Oracle’s VirtualBox is a free, open-source software that allows you to install different operating systems on your Ubuntu machine. Some admins prefer it over VMware Workstation, especially in a Linux environment, because it’s free, easy to use, and has great learning resources.
One of the most common uses of VirtualBox is trying out different operating systems without actually installing them on your machine. For example, you can use VirtualBox to run Windows on a Linux computer or vice versa. It’s like having a computer inside your computer.
However, you can use VirtualBox for any scenario where you need a virtual machine on your system.
In this short tutorial, we’ll show you how to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu. We’ll discuss two easy methods of accomplishing this task and then discuss using VirtualBox for the first time.
Let’s start with the basic requirements to Install VirtualBox on Ubuntu.
Table Of Contents
- The Basic Requirements
- How to Install VirtualBox on Ubuntu
- How to Use VirtualBox After Installation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The Basic Requirements
Before proceeding with installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu, make sure you have the following:
- A system running Ubuntu
- An account that has sudo access.
- Access to a terminal
How to Install VirtualBox on Ubuntu
Let’s now discuss the two ways of installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu.
Method #1: Install VirtualBox from Ubuntu Repository
The easiest way to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu is through the official Ubuntu repositories.
This method has the following steps.
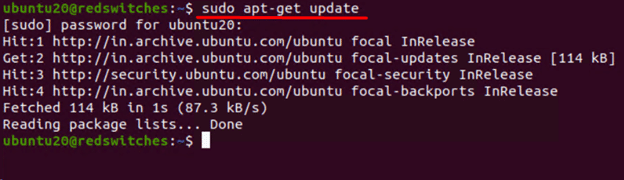
Step #1: Update the Package Index
The first step is to update the system’s package index. For this, launch the terminal and enter the following command:
# sudo apt-get update
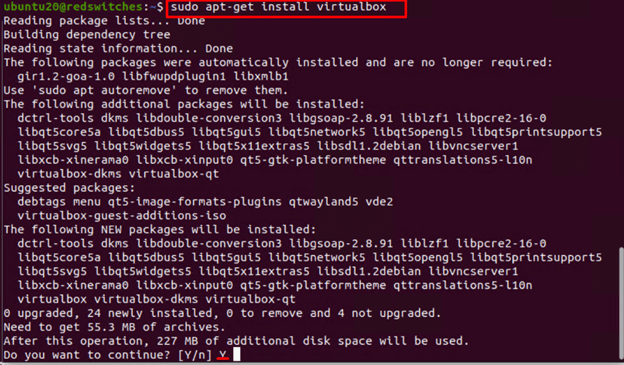
Step #2: Install VirtualBox
Next, use the following command to download and install VirtualBox:
# sudo apt-get install virtualbox
After the core installation, the process will continue to download and install additional files. Once the process finishes, you’ll see the successful message about the Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension pack.
Step #3: Verify VirtualBox Installation
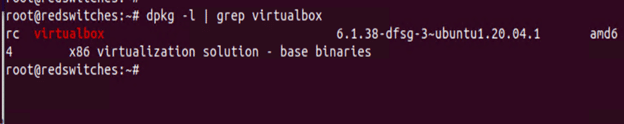
Finally, use the dpkg command to extract information about VirtualBox installation.
# dpkg -l | grep virtualbox
As you can see, the output shows information about VirtualBox installation on the system.
Method #2: Install VirtualBox From Oracle Repositories
You can get the VirtualBox repository from Oracle instead of Ubuntu. You can opt for this approach if you prefer a more recent VirtualBox version, as Ubunutu’s repository tends to have a slightly older version to ensure stability for the maximum number of users.
Step #1: Install Pre-installation Dependencies
Before you install VirtualBox, you should install the software-properties-common package that Ubuntu Virtualbox requires for proper functioning. For this, launch the terminal and enter the following command:
# sudo apt-get install software–properties–common
Step #2: Download the GPG Keys
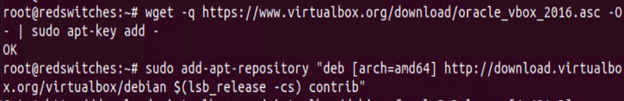
Now, use the following wget command to download and install GPG keys:
# wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
Step #3: Download the VirtualBox Repository
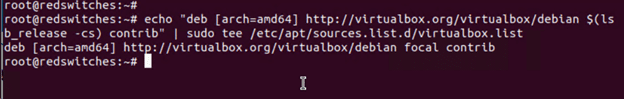
Use this command to add the VirtualBox repository to the Ubuntu package index:
# echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian $(lsb_release -cs) contrib" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/virtualbox.list
Step #4: Install VirtualBox
Now, you can go ahead and install the most recent version of VirtualBox. But before that, update the Ubuntu package index with the following command:
# sudo apt-get update
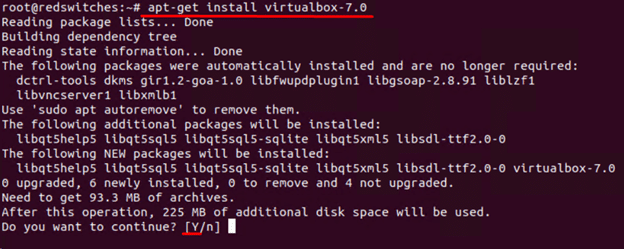
Next, install VirtualBox 7.0 on Ubuntu with the following command:
# sudo apt-get install virtualbox–7.0
Alternatively, If you are on a 32-bit Ubuntu installation, you’ll need to use VirtualBox 5.2. For this, use the following command:
# sudo apt-get install virtualbox–5.2
How to Use VirtualBox After Installation
Now that you have VirtualBox on your system, we recommend launching it to see it in action.
Launch the terminal and run the following command:
# virtualbox
You’ll see the application window in the Ubuntu GUI. Look for the Add or New button to create a virtual machine. Choose your operating system and version in the next window, and click Next.
This window contains options to customize your virtual machine, such as memory and hard drive settings. If you’re unsure, stick with the defaults.
Once your choices are set, a new virtual machine will appear in the left column. Click the green Start arrow, and your virtual machine will boot up in a new window.
Conclusion
Installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu is straightforward, enabling users to create and manage virtual machines effortlessly. This step-by-step guide highlighted 2 easy ways to download VirtualBox from Ubuntu and Oracle.
RedSwitches offers the best dedicated server pricing and delivers instant dedicated servers, usually on the same day the order gets approved. Whether you need a dedicated server, a traffic-friendly 10Gbps dedicated server, or a powerful bare metal server, we are your trusted hosting partner.
FAQs
Q. What is VirtualBox, and why should I install it on Ubuntu?
Oracle’s VirtualBox is a free, open-source tool that lets you install different operating systems on your computer. It’s powerful and versatile, allowing you to run multiple operating systems at the same time on a single machine. When you install it on Ubuntu, you can easily create and handle virtual machines for tasks like testing, development, or running various operating systems simultaneously.
Q. Is VirtualBox free to use on Ubuntu?
Yes, VirtualBox is free and open-source software, making it accessible for personal and commercial use.
Q. How do I update the system repositories before installing VirtualBox?
Before installing VirtualBox, run the following command to update the system repositories:
# sudo apt update
Q. Can I install VirtualBox directly from the Ubuntu Software Center?
Yes, you can install VirtualBox from the Ubuntu Software Center. Alternatively, you can use the terminal and run:
# sudo apt install virtualbox
Q. Are there any system requirements for installing VirtualBox on Ubuntu?
VirtualBox has modest system requirements. Ensure your system meets the minimum specifications, including sufficient RAM and disk space for your virtual machines.
Q. What is the purpose of the VirtualBox Extension Pack, and how can I install it?
The Extension Pack provides additional features, such as USB support. You can install it by downloading the pack from the official VirtualBox website and then installing it using the command:
# sudo vboxmanage extpack install --replace
Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-[version].vbox-extpack
Q. Can I use VirtualBox on Ubuntu to run Windows on a virtual machine?
You can run Windows and other operating systems on a virtual machine created with VirtualBox on Ubuntu.
Q. Is VirtualBox compatible with other Linux distributions, or is it specifically for Ubuntu?
VirtualBox is compatible with many Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and others.
Q. How do I uninstall VirtualBox from my Ubuntu system?
To uninstall VirtualBox, run the following command:
# sudo apt remove --purge virtualbox-6.0
Q. Where can I find additional support or documentation for VirtualBox on Ubuntu?
You can refer to the official VirtualBox documentation, community forums, or online resources for additional support and information.