Key Takeaways
- A well-structured backup strategy is critical for safeguarding data against unforeseen events. This also ensures operational resilience.
- Identifying and prioritizing critical data is a foundational step in creating an effective backup plan.
- The choice of backup method should align with the organization’s data requirements and recovery goals.
- Scheduling backups according to the importance and frequency of data changes minimizes potential data loss.
- Incorporating both onsite and offsite (including cloud) storage solutions enhances data protection and recovery capabilities.
- Disaster recovery plans are essential to a backup strategy. This enables swift response to data loss incidents.
- Testing and validating backup processes ensures reliability and effectiveness in real-world recovery scenarios.
- Security measures, such as encryption, protect backup data from unauthorized access.
- Continuous management and proactive monitoring of backup systems are necessary for their maintenance.
- Protecting endpoints and SaaS applications is increasingly important in comprehensive backup strategies.
Data is the backbone of every organization in today’s digital landscape. The importance of an effective backup strategy must be considered. Statistics reveal a startling reality: 93% of unexpected data loss causes business failure and closure. These figures underscore the critical need for robust backup solutions.
Understanding server backup strategies is crucial whether you are an IT professional or a business owner. A solid backup plan protects against system failures, cyberattacks, and natural disasters. This blog will cover key steps and considerations for effective backup planning. This ensures not only data protection but also business continuity during unexpected events.
We will explore server backups in depth. This includes identifying critical data. We’ll also discuss selecting appropriate backup methods. Testing recovery procedures is another important aspect. Join us to learn about these facets of dedicated server backups.
All are tailored to fortify your organization’s data resilience.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Backup Strategy?
- Components of a Comprehensive Backup Strategy
- Why Is It Important to Have a Backup Strategy?
- Backup Strategy: The Essentials
- How to Create a Backup Strategy
- Who Needs a Backup Strategy?
- Why You Should Back Up Your Data
- Protection from Data Loss
- Defense Against Malware and Ransomware
- Swift Recovery from Data Loss
- Peace of Mind
- Remote Access
- Backup Strategy: Understanding the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
- Considering Storage Options for Full Backups
- External Hard Drives: Convenient and Portable
- Cloud Storage: Accessible and Scalable
- Hybrid Approaches for Businesses
- Individual Considerations
- Understanding The Challenges in Data Backup
- Navigating Business Data Backup Solutions
- Data Backup Best Practices: Ensuring Data Safety and Compliance
- Conclusion: Securing Your Digital Assets with a Robust Backup Strategy
- FAQs
What is a Backup Strategy?
Credit: Shutterstock
A backup strategy is a comprehensive plan. It safeguards essential business data. Regular backups are ensured and can be restored if data loss occurs. This approach minimizes downtime, a typical result of data loss. Downtime can impact business operations. The strategy covers backup disaster recovery processes. These are pivotal for continuous business operations.
The strategy involves identifying crucial business data. Appropriate backup methods, like full, incremental, or differential backups, are selected. Storage mediums are chosen, including external drives, network storage, and cloud solutions. Regular backup schedules are established to keep data updated. Backups are stored in many locations, both onsite and offsite.
You can also check: Backup Disaster Recovery Solutions
Backup processes are automated for consistency and to reduce human error. Security measures, like encryption, protect backup data from unauthorized access. Regular testing ensures backups can be restored. The entire process complies with data protection regulations. Proper documentation and training in backup and recovery procedures are crucial.
By prioritizing these elements, a backup strategy is crucial. It ensures quick recovery from data loss incidents. This reduces downtime and safeguards ongoing business operations.
Components of a Comprehensive Backup Strategy
Credit: Freepik
A comprehensive backup scheme is essential for safeguarding critical information, applications, and systems.
Ensuring the ability to restore data in the event of loss or damage is of paramount importance. Such incidents can arise from various sources. This includes hardware failures and cyberattacks. Both of which can have detrimental effects on an organization’s operations. Business continuity hinges, thus minimizing downtime and preventing potential financial and reputational losses.
To develop an effective backup solution, one must carefully consider several key components:
Backup Frequency and Retention: Adjust the frequency of backups to meet the client’s specific needs, taking into consideration any compliance requirements.
The backup frequency can vary based on the nature of the data. Critical data may necessitate real-time backups, while archived or static information may only require periodic backups. Common backup intervals typically include daily and weekly backups.
Additionally, the retention period for these backups must be determined, ensuring data is kept appropriately.
Backup Types: There are various backup types, including full, incremental, or differential backups. The choice depends on factors like the volume of the client’s data, how it changes, and their recovery time objectives.
Backup Locations: Deciding where to store backup data is crucial. Options include onsite, offsite, cloud-based, or a hybrid cloud security strategy. This decision should factor in security and accessibility considerations.
Read more about Hybrid Cloud Security Strategy
Disaster Recovery: A disaster recovery plan is essential. It allows for a rapid response to incidents. This helps to reduce further damage. The plan should include data restoration procedures. It must also cover communication protocols. Other contingencies are essential, too. They ensure a quick recovery.
Regular Testing and Validation: It’s essential to test and confirm backups. This guarantees the integrity of the backup data. It also ensures the data is usable when needed. This process confirms that data is recoverable and accessible during a disaster.
Security Measures: Encryption is vital to safeguarding data. Access controls are crucial in ensuring that only authorized individuals can access it.
Additionally, monitoring is essential for proactive security measures. Together, these elements work seamlessly to protect backup data from unauthorized access or theft.
Ongoing Management and Monitoring: Continuous management is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of a backup solution. Regular monitoring is also vital. It helps keep the solution up-to-date with the latest requirements and threats. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) focus on these aspects. They provide robust backup solutions that align with their clients’ needs. This commitment to continuous management ensures data protection and bolsters business resilience.
Why Is It Important to Have a Backup Strategy?
Credit: Freepik
A backup strategy is crucial for several reasons, including ensuring the safety of sensitive data. Most companies, at some point, need to recover data. Acronis reports that 33% of users had to do data backup recovery more than once in the previous year, accounting for 72% of all users. If a business’s data is hacked, it could have severe implications. This is something that businesses should have anticipated.
However, it’s about more than just backing up data. What happens if dedicated servers fail or there are issues with your backup cloud storage? This is where integrating a disaster recovery plan with your backup strategy comes into play. It guarantees a system for accessing data when things go awry.
Downtime periods can lead to substantial financial losses. A well-structured backup plan can neutralize downtime caused by various factors. These include system errors, cyber-attacks, or natural disasters. By having such a strategy, you can maintain business continuity and protect your organization’s bottom line. A backup strategy isn’t just a data protection measure; it’s a critical component of your overall business resilience.
Check out how CommonSpirit Cyber Attack affected the Healthcare Providers.
Backup Strategy: The Essentials
Credit: Freepik
Implementing a robust backup strategy is vital. It protects data against loss due to system failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Understanding backup strategy ensures the safety and availability of critical business data.
We’ll explore fundamental components. These include the backup method, schedule, recovery objectives, and location.
Backup Method
Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
Full Backups: This method involves creating a complete copy of all data. While it requires more storage space and time, it simplifies recovery.
Incremental Backups: Incremental backups preserve modified data since the previous backup. This leads to faster operations and reduced storage consumption. However, recovery can become intricate, requiring access to the most recent full backup and all subsequent incremental backups.
Differential Backups: Differential Backups, on the other hand, are also incremental. They store data changed since the last full backup and strike a balance between efficiency and simplicity. They excel in both storage space and time savings. Furthermore, they offer a straightforward and streamlined recovery process compared to incremental backups.
Also read Incremental vs Differential Backup: Which Is The Best Backup Strategy For You?
Backup Schedule and Recovery Objectives
Establishing a Regular Backup Schedule: Establishing a regular backup schedule is crucial to ensure your data is consistently updated. The frequency should align with the importance of the data and how often it changes. Typical schedules include daily, weekly, or monthly backups.
Setting Recovery Objectives
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This is the maximum acceptable time to restore operations after data loss.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This indicates the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time.
For example, an RPO of six hours means you can tolerate losing six hours’ worth of data.
Backup Location
Onsite Storage: Onsite backups provide quick access to data and are helpful for rapid recovery from data loss. This method typically involves external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), or servers.
Offsite Storage: Offsite backups protect data against local disasters like fires or floods. This can include cloud solutions or physically storing backup media in a different location.
Cloud Storage: Cloud storage has become increasingly popular due to its scalability, flexibility, and ease of access. It allows for offsite storage without the need to transport backup media. Cloud solutions often offer enhanced security measures and redundancy.
A comprehensive backup strategy is essential and must include a well-thought-out backup method. A regular schedule must align with clear recovery objectives. The strategy should balance onsite and offsite backup locations to ensure comprehensive data protection and expedite recovery in case of data loss incidents.
How to Create a Backup Strategy
Creating a backup strategy can seem daunting initially, but it becomes manageable when broken down. A good start is to use designated backup software tools, which make backups easier. With the right tools, creating a backup strategy is easy.
One joint plan is the 3-2-1 strategy. This involves having three copies of your data. Two copies are on different mediums, while one copy is offsite. This strategy diversifies backup storage. It protects data against various loss situations.
This is a standard strategy, but it only covers where backups are stored. Other elements also impact your strategy’s success.
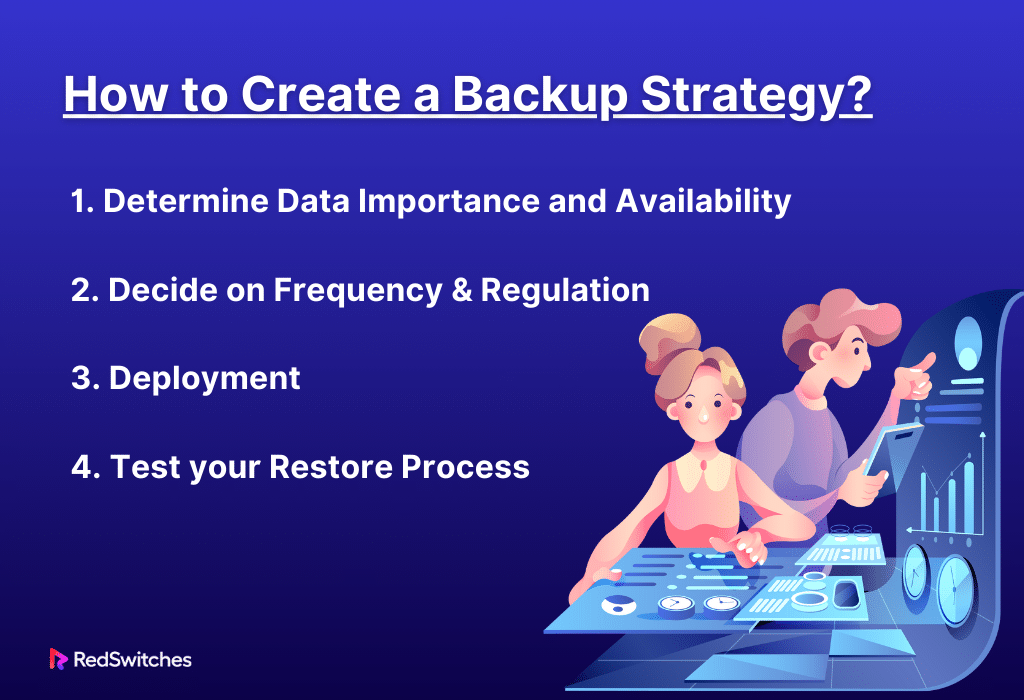
Here are four steps to build an effective backup strategy:
1) Determine Data Importance and Availability
Various industries gather diverse data types. It’s essential to pinpoint the data that plays a pivotal role in business operations. Once identified, prioritize the backing up of this critical data. Speedy accessibility of this vital information is crucial following any data loss. Therefore, determine the timeframe within which you require the lost data to be restored. Weigh this against the associated costs and resource allocations for various backup sizes. This decision often involves choosing between onsite, offsite, or cloud-based backup solutions.
2) Decide on Frequency and Regulation
The frequency of backups plays a crucial role as backup types have varying schedules. This impacts the data you can recover out of data loss. Most recent backups provide the latest information. To ensure proper data protection, regulations come into play. Assessing the volume of data your business generates and your production rate is essential. Based on this evaluation, determine the optimal backup frequency. Implementing backup regulations allows you to maintain the frequency and quality of your backups.
3) Deployment
Once you’ve carefully planned your backup strategy, it’s time to implement it. Decide whether you’ll opt for manual or automated backups. Then, establish a schedule that aligns with your chosen backup frequency and the availability of your data. Ensuring that your deployment frequency aligns with your backup strategy goals is essential. In doing so, ensure that your backup frequency syncs with your objectives. Also, your backup distribution strategy aligns with your goals.
4) Test your Restore Process
The last crucial step in the backup process is testing your procedure. Never assume your strategy is effective until it has been thoroughly tested. A failed backup strategy should still be able to restore data successfully. To do this, conduct simulations that mimic real data loss scenarios. Testing offers valuable insights and assesses how quickly your company can recover. Additionally, it helps uncover any overlooked issues in your backup and restoration process.
Who Needs a Backup Strategy?
Credit: Freepik
Any organization with data on a device needs a backup strategy. This includes businesses of all sizes and types, from small startups to large corporations. Even non-profit organizations and educational institutions.
Implementing a strategy significantly decreases downtime, thus supporting ongoing business operations. Downtime can prove costly and disruptive, but a backup strategy can effectively mitigate these challenges.
Every type of organization, regardless of size, requires a backup plan. Some may need less planning and detail, while others require more complex strategies. But every backup plan is crucial for business success.
Having a well-defined strategy in place is crucial. It significantly reduces stress when dealing with unexpected data loss. Data loss can occur suddenly, but being prepared mitigates its consequences.
A backup plan isn’t merely a choice; it’s an essential requirement for any organization. It safeguards data, enables business continuity, and offers peace of mind. Every organization should prioritize the development and maintenance of a robust backup strategy.
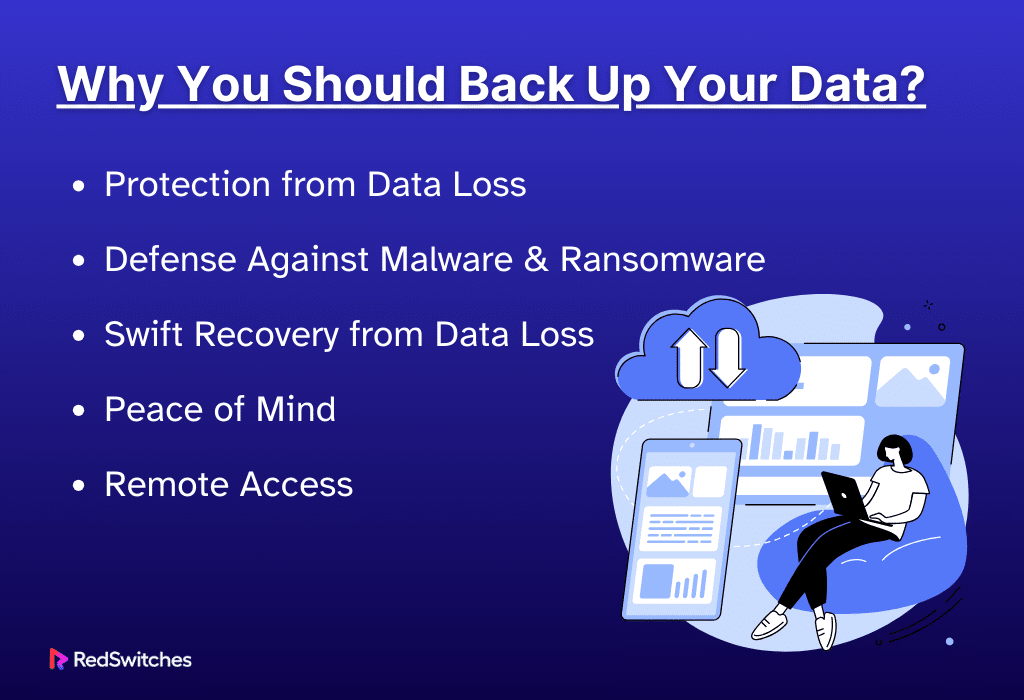
Why You Should Back Up Your Data
Backing up your data is an essential practice. It provides security and peace of mind. By understanding these points, you will see why backing up data is not just a recommendation but a necessity. It protects against data loss, combats malware threats, and ensures quick data recovery.
Most importantly, it provides peace of mind and flexibility in accessing your data from anywhere. Regular backups should be a part of everyone’s data management strategy.
Here’s why regular backups are crucial for every computer user and organization.
Protection from Data Loss
Data loss poses a genuine threat; your computer could unexpectedly crash, or your hard drive might fail. Thus, resulting in the potential loss of all your valuable data. The key to safeguard against this peril is data backup. This serves as a safety net that shields you from the devastating total data loss.
Furthermore, it enables you to recover previous versions of your files. In today’s digital landscape, this safety net is indispensable.
Defense Against Malware and Ransomware
Cyber threats lurk around every corner, with malware and ransomware capable of striking when you least expect it. These malicious programs have the power to encrypt and lock away your valuable data. You create a protective shield for yourself by diligently backing up your data. This way, you guarantee that your data stays accessible, even in the unfortunate event of your primary system being compromised.
Swift Recovery from Data Loss
Storing data is essential to avoid disruptions in your operations. The recovery process can be time-consuming and tiresome. However, having a backup in place ensures a swift recovery. You can quickly restore your data and return to work, easily maintaining productivity and business continuity.
Peace of Mind
Having the assurance that your data is backed up brings a sense of tranquility. If something goes awry, there’s no need to panic; you have a reliable backup. This knowledge provides a comforting reassurance that you can always recover your data, a priceless peace of mind.
Remote Access
Backups provide not only safety but also convenience. Picture yourself working remotely or while traveling. Having a data backup allows you to access your files from anywhere, as long as you have an internet connection. This level of accessibility is incredibly valuable in our modern, mobile, and interconnected world.
Backup Strategy: Understanding the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is critical in data backup. It has been vital in data protection for nearly two decades. Initially, the 3-2-1 rule was created for smaller storage devices, where users relied on 30 GB hard drives and CDs. Today, we have access to hard drives with capacities as large as 22 TB and many cloud storage options. Modern storage concerns extend beyond just capacity.
Security, data integrity, and handling of failover situations are essential. Each issue needs careful attention. The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a solid base. Understanding the evolving landscape of data storage and security threats is crucial. In today’s world, cyberattacks have become increasingly prevalent. While the 3-2-1 rule provides a solid foundation, we must adapt and enhance our approach to address new challenges and leverage emerging technologies. We’ll delve into more advanced data protection methods in the subsequent discussion.
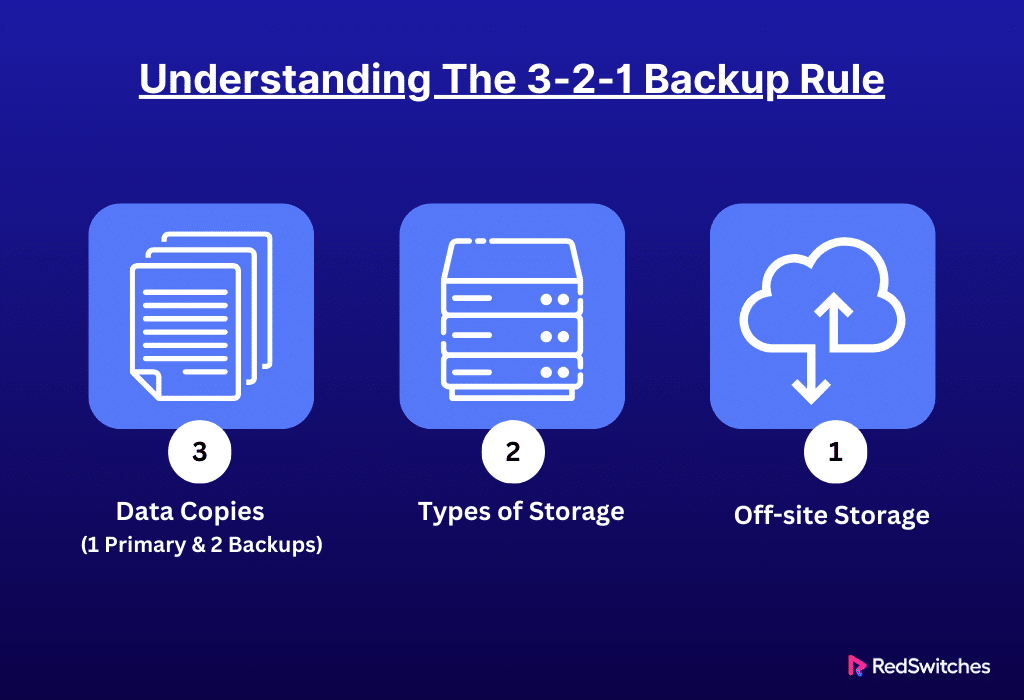
The 3-2-1 rule, in essence, offers a simple yet robust strategy for safeguarding data against loss, built upon three fundamental principles.
Three Copies of Your Data
Begin by making three copies of your data. Your original data resides on your primary device, while you should have at least two additional backup copies. This redundancy ensures that if one backup fails, you still have another one to rely on.
Two Different Storage Devices
This principle is crucial. It involves storing your backups on diverse storage media to mitigate risks. You have several options, including PCs, external hard drives, USB flash drives, Network Attached Storage (NAS), and cloud storage services. The variety in storage mediums helps safeguard your data against device-specific failures.
One Offsite Backup Copy
The final rule emphasizes the importance of storing one backup copy offsite. This step is essential for protecting your data against local disasters like fires, floods, or thefts. An offsite backup ensures that your data remains accessible even if a disaster were to destroy your primary storage.
Backup Strategy: Identifying the Best Storage Location for a Full Backup
It’s essential to grasp the 3-2-1 rule of backups and determine where to store them. The choice of storage media relies on various factors. This includes your data’s characteristics and your business’s scale. Your selected backup service also factors into the decision. For individuals, backup software can be a helpful tool for finding storage destinations. Or, you can select a suitable media based on your personal preferences.
Considering Storage Options for Full Backups
Full backups are generally much larger than incremental or differential backups. They have a noticeable difference in size. This renders smaller storage alternatives like optical disks and USB drives. Those are impractical for most full backup requirements.
As a result, two prominent alternatives emerge: external hard drives and cloud storage. Both of which align with the 3-2-1 backup strategy.
External Hard Drives: Convenient and Portable
Ease of Use: External hard drives are user-friendly, offering high portability. This makes them a practical choice for storing significant amounts of data.
Quick Data Recovery: They facilitate rapid data access and quick data recovery. This is essential for urgent restoration needs.
Suitability for PC Restoration: External hard drives are convenient for transferring data. Especially when migrating data from a PC’s hard drive to a new machine. They are a popular and reliable option for personal backup solutions.
Cloud Storage: Accessible and Scalable
Remote Access: Cloud storage requires an internet connection for seamless access to your backup data from any device at any time. By offering unparalleled flexibility and convenience.
Options for Individual Users: Some users have more minor backup needs. Free cloud services can be sufficient for them. Services like Google Drive, iCloud, or Dropbox are options.
Business and Sensitive Data: Many entities regularly deal with critical or sensitive data. Contemplating the adoption of dedicated cloud storage solutions is imperative in such cases. Paid cloud services offer enhanced security features, with encryption a notable example. These services are advantageous when handling larger volumes of data.
Hybrid Approaches for Businesses
Combining Strengths: Many businesses opt for a hybrid approach. They use external hard drives and cloud storage to provide a more comprehensive and secure backup solution.
Balancing Needs and Resources: This method offers a balance that provides immediate accessibility via external drives. It also offers remote, scalable backup through cloud storage.
Individual Considerations
Data Sensitivity and Volume: The choice depends on the data type and size, and your budget.
Security vs. Accessibility: External hard drives give you control. Cloud storage offers access and better security.
Selecting the right storage solution is paramount, whether you’re using it for personal or business purposes. This decision significantly influences your overall backup strategy. It’s essential to strike the perfect balance between security, accessibility, and storage capacity. This ensures not only the safety of your data but also smooth and effective data recovery processes.
Understanding The Challenges in Data Backup
Credit: Shutterstock
The demand for backup capabilities is rising. It’s driven by factors reshaping the need for organizational backup. Let’s delve into some challenges faced when backing up your data:
Exponential Growth of Data
One primary challenge is the exponential growth of data. Organizations generate and retain more data than ever, recognizing its potential value. This results in vast data stores and an increasing demand for secure storage solutions. Backup applications must evolve to provide insights into the data they safeguard.
Surge in Unstructured Data
Another significant challenge is the surge in unstructured data. This type of data strains image-based and file-by-file backup methods. This leaves organizations struggling as servers become overwhelmed with millions of files.
Increasing Technological Complexity
Technology environments within organizations are increasingly complex. Data growth is one aspect, but the evolving technological landscape adds another layer of intricacy. Organizations use multiple storage systems, each requiring a unique approach to protection. The mix of bare metal and various hypervisor systems compounds this complexity. Hence, increasing the risk of errors and jeopardizing backup quality.
Regulatory Compliance
Data’s value is clear to governments and regulatory bodies. There is an increasing array of regulations demanding data protection and retention. For instance, the GDPR mandates data deletion upon customer request.
Ransomware Threats
Ransomware threats are on the rise. The role of backups in incident response is important in the face of cybercrime. Ransomware poses a significant threat. It often gains access through user endpoints and quickly spreads across all accessible servers. Malware creators have become more sophisticated. They strategically delay attacks to ensure that the malware embeds itself within the backup dataset. Consequently, when these attacks are triggered, they frequently target backup applications as their primary victims.
Navigating Business Data Backup Solutions
The evolution of data backup tools has provided many options for safeguarding organizational data. Selecting an appropriate solution is crucial for maximizing data protection efficacy.
Here’s an overview of the most prevalent data backup solutions.
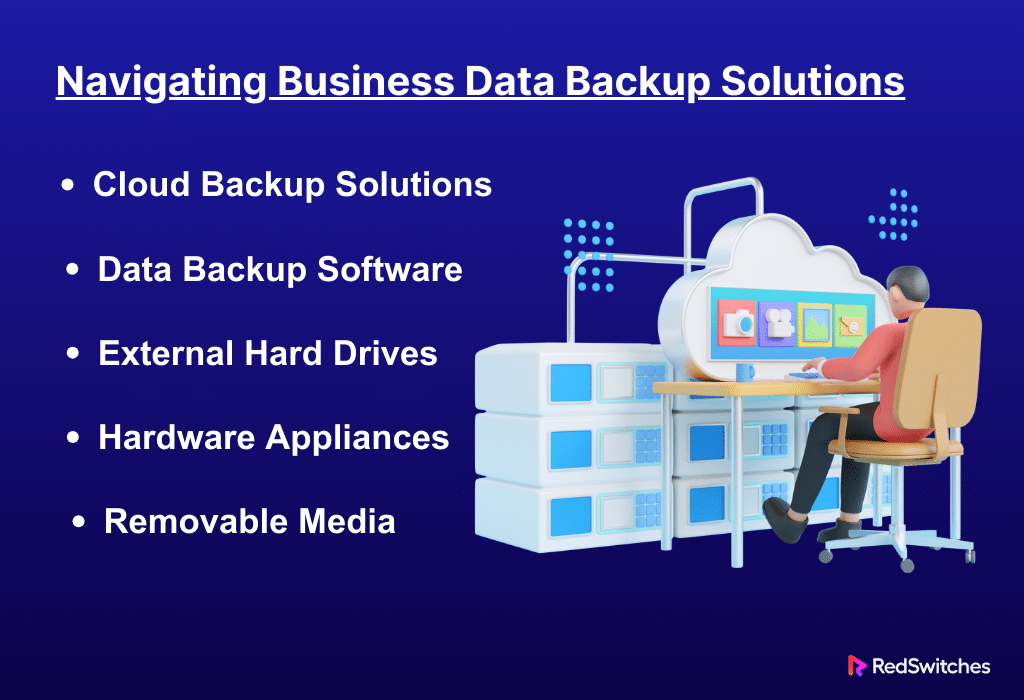
Cloud Backup Solutions
The shift to cloud-based services has gained momentum in recent years. Companies of all sizes are adopting cloud backup for its convenience and reliability. Cloud backups ensure offsite critical data storage. They offer enhanced security and easy accessibility in disaster scenarios. However, cloud backup services may incur significant costs, especially for plans with unlimited storage options.
Data Backup Software
Data Backup Software provides unmatched flexibility. It allows for precise backup configurations, automation, and targeted device allocation. It’s a vital component of comprehensive data backup strategies for tailored data protection.
External Hard Drives
External Hard Drives are indispensable for data backup for many organizations. Especially when paired with archival software, they facilitate rapid file restoration, minimizing RPOs. However, as data demands grow, reliance on a single drive becomes impractical. Thus, necessitating a more sophisticated approach to data redundancy.
Hardware Appliances
Backup appliances provide substantial storage capacity and integrated backup software. Installation involves connecting these devices to the network and configuring backup protocols. Positioning these appliances offsite or outside the leading network is advisable for enhanced security.
Removable Media
Traditional backup methods, such as USB drives and optical discs, offer straightforward manual backup solutions. These are more suited to smaller operations with limited data. For larger data sets, the practicality of this method diminishes. However, the importance of secondary, offsite storage becomes paramount to mitigate risks of data loss.
One of the most effective methods is utilizing a dedicated server for backups.
Dedicated servers provide the highest level of security for data backup. These dedicated servers offer additional storage for redundancy, making them an ideal choice for ensuring the safety of your data.
Choosing the Right Backup Solution is essential for Effective Data Protection. Organizations must weigh their specific needs against the features and limitations of each backup option to find the most suitable solution.
Data Backup Best Practices: Ensuring Data Safety and Compliance
A robust backup strategy is crucial in the realm of MSPs. It guarantees the security, availability, and integrity of client data. This blog section explores essential practices. MSPs should adopt these to create a resilient and efficient backup environment. These practices serve their clientele effectively.
Engaging Clients and Prioritizing Data
The initial step is crucial. It involves engaging with clients and understanding their data priorities. This is critical for identifying data segments necessary for daily operations and revenue generation. The next step involves implementing a data classification framework. This framework enables MSPs to categorize data based on sensitivity, value, and criticality. This categorization process determines the required level of protection and sets the backup frequency.
Tailoring Backup Frequency to Client Needs
The frequency of backups plays a crucial role in any data backup strategy. MSPs must assess their clients’ Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for data loss in incidents. This analysis helps establish a backup schedule that aligns with business requirements. It considers data change rates, ensuring minimal loss for critical systems.
Also Read: Backing Up Your data on a Dedicated Server: How & Why
Regular Testing and Monitoring
A strategy’s efficacy is contingent upon regular testing and monitoring. This involves simulating data restoration scenarios to validate the integrity and usability of the backed-up data. Employing automated monitoring tools can significantly enhance the oversight of backup systems. This enables MSPs to identify and rectify potential issues preemptively, ensuring the continuous availability of critical data.
Maintaining Physical and Cloud Backups
Cloud backups offer scalability and flexibility. However, it’s imperative to maintain physical backups as an added layer of protection. These should be securely stored offsite to safeguard against large-scale data breaches or catastrophic events. This dual approach enhances data resilience and ensures compliance with industry-specific regulations. This may mandate physical backups.
Diversification and the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
Adhering to the 3-2-1 backup rule is essential. This means maintaining three copies of data on two different media. With one stored offsite. This approach mitigates the risk of complete data loss and ensures business continuity.
Leveraging Automation and Education
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining backup processes. It reduces manual intervention and minimizes the risk of human error. Scheduled backups and automated detection are essential facets of a modern backup strategy.
Furthermore, data handling, incident response, and security data backup best practices empower teams. This enhances their active contribution to the backup process. Thus, improving the overall data protection posture.
Endpoint and SaaS Application Protection
Protecting endpoints and SaaS applications are paramount in today’s distributed work environments. Endpoint protection should include comprehensive security measures to safeguard devices against cyber threats. While backup solutions for SaaS applications ensure the recoverability of critical data stored.
Conclusion: Securing Your Digital Assets with a Robust Backup Strategy
Crafting a backup strategy for servers is not just a best practice but a necessity today. A well-thought-out backup strategy is integral to the safety of any business. Implement critical components of a plan for backup strategy: regular updates and testing. Diversify storage media and locations. Use automation. Enforce stringent security measures. Businesses can ensure their critical data is protected against loss or damage.
The most effective backup strategy is tailored to your specific needs. That reflects the unique aspects of your business and the data you handle. Consider employing incremental backups for efficiency.
Leverage cloud solutions for flexibility. Adhere to the tried-and-true 3-2-1 backup rule. The goal is to safeguard your digital assets against all forms of disruption. This includes hardware failures to cyber threats.
Concerned about protecting your data from cyber threats or unforeseen calamities? Opt for a RedSwitches managed dedicated server equipped with backup services now!
Rest assured, we’ll back up your data, eliminating the stress of potential data loss.
Our dedicated servers are equipped with premium storage solutions.
FAQs
Q. What are backup questions?
Question 1: “Is the selected small business backup solution designed for business continuity?”
Question 2: “Which data types are included in the backup?”
Question 3: “Which operating systems or environments are supported for backup?”
Question 4: “How frequently can backups be scheduled?”
Question 5: “What is the estimated data recovery time?”
Question 6: “What are your RTO and recovery point objectives (RPO)? These metrics define how quickly and how much data you need to recover?”
Q. What are some important things to consider when developing your backup strategy?
- Increase backup frequency for enhanced data protection.
- Align your backup strategy with specific service-level demands.
- Adhere to the 3-2-1 backup rule for redundancy.
- Leverage cloud backup solutions with intelligent features.
- Automate disaster recovery runbooks for efficient response.
- Avoid using backup as a means for long-term data retention.
Q. Which backup strategy required least backup time?
That typically requires the least amount of time is Incremental Backup. This approach only backs up data that has changed or been updated since the last backup, whether a full or another incremental backup. As a result, it often consumes significantly less time and resources than a full backup. However, while incremental backups are faster, they may lead to more complex restoration processes, requiring the last full backup and all subsequent incremental backups to restore the system.
Q. What are some of the requirements for a safe backup strategy?
- Step 1: “Identify which data needs to be included in the backup.”
- Step 2: “Determine the frequency at which data should be backed up.”
- Step 3: “Select and implement a suitable backup and recovery solution.”
- Step 4: “Regularly test and monitor the effectiveness of your backup system.”
Q. Where should backups be stored?
For home users with a modest amount of personal data, it’s advisable to store primary files on the computer’s hard drive, while maintaining at least two backup copies on solid-state storage, optical storage (stored in protective cases), or remote storage for added redundancy.
Q. How can a backup strategy be made most effective?
To make a backup scheme most effective, consider the following key elements:
- Regularly Update and Test
- Automate Backup Processes
- Diversify Storage Media and Locations
- Implement Security Measures
- Monitor and Review
Q. What is the best way to backup a dedicated server?
- Combine Full and Incremental Backups.
- Balance Offsite and Onsite Backups.
- Use Cloud Backup.
- Test Regularly.
- Automate Schedules.
Q. What is a 3-2-1 backup strategy?
A 3-2-1 backup strategy involves creating three copies of your data. You store these copies on two different types of media. One copy remains offsite for disaster recovery purposes.
Q. Why is data protection important?
It safeguards against data loss, corruption, or unauthorized access. This ensures the integrity and availability of critical information.
Q. What are the best backup strategies to follow?
Implement the 3-2-1 backup rule. Regularly back up data. Conduct risk assessments. Ensure offsite storage of backup copies.
Q. How does a 3-2-1 backup method enhance data security?
It enhances security by creating redundancy. It provides protection against hardware failures, human error, and cyber threats. It enables effective disaster recovery.
Q. Why is having on-site backup essential?
On-site backup is essential for quick data recovery. It minimizes downtime in case of system failures. It ensures data accessibility without relying solely on offsite backup solutions.
Q. What are the basic principles of the 3-2-1 backup strategy?
The principles include creating multiple copies of data, using diverse storage media, and maintaining at least one offsite backup copy to mitigate risks and ensure data continuity.
Q. How can a backup strategy best practices guide help in implementing effective data backup?
It assists in identifying critical data, defining backup schedules, selecting appropriate storage solutions, and establishing protocols for regular testing and maintenance of backups.
Q. What is the significance of business impact analysis in backup and disaster recovery planning?
Business impact analysis evaluates potential risks. It determines the impact of data loss on business operations. It designs comprehensive backup and disaster recovery plans to mitigate adverse impacts.
Q. Why is online backup becoming increasingly popular for data protection?
Online backup offers scalability, automatic backups, remote data access, and cost-effectiveness. This makes it a popular choice for businesses seeking secure and convenient data backup solutions.
Q. How does the 3-2-1 backup approach ensure resilience against data loss due to various incidents?
It ensures resilience by creating redundant copies. It protects against localized incidents like hardware malfunctions or data corruption. It enables recovery from broader disasters like system failures or natural calamities.