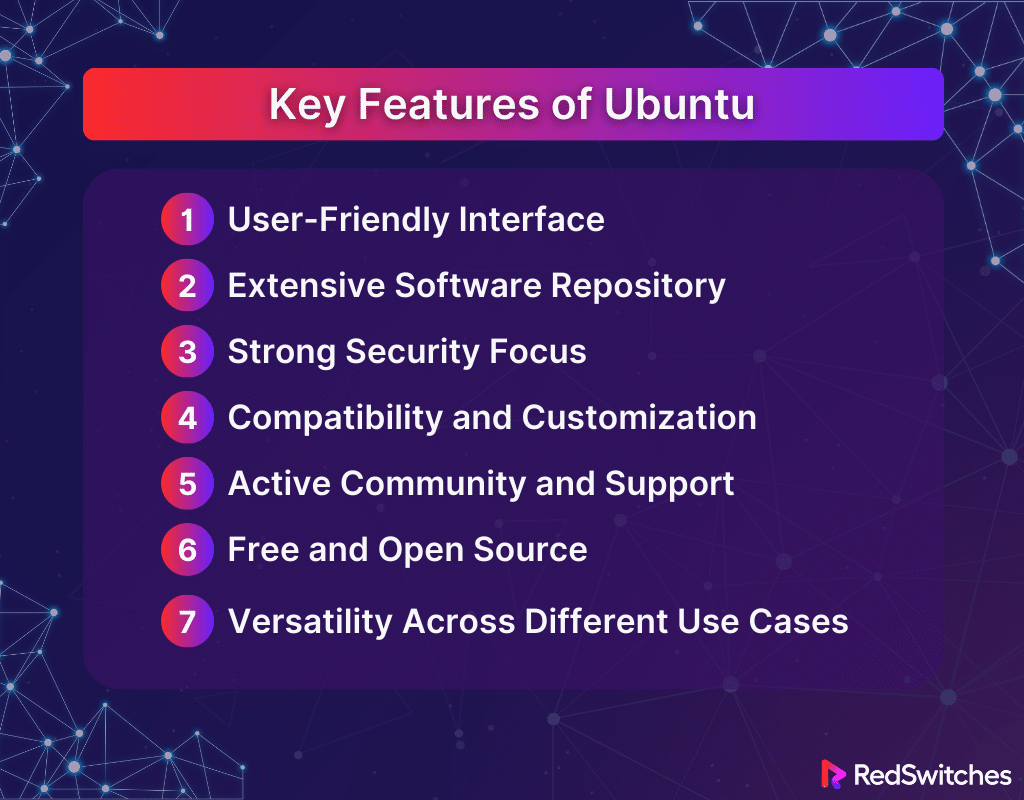
Key Features of Ubuntu
Exploring the key features of Ubuntu when comparing Linux Mint vs Ubuntu can help you pinpoint the Linux Distribution that best suits your preferences and needs. Below are the key features of Ubuntu:
User-Friendly Interface
Ubuntu is renowned for its clean and approachable user interface. The default desktop environment, GNOME, provides a straightforward and intuitive experience that feels familiar to users transitioning from other operating systems such as Windows or macOS. Customization options abound, allowing users to tweak the look and feel to their preference, making Ubuntu not only accessible but also adaptable to individual tastes.
Extensive Software Repository
Ubuntu’s extensive software repositories are among its most compelling features. With thousands of applications available for easy installation via the Ubuntu Software Center, users can access various programs for productivity, entertainment, development, and more. Ubuntu supports free and proprietary software, ensuring users can find virtually any tool they need.
Strong Security Focus
Security in Ubuntu is taken incredibly seriously. The distribution has a built-in firewall and malware protection, making it a secure choice. Regular security patches and updates are released to address vulnerabilities. Long-Term Support (LTS) releases offering five years of security updates guarantee stability and security for the long haul.
Compatibility and Customization
Ubuntu boasts high compatibility with a wide range of hardware, often working with minimal setup. It supports various customizations that allow users to modify their desktop environment, manage user permissions, and tailor system operations to their needs. With the power of Linux under the hood, users can also utilize many terminal commands and scripts to personalize their experience further.
Active Community and Support
The Ubuntu community is active and vibrant, providing a backbone of support for new users. From forums and online tutorials to dedicated Q&A sites like Ask Ubuntu, significant knowledge and assistance are readily available. This strong community support makes troubleshooting a breeze and learning about the system a communal experience.
Free and Open Source
As a free and open-source operating system, Ubuntu allows users to download and use the OS without charge and view and modify the source code. This openness encourages innovation and collaboration, allowing developers and enthusiasts to contribute to the OS’s continuous improvement. The open-source nature also fosters transparency and trust, setting Ubuntu apart from proprietary alternatives.
Versatility Across Different Use Cases
Ubuntu is a versatile player in the OS market, suitable for desktops, servers, and cloud environments. It’s a top choice for running web servers, as a platform for virtualization, and for cloud computing with its optimized version for OpenStack.
Ubuntu’s flexibility also extends to personal computing, with flavors like Ubuntu Studio catering to creative professionals and Ubuntu Kylin offering a version tailored for Chinese users.
Are you wondering which is better, Ubuntu or Windows? Read our informative blog, ‘Battling Giants: Ubuntu vs Windows – Who Reigns Supreme?‘ for answers.
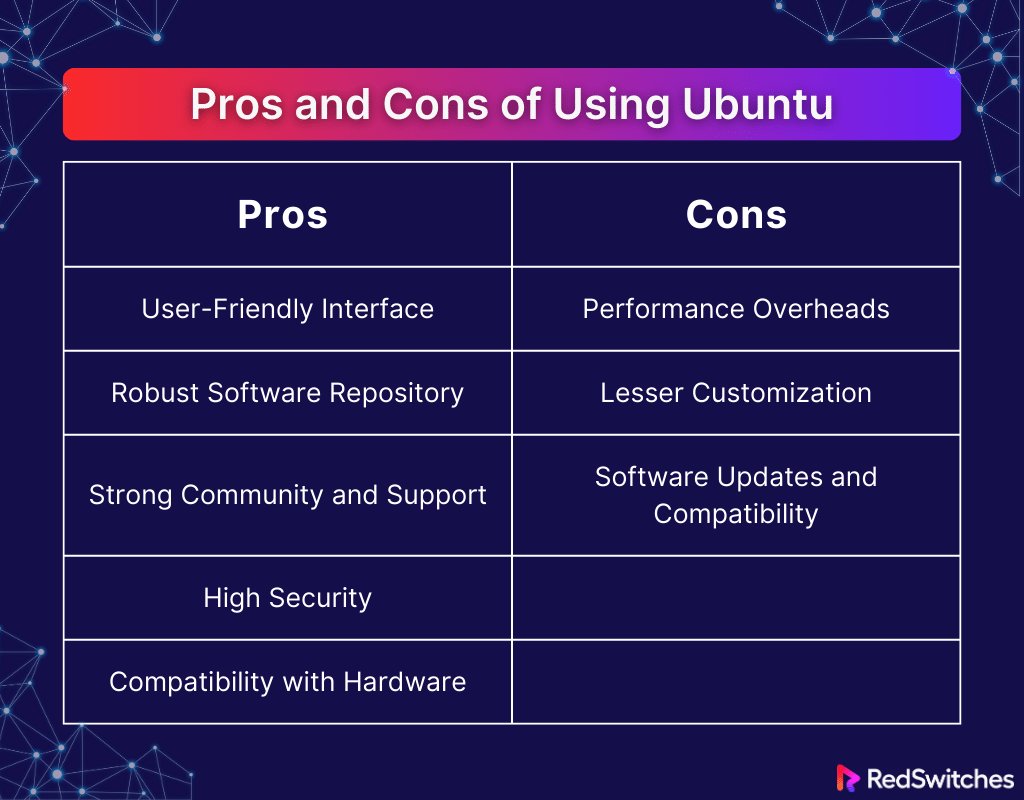
Pros and Cons of Using Ubuntu
Weighing the pros and cons of Ubuntu can offer valuable insight into which Linux distribution, between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, offers the most pros for you. Below are the pros and cons of Ubuntu:
Pros
User-Friendly Interface
Ubuntu provides a polished, modern user interface with its GNOME desktop environment, which is intuitive for users migrating from other operating systems. This accessibility makes it an ideal starting point for those new to Linux. The unity of design and functionality creates a comfortable, cohesive user experience.
Robust Software Repository
With access to a massive software repository, Ubuntu makes finding and installing new applications incredibly easy. The Ubuntu Software Center simplifies the process, offering a range of free and commercial software. The compatibility with .deb packages, commonly used in Debian-based distributions, broadens the spectrum of available software.
Strong Community and Support
Ubuntu benefits from a vibrant, active community ready to help new users. Official forums, Ask Ubuntu, and extensive documentation mean support is readily available. For businesses, paid professional support options are also available, which is a testament to the reliable infrastructure that Ubuntu promises.
High-Security
Ubuntu is a very secure operating system with a strong emphasis on security features such as AppArmor and the regular roll-out of security updates. It’s less vulnerable to viruses than other operating systems, providing peace of mind for users sensitive to data breaches. The option for advanced users to configure and harden their system further enhances its security profile.
Compatibility with Hardware
Ubuntu works well with a wide range of hardware, often without installing additional drivers. Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, has partnerships with big hardware manufacturers to ensure compatibility. This broad hardware support eases installation and use, making Ubuntu a versatile choice for different devices.
Cons
Performance Overheads
While Ubuntu is efficient, its user-friendly design introduces some performance overhead compared to more streamlined Linux distributions. While attractive, the default Ubuntu desktop environment can be resource-intensive, potentially slowing down older hardware. This can be a point of contention for power users seeking maximum performance.
Lesser Customization
Ubuntu’s GNOME desktop focuses on simplicity, which sometimes comes at the expense of deep customization. Users looking for a highly personalized desktop environment might find Ubuntu’s options limiting. This contrasts with other Linux distributions that offer more flexibility.
Software Updates and Compatibility
Although software updates are generally beneficial, they can sometimes cause issues with compatibility, especially for those using Ubuntu for development purposes. Some updates have been known to introduce bugs or break existing features. The semi-annual release cycle can also be a double-edged sword for users who require the most stable environment possible.
Do you want to learn more about Ubuntu? Read our Ubuntu blog.
Also Read: Reinstall the Ubuntu Operating System in 4 Easy Steps
Use Cases of Ubuntu
When contemplating between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, understanding the unique use cases of each can help you decide which Linux distribution is best for you. Below are the use cases of Ubuntu:
Personal and Desktop Computing
Ubuntu provides a sleek and intuitive desktop experience, rivaling mainstream operating systems. It comes with essential applications for daily use, such as office suites, browsers, and media apps, all available from the get-go. Its user interface, GNOME by default, is both aesthetically pleasing and customizable, making it a hit among users transitioning from other operating systems.
Web Server Deployment
Ubuntu’s stability and security make it an ideal choice for hosting websites, powering many of the internet’s web servers. Its extensive support for software like Apache and NGINX and database systems like MySQL simplifies the web server deployment process. System administrators favor Ubuntu for its predictable release cycle and long-term support options.
Cloud Computing
Ubuntu is a leader in cloud computing, with its server edition optimized for scale and performance in cloud environments. It supports various public clouds, including AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure, and offers Ubuntu Cloud Images for a smooth cloud experience. Canonical’s Ubuntu Advantage program provides enterprise-grade support for cloud deployments, ensuring reliability and compliance.
IoT and Embedded Systems
In IoT (Internet of Things), Ubuntu Core presents a specialized, lightweight version tailored for connected devices. It features transactional updates and a secure application containment system, ensuring devices remain secure and functional in the field. This makes it a prime choice for IoT projects requiring long-term stability and robust security.
Education and Research
Educational institutions and research centers often use Ubuntu for its no-cost licensing and rich software repository. It can power everything from student laptops to research clusters, facilitating learning and discovery. The Ubuntu community maintains extensive educational applications, making it an invaluable tool for educators and students.
Software Development
Ubuntu’s versatility makes it a top choice among developers. It offers a wide range of programming tools and languages, supporting various IDEs and a wide ecosystem of libraries. Whether web development, application development, or game development, Ubuntu offers a stable and feature-rich platform for developers of all stripes.
Enterprise Servers and Data Centers
For enterprise environments, Ubuntu Server is a go-to solution, offering scalable and secure infrastructure for business applications. It boasts certified hardware compatibility and enterprise-grade support, making it a reliable backbone for critical services. Its commitment to regular security updates and packages tailored for enterprise needs further bolsters its position in corporate data centers.
Are you looking for information on Rocky Linux vs Ubuntu? Read our detailed blog, ‘A Comparison of Rocky Linux vs Ubuntu: Choosing the Ideal Linux Distribution.’
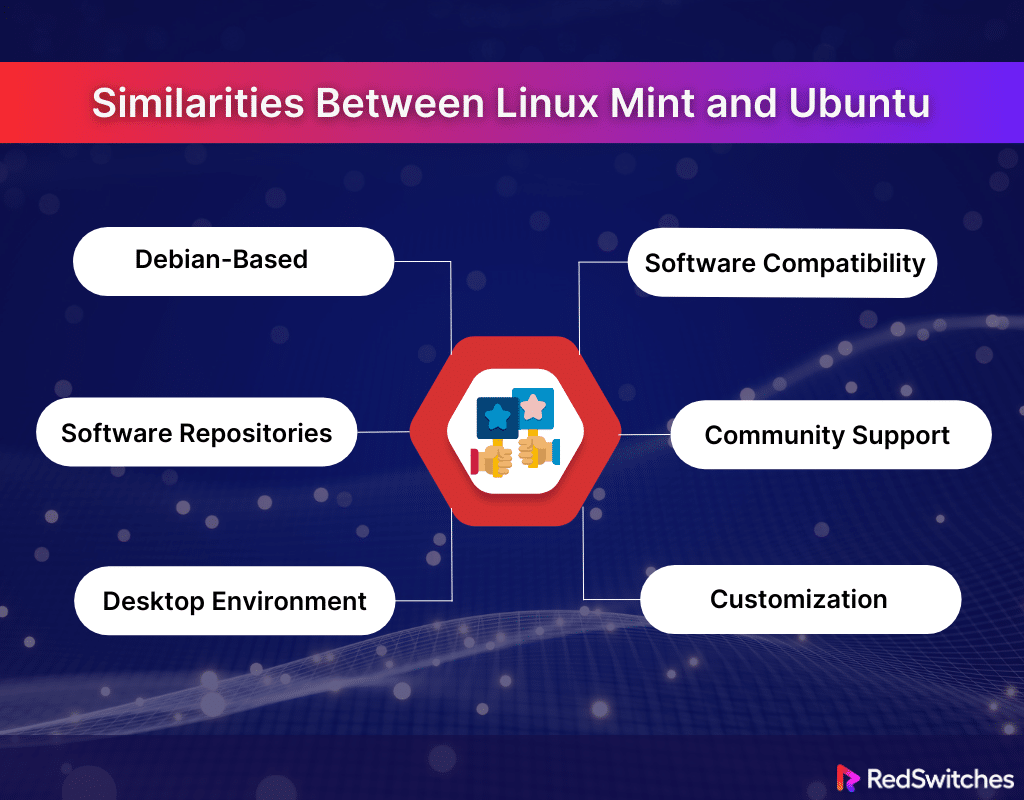
Similarities Between Linux Mint and Ubuntu
Although Linux Mint and Ubuntu may have varying use cases and features, they are also similar in certain ways. Below are the similarities between Linux Mint and Ubuntu:
Debian-Based
Both Linux Mint and Ubuntu are built upon the sturdy and widely respected foundations of Debian. They inherit many of the underlying features and philosophies of Debian. This Debian base ensures stable releases and a consistent performance ethos for both distributions. Users familiar with Debian will find comfort in package management and system administration similarities.
Software Repositories
Linux Mint and Ubuntu utilize the same software repositories, giving users access to various applications and updates. This makes the software available on both systems virtually identical, ensuring that users have the latest and most secure versions of their favorite applications. The shared repositories also mean that updates are delivered similarly, keeping both systems up-to-date with the latest developments.
Desktop Environment
While Ubuntu comes with its GNOME-based desktop environment by default, it also supports a range of other environments, much like Linux Mint. Linux Mint is well-known for its Cinnamon desktop environment, which offers a user-friendly experience akin to what Ubuntu offers.
Both distros allow users to switch to KDE (a desktop environment known for its modern graphical interface), XFCE (a desktop environment optimized for performance), and MATE (a desktop environment offering a straightforward and traditional user interface), providing a familiar setting for various preferences and resource requirements.
Ubuntu Software Compatibility
Software designed for Ubuntu is generally compatible with Linux Mint, making it easier for users switching between the two or wanting to try out new applications. The compatibility also extends to PPAs (Personal Package Archives), which are repositories used by developers to distribute software updates. Consequently, Linux Mint users can benefit from the wide range of software developed for Ubuntu’s more extensive user base.
Community Support
The community support surrounding both Linux Mint and Ubuntu is extensive and welcoming, with many forums, tutorials, and online groups dedicated to users of all levels. New users can expect a wealth of information and help, making the transition to Linux or troubleshooting issues less stressful. Both communities are active and known for their friendly assistance to newcomers.
Customization
Both Linux Mint and Ubuntu score highly on customization, allowing users to tailor their desktop environment to their liking. Users can modify everything from the appearance to the functionality with themes, applets, and extensions. The flexibility in customization allows individuals to create a personal computing experience that meets their specific needs and aesthetic preferences.
Now that we have discussed the definitions, features, pros, cons, and use cases of Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, let’s explore their differences.
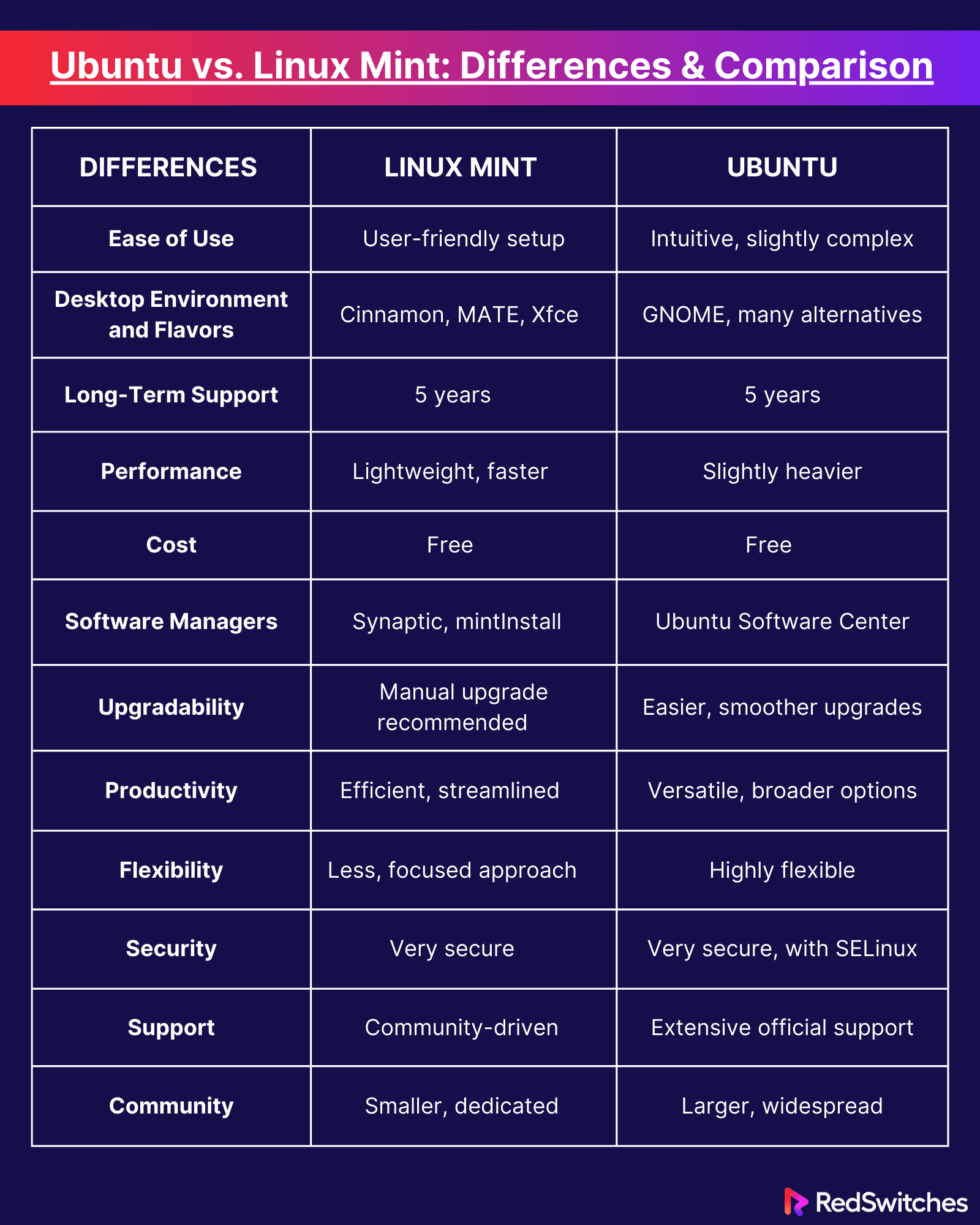
Ubuntu vs Linux Mint: Differences and Comparison
Comparing the differences between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu can help simplify the decision-making process of which is best suited for you. Below are the key differences between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu:
Ease of Use
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of ease of use:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu is renowned for its user-friendly approach to Linux. It’s designed to be approachable for users transitioning from Windows or macOS, focusing on a straightforward and navigable interface. Including the Ubuntu Software Center makes finding and installing new applications a breeze.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint takes user-friendliness a step further. It aims to provide an even more familiar experience for users coming from Windows with its layout and navigation. Linux Mint often includes a full set of media codecs and drivers out of the box, reducing the need for users to install additional software to get started manually.
Desktop Environment and Flavors
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of desktop environment and flavors:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu initially used the GNOME desktop environment, but it introduced its own Unity interface, which it used for several years before switching back to GNOME. Beyond the standard edition, Ubuntu comes in various ‘flavors’ that feature other desktop environments, like Xubuntu (XFCE), Lubuntu (LXQt), and Kubuntu (KDE).
Linux Mint
Linux Mint provides a more traditional desktop environment with its flagship Cinnamon desktop. It is known for its classic look and feel. Additionally, Mint offers variations with the MATE and XFCE desktop environments for those seeking a lighter footprint or a different style of navigation and customization.
Long-Term Support
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of long-term support:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu releases new versions every six months and offers Long-Term Support (LTS) releases every two years, supported for five years with updates and security patches. This makes Ubuntu a reliable choice for businesses and users looking for stability over a more extended period.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint also provides long-term support that aligns with Ubuntu’s LTS releases since Mint is based on Ubuntu’s LTS versions. They typically support these releases with updates until the next LTS version becomes available.
Performance
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of performance:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu’s performance can vary depending on the desktop environment used. Standard Ubuntu with GNOME is known to be a bit heavier on resources. Lighter flavors like Xubuntu and Lubuntu are tailored toward better performance on older or less powerful hardware.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint, particularly with the Cinnamon desktop, is optimized for performance and tends to use fewer resources than Ubuntu with GNOME. This can lead to a responsive experience on various hardware, especially for systems with more modest specifications.
Cost
Credits: FreePik
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of cost:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu, like Linux Mint and many other Linux distributions, is free to download, use, and share. This open-source operating system can be installed on any number of computers without worrying about licensing fees. Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, does offer paid professional support services for businesses, which is an optional cost.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint is also free of charge and operates on a donation-based model to support the project. There are no hidden costs or premium versions, ensuring users can access all its features without spending a penny.
Software Managers
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of software managers:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu comes with the GNOME Software Center in its default GNOME desktop environment, providing a user-friendly interface to browse and install thousands of applications and utilities. The powerful APT command-line tool is available for more advanced users for software management tasks.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint boasts its own Software Manager, praised for its simplicity and ease of navigation. It’s often considered more straightforward than Ubuntu’s Software Center, especially for new users. Mint also inherits the APT command-line prowess from its Ubuntu base.
Upgradability
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of upgradability:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu allows relatively smooth transitions between versions, especially from one LTS release to another. Standard releases also have upgrade paths, although they may sometimes involve a fresh installation for major version jumps or for users who prefer a clean start.
Linux Mint
Historically, Linux Mint has recommended a fresh installation for major new releases to ensure stability, although it has been working on improving the in-place upgrade process. The Mint team ensures each version is as stable as possible before suggesting users upgrade.
Productivity
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of productivity:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu is known for its clean and modern GNOME desktop environment, which can be a slight departure from the traditional desktop layout. It includes many productivity tools and is compatible with most modern software applications. Users looking for a different experience can opt for other flavors of Ubuntu, each with its own set of productivity tools suited to the desktop environment of choice.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint is praised for its Cinnamon desktop environment, which offers a Windows-like experience, often making the transition easier for new Linux users. It comes pre-packed with a full productivity software suite, like the LibreOffice suite, and its familiar interface allows users to get up to speed quickly.
Flexibility
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of flexibility:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu is renowned for its flexibility. With multiple official flavors like Kubuntu, Lubuntu, and Xubuntu, users can select a desktop environment that matches their preferences or system requirements. This adaptability extends to servers, with Ubuntu being a popular choice in cloud and server environments due to its robustness and versatility.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint may not offer as many official flavors, focusing instead on refining key experiences centered around the Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce desktop environments. While this approach provides a more streamlined selection process, it may not match the sheer breadth of Ubuntu’s offerings. Linux Mint excels in offering a consistent and stable user experience.
Security
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of security:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu has a strong track record in security, thanks in part to Canonical’s professional oversight and proactive security patching. Ubuntu benefits from features like AppArmor (a kernel enhancement to confine programs to a limited set of resources) and regular, scheduled releases of security updates.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint also maintains a strong security posture, issuing updates and patches derived from its Ubuntu base. Mint users have the advantage of receiving security updates almost as promptly as Ubuntu users. Mint’s approach to update management and default security settings has been a topic of discussion, with some experts suggesting it lags slightly behind Ubuntu.
Support
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of support:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu users can avail themselves of extensive documentation, paid professional support from Canonical, and vast community forums. This multi-tiered support structure makes Ubuntu attractive for enterprises and individual users looking for a well-supported Linux experience.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint, while not backed by a large corporation like Canonical, offers impressive support through its active forums, community-driven tutorials, and a user guide that comes with every installation. The support here is more community-focused, which can be incredibly beneficial for users who prefer a more personal touch.
Community
Credits: FreePik
Below is the difference between Linux Mint vs Ubuntu in terms of community:
Ubuntu
Ubuntu’s community is one of the largest in the Linux world, thanks to its longevity and the backing of Canonical. This extensive community spans various online forums, local user groups, and events like the Ubuntu Summit, ensuring users always have somewhere to turn for advice and camaraderie.
Linux Mint
The Linux Mint community, while smaller, is often praised for its friendliness and accessibility, especially for new users. The Mint forums are known for their helpful and supportive atmosphere, making it an excellent place for newcomers to Linux to start their journey.
Also Read: How to Format Disk Partitions in Linux.
Conclusion – Linux Mint vs Ubuntu
Through our comprehensive exploration of Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, we’ve highlighted 12 key differences that can sway your choice. From the user-friendly nature of Linux Mint to Ubuntu’s broad horizons, both distributions have carved out their niches that resonate with different user bases and needs.
As we close this chapter on Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, it’s essential to consider the platform on which your chosen environment will thrive. RedSwitches offers a remarkable hosting experience that caters to the nuances of Linux Mint and Ubuntu. With robust servers, spectacular uptime, and dedicated support, RedSwitches Hosting ensures that a reliable and performance-oriented foundation supports your foray into the Linux ecosystem.
Whether you choose Mint’s elegance and simplicity or Ubuntu’s widespread support, make us your partner in unlocking the full potential of your Linux experience. Contact us today to learn how our services can enhance your journey with the Linux distribution that suits you best.
FAQs
Q. Which is better, Linux Mint or Ubuntu?
When considering Linux Mint vs Ubuntu, which is better, it’s not about which is better but which is more suitable for your needs. Ubuntu is better for users seeking the latest features and a more extensive software repository. Linux Mint is favored for its user-friendliness and ease of use, especially for those transitioning from Windows.
Q. How is Linux Mint different from Ubuntu?
Linux Mint and Ubuntu differ primarily in their user interface and usability. Mint offers a more classic desktop experience with a simple layout, whereas Ubuntu uses the GNOME desktop environment, which is more modern and feature-rich. Linux Mint also includes a range of pre-installed software for a smoother out-of-the-box experience.
Q. Is Mint based on Ubuntu?
Yes, Mint is based on Ubuntu. It takes Ubuntu’s core and adds its desktop environments and user-friendly features. This means it enjoys the stability and support of Ubuntu’s long-term releases and its own customizations.
Q. What are the key differences between Linux Mint and Ubuntu?
Linux Mint and Ubuntu are both popular Linux distributions, but they differ in their default desktop environments and target users. Ubuntu uses the GNOME desktop by default, while Linux Mint comes with the Cinnamon desktop. Additionally, Linux Mint is known for being more user-friendly and suitable for beginners, while Ubuntu is geared towards a broader range of users.
Q. Which desktop environment does Ubuntu use?
Ubuntu uses the GNOME desktop environment as its default. However, it also offers different flavors with other desktop environments such as Ubuntu Mate and Kubuntu.
Q. What about the desktop environment in Linux Mint?
Linux Mint is known for its Cinnamon desktop environment, which provides a traditional and user-friendly interface for Linux users.
Q. Is Ubuntu based on Debian?
Yes, Ubuntu is based on Debian, one of the most popular and long-standing Linux distributions. It inherits many characteristics and features from Debian.
Q. Is Linux Mint also based on Debian?
Linux Mint is based on Ubuntu, which in turn is based on Debian. This makes Linux Mint a derivative of a derivative, with Ubuntu being its upstream distribution.
Q. What are the differences in software availability between Ubuntu and Linux Mint?
Ubuntu offers a wider range of software in its official repositories and Software Center compared to Linux Mint. Users may find that Ubuntu has a more extensive selection of applications and updates.
Q. Which distribution is recommended for beginners, Ubuntu or Linux Mint?
Linux Mint is often recommended for beginners due to its user-friendly nature and familiar interface. However, Ubuntu also offers a smooth and intuitive experience for new Linux users.
Q. How does the performance of Ubuntu compare to Linux Mint?
In general, Linux Mint is perceived to be lighter and faster than Ubuntu, especially in terms of system resource usage and responsiveness. Some users find that Ubuntu may appear to run slower on older or less powerful hardware.
Q. Can you explain the differences in package management between Ubuntu and Linux Mint?
Both Ubuntu and Linux Mint use the APT (Advanced Package Tool) for package management, as they are both Debian-based. However, Linux Mint relies more on individual users and community feedback for software selection and updates.
Q. How easy is it to install and use Ubuntu and Linux Mint?
Both Ubuntu and Linux Mint offer user-friendly installation processes and intuitive interfaces. However, Linux Mint may seem a little easier for new users to navigate and customize, while Ubuntu provides a polished and professional desktop experience.