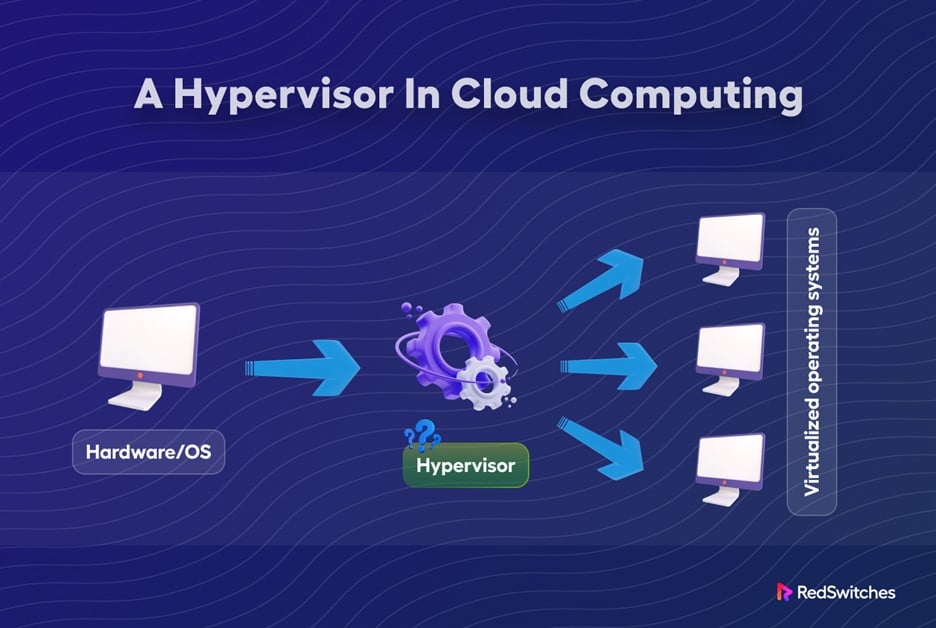
If you want to store data in the cloud with features like recovery and backup, then you need a hypervisor in cloud computing. The cloud has transformed how people and companies use computing infrastructure. One component of the cloud is the hypervisor. What is a hypervisor in cloud computing?
A hypervisor is a program that develops and operates virtual machines. It allows the virtualization of cloud resources. The technology has reshaped how businesses use cloud resources, making them dynamic and scalable.
This article will define a hypervisor, look at how it works, and the various types. We’ll explore the benefits of a hypervisor to help you understand how they facilitate the delivery of cloud services. Understanding different types of hypervisors in cloud computing when picking a cloud hosting provider for your business is crucial.
Table of Content
- What Is a Hypervisor?
- Importance of a Hypervisor
- How Does a Hypervisor Work?
- What Are the Types of Hypervisor In Cloud Computing?
- Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisors
- What are Cloud Hypervisors?
- What Are the Main Benefits of Hypervisors?
- What is the Difference Between Hypervisors and Containers?
- Security Considerations for Hypervisors
- Hypervisors Use Cases
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
What Is a Hypervisor?
It’s an OS that runs and manages one or multiple virtual machines on a computer. It’s a vital component of virtual machines and cloud computing. A hypervisor is essential in cloud environments enabling businesses to operate virtualized systems. It also simplifies the scaling and managing of traditional on-premises systems.
There are two types of hypervisors in cloud computing, and they are:
- Type 1: They’re regarded as “bare-metal” hypervisors because they operate directly on the host computer’s hardware.
- Type 2: They operate inside the host OS, hence the term “hosted” hypervisor.
Some of the features of hypervisors are:
- Resource Sharing: It is one of the core features of a hypervisor. They enable resource sharing, such as bandwidth, across several VMs. It ensures the proper functioning of the VMs.
- Partitioning: Another core feature is partitioning among the machines. It comes in handy when one of the VMs crashes. It isolates the ineffective VM so it doesn’t disrupt the other VMs.
- Protection: It is essential to have a secure environment when using the cloud. A hypervisor ensures protection when multiple VMs are in operation by partitioning them from each other. It’s an effective protection measure in case of a security breach.
- Functionality: Different OSs can operate on the same host computer through a hypervisor. It improves the functionality between multiple systems or apps.
Importance of a Hypervisor
The cloud and various virtualization types depend on hypervisors in resource sharing. Businesses should take advantage of this feature to scale and boost production.
Hypervisors add another level of protection by isolating guest operating systems from the host OS and each other. Hackers will have a more challenging time breaking in and stealing private information.
In addition, hypervisors also enable businesses to create and deploy new VMs, which improves agility and flexibility. It’s vital in the modern business landscape, where organizations must adjust swiftly to shifting market conditions and client demands.
How Does a Hypervisor Work?
Hypervisors insert a virtualization software layer between the underlying hardware and the OS. The virtualization layer allows various operating systems to operate on the same physical hardware. They achieve that by abstracting the physical hardware into virtual hardware.
When a virtual machine gets established, the hypervisor assigns it specific hardware resources like a computing unit (CPU), memory, and storage. The VM then runs its operating system and applications as if running on its physical machine. The hypervisor ensures that each VM has the resources to run efficiently. In addition, it separates each virtual machine from the others. As a result, problems with one won’t affect the others or the host OS.
What Are the Types of Hypervisor In Cloud Computing?
Learning the different types of hypervisors in cloud computing can aid companies in selecting the most appropriate hypervisor data center. The two types of hypervisors in cloud computing are bare metals (type 1) and hosted (type 2). Each hypervisor variety comes with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
Type 1 Hypervisors
Type 1 hypervisors are commonly used in large-scale data centers and public cloud environments. They offer a reliable and fast virtualization service for essential applications. Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware are examples of Type 1 hypervisors.
Hypervisors don’t require a host OS to function, hence the name bare metal hypervisor. As a result, their virtualization environment is more streamlined and efficient, resulting in less wasted resources and higher performance.
Type 2 Hypervisors
Type 2 hypervisors are like any other application—you can install and operate them on the host OS. It facilitates their use in development and testing, but they are not suited for use in real settings. Oracle VirtualBox is an example of a Type 2 hypervisor.
Type 2 hypervisors, which operate on a host OS like Windows or Linux, are sometimes called “hosted” hypervisors. They’re easier to run than Type 1 hypervisors, making them a popular choice for desktop virtualization.
However, the overhead and performance of Type 2 hypervisors are higher. In addition, Type 2 hypervisors aren’t well suited for high-performance applications as Type 1 hypervisors.
Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisors
- Architecture: Type 2 runs on the host OS, while Type 1 runs on the hardware.
- Performance: Type 1 is more efficient and has less overhead than Type 2.
- Complexity: Type 1 is more challenging to deploy and manage than Type 2.
- Usage cases: Type 1 hypervisors shine with intensive applications in large-scale data centers. Type 2 hypervisors best serve desktop and other lightweight virtualization use cases.
Businesses intending to use cloud computing solutions must familiarize themselves with the critical distinctions between the two hypervisors. Picking the correct hypervisor is essential for your virtualized environment’s efficiency, scalability, and safety.
What are Cloud Hypervisors?
It is an OS that allows the sharing of cloud resources among several VMs. It also acts as a link of communication between the hardware and VMs. VMs can access the hardware through the hypervisor and share the bandwidth, processing power, and much more.
One feature of a hypervisor that makes it stand out is allowing resource sharing between several VMs. At the same time, it can partition the VMs to help curb breaches or instability if one of the VMs fails.
Not only that, hypervisors can provide a flexible allocation of cloud resources on demand. Businesses can benefit from that since it can help them improve production and service delivery.
As described above, a hypervisor is an essential component of cloud computing. It helps to facilitate excellent cloud resource allocation along with lower operating costs. Businesses can take advantage of hypervisors when they are mapping out their cloud systems.
What Are the Main Benefits of Hypervisors?
There are several benefits that hypervisors offer, and they include:
1. Hardware Independent
A hypervisor can support any physical machine that a VM operates on. It can do that because service providers can build hardware-independent VMs through a hypervisor. It makes it cost-effective and dynamic.
2. Portable
It is easy to move VMs between servers through a hypervisor. It’s a feature that benefits SMEs since they can leverage the best deals service providers offer. In addition, the flexibility helps avoid vendor lock-in.
3. Speed
Launching new products and apps is fast and easy when using a hypervisor. Organizations trying to stay on top of the competition will find this ideal in their operations.
4. Efficiency
A hypervisor can enable resource sharing between multiple VMs. It is a feature that can help businesses cut expenses like emissions and power consumption.
5. Scalability
Hypervisors allow server scaling of businesses computing resources up or down quickly and easily. This scalability allows businesses to handle increased demand or traffic without investing in expensive physical hardware.
What is the Difference Between Hypervisors and Containers?
Hypervisors and containers are two different virtualization technologies used in cloud computing. Having defined what is hypervisor in cloud computing, here is a table outlining the differences between the two:
|
Feature |
Hypervisor |
Containers |
| Technology | It has Type 1 and Type 2 virtualization technology. | It has operating system-level virtualization technology. |
| Flexibility | It can run multiple OSs and applications on a single server. | It’s limited to applications that can run on the host OS. |
| Performance | The overhead from virtualization can affect performance. | There is minimal overhead, as there is no virtualization layer. |
| Resource Isolation | It has strong isolation, where each virtual machine has its resources. | It has lightweight isolation, where containers share a host’s resources. |
| Scalability | The physical hardware resources limit scalability. | It is highly scalable and can run multiple containers on a single OS. |
| Security | It isolates each virtual machine from other VMs. | The containers share a kernel, increasing the risk of attacks. |
| Virtualization | It has full virtualization, where virtual machines run on a hypervisor. | Virtualization is lightweight enabling containers to operate on the host OS. |
Security Considerations for Hypervisors
The growth of technology, especially virtualization, has brought a lot of security concerns. It has led to the rise in the adoption of hypervisors for cloud security. The good thing about hypervisors is that they can host multiple VMs on a sole physical server. The only drawback is that if the hypervisor build is wrong, it can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
So, what are the security considerations businesses need to take for the many types of hypervisors? Here’s what to factor in:
- Hypervisor Hardening means designing and building a hypervisor that can withstand cyber attacks. It is a crucial process in guaranteeing protection. In addition, updating it regularly and applying security patches will help secure it well.
- Guest OS Security: Protecting guest OS is crucial since it’s running on the VMs. Some ways you can safeguard it are through passwords, the application of security patches, and much more.
- Segmentation of the Network: In case of a cyber-attack, network segmentation can help curb the impact. One way you can accomplish network segmentation is by putting VMs with different protection protocols and separating them into segments.
- VM Partitioning: Partitioning each VM operating on the hypervisor is crucial. The reason being it curbs the malware spread. Some of the ways you can partition VMs are through private networks or firewalls.
Virtualization in the cloud is a vulnerable technology, but leveraging hypervisor security can help curb cyber attacks. So, applying a hypervisor in your cloud can help keep your environment safer.
Hypervisors Use Cases
There are many use cases of hypervisor types in cloud computing. Some common ones are:
Resource Optimization
Using a hypervisor can help businesses combine multiple VMs onto a single server. In return, it can help businesses utilize idle resources, increasing productivity.
Desktop Virtualization
Users can use a hypervisor as a virtual desktop to simplify management and tighten cloud security. It makes it valuable for companies with a mobile workforce.
Workspace Utilization
A hypervisor enables businesses to have space efficiency in their infrastructure by sharing a sole server. It makes it a budget-friendly way for users to use cloud resources.
Power Usage
The hypervisor nature of pooling several VMs to a single server can help reduce power usage within a company. In return, it can lower power costs and use.
Legacy System Continuity
Using a hypervisor to operate legacy systems is possible. It helps simplify the operation and integration of new software and hardware.
Failure Recovery
It is possible to use a hypervisor in disaster recovery. It migrates all VMs to physical data centers whenever an outage or failure occurs.
There are a multitude of use cases of hypervisors in the cloud. Businesses must use these hypervisor benefits to boost productivity and cut expenses.
Final Thoughts
Businesses need to understand how a hypervisor in the cloud works. It will enable them to choose the suitable hypervisor architecture in cloud computing. Not only that, businesses will be able to take advantage of the unique features and benefits of the cloud.
So, if you are looking for a reputable cloud hosting provider, who can offer top-rated cloud hosting services, then RedSwitches is your best bet. In addition, RedSwitches is capable of optimizing and managing your hypervisor.
Whether you want a reliable platform for your VMs or a reliable cloud solution, we have the necessary expertise. So, don’t settle for less. To learn more about “what is a hypervisor in cloud computing,” visit our resources section. Also, you can check the cloud computing concepts section to see how you can expand your startup through the cloud. When you’re ready to take the next step, consider RedSwitches for all your cloud hosting needs. Our reputation for excellence speaks for itself.
FAQs
Q-1) Is a Hypervisor a Server?
No, it’s not a server but an OS that runs VMs on a single server and facilitates virtualization. Several VMs can work together on one physical server thanks to a hypervisor.
Q-2) What Type of Hypervisor Is Linux?
Linux isn’t a hypervisor but an OS you can use to build it. The two categories of virtualization OS are hosted and bare-metal hypervisors.
Q-3) Is Kubernetes a Hypervisor?
Kubernetes is not a hypervisor but a free OS to manage multiple containers. One of the goals of Kubernetes is automating container app processes like scaling and upkeep.
Q-4) Is Hypervisor an IaaS?
Yes, hypervisors are components of IaaS in the cloud. IaaS is a service model that delivers on-demand cloud resources to users and organizations through the Internet.