Are you confused about the SOC 1 vs SOC 2 debate, especially the differences between the reports?
As businesses become more aware of the importance of security, especially in the context of interconnected systems, they need a reliable framework to understand the compliance and security of the processes by third-party service providers.
This article explores the SOC 1 vs SOC 2 discussion and goes into the details of the two versions. Finally, we’ll round off with the key differences and benefits offered by these reports.
Table Of Contents
- An Overview of the SOC Reports
- What is a SOC Report (& Why is it Important for Your Business?)
- What is SOC 1?
- What is SOC 2?
- What are SOC Trust Service Criteria?
- SOC Reports – Type 1 Vs. Type 2
- Key Differences Between SOC 1 and SOC 2 Reports
- Benefits of SOC 1 and SOC 2 Audit & Reports
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Let’s start with the introductions.
An Overview of the SOC Reports
The growing popularity of cloud computing has caused businesses to prioritize security as a crucial aspect of their operations.
If your business offers services to other companies, you can potentially impact your clients’ financial reporting. As a result, auditors on both sides may need assurance that your service controls are appropriate and work seamlessly.
Thus, SOC audits have become vital for companies to prove they have proper (and strict) controls in place to safeguard confidential data.
SOC reports come in two variations – SOC 1 and SOC 2, each serving a distinct purpose by employing unique frameworks. Although both reports assist businesses in building customer trust, they differ fundamentally in approach and reporting elements. That’s why understanding the SOC 1 vs SOC 2 debate is critical for building your business’s reputation.
What is a SOC Report (& Why is it Important for Your Business?)
A System and Organization Controls (SOC) report is a document that summarizes the findings of an audit of a service organization’s controls over the security, accessibility, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of its systems and data.
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) establishes standards for evaluating such controls to ensure that the organization meets its client’s expectations and needs concerning security and reliability.
Service organizations that handle sensitive information or provide critical services must have a SOC report. Clients may request this report as part of their due diligence process to ensure the organization has adequate controls in place. A SOC report can help organizations identify areas for improvement and demonstrate their commitment to security.
The SOC standard is well-known in the U.S., and SOC reports are now a common business requirement. Currently, there is SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3, and SOC for Cybersecurity.
This article will focus on SOC 1 and SOC 2, which are the most common in the industry.
Let’s go into the details of these reports.
What is SOC 1?
SOC 1, or Service Organization Control 1, is a report used for audits of financial statements of companies that provide outsourced services. It assures users that their financial data is accurate and free from any errors or misstatements. Simply put, it is a report that explains how a service organization’s internal controls function and operate.
Businesses that must have a SOC 1 report include banks, insurance companies, healthcare providers, data processing companies, and other financial institutions that outsource vital functions to service providers.
In today’s technology-driven world, businesses want to ensure that their financial information is safe, trustworthy and meets regulatory standards.
SOC 1 reports are important for organizations because they demonstrate that they have the appropriate internal controls in place to protect their client’s financial information. They also prove that the company’s controls operate efficiently, accurately, and up to industry standards.
Ultimately, getting a SOC 1 report helps businesses increase their credibility, reduce risks, and expand their market potential by differentiating themselves as reliable service providers.
The objective of a SOC 1 audit is to assess the Internal Control over Financial Reporting (ICFR). The main area of concern for such an audit is anything that may impact the financial statements of the entity being audited.
What is SOC 2?
SOC 2 is a security framework that guides organizations in safeguarding customer data from unauthorized access and security incidents.
Recent headlines show the importance of SOC 2. High-profile data breaches at Experian, Equifax, Yahoo, LinkedIn, and Facebook have made news in recent years. On average, a data breach in the United States incurs a cost of $9.44 million, and it is projected that cybercrime will amount to $8 trillion by 2023.
That’s why businesses are prioritizing information and data security due to the evolving threat landscape. A single data breach can cost millions, damaging reputation and causing unrecoverable loss of customer trust.
SaaS companies can get several standards and certifications to demonstrate their dedication to information security. However, SOC 2 report is a highly respected and widely accepted report, especially for businesses that collect customer data.
The AICPA created SOC 2 in 2010 as an auditing procedure that ensures service providers are able to protect their organization’s interests and deliver ironclad client privacy. SOC 2 compliance is a minimum requirement for security-conscious businesses that collect and process customer information.
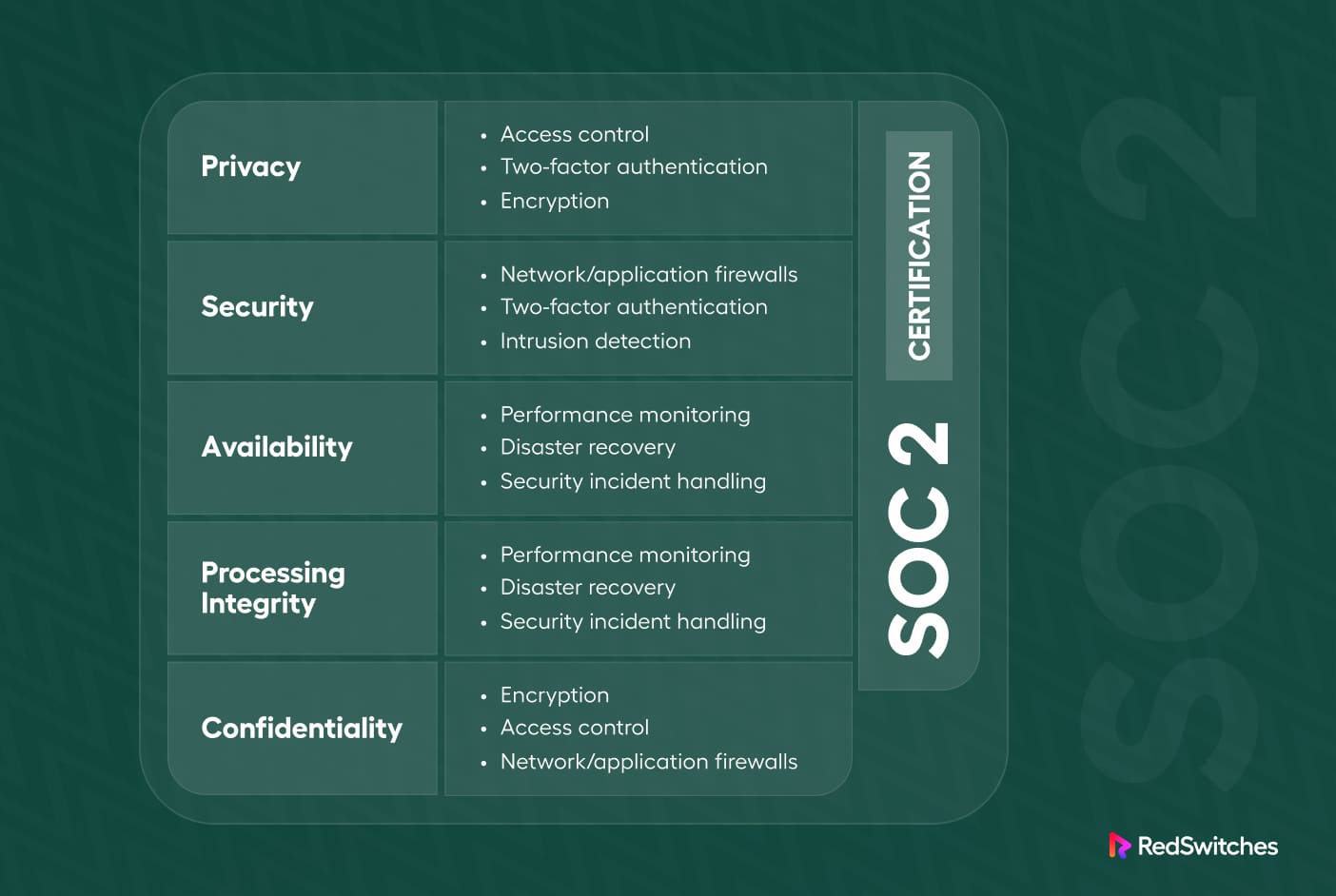
SOC2 sets criteria for managing customer data based on five “trust service criteria” (TSC). They are security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
An independent auditor evaluates a company’s security posture during a SOC 2 audit. The auditor focuses on one or all of the TSC.
A company must meet specific requirements for each TSC and implement appropriate internal controls. The Security TSC is mandatory in a SOC 2 audit, while the other four are optional. Based on the assessment, SOC 2 certification is issued by the auditor.
What are SOC Trust Service Criteria?
SOC audits are carried out to test a business’s performance and stance on the established Trust Service Criteria that make up the SOC 2 evaluation criteria. Here’s a look at the current TSC.
Security
The security principle protects system resources from unauthorized access. Access controls prevent system abuse, theft, data removal, software misuse, and information alteration or disclosure.
IT security tools like WAFs, two-factor authentication, and intrusion detection help prevent security breaches that lead to unauthorized systems and data access.
Availability
The availability principle focuses on the accessibility of a system, product, or service based on the contract or SLA. Both parties set the minimum acceptable performance level for system availability.
This principle usually doesn’t cover system functionality or usability. Instead, it focuses on the security-related criteria that can impact systems availability. For this criteria, the important factors are consistent monitoring for network performance and availability, the ability to handle security incidents, and having a site failover plan.
Processing Integrity
The processing integrity principle checks if a system fulfills its purpose.
This means delivering correct data at the right price and on time. For this, processing must be authorized, complete, valid, accurate, and timely.
However, processing integrity does not guarantee data integrity. Detecting errors in data before input (usually known as data validation) is not usually the processing entity’s responsibility. Quality assurance procedures and monitoring data processing can ensure processing integrity.
Confidentiality
Confidential data is limited to specific individuals or organizations. Examples include business plans, intellectual property, and sensitive financial information. Encryption is crucial for protecting confidentiality during transmission. Network and application firewalls, along with strict access controls, can safeguard information on computer systems.
Privacy
The privacy principle covers how personal information is collected, used, retained, disclosed, and disposed of according to an organization’s privacy notice and the AICPA’s generally accepted privacy principles (GAPP).
This criterion applies directly to Personal Identifiable Information (PII). This includes details that can identify an individual, such as name, address, and Social Security number. Sensitive personal data related to health, race, sexuality, and religion requires extra protection. Controls must be implemented to safeguard all PII from unauthorized access.
SaaS and cloud computing vendors aren’t required to comply with SOC 2. However, its importance in securing your data cannot be overstated.
At Redswitches, all our data centers and services we offer maintain SOC 2 compliance.
SOC Reports – Type 1 Vs. Type 2
It is important that businesses should understand SOC 1 vs SOC 2 differences because these reports are an important part of setting up a respectable business persona.
Now that you have read about SOC1 and SOC 2 let’s discuss the types of reports available with both SOC 1 and SOC 2 audits. Then, we’ll see the SOC 1 vs SOC 2 differences in detail.
SOC 1 Type I – The Type I report provides your auditor’s opinion on your system’s design suitability. It confirms that your system can achieve its objectives on a specific date.
SOC 1 Type II – The Type 2 report includes all the details of Type 1 but emphasizes examining the controls to validate their efficiency over a specific duration. Due to this, a Type 2 report offers higher assurance than a Type 1 report.
SOC 2 Type I is a snapshot of controls at a specific time, with tests to validate their appropriateness. SOC 2 Type II measures control effectiveness over 12 months.
Consider your goals, cost, and timeline constraints when choosing between Type I and Type II reports. Type I reports are faster, but Type II reports offer greater assurance to customers.
We recommend opting for a SOC 2 Type II report. Many customers have started to phase out Type I reports and demand Type II reports instead. Choosing a Type II report from the start can save time and money because you only need to run a single audit cycle.
Key Differences Between SOC 1 and SOC 2 Reports
It is crucial to understand the fundamental differences between SOC 1 and SOC 2 to evaluate the best option for your business. You should know that these two reports differ in several ways, including:
Focus
If your business handles financial information that could impact your client’s financial reporting, you need a SOC 1 audit as it concentrates on internal control over financial reporting (ICFR).
On the other hand, a SOC 2 audit focuses on the five TSCs and offers proof of continuous, long-term processes that secure customer data.
Scope
While SOC 2 reports cover a service organization’s controls connected to various security and operational areas, SOC 1 reports only cover controls that are pertinent to their client’s financial reporting.
Audience
SOC 1 reports are designed to mainly cater to the service organization’s clients and their evaluators, whereas SOC 2 reports are usually utilized to offer reassurance to a more extensive group of interested parties, which includes governing bodies, financiers, and commercial associates.
Auditing Standards
SOC 1 reports are based on the Statement on Standards for Attestation Engagements (SSAE) No. 18. In contrast, SOC 2 reports are based on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC) developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).
Benefits of SOC 1 and SOC 2 Audit & Reports
Service organizations may receive requests or demands for a SOC report from user entities and auditors. However, it’s important for service organizations don’t see these audits as a mere “check-the-box” exercise.
Having a SOC report can provide several benefits for a service organization. A few of these are listed below:
Increased Trust and Credibility
SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports assure customers that a service organization has effective controls to achieve its objectives. This boosts customer confidence and trust in the organization’s ability to deliver services securely and effectively.
Operational Improvement
SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports are helpful for assessing controls related to services provided by a service organization. These reports are useful for user entities and the service organization itself. By providing feedback on controls and processes, SOC reports can assist service organizations in improving their operations and service quality.
Competitive Advantage
A SOC 1 or SOC 2 report can give a competitive edge over other service organizations without reports. This is crucial in industries like healthcare or financial services, where security and data protection are crucial operational requirements. SOC compliance helps understand how the service organization oversees third parties that provide services to customers. Many service providers use SOC compliance as a distinct operational edge that distinguishes them from their competitors.
Cost Savings
Using SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports can save service organizations and their customers time and resources. Customers won’t need to perform their audits or assessments. One report can address the collective needs of multiple user entities, reducing the compliance burden.
Conclusion
SOC 1 vs SOC 2 is an important consideration for organizations that collect or process user data or operate in industries where security and privacy are essential requirements for business continuity.
SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports have different purposes and provide assurance in different areas. SOC 1 reports focus on financial reporting controls, while SOC 2 focuses on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy controls. You need to consider your organization and customers’ specific needs and requirements before you finalize which report you need. A well-executed SOC 1 or SOC 2 audit report can demonstrate your commitment to security, quality, and transparency and help manage risks and drive business growth.
FAQs
Q-1) How much do SOC 1 and SOC 2 cost?
The cost to become SOC 1 and SOC 2 compliant depends on several variables, including the scope, required level of assistance, etc. Conducting a SOC 1 audit will generally cost you between $7000 and $20,000, and for a SOC 2 audit, between $7000 and $50000.
Q-2) How long does it take to prepare SOC 1 report?
The time frame for achieving SOC 1 compliance depends upon how well-equipped and resource-rich an organization is. A SOC 1 Type 1 and a readiness evaluation can be finished on the first try in two to three months.
Q-3) How long does it take to prepare SOC 2 report?
Preparation for the SOC 2 audit might take as much time as the actual audit, which normally lasts five weeks to 3 months. Factors like the scope of your audit and the number of associated controls also influence the length of time. However, a compliance automation solution like Sprinto can reduce the time from months to days.
Q-4) Who are the intended users of SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports?
Companies that provide billing management systems, payroll software, and financial reporting tools are required to choose SOC 1 compliance. On the other hand, enterprises such as data center hosts, SaaS providers, cloud service providers, HR management services, and recruitment platforms are advised to consider adopting the SOC 2 framework.