In the dynamic world of virtualization technologies, picking the best platform for your business is essential. Proxmox and ESXi are prominent players often chosen because of their unique features and benefit sets. Businesses are debating between Proxmox and ESXi more and more as they look for effective ways to manage their virtual environments.
We examine the nuances of these platforms in-depth in this enlightening blog post, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and unique features. After completing this comparison, you will have a thorough grasp of which solution best suits your company’s requirements, enabling you to make an informed choice regarding virtualization. Also, you will be able to answer the Proxmox vs ESXi debate with ease.
Let’s Begin.
Table Of Contents
- What is Proxmox?
- What is ESXi?
- Proxmox vs ESXi: The Ultimate Comparison
- How to Pick the Best Hypervisor
- Use Cases and Real-Life Examples
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Proxmox?
Credits: Freepik
A comprehensive open-source server virtualization management solution is Proxmox VE. It provides the ability to use Linux OpenVZ and KVM technologies to administer virtual server (VPS) technology. After installing Proxmox on your server, Proxmox VE provides an easy-to-use web interface for management that usually just requires a few clicks.
Under the auspices of the Internet Foundation of Austria, Proxmox Server Solutions developed Proxmox VE in Austria. It is available under the GNU General Public Licence. As an open-source solution, it can be modified to meet your needs.
Key Features of Proxmox
Before jumping into the proxmox ve vs ESXi debate, Let’s understand the key features of Proxmox.
High-Availability Cluster Management: A technique for controlling a large number of nodes.
- Definition: High availability (HA) in Proxmox refers to the ability to ensure continuous operation and minimal downtime by distributing workloads across multiple nodes. It’s a technique for controlling many nodes in a cluster.
- How it works: In a Proxmox HA cluster, if one node fails, the workload is automatically shifted to another available node, ensuring that services remain uninterrupted.
- Benefits: Improved system reliability and fault tolerance, critical for environments where continuous service availability is essential.
Capabilities for Live Migration: Providing little downtime.
- Definition: Live Migration allows virtual machines (VMs) to be moved from one Proxmox host to another without noticeable downtime.
- How it works: During live migration, the state of the VM is transferred from the source to the destination host while the VM continues to run. This ensures continuous service availability during the migration process.
- Benefits: Enables resource optimization and load balancing and facilitates maintenance without disrupting running applications.
Backup Server: The backup server guarantees Redundancy and incremental backups for live restores and single-file backups. Configuration files are synchronized via a database-driven file system.
- Definition: Proxmox includes a built-in backup server that ensures data redundancy and allows for both incremental and full backups of virtual machines.
- How it works: Configuration files and virtual machine images are synchronized via a database-driven file system, allowing for efficient and consistent backups.
- Benefits: Provides a reliable backup solution for disaster recovery, live, and single-file restores. Incremental backups help save storage space and reduce backup times.
Third-Party Support: Since JSON is the primary data format, third-party solutions can seamlessly integrate with RESTful APIs.
- Definition: Proxmox uses JSON as its primary data format and provides RESTful APIs, allowing seamless integration with third-party solutions.
- How it works: The JSON format facilitates accessible communication and data exchange with other systems, while the RESTful APIs enable external tools and applications to interact with Proxmox.
- Benefits: Enhances flexibility and interoperability by integrating Proxmox into larger IT ecosystems and management solutions.
Multi-Master Policies: Used for maintenance and to deploy tasks across the cluster.
- Definition: Multi-Master policies in Proxmox are used for maintenance tasks and deploying tasks across the cluster.
- How it works: During maintenance, tasks can be distributed and executed across multiple nodes simultaneously, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Benefits: Streamlines cluster management, making it easier to perform updates, patches, and other maintenance tasks across the entire infrastructure.
Built-in Security: Integrated firewalls with distinct controls for aliases, IP settings, security groups, and macros are examples of built-in security.
- Definition: Proxmox includes integrated firewalls with distinct controls for aliases, IP settings, security groups, and macros.
- How it works: The built-in security features allow administrators to define and enforce network security policies within the Proxmox environment.
- Benefits: It enhances the virtualized infrastructure’s overall security posture by providing granular control over network access and communication between VMs.
Pros and Cons of Proxmox
Credits: Freepik
Pros
First, let’s start with the Pros.
Open Source Nature
Being open-source software, Proxmox has several noteworthy benefits. This indicates that the public can see the source code without restriction. Open-source software promotes cooperation, creativity, and a robust user and development community. Proxmox gains from this cooperative setting, which guarantees ongoing development and assistance from various sources.
Combination of Technologies for Virtualization
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and LXC (Linux Containers) are two virtualization technologies that Proxmox VE delivers in a compelling combination. Because of this versatility, customers can select the virtualization technique that best fits their needs.
While LXC provides lightweight containerization for applications with minimal overhead, KVM supports full virtualization, making it perfect for running various operating systems.
Easy-to-use online Interface
Proxmox has an easy-to-use online interface, making managing virtual machines and containers easier. The interface offers simple controls for building, setting up, and keeping an eye on virtualized environments. This simplicity of use is especially helpful for individuals who do not have a lot of virtualization technology experience.
Centralized Management
Virtual machines and containers can be managed centrally with Proxmox. Administrators can keep an eye on and manage several virtualized instances from a single dashboard. Various virtualized workloads within an organization are easier to oversee and maintain thanks to this centralized method that streamlines the management process.
High Availability (HA) Support
Proxmox provides high-availability support, enabling businesses to guarantee the ongoing operation of vital services and applications. Proxmox can automatically move virtual machines to healthy nodes in the event of a hardware malfunction or other problems, reducing downtime and improving the overall dependability of the virtualized system.
Cons
Learning Curve
Although Proxmox has an intuitive UI, users unfamiliar with virtualization ideas may still need to go through a learning curve. It may take time and effort to fully comprehend the nuances of virtual machines, containers, networking configurations, and cluster management, especially for novices.
Limited Official Support
In contrast to commercial virtualization systems, Proxmox does not provide official paid support packages for companies that need specialized support services. Organizations using mission-critical applications would prefer to have access to official, guaranteed support from the software manufacturer, even though there is a vibrant community that might offer assistance.
Hardware Compatibility
The underlying hardware significantly impacts Proxmox’s stability and performance. Certain hardware parts might not work perfectly with Proxmox, which could cause problems with virtualization support, device drivers, or system stability in general. To prevent such issues, users must confirm that Proxmox is compatible with their hardware.
Complex Networking Configurations
Although Proxmox has sophisticated networking features, users not well-versed in networking may find it difficult to configure complex network configurations. For novice users, implementing features like VLANs, bonding, or firewall rules may require a thorough understanding of networking concepts.
Resource Overhead for Virtualization
Resource overhead is a natural byproduct of virtualization. Running numerous virtual machines and containers on a single host system can burden CPU, memory, and storage resources, even if Proxmox tries to minimize this overhead. Organizations must carefully plan how to allocate their resources to prevent performance bottlenecks and guarantee peak performance for every virtualized instance.
What is ESXi?
Credits: DevianArt
Created for VMware’s server virtualization and container-based application development platform, vSphere, the VMware ESXi Server is a bare metal (Type-1) hypervisor.
Consider a hypervisor as an operating system that permits the productive operation of numerous virtual machines, virtual appliances, and containers on a single physical server.
ESXi is one of the two main parts of VMware’s well-known container and virtual machine (VM) management solution, vSphere. Installed directly on the host machine’s local disc, ESXi servers are controlled by a VMkernel based on the Linux kernel. A VMkernel submits a resource request to the host’s physical hardware for processing whenever it receives one.
Key Features of ESXi
VMware ESXi is a part of vSphere that supports the following essential features:
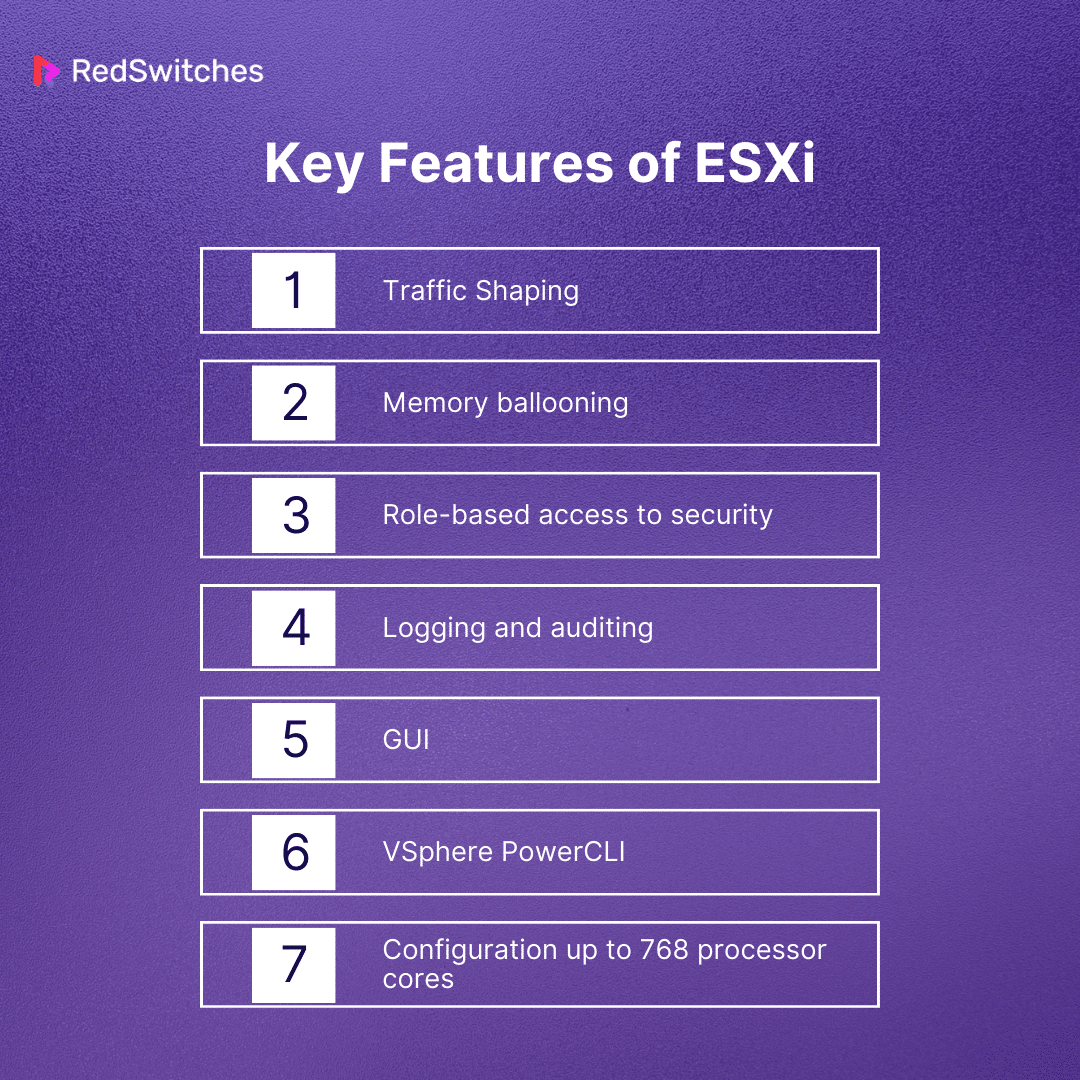
Traffic Shaping
- Definition: Traffic shaping in VMware ESXi allows administrators to control and prioritize network traffic within the virtualized environment.
- How it works: Network traffic shaping helps manage bandwidth utilization by setting policies to control data flow. This is crucial for optimizing network performance and ensuring critical applications receive the necessary resources.
- Benefits: Ensures efficient network utilization, minimizes congestion, and prioritizes essential workloads for consistent performance.
Memory Ballooning
- Definition: Memory ballooning is a memory management technique in VMware ESXi that allows the hypervisor to reclaim unused memory from virtual machines.
- How it works: When a VM has unused memory, the hypervisor can reclaim it and allocate it to other VMs that may need it, optimizing overall memory utilization.
- Benefits: Improves resource efficiency by dynamically adjusting memory allocations based on the needs of individual VMs, maximizing the use of available resources.
Role-based Access to Security
- Definition: Role-based access control (RBAC) in VMware ESXi enables administrators to define and assign specific roles and permissions to users or groups.
- How it works: RBAC ensures that users have the appropriate access and permissions based on their roles, helping enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Benefits: Enhances security by controlling access to critical functions and resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized actions and potential security breaches.
Logging and Auditing
- Definition: ESXi provides comprehensive logging and auditing capabilities to track and monitor activities within the virtualized environment.
- How it works: Logs capture information about system events, user actions, and changes, providing an audit trail that can be crucial for troubleshooting, compliance, and security analysis.
- Benefits: Facilitates troubleshooting, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, and enhances security by tracking and analyzing changes and events.
GUI
- Definition: ESXi features a graphical user interface that visually represents the virtualized infrastructure, making it easier for administrators to manage and monitor the environment.
- How it works: The GUI offers a user-friendly interface for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting VMs and hosts.
- Benefits: Simplifies management tasks, especially for users who may not be familiar with command-line interfaces, improving overall usability and accessibility.
vSphere PowerCLI
- Definition: VMware PowerCLI is a command-line interface for managing and automating VMware vSphere environments.
- How it works: PowerCLI allows administrators to automate repetitive tasks, deploy configurations, and perform management operations using PowerShell scripts.
- Benefits: It enhances efficiency and scalability by automating routine tasks, enabling administrators to manage large-scale vSphere environments more effectively.
Configuration Up to 768 Processor Cores
- Definition: ESXi supports configurations with up to 768 processor cores, allowing for high-performance computing in virtualized environments.
- How it works: This capability enables ESXi to handle large workloads and resource-intensive applications by efficiently utilizing a significant number of processor cores.
- Benefits: Supports the deployment of resource-intensive workloads, ensuring scalability and performance for demanding applications.
Pros and Cons of ESXi
Credits: Freepik
Before moving to the core section of our blog, the Proxmox vs ESXi battle, let’s examine ESXi’s pros and cons.
Pros
Excellent Performance and Scalability
The excellent performance and scalability of VMware ESXi are well known. It effectively uses system resources, enabling users to operate several virtual machines (VMs) on one host without sacrificing functionality. This feature is essential for companies with resource-intensive applications and high workloads.
Sturdy Hypervisor
ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor that runs directly on the hardware and doesn’t require a host operating system. This architecture reduces superfluous overhead, creating a more reliable and efficient virtualization environment.
It offers a solid basis for virtualization, guaranteeing reliability and peak performance.
VMware vSphere Ecosystem
NSX for network virtualization, vSAN for software-defined storage, and vCenter Server for centralized management are all part of the VMware vSphere ecosystem, which ESXi effortlessly integrates with. This integrated ecosystem, including automated load balancing, live migration, and sophisticated networking capabilities, improves virtualization.
High Availability and Live Migration
High availability and live migration are made possible by VMware ESXi’s technologies, such as vMotion, which permits live, uninterrupted VM migration across hosts. With the capacity to maintain virtualized workloads continuously, services can be interrupted for disaster recovery planning, load balancing, and hardware maintenance.
ESXi supports high availability (HA) features, such as restarting virtual machines (VMs) on healthy hosts immediately after a host failure.
Advanced Management Tools
vCenter Server and vSphere Client, two of VMware’s powerful management tools, offer user-friendly interfaces for setting up, keeping an eye on, and administering virtualized environments. Administrators can effectively manage large-scale installations and guarantee optimal resource utilization with the help of these technologies, which simplify complex operations.
Cons
Cost of Licencing
The expense of ESXi’s licensing is one of its main disadvantages. VMware provides a free, feature-limited version of ESXi; nevertheless, licenses are needed to access the full range of advanced functionality and administration tools, including vMotion and vCenter Server. Entry barriers for small enterprises and individuals may arise from the expense of obtaining a license.
Complexity for Novices
Those unfamiliar with virtualization may find ESXi’s vast feature set and configuration possibilities daunting. Setting up and configuring advanced elements like networking and storage might have a high learning curve, resulting in mistakes or less-than-ideal settings, especially for people unfamiliar with virtualization technology.
Resource Overhead
Virtualization inevitably adds some resource overhead, even with ESXi’s extreme efficiency. On a host, running more virtual machines (VMs) uses CPU, memory, and storage. The total performance of virtual machines (VMs) may be impacted by this overhead, mainly if the host hardware is undersized or not optimized.
Limited Capabilities in the Free Version
Several advanced capabilities accessible in the premium versions of ESXi are absent from the free version, which individuals and small enterprises frequently utilize. Due to these restrictions, Users may be unable to use features like automated resource balancing (DRS), backup APIs, and live migration (vMotion). Customers who need these functionalities have to pay extra for upgraded licenses.
Proxmox vs ESXi: The Ultimate Comparison
It is time to focus on the blog’s core part, i.e., the differences between Promox and ESXi.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Performance
In the first proxmox vs ESXi argument, we will discuss their performance impact.
Excellent performance capabilities are provided by both type-1 hypervisors, making them ideal for a wide range of configurations. Proxmox is inferior to ESXi, the industry-standard virtualization solution, in terms of RAM and host capacity.
While ESXi provides multiple performance tiers based on licensing, increasing the number of servers in a cluster and RAM quantity per host, Proxmox delivers the same capacity for free to all users.
Promax
Proxmox Backup Server is an enterprise-level tool for backing up and recovering virtual machines (VMs), containers, and hosts regarding backup solutions. Zstandard compression, deduplication, incremental backups, and authorized encryption are supported features.
ESXi
File-based backups utilizing native apps are necessary, and the free edition restricts the options for ESXi backup solutions. Furthermore, using the free edition at an enterprise level is not advised because it lacks backup options in the vCenter interface.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Clustering
The second aspect of the proxmox vs ESXi debate will be concerning clustering.
Proxmox
Proxmox provides centralized management of numerous servers via a single web management dashboard and enables clustering. It is convenient to manage server farms using the online console.
Proxmox Cluster makes it easier to migrate virtual machines and containers within the cluster and offers a variety of authentication mechanisms.
Proxmox excels in offering a user-friendly web management dashboard for centralized control of multiple servers, enabling seamless migration of virtual machines and containers within the cluster. Proxmox Cluster simplifies the management of server farms, offering flexibility and a range of authentication mechanisms.
Using the online console, create clusters with up to 32 physical nodes and configure each individually. Use two Proxmox servers or more for a multi-node solution to achieve maximum availability.
ESXi
VMware vCenter Server is a prerequisite for ESXi cluster creation. In addition to shielding the virtual machines (VMs) in the cluster from actual server failures, several hosts supply the cluster configuration with processor, memory, and network resources.
Within a cluster of up to 32 ESXi hosts, the maximum capacity for an ESXi cluster is 1024 datastores.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Ease of Use
Proxmox
When debating proxmox vs ESXi, ease of use or user-friendliness is essential.
Proxmox’s integrated graphical user interface allows users to perform all administration duties in one location, negating the need for a separate management tool. The web interface, built on the ExtJS JavaScript framework, supports all browsers.
If you are familiar with Linux, Proxmox is relatively simple to understand and use because it is built on top of Linux (Debian). The Proxmox GUI is still developing, though, as it is open-source, and certain sophisticated features still need the command line.
ESXi
The vSphere web client is user-friendly for managing virtual machines and provides sophisticated configuration tools. However, you’ll need the vCenter Server tool and a guest virtual machine or its host to administer multiple ESXi hosts.
In contrast to Linux-based Proxmox, ESXi comes with its own Linux and management tools that need to be learned by the users.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Portability
Which is more portable in the proxmox vs ESXi debate? Let’s find out.
Proxmox
Numerous image formats, such as HDD, QCOW, QCOW2, QED, VDI, etc., are supported by Proxmox. The extensive image support enhances the guest virtual machine’s OS support and VM portability.
However, importing and exporting an image requires using the Proxmox Backup Server software and the CLI. The best way to transfer an image to a different virtual machine is to back up the configuration and restore it to a different virtual machine.
Proxmox offers extensive image format support. You must use the Proxmox Backup Server software and command-line interface (CLI) to achieve portability. The recommended approach for transferring images to different virtual machines is to back up the configuration and restore it on the target virtual machine. This method ensures a systematic and reliable transfer process.
ESXi
With a few GUI clicks, ESXi lets you shut down a virtual machine (VM) on one server and restart it on another when using storage area network (SAN) storage. Thanks to the sophisticated ESXi portability features, users can have consistent shared access while relocating computing resources.
ESXi simplifies the portability of virtual machines with its user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI). Users can shut down a virtual machine on one server and restart it on another with just a few clicks. This streamlined process is particularly efficient when utilizing storage area network (SAN) storage, providing seamless VM migration.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Security
Security is a crucial aspect for users in the proxmox vs ESXi argument. So, which platform is more secure? Let’s find out.
Proxmox
Proxmox, a Linux-based system, offers enterprise-level performance, sophisticated integrated security features, and automated backups for user-specified nodes. Furthermore, because every virtual machine (VM) on Proxmox runs inside a container, any possible problems or malicious code in one VM doesn’t impact others.
Because it is open-source, Proxmox developers can more swiftly address problems and security holes because the development community prioritizes it.
ESXi
ESXi increases security by just launching the services required to function.
For instance, by default, ESXi disables the Shell and SSH interfaces, and users are limited to utilizing the vSphere Client for all tasks. Role-based access is offered to users via the vSphere Client.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Hardware Compatibility
This section will discuss hardware compatibility in the proxmox vs ESXi war.
Proxmox
Proxmox VE is very hardware-friendly because it works with many different kinds of hardware. This implies that it can be used, provided it supports virtualization, even on very old computers.
When it comes to hardware passthrough functionality, Proxmox VE shines, enabling users to assign particular hardware components to virtual machines directly. This functionality comes in handy when direct access to real hardware—like GPUs or USB controllers—is essential to achieving peak performance.
Hardware passthrough is a feature of Proxmox that improves flexibility and helps customers who need specific hardware configurations in their virtualized environments.
ESXi
To specify what hardware is compatible and what is not, VMware keeps an updated Hardware Compatibility List (HCL). You should not install VMware ESXi if your hardware isn’t on this list (which is improbable). If you continue and run into problems, VMware will offer minimal assistance.
The strict certification requirements that ESXi uphold are detailed in its Hardware Compatibility List (HCL). This guarantees that VMware has thoroughly tested and validated the mentioned hardware components. Compared to Proxmox, this may be less flexible, but it offers a high degree of performance and stability assurance.
Businesses that use ESXi may confidently choose hardware from the HCL, reducing compatibility issues and guaranteeing a dependable virtualized environment.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Support
So, how is the support in the proxmox vs ESXi battle? Do both have the same support? Let’s find out.
Proxmox
Proxmox is open-source software with a thriving community and a comprehensive Wiki offering resources to address various problems users may encounter.
However, access to the Proxmox Enterprise Repository, frequent software and security upgrades, and the Proxmox technical support staff are all included with a Proxmox VE Subscription.
Users can schedule system administrator training or send a ticket to Proxmox developers with a premium membership.
ESXi
The main distinction between a commercial and a free ESXi is support.
The free ESXi version provides adequate online documentation and access to an active vSphere Community, including an ESXi section.
Although the free version is an excellent option for a home setup, we do not recommend using it in a production setting because of the lack of official support.
VMware offers various service-level agreement tiers and paid subscription support to its consumers. Its ESXi certification programs can be pricey but are worthwhile.
Proxmox vs ESXI: Pricing
Ultimately, the ultimate price battle in the proxmox vs ESXi is very important. Who leads? Let’s understand.
Proxmox
Proxmox gives all its features away for free, with the option to subscribe for a fee. If you subscribe, you can access the enterprise repository and receive technical support from Proxmox engineers.
Proxmox VE is rooted in an open-source framework, allowing users to access core features like KVM virtualization and LXC container-based virtualization without incurring upfront licensing costs. Proxmox VE is an attractive choice for small businesses, individual users, and those seeking a cost-effective virtualization solution.
ESXi
A premium subscription is required if ESXi is utilized in an enterprise setting, as the free version lacks official support.
ESXi’s licensing options, such as vSphere Standard, Enterprise, and Enterprise Plus, have different features, scalability, and support levels. Users pay according to the chosen tier, and the cost increases with the additional capabilities. ESXi’s enterprise-grade features, including vMotion for live VM migration and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) for automated resource optimization, are noteworthy but come at a price.
How to Pick the Best Hypervisor
After learning the ultimate debate of Proxmox vs ESXi, in this section, we will learn that factors need to be considered when choosing the ideal Hypervisor.
Cost-Effectiveness
It’s essential to balance price and functionality when selecting a hypervisor. It’s crucial to ascertain which features are most important to your company and contrast them with what the hypervisor offers.
For instance, a hypervisor may be paid for yet remain free and fulfill your requirements despite lacking some capabilities. Therefore, finding the ideal balance between functionality and affordability is critical.
Management Tools
What management tools are available in the hypervisor? Ascertaining the necessary facilities for managing your virtual machines is crucial. Regarding integrations with other third-party solutions and creative features within the solution, some hypervisors provide more effective management tools and utilities than others.
Performance Metrics
Every hypervisor has both strengths and weaknesses when it comes to performance. As a result, you must evaluate their total performance and select the one that best meets your company’s objectives. Essential factors include memory management, data recovery from virtual environments, and software stability.
Overall Ecosystem
When choosing the ideal hypervisor for your company, it’s essential to consider factors like third-party developers, support, and documentation availability. When something goes wrong with your hypervisor, and you need to fix it fast, all these are required.
Use Cases and Real-Life Examples
Credits: Freepik
Now, let’s consider real-life examples/applications of both virtualization platforms.
Proxmox
KVM or Kernel-based Virtual Machine for virtual machines and LXC (Linux Containers) for lightweight container-based virtualization are the two virtualization technologies combined in Proxmox Virtual Environment (Proxmox VE), a potent open-source virtualization platform. Proxmox is a flexible and affordable server virtualization solution widely utilized in enterprise settings.
One real-world use case is its implementation in data centers, where it facilitates disaster recovery, smooth virtual machine migration, and practical resource utilization.
Proxmox is also well-liked by system administrators and developers for its capacity to create isolated development environments and testing scenarios, guaranteeing software programs’ stability before deployment.
Proxmox is frequently used as the infrastructure base for private clouds. Businesses use Proxmox VE to create and maintain their private clouds, taking advantage of the efficiency of Linux Containers (LXC) and the flexibility of KVM virtual machines.
With the help of this use case, companies can create a highly adaptable and scalable cloud environment that meets their unique requirements. Because of its integrated management interface, Proxmox is a great choice for setting up and managing a private cloud architecture because it makes managing virtual resources easier.
ESXi
One of the top hypervisors in the virtualization market, VMware ESXi, is well known for its scalability and resilience. With its ability to run numerous virtual computers on a single physical server, it finds wide-ranging applications in enterprise IT infrastructures.
One noteworthy application is in cloud computing settings, where ESXi makes it easier for companies to create virtualized instances on demand and scale their resources according to demand.
Furthermore, ESXi is frequently used in server consolidation projects, saving enterprises hardware costs by allowing them to host several virtual servers on a single physical server.
Disaster recovery scenarios are another real-world use for virtualized environments; they allow for the quick restoration of virtualized environments in case of a system breakdown, minimizing downtime and data loss.
VMware ESXi is widely used in Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) deployments. Thanks to ESXi, organizations can host several virtual desktops on a single physical server in this use case.
This helps to guarantee data security, simplify desktop administration, and offer a standardized user experience. Effective VDI deployments are made possible by ESXi’s ability to centralize desktop computing resources, making it more straightforward for IT staff to maintain, update, and secure desktop environments throughout the company.
Also Read: VDI vs VM: Understand The Differences
Conclusion
In summary, the Proxmox vs ESXi argument comes down to the individual user’s requirements and preferences. We have examined the characteristics, benefits, and limitations of Proxmox and ESXi, going into great detail about each.
The decision ultimately comes down to your company’s particular needs, whether you choose ESXi’s stability and scalability or Proxmox’s open-source flexibility and container-based virtualization.
Recall that the correct hypervisor can improve dependability and efficiency while completely changing your virtualization experience. When choosing, consider the real-world applications we have looked at, which show you how these platforms are used in various settings, such as data centers, cloud computing environments, and disaster recovery plans.
RedSwitches is prepared to meet your infrastructure requirements when implementing the hypervisor of your choice. We guarantee that your virtualization journey is smooth and optimized for your unique goals thanks to our knowledge and dedication to dependable, seamless hosting solutions.
FAQs
Q. ProxMox vs ESXi: Which one is better?
Depending on the use case, Proxmox or ESXi should be chosen; Proxmox provides open-source flexibility, but ESXi excels in scalability and robustness.
Q. Proxmox vs ESXi containers: What is the difference between them?
While Proxmox combines traditional and lightweight virtualization with LXC (Linux Containers), ESXi mainly uses VMs (Virtual Machines).
Q. Is Proxmox better than VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is more user-friendly and appropriate for individual or small-scale virtualization needs, whereas Proxmox is designed for enterprise-level virtualization with sophisticated capabilities.
Q. Is it possible to use ESXi and Proxmox in the same environment?
In a network, Proxmox and ESXi can coexist, yes. But to guarantee compatibility and effective resource use, extensive planning is necessary.
Q. ProxMox vs ESXi: Which is a more affordable hypervisor for small businesses?
Proxmox is sometimes considered more affordable for small enterprises because of its open-source design, which offers powerful virtualization features without ESXi licensing.
Q. What is the difference between Proxmox and ESXi?
Proxmox is an open-source hypervisor that supports both virtual machines (VMs) and containers, while ESXi is a proprietary hypervisor developed by VMware that primarily focuses on virtual machines.
Q. Can Proxmox support the same guest operating systems as ESXi?
Yes, Proxmox supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including popular options like Windows, Linux, and more, similar to ESXi.
Q. Does ESXi offer a free version like Proxmox VE?
Yes, VMware offers a free version of ESXi, which provides basic hypervisor functionality for small-scale environments, similar to Proxmox VE.
Q. What are some key features of Proxmox that differentiate it from ESXi?
Proxmox VE offers features such as integrated container support, a web-based management interface, and strong support for open-source technologies, distinguishing it from ESXi.
Q. How does ESXi 8.0 compare to the features offered by Proxmox?
ESXi 8.0 introduces various enhancements and updates but differs in approach from Proxmox, as it focuses primarily on VM management, while Proxmox offers a broader range of features including container support.
Q. Which is better for managing multiple hosts – Proxmox or ESXi?
Proxmox offers robust tools for managing multiple hosts, including a centralized web interface, making it well-suited for environments with multiple hypervisor instances. ESXi also provides features for managing multiple hosts but through VMware vSphere’s centralized platform.
Q. Can you explain the differences between Proxmox VE and VMware ESXi in terms of open-source support?
Proxmox VE is fully open source, while ESXi offers a free version but is not fully open source. This distinction in licensing and development model impacts the communities and customizability of the platforms.
Q. What are the main factors to consider when deciding between Proxmox and ESXi?
When deciding between Proxmox and ESXi, considerations should include the types of workloads (VMs or containers), management preferences, open-source versus proprietary needs, and integration with existing infrastructure.
Q. Can Proxmox vs ESXi be compared for their management APIs?
Proxmox VE offers an extensive API for management and automation, while ESXi also provides API support. Both platforms offer options for integrating into existing automation and orchestration tools.
Q. What are the key differences in the virtualization approach between Proxmox and ESXi?
The virtualization approach of Proxmox encompasses both VMs and containers within a single platform, while ESXi focuses primarily on VM-based virtualization. This affects the deployment and management of different types of workloads.