Key Takeaways
- Regularly update backup plans to align with changing data and business needs.
- Use a combination of full, incremental, and differential backups for thorough and efficient data protection.
- Implement continuous data protection (CDP) for frequently changing or critical data.
- Prioritize important data for more frequent backups and categorize it based on importance.
- Automate backups to ensure regularity and reduce human error, saving time and resources.
- Choose backup solutions that match your needs, considering data volume, type, and recovery time objectives.
- Test backup systems regularly to ensure data integrity and reliability in disaster recovery.
- Combine local and cloud backups for a balanced approach to data security and accessibility.
- Educate staff and users on backup best practices and the importance of data protection.
- Stay compliant with industry regulations and continuously adapt backup strategies to meet legal and technical requirements.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, safeguarding our data cannot be overstated. As technology continually evolves, so does the potential for data loss. Presenting significant risks to businesses and individuals alike. Almost 70% of small businesses close down within a year after losing a lot of data. This alarming figure underscores the critical need for robust data protection strategies. This is where scheduled backups are pivotal.
For critical data on a dedicated server, prioritize frequent backups. Scheduled backups automate saving data, providing a reliable safeguard against loss. They’re crucial for everyone, from individuals to businesses.
This article will explore the importance, setup, and best practices of scheduled backups. It’s designed to be accessible, even for those without technical expertise. Our goal is to guide you in protecting your digital assets in a world where data is increasingly vital. Let’s dive in and learn how to secure our data effectively with scheduled backups.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Scheduled Backups
- The Importance of Automating Data Protection
- The Advantage of Automated Backup Software
- Automation in Various Environments
- Types of Scheduled Backups
- Setting Up Scheduled Backups
- Best Practices for Scheduled Backups
- Choosing the Right Backup Solutions
- Managing Maintaining Backup Systems
- Manual vs Automatic Backups: Which Are Better and Why?
- Key Issues and Overcoming Common Challenges in Scheduled Backups
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding Scheduled Backups
Credits: Freepik
Scheduled backups are an integral part of data protection strategies. This section will delve into what scheduled backups are. How do they differ from manual backups, and why are they crucial for data security?
What Are Scheduled Backups?
Scheduled backups are automated processes to copy and store data regularly. Unlike manual backups, where an individual must initiate the process. Scheduled backups occur without direct intervention. They can be daily, weekly, or at any other interval that suits the user’s needs.
The Role of Scheduled Backups in Data Protection
- Preventing Data Loss: They protect your data from computer problems, hackers, or mistakes.
- Business Continuity: Regular backups help businesses keep working despite losing data.
- Compliance and Regulations: Some businesses must back up data regularly to meet legal requirements
How Scheduled Backups Work
- Setting the Schedule: Users decide how often the backup should occur. This could be as often as every hour or as little as once a month, based on how important the data is and how much it changes.
- Choosing Data: Users select which data or systems need regular backing up.
- Where to Save: You can save backup data in the cloud, external drives, or network storage.
- Check and Care: Keep an eye on backups to ensure they work right and don’t have problems.
Scheduled backups are a cornerstone of effective data management and protection. By understanding and implementing them. Users can significantly reduce the risk of catastrophic data loss.
The Importance of Automating Data Protection
Credits: Freepik
Data protection in data management is not just a convenience but a necessity. This section explores why automating data protection through scheduled backups is crucial for safeguarding data.
Why Automate Data Protection?
Automating data protection is about more than just convenience. It’s a strategic approach to ensuring data safety and accessibility.
- Mitigating Human Error: People forget or make mistakes. Automated backups eliminate the risk of forgetting to back up data.
- Always Safe Dat Automatic backups keep your data safe regularly, making it easier to get back if needed.
- Save Time and Effort: Automated backups free up time and resources, letting people and businesses focus on important tasks.
Setting up automatic backups is vital to prevent data loss. It keeps things secure, saves time, and helps keep your work going. It’s important for anyone who cares about their digital data to use these automatic processes.
Also Read: 3-2-1 Data Backup Rule: Data Protection Strategy & Its Benefits
The Advantage of Automated Backup Software
Automated backup software plays a crucial role in today’s digital landscape. Offering a range of benefits, from enhanced security to efficient resource management. This section will delve into these advantages in detail.
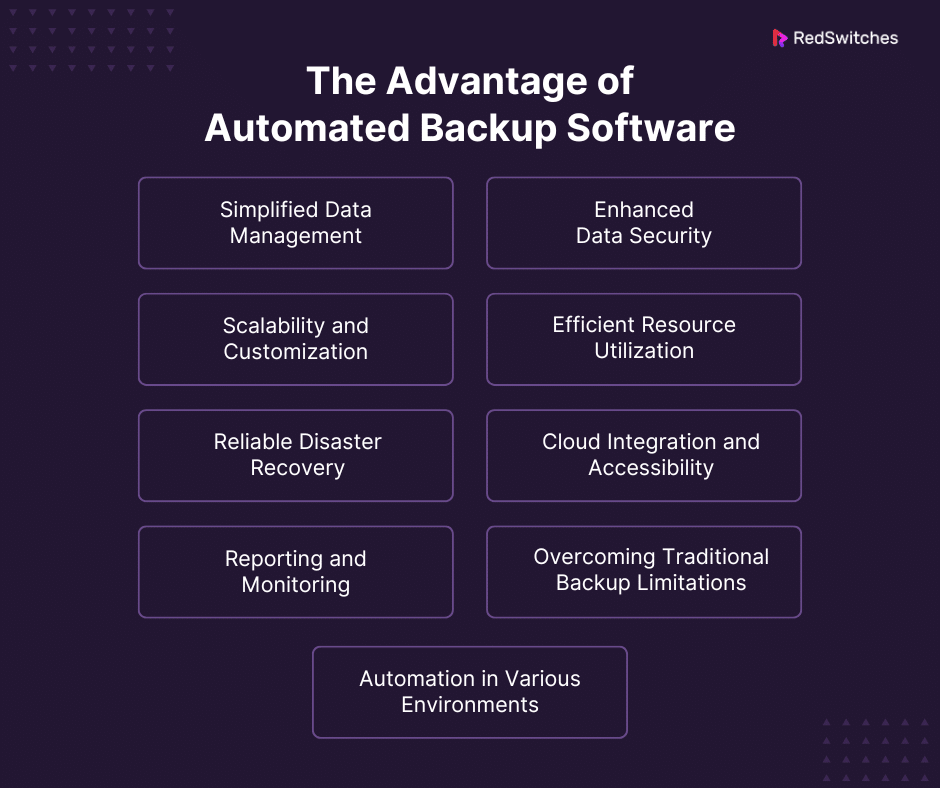
Simplified Data Management
Automated backup software significantly simplifies the process of data management.
- Ease of Use: These tools are designed with user-friendly interfaces. This simplifies setting up and managing backups.
- Scheduling Flexibility: Users can set backup schedules that suit their data requirements.
- Automatic Updates: The software can update to include new files, ensuring no critical data is missed.
Enhanced Data Security
One of the key benefits of automated backup software is its enhanced security.
- Encryption Protocols: It encrypts data during backups, safeguarding it during storage and transfer.
- Reduced Human Error: By automating the backup process, the risk of human errors, common in manual backups, is minimized.
- Version Control: These systems maintain multiple versions of files. Protecting against data corruption and security threats like ransomware.
Scalability and Customization
Automated backup software adapts to varying data needs, making it scalable.
- Adaptable to Growth: It can manage increasing amounts of data, suitable for personal and business growth.
- Customizable Options: Users can tailor backup frequency and data retention features to match their needs. Organize your dedicated server’s data into categories for tailored backup schedules.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Automated backup software optimizes the use of resources.
- Time Conservation: It saves significant time by eliminating the need for manual backups.
- Reduced Workload: This automation allows IT staff and individuals to focus on other critical tasks.
- Cost Efficiency: In the long term, the efficiency and reliability of automated backups can lead to substantial cost savings.
Reliable Disaster Recovery
Automated backup software ensures preparedness for any data loss incident.
- Rapid Data Restoration: In the event of data loss, the software enables quick data recovery.
- Business Continuity: This quick restoration capability is vital for businesses to maintain operations with minimal downtime.
- Compliance and Testing: The software facilitates regular backup testing. Which is essential for compliance with data protection regulations.
Cloud Integration and Accessibility
Integration with cloud services enhances the functionality of automated backup software.
- Cloud Storage in Backups: Automated backups often use cloud storage, adding extra data protection.
- Access Anywhere: This is great for remote teams, as they can access their data anywhere.
Reporting and Monitoring
Stay informed about the health of your data with automated backup software.
- Instant Alerts: The software can send real-time notifications about backup statuses.
- Insightful Reports: Regular reporting provides insights into backup health and alerts to potential issues.
Overcoming Traditional Backup Limitations
Credits: Freepik
Automated backup software addresses several limitations of traditional backup methods.
- Efficient Data Handling: It can efficiently manage large volumes of data.
- Less Need for Physical Storage: Using things like cloud storage means you don’t need as much physical storage space.
In summary, automatic backup software is very important for protecting data today. It makes data safer and easier to manage, uses resources well, and helps recover from disasters reliably. This software is essential for anyone who cares about their digital information. Buying it is a smart move to protect your data from many dangers.
Also Read: Backing Up Your data on a Dedicated Server: How & Why
Automation in Various Environments
Automated backup solutions are versatile and can be tailored to fit different environments and needs. This section explores how automation can be effectively implemented across various settings. From personal use to large enterprises.
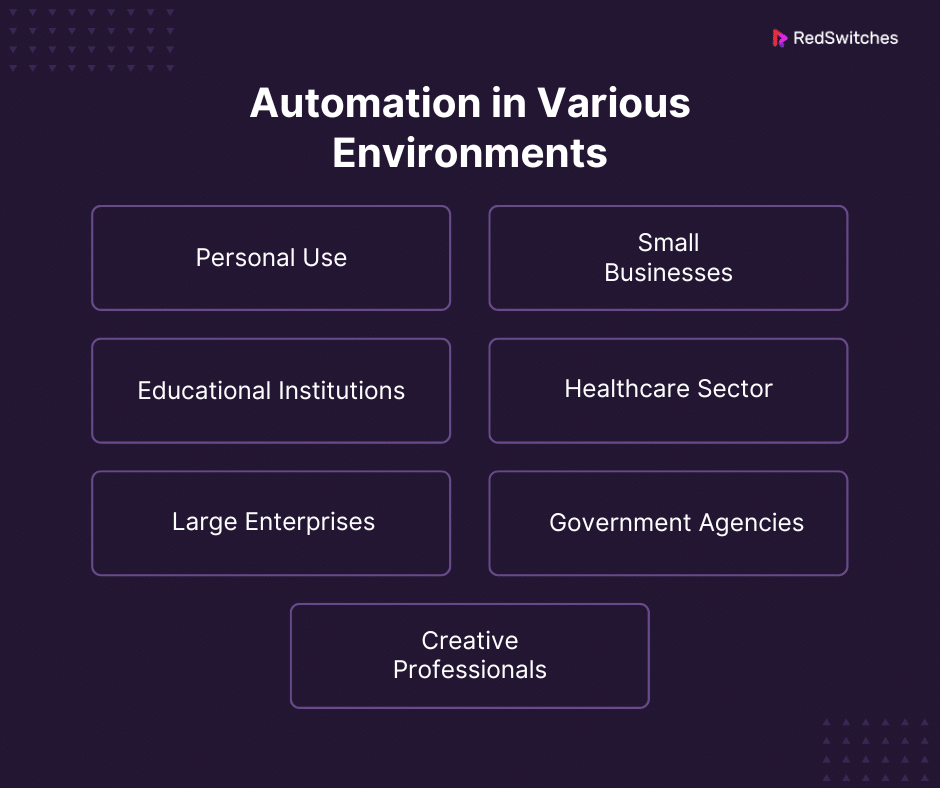
Personal Use
For individual users, data protection is often about safeguarding personal memories and important documents.
- Simplified Solutions: Home users benefit from user-friendly software that requires minimal technical knowledge.
- Cloud-Based Services: Individuals often prefer cloud backups for convenience and accessibility.
- Affordable Options: Many cloud-based backup solutions offer free or low-cost plans suitable for personal data storage needs.
Small Businesses
Small businesses need efficient and cost-effective backup solutions that can grow with them.
- Grow with Your Needs: The best backup solutions can grow as your data needs increase.
- Cloud for Small Business: Small businesses often pick cloud backups because they’re cheap and easy to access from anywhere.
- Choose What’s Important: Knowing which data is most important and picking a backup solution that fits your business’s needs is essential.
Educational Institutions
Schools and universities handle a vast amount of data, including sensitive student information.
- Strong Backups for Education: Schools need robust backup systems to keep student information and research safe.
- Follow Education Rules: They must use automated backups to meet rules about protecting student data.
- Manage Lots of Dat Schools need backup solutions to handle and recover much data quickly.
Healthcare Sector
The healthcare sector deals with critical patient data, making data protection crucial.
- HIPAA Compliance: Backups must comply with healthcare regulations like HIPAA for patient data confidentiality.
- High-Security Standards: Backup solutions with strong encryption and security features are essential.
- Reliable Recovery: Fast and reliable data recovery is crucial for patient care continuity.
Large Enterprises
Credits: Freepik
Large corporations handle enormous amounts of data and require comprehensive backup solutions.
- Tailor-Made Backups for Big Companies: Large businesses often need unique backup solutions. This is for their complicated data setups.
- Mix of Local and Cloud Backups: They usually use on-site and cloud backups for better safety and easy access.
- Top-Notch Security Needed: These solutions need strong security and encryption. This is to keep important company data safe.
Government Agencies
Government data is critical and sensitive and needs the best security and reliability.
- Top Security Standards: Backup solutions must meet strict government security rules.
- Frequent Rule Checks: Backup systems need to follow regulations and be checked regularly.
- Ready for Emergencies: Robust recovery plans from disasters are vital to keep government operations going in tough times.
Creative Professionals
Artists, photographers, and videographers store large files and require efficient backup solutions.
- Need for Big Storage: Backup solutions with much storage space are best for large media files.
- Quick Transfer Speeds: Backups need to transfer data fast for efficiency.
- Easy to Get Files: Accessing your backed-up files easily is important for ongoing work and dealing with clients.
Automated backup solutions are flexible and can be adjusted for many situations and needs. They’re useful for everyone, from individual users to big businesses and government bodies. The ability to customize these backup plans to fit specific needs is a major plus. This flexibility ensures that, no matter the situation, data is kept safe and secure efficiently.
Also Read: Incremental vs Differential Backup: Which Is The Best Backup Strategy For You?
Types of Scheduled Backups
Scheduled backups are a cornerstone of data protection strategies. Various types exist, each suited to different needs and scenarios. This section explores the common scheduled backup types, outlining their features and best use cases.
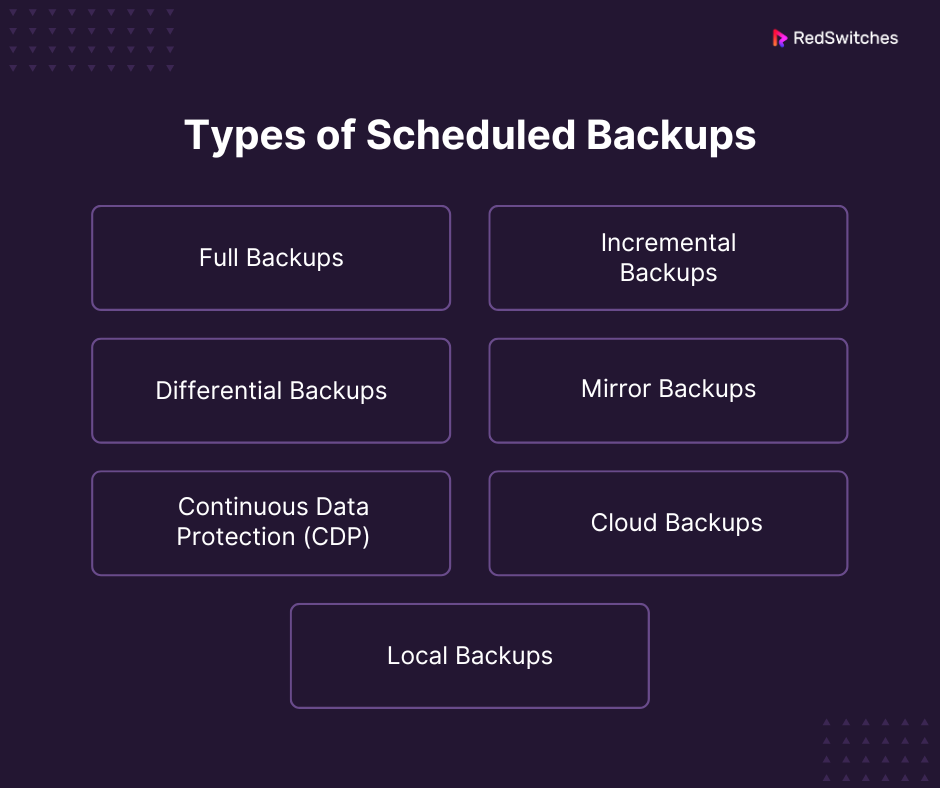
Full Backups
Full backups involve copying all selected data to the backup storage. Combine full and incremental backups on a dedicated server for better efficiency.
- Complete Data Copy: Every file and folder in the chosen scope is copied.
- Storage Space: They require significant storage space, as each backup is a complete data set.
- Time-Consuming: Full backups usually take more time due to the volume of data.
- Restoration Ease: Restoring from a full backup is straightforward as it contains all data in one set.
Incremental Backups:
Incremental backups save changes made since the last backup.
- Efficient Storage Use: Only changed data since the last backup, whether full or incremental, is copied, saving storage space.
- Faster Backups: They are quicker than full backups, making them suitable for frequent backup schedules.
- Complex Restoration: Restoration can be time-consuming, requiring the last full backup and all subsequent incremental backups.
Differential Backups
Differential backups cover data changes made since the last full backup. Use differential backups on a dedicated server to complement full backups.
- Moderate Storage Needs: They require more storage than incremental but less than full backups.
- Balance Between Speed and Storage: Faster than full backups but slower than incremental ones.
- Simpler Restoration Than Incremental: Restoration requires the last full and differential backups.
Mirror Backups
Mirror backups create an exact copy of the selected data.
- Direct Copy: They replicate the source data without compression, creating an exact mirror.
- Immediate Data Access: Data from mirror backups can be accessed directly without restoring processes.
- Lack of Historical Dat Mirror backups don’t keep historical versions of files; they simply mirror the current state.
Continuous Data Protection (CDP)
CDP involves continuous data backup as changes occur. Implement CDP on a dedicated server to track real-time data changes.
- Real-Time Backup: Data is backed up immediately as changes are made, offering the most up-to-date backup.
- High Storage Requirements: Continuous backups can consume significant storage space and resources.
- Ideal for Critical Dat Best suited for environments where data changes frequently and needs immediate backup.
Cloud Backups
Credits: Freepik
Cloud backups involve storing data on remote servers accessible via the Internet.
- Remote Storage: Data is stored off-site, offering protection against physical damage at the primary site.
- Scalability: Cloud storage can be easily scaled up or down based on needs.
- Dependent on Internet Connectivity: Effective cloud backups require a stable Internet connection.
Local Backups
Local backups involve storing data on local devices like external hard drives or network-attached storage.
- Quick Access: Data is stored locally for fast access and restoration.
- Physical Security Risks: Local backups can be vulnerable to physical risks like theft or damage.
- Great for Big Files: These backups are perfect for places with large files. This is where fast access is needed without depending on internet speed.
Knowing the different scheduled backup types is key to choosing the right one for your needs. Each type, from full backups for complete protection to incremental and differential backups for saving space, has pros and cons. The choice depends on how much data you have, how often it changes, how much storage you have, and what you need to protect your data.
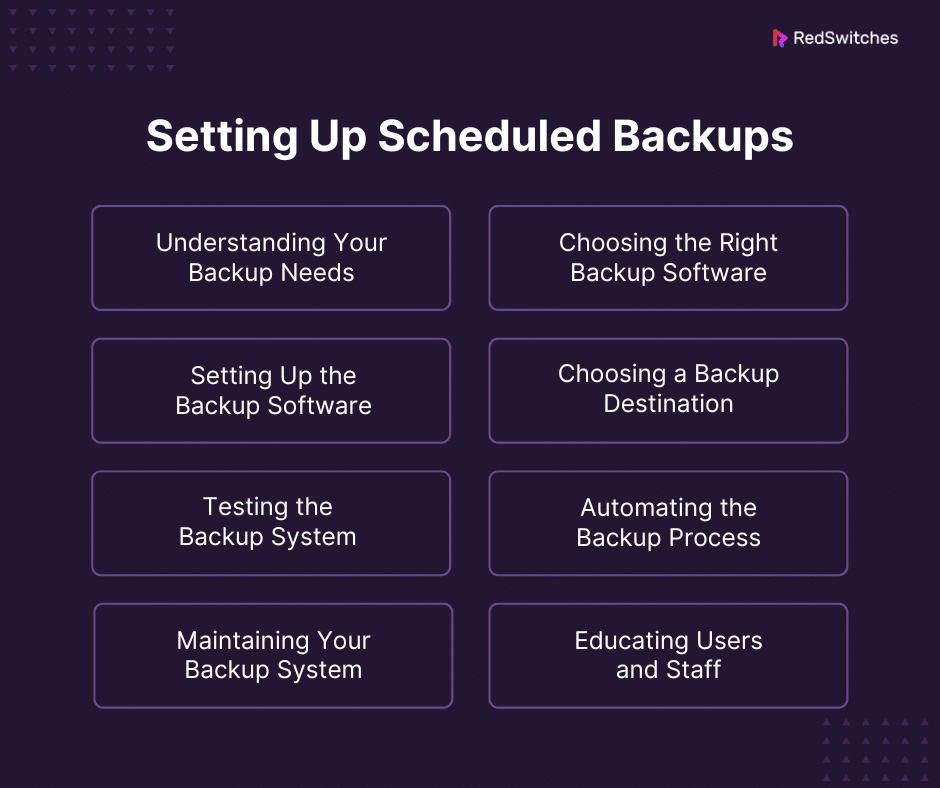
Setting Up Scheduled Backups
Setting up scheduled backups is crucial in ensuring data safety and availability. Set a regular backup schedule for your dedicated server to ensure data safety. This section outlines a detailed process for setting up these backups, tailored to different user needs.
Understanding Your Backup Needs
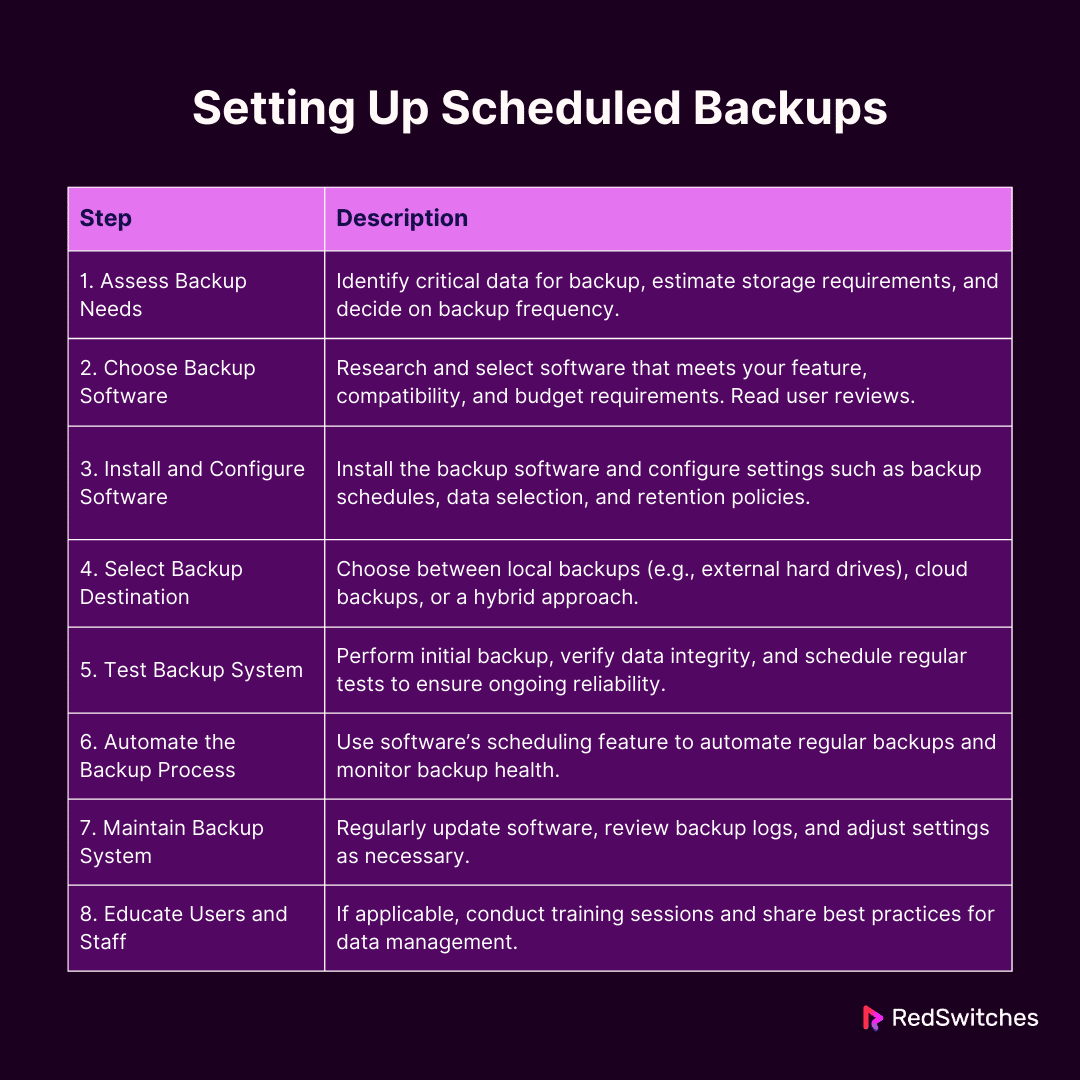
Before setting up, assess your backup requirements.
- Identify Critical Data: Determine which files and systems are essential and need regular backups.
- Estimate Storage Needs: Estimate the amount of storage required based on the data size.
- Consider Backup Frequency: Decide how often your data needs backing up – this could range from hourly to weekly.
Choosing the Right Backup Software
Selecting appropriate backup software is critical.
- Research Options: Look for software that matches your requirements regarding features, scalability, and budget.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system and other tools you use.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Look for user reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability and performance.
Setting Up the Backup Software
Once you have chosen your software, set it up properly.
- Install the Software: Follow the installation guide provided by the software.
- Configure Backup Settings: Set up backup schedules and choose what data to back up. And select your backup destination (local, network, or cloud storage).
- Set Retention Policies: Decide how long you want to keep your backups.
Choosing a Backup Destination:
Decide where your backups will be stored.
- Local Backups: External hard drives or network-attached storage devices are good for quick access and restoration.
- Cloud Backups: Cloud services offer off-site storage and are excellent for disaster recovery.
- Hybrid Approach: Local and cloud storage can provide quick access and off-site security.
Testing the Backup System
Testing is essential to ensure everything works correctly.
- Perform Initial Backup: Run a backup to ensure the system works as expected.
- Check Data Integrity: Verify the backup to ensure all files are copied correctly and can be restored.
- Schedule Regular Tests: Regularly test your backup system to ensure it remains reliable over time.
Automating the Backup Process:
Automate your backups to ensure consistency. On a dedicated server, automate backup processes to maintain data consistency.
- Schedule Regular Backups: Automate backups using the software’s scheduling feature.
- Monitor Backup Health: Use the software’s monitoring tools to monitor backup statuses and receive alerts for any issues.
Maintaining Your Backup System
Regular maintenance is crucial for ongoing reliability.
- Update Software Regularly: Keep your backup software updated to ensure you have the latest features and security patches.
- Review Backup Logs: Regularly review backup logs to identify and resolve any issues.
- Adjust Settings as Needed: Adjust your backup settings accordingly as your data and requirements change.
Educating Users and Staff
If you’re in an organization, educate others about the importance of backups.
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions to familiarize staff with the backup process.
- Best Practices: Share best practices for data management to complement the backup strategy.
Setting up scheduled backups is easy and can prevent data loss. Just assess your needs, pick the right software, test your setup, and keep it running well. This way, your data stays safe and you can get it back if lost. The most important thing is to have a regular and well-kept backup plan. Ensure your dedicated server has enough storage for comprehensive backups.
Also Read: Backup Disaster Recovery Solutions: What’s The Better Investment?
This table gives a clear guide for each step in setting up scheduled backups, offering a thorough way to protect your data.
Best Practices for Scheduled Backups
Implementing best practices in scheduled backups is essential for effective data protection. Protect your dedicated server’s data with a mix of backup strategies. This section offers detailed guidance on maximizing the efficiency and reliability of your backup strategy.
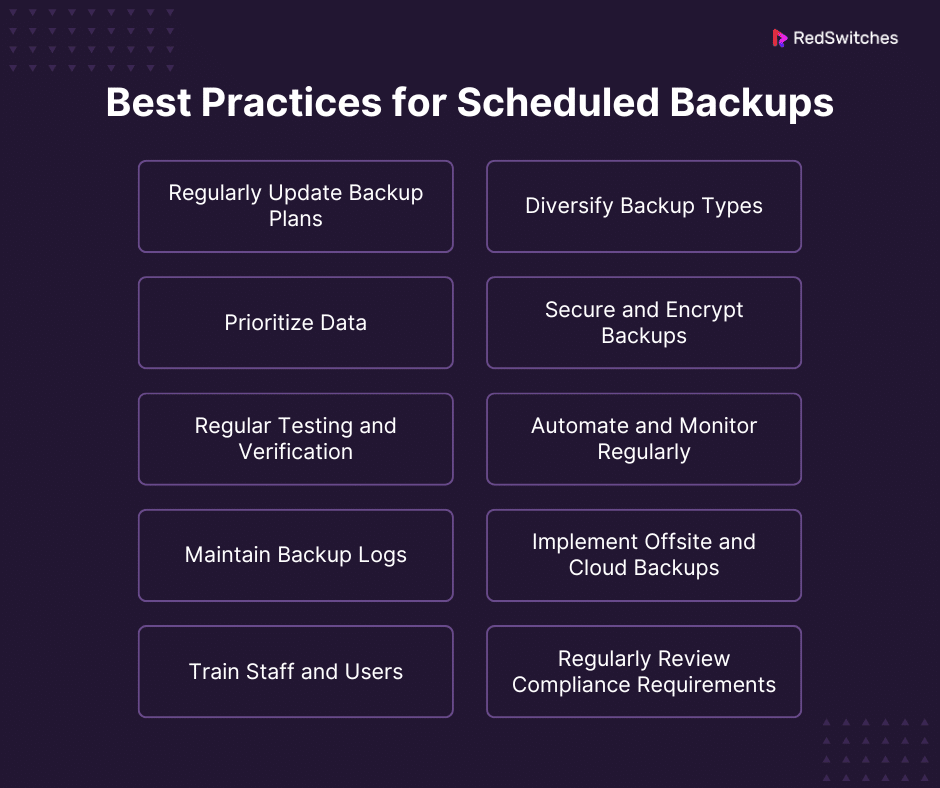
Regularly Update Backup Plans
Keep your backup plans current with your needs.
- Review and Update: Regularly assess and update your backup strategy to align with data and business requirements changes.
- Adapt to Changes: Modify backup plans when new software, hardware, or data types are introduced.
Diversify Backup Types
Using a mix of backup types can enhance data security.
- Mix Different Backup Types: Use a mix of full, incremental, and differential backups. This way, you get both thoroughness and speed.
- Use Continuous Protection for Key Dat Consider using continuous data protection (CDP) for greatly changing data. It records changes as they happen.
Prioritize Data
Not all data requires the same level of backup frequency.
- Find Important Dat Determine which data is important for what you do and back it up more often.
- Divide Data into Groups: Put your data into different categories based on importance, and plan your backups.
Secure and Encrypt Backups:
Ensure your backups are secure from unauthorized access.
- Implement Encryption: Use encryption for both in-transit and at-rest data to protect against unauthorized access.
- Secure Access: Limit access to backup data to authorized personnel only.
Regular Testing and Verification
Regular tests ensure backups are reliable and effective. Regularly test the backup system of your dedicated server for reliability.
- Routine Restores: Periodically restore data from backups to verify their integrity and the effectiveness of your backup process.
- Monitor Backup Health: Use monitoring tools to track the health and status of your backups continuously.
Automate and Monitor Regularly
Leverage automation for consistency and efficiency.
- Schedule Automated Backups: Use automated schedules to ensure regular and consistent backups without manual intervention.
- Set Up Alerts: Configure alerts for backup failures or issues to address problems promptly.
Maintain Backup Logs
Credits: Freepik
Documenting backup activities can provide valuable insights.
- Keep Detailed Logs: Maintain logs of all backup activities, including successes and failures.
- Review Logs Regularly: Review these logs to identify trends or recurring issues.
Implement Offsite and Cloud Backups
Offsite backups provide additional security.
- Use Offsite Storage: Store backups in a location separate from the primary data to protect against physical disasters.
- Leverage Cloud Solutions: Utilize cloud storage for additional redundancy and accessibility.
Train Staff and Users
In organizational settings, training is key.
- Educate on Best Practices: Train staff and users on best backup practices and the importance of data protection.
- Promote a Backup Culture: Encourage a culture of regular backups and data security awareness.
Regularly Review Compliance Requirements
Stay compliant with industry standards and regulations.
- Understand Regulations: Be aware of data protection regulations relevant to your industry.
- Align Backups with Compliance: Ensure your backup strategies meet these regulatory requirements.
You need a complete plan to do scheduled backups. This includes updating your backup plans often. Using different kinds of backups. Choosing which data is most important. Keeping it secure and encrypted, and testing regularly. Also, keeping logs, training your team, and following rules and regulations are key to a good backup strategy. By following these steps, you can ensure your data is safe and can be recovered if there’s a problem.
Also Read: The 12 Best WordPress Security Plugins to Shield Your Site!
Choosing the Right Backup Solutions
Selecting the right backup solution is crucial for adequate data protection. This section will guide you through choosing a backup solution that fits your needs, and discussing various options and considerations.
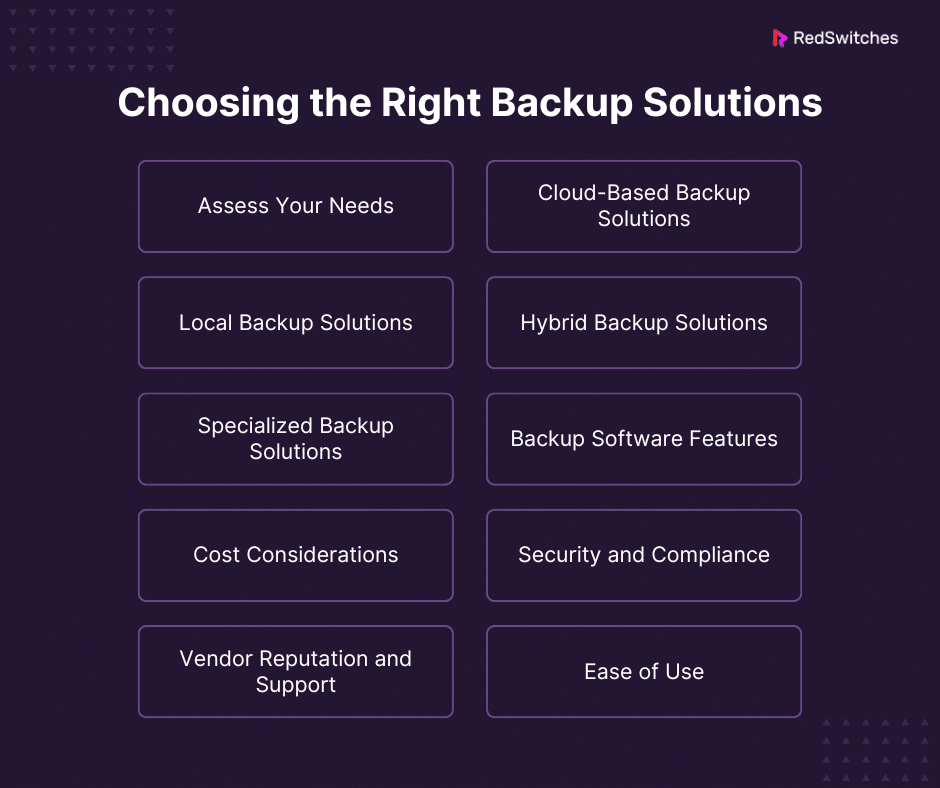
Assess Your Needs
Start by understanding your specific backup requirements.
- Data Volume: Estimate the data you need to back up.
- Data Type: Consider the data types, such as documents, media, or databases.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): Determine how quickly you need to recover your data after a loss.
Cloud-Based Backup Solutions
Cloud backups are increasingly popular for their convenience and scalability.
- Accessibility: Cloud storage allows access to data from anywhere.
- Scalability: Easily adjust your storage capacity based on current needs.
- Security: Look for cloud providers with strong encryption and security measures.
Local Backup Solutions
Local backups involve storing data on physical devices.
- Speed: Local backups and restorations can be faster, as they don’t depend on internet speeds.
- Control: You have complete control over your backup hardware.
- One-Time Cost: Typically involves a one-time purchase of hardware like external hard drives or NAS devices.
Hybrid Backup Solutions
Combining local and cloud backups offers the best of both worlds.
- Flexibility: Provides both the security of local backups and the accessibility of cloud backups.
- Data Redundancy: Offers more protection by storing data in multiple locations.
Specialized Backup Solutions
Some sectors require specialized backup solutions.
- Healthcare: Look for HIPAA-compliant solutions that ensure patient data privacy.
- Finance: Requires solutions that comply with financial data protection regulations.
- Media and Entertainment: Solutions that handle large file sizes and volumes.
Backup Software Features
Evaluate the features offered by backup software.
- Automation: Check for the ability to schedule automatic backups.
- Data Compression: Reduces storage space requirements.
- Incremental Backup Support: Saves time and space by backing up only changed data.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor in choosing a backup solution.
- Initial Investment: Consider the upfront cost of acquiring backup hardware or software.
- Ongoing Costs: Consider ongoing subscription or storage fees for cloud solutions.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Evaluate the long-term benefits versus the costs.
Security and Compliance:
Ensure the backup solution meets your security and compliance needs.
- Data Encryption: Essential for protecting sensitive data.
- Compliance Standards: Ensure the solution meets industry-specific compliance standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Consider where your data is stored, especially for cloud solutions.
Vendor Reputation and Support:
Choose a reputable vendor with reliable support.
- Vendor History: Research the vendor’s track record in the industry.
- Customer Reviews: Look for customer feedback and reviews.
- Support Services: Ensure the vendor offers robust customer support.
Ease of Use
Consider the ease of setting up and managing the backup solution.
- User Interface: Look for an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Documentation: Good documentation can simplify setup and troubleshooting.
- Community and Resources: A strong user community and available resources can be helpful.
Also Read: 10 Best Tools to Manage Multiple WordPress Sites From a Single Dashboard
Managing and Maintaining Backup Systems
Effective management and maintenance of backup systems are crucial. It is for ensuring data integrity and availability.
Regular Monitoring and Updates
Consistent monitoring is key to a healthy backup system.
- Routine Checks: Regularly check backup logs for errors or failures.
- Software Updates: Keep your backup software updated to benefit from the latest features and security enhancements.
Testing Backup Integrity
Regular testing ensures your backups are reliable.
- Scheduled Testing: Test your backups periodically to ensure data can be successfully restored.
- Simulate Scenarios: Simulate different data loss scenarios to test the effectiveness of your backups.
Storage Management
Efficient storage management is essential for effective backups.
- Capacity Planning: Regularly review storage utilization and plan for future capacity needs.
- Storage Health: Monitor the health of your storage devices to prevent data loss due to hardware failure.
Security Practices
Securing your backup systems is crucial to protect data.
- Access Control: Restrict access to backup systems to authorized personnel only.
- Secure Transmission: Ensure data is encrypted during transmission to and from backup locations.
Documentation and Procedures:
Maintain comprehensive documentation for your backup processes.
- Document Procedures: Keep detailed records of your backup procedures and schedules.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Include your backup system in your broader disaster recovery and business continuity plans.
Training and Awareness:
Educate your team about the importance of backups. Train staff on managing backups on the dedicated server for better data security.
- Staff Training: Provide regular training to staff responsible for managing backups.
- Promote Awareness: Foster a culture of data protection awareness within your organization.
Regular Compliance Checks
Ensure your backup system complies with relevant regulations.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of any data protection regulation changes affecting your backups.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure industry standards and regulations compliance.
Vendor Support and Relationships:
Credits: Freepik
Maintain a good relationship with your backup solution providers.
- Utilize Support: Leverage vendor support for troubleshooting and advice.
- Stay Informed: Keep up to date with any changes or updates from your backup solution provider.
Manual vs Automatic Backups: Which Are Better and Why?
The debate between manual and automatic backups centers around convenience, reliability, and control. This section explores the pros and cons of each to determine which is better for various scenarios.
Manual Backups
Manual backups involve user-initiated processes to copy data.
Pros:
- Control: Users have complete control over what, when, and how to back up.
- Flexibility: Ideal for irregular backup needs or smaller sets of data.
Cons:
- Time-Consuming: Requires significant time and effort to manage.
- Risk of Human Error: Forgetting to perform backups or errors during the process can lead to data loss.
- Inconsistency: Manual backups may not happen regularly, leading to potential gaps in data.
Automatic Backups:
Automatic backups are scheduled to occur without user intervention.
Pros:
- Consistency: Regular and timely backups ensure data is always up-to-date.
- Time Efficiency: Once set up, they require minimal user intervention, saving time and effort.
- Reduced Human Error: Automation eliminates the risk of forgetting or incorrectly performing backups.
Cons:
- Less Control: Users have less control over the specifics of each backup process.
- Setup Complexity: Initial setup can be complex, requiring a clear understanding of needs and schedules.
Comparing Effectiveness
The effectiveness of manual versus automatic backups depends on the user’s needs.
- For Small or Personal Data Sets: Manual backups might be sufficient and more manageable.
- For Large or Business Data Sets: Automatic backups are generally better due to their consistency and reliability.
Security Considerations
Both methods require security measures, but automatic backups often have integrated security features.
- Encryption and Password Protection: Essential for both types to protect against unauthorized access.
Cost and Resource Implications
Automatic backups might involve software or cloud storage services costs, whereas manual backups often utilize existing resources.
- Budget and Resources: The choice may depend on available budget and resources.
Scalability and Growth
Automatic backups are more scalable, and better suited for growing data needs.
- Adapting to Change: Automated systems can be more easily adjusted to accommodate increasing data volumes.
In conclusion, automatic backups generally offer more consistency, efficiency, and reliability benefits, especially for larger or more critical data sets. While offering more control, manual backups are prone to human error and inconsistency. The choice should be based on the user or organization’s needs, resources, and data volume.
Also Read: Mastering WordPress Cron Jobs: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
Key Issues and Overcoming Common Challenges in Scheduled Backups
Scheduled backups are crucial but can encounter various challenges. This section discusses common issues and offers solutions to overcome them.
Data Volume and Storage Limitations
As data grows, storage can become a constraint.
Solutions:
- Regularly Review Storage Needs: Assess and upgrade storage capacity.
- Data Compression and Deduplication: Implement these technologies to reduce storage requirements.
Software and Compatibility Issues
Backup software may face compatibility issues with existing systems.
Solutions:
- Regular Updates: Regularly update both backup software and systems.
- Compatibility Checks: Ensure the software is compatible with your current systems before implementing.
Network and Connectivity Issues
Reliable network connections are essential for scheduled backups, especially cloud-based ones.
Solutions:
- Robust Network Infrastructure: Invest in reliable networking equipment.
- Backup Timing: Schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize network strain.
Security Vulnerabilities
Backup systems can be targets for cyber threats.
Solutions:
- Regular Security Updates: Keep all systems and software updated with the latest security patches.
- Encryption: Encrypt backups both in transit and at rest.
Human Error
Mistakes in setting up and maintaining backups can lead to data loss.
Solutions:
- Training and Guidelines: Provide adequate training and clear backup management guidelines.
- Regular Audits: Regularly audits backup procedures to catch and correct errors.
Compliance and Legal Challenges
Credits: Freepik
Staying compliant with data protection laws and regulations can be challenging.
Solutions:
- Stay Informed: Keep updated on relevant data protection regulations.
- Compliance Checks: Regularly review backup processes for compliance.
Disaster Recovery Preparedness
Backups are part of a broader disaster recovery plan.
Solutions:
- Comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan: Include backups as a key component of a wider disaster recovery strategy.
- Regular Drills: Conduct disaster recovery drills to ensure readiness.
Keeping Backups Current
Ensuring backups remain current and relevant is crucial.
Solutions:
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review and update backup schedules and policies.
- Automated Scheduling: Use automated tools to ensure backups are performed regularly.
By addressing these challenges proactively, scheduled backups can be a reliable component of your overall data protection strategy. Regular reviews, updates, training, and adherence to best practices are key to overcoming these common issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of scheduled backups in safeguarding your data is indispensable. Whether managing personal data or overseeing a business’s digital assets. Implementing a robust backup strategy is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity. With the evolving challenges in data management and the risks associated with data loss. Regular, automated backups are vital to a comprehensive data protection plan.
Now, if you’re seeking a reliable and efficient solution for your backup needs. Consider exploring what RedSwitches has to offer. They provide a range of services catering to your specific backup requirements. Ensuring that your data is secure, accessible, and protected against any unforeseen circumstances. Don’t wait for a data disaster to strike. Visit RedSwitches to see how their services can fortify your data protection strategy. Your peace of mind is worth that proactive step.
FAQs
Q. What is a backing schedule?
A backup schedule is a plan that tells you when and how often to back up your data. It’s really important to have this schedule to make sure your data is backed up regularly. This way, you won’t lose data if there are computer problems, data errors, or unexpected events.
Q. What is the best backup schedule?
The proper backup schedule depends on your or your organization’s needs and how you use your data. Common plans include
- Daily backups for very important data.
- Weekly full backups, plus daily smaller updates or changes.
- Monthly backups for data that are not as critical.
The main goal is to find a balance between having recent backups and the effort and resources needed to make them.
Q. How do I create a backup schedule?
To set up a backup schedule, here’s what to do:
- Look at how important your data is and how often it changes.
- Decide on the backups you need: full, incremental, or differential.
- Choose how often to back up: daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Pick a trustworthy backup software or system.
- Ensure you have enough storage space.
- Set it up to run automatically at the times you decide.
Q. What are two ways to include files for scheduled backups?
Two ways to include files for scheduled backups are:
- Selective File Backup: Manually selecting specific files and folders to be included in the backup process.
- Automated Criteria-Based Inclusion: Setting criteria or filters in the backup software to automatically include files based on parameters like file type, size, or modification date.
Q. What is the importance of automating scheduled backups for data protection?
Automating scheduled backups ensures that your critical data is consistently and reliably backed up, providing a safety net in case of data loss or system failure.
Q. How can I configure automated scheduled backups?
You can configure automated scheduled backups by accessing the backup settings in your chosen backup software or system and specifying the frequency, time, and specific data or files to be included in the backup.
Q. What types of backups can be automated?
Automated backups can include full, differential, or incremental backups, each serving different purposes regarding data restoration and storage efficiency.
Q. Can I schedule automated backups to be stored on OneDrive?
Yes, you can create a new backup configuration that specifies OneDrive as the destination for automated scheduled backups.
Q. How do I set up notifications for automated scheduled backups?
You can specify notification settings within your backup configuration, enabling email or system notifications to alert you of successful or failed backup executions.
Q. What is the step-by-step process for scheduling automated backups?
The process typically involves configuring the backup settings, specifying the backup content, selecting the destination, setting the schedule, and enabling any desired notification options.
Q. How can I automate the restoration of backed-up data?
You can schedule automated restoration tasks by configuring the backup software to restore specific data periodically or by utilizing backup job scheduling features.
Q. Does the backup and restore feature support the deletion of old backups?
Yes, you can configure retention policies to automatically delete or archive previous backups as part of the automated backup and restore process.
Q. Can I automate backups for specific system configurations or user files?
To ensure comprehensive data protection, you can specify and automate backups for specific system configurations, user files, databases, and other designated data.
Q. Are there any default automated backup configurations available for quick setup?
Some backup software provides default automated backup configurations tailored for common use cases, allowing users to initiate automated scheduled backups without extensive configuration quickly.