Key Takeaways
- Firewalls serve as vigilant sentinels, scrutinizing both inbound and outbound traffic for safe passage.
- Effective firewall configuration hinges on tailored configurations that match your network’s unique needs and architecture.
- Implementing best practices like default traffic blocking and least privilege principles strengthens network defense.
- Continuous firewall configuration and maintenance, including updates and adjustments, is crucial for optimal security.
- Balancing security and accessibility is key; overly strict policies hinder legitimate use, while lax settings invite risks.
- A multi-layered security approach, beyond firewalls, enhances overall protection.
- Recognizing and rectifying common firewall setup errors prevents vulnerabilities and strengthens security.
Setting up a wireless router used to be a big deal. Now, it is all about configuring a firewall. A good firewall is critical to keeping your data and apps safe. It protects against cyber threats. However, setting it up right can be tricky.
This guide is for beginners and pros alike. We’ll go through the basics and the advanced stuff. You’ll learn how to set up your firewall just right. It gets good traffic in and keeps lousy traffic out.
We’ll show you the best practices. You’ll gain an understanding on how to make a security plan that fits your company’s needs. This will help you stay safe and follow the rules. Let’s start this journey to make your network more robust and safer.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Firewall Configuration?
- Importance of Basic Firewall Configuration
- Components Involved in Firewall Configuration
- Exploring Firewall Types
- How to set up your firewall
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Firewall Configuration
- Firewall Configuration Setup: Navigating the Challenges
- Six Best Practices for Secure Network Firewall Configuration
- Mistakes To Avoid When Setting Up a Firewall
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Firewall Configuration?
Credit: Freepik
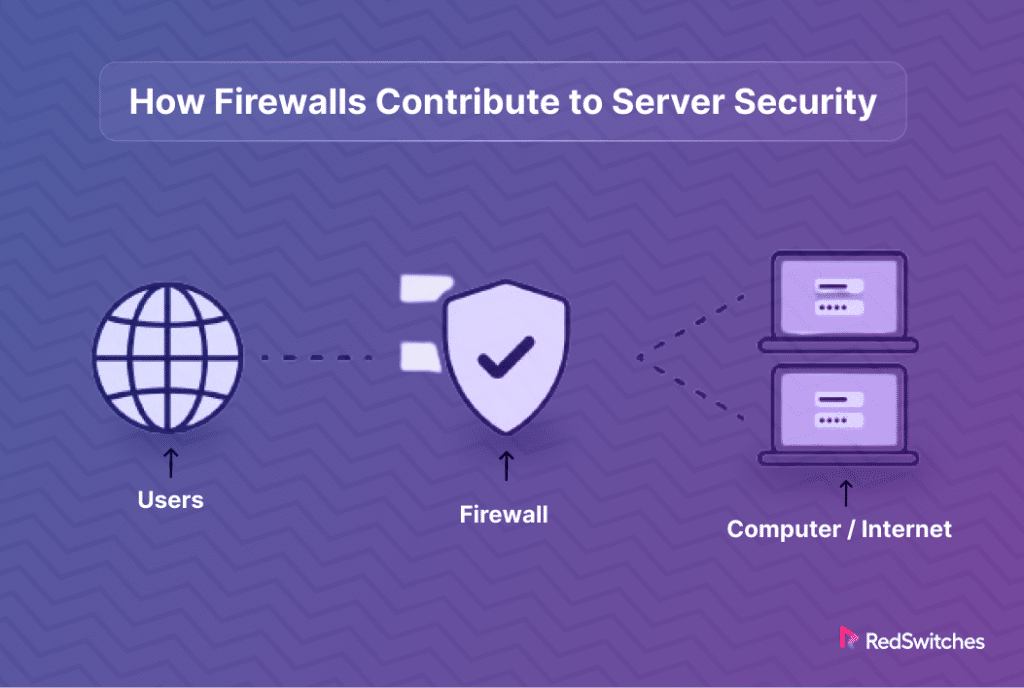
At its core, a firewall serves as the gatekeeper of your network’s security. It blends hardware and software elements to scrutinize incoming and outgoing digital traffic. Think of it as a vigilant sentinel, standing guard at the boundaries of your network. Its mission? To distinguish between safe and hazardous traffic. It achieves this by enforcing predefined security rules, effectively deciding which traffic to allow and which to block.
A firewall acts as a demarcation line. It separates your internal network from the vast, unpredictable expanse of the external internet. This separation protects your network from online threats and unsolicited traffic. The firewall’s capability to log traffic is an added boon. It provides network administrators with valuable insights, aiding them in threat detection and more informed network management.
The essence of firewall configuration lies in its meticulous setup. This involves specifying which domain names and Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are deemed safe. The configuration is tailored to the network’s nature—public or private. Security rules are then crafted. These rules are the foundation upon which access is either granted or denied, forming a robust defense mechanism against potential intrusions by hackers or harmful software.
A firewall’s out-of-the-box settings might not suffice for optimal protection. Custom configuration is vital to fortifying your network’s defenses, ensuring the firewall can effectively fend off cyberattacks. This is a technical necessity and a strategic imperative to safeguard your organization from the dire consequences of data breaches and cyber threats.
You can read about Cybersecurity Frameworks here.
Importance of Basic Firewall Configuration
The bedrock of any robust network security framework begins with the basic configuration of your firewall. It’s a fundamental step that, if overlooked or improperly executed, can open the floodgates for cybercriminals to infiltrate your protected internal networks. These attackers are perpetually scanning the digital horizon for networks crippled by outdated defenses or misconfigured dedicated servers.
According to security specialists Gartner, 99% of firewall breaches stem from misconfigurations rather than inherent flaws in the firewall systems. This statistic is not just a number but a clarion call to underscore the critical nature of precise firewall setup. Default settings often found in firewalls and commonly used protocols like FTP fail to provide the robust shield needed to ward off sophisticated cyber threats.
This inadequacy mandates a tailored approach to firewall configuration that is meticulously aligned with your network’s unique demands and architecture.
Firewalls are the gatekeepers of your network’s security, thoroughly scrutinizing both inbound and outbound traffic. Their role is to permit only legitimate traffic through, based on predefined rules, while denying entry to suspicious or unauthorized connections. However, the efficacy of these digital sentinels is contingent upon the precision of the firewall policies in place.
These policies, essentially a compilation of security rules, delineate the conditions under which network traffic is allowed or blocked. They specify permissible ports, approved IP addresses, or domain names and enforce security zones to segment and safeguard the network. The art and science of firewall configuration lie in striking the perfect balance with these policies. Too lenient, and you risk exposing your network to potential breaches; too stringent, and you might inadvertently hamper the performance and accessibility for legitimate network users.
Navigating the complexities of firewall configuration to enhance your network’s defense mechanism is more than just a technical challenge—it’s a strategic imperative. Let’s delve deeper into how to refine your firewall setup for optimal security and performance.
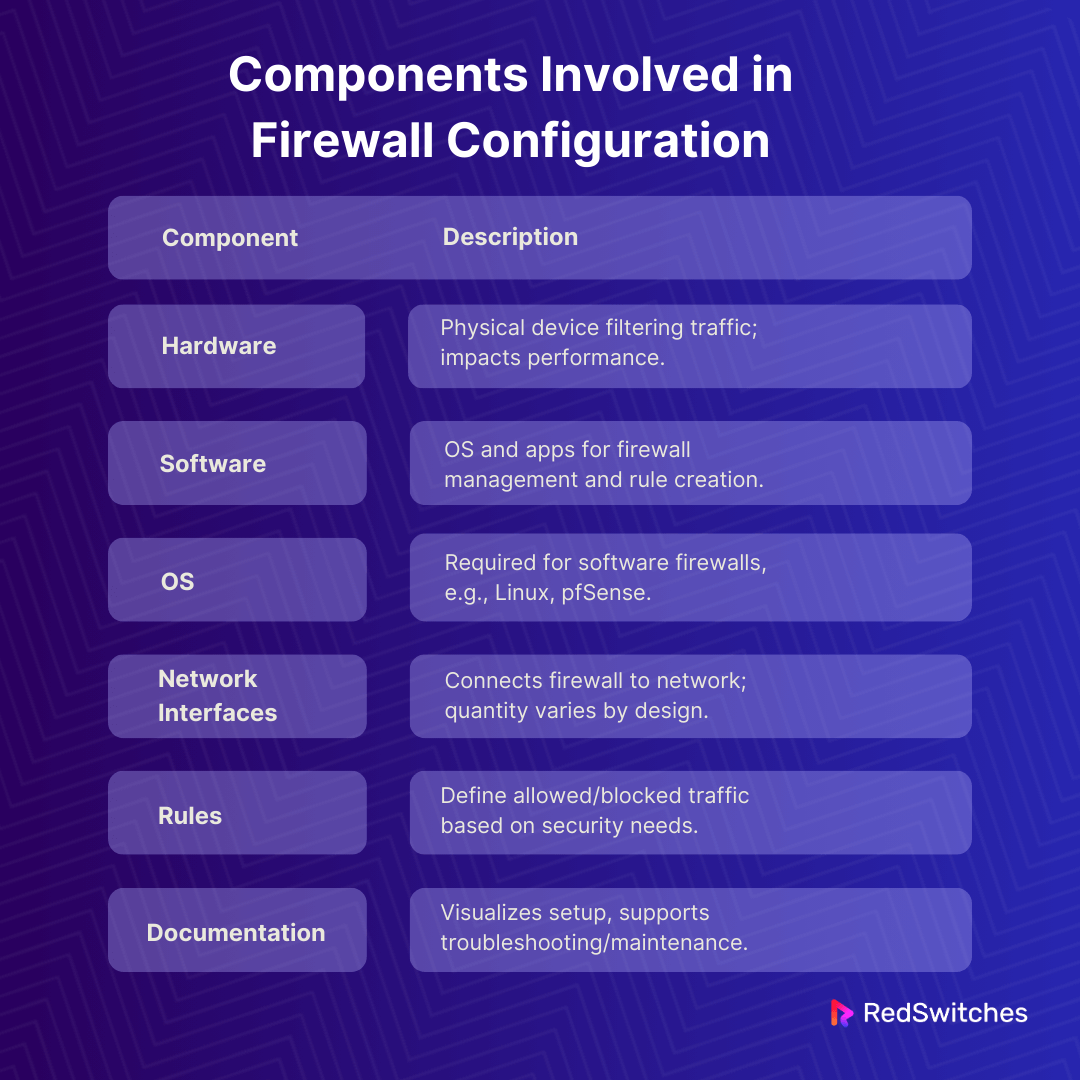
Components Involved in Firewall Configuration
Credit: Freepik
Setting up a firewall involves various elements. In short, setting up a firewall means considering hardware and software. Plus, it would help if you had the proper rules and documentation. Understanding each part makes the process smoother. Let’s look into some:
Firewall Hardware
Credit: Freepik
First, there’s the hardware. This is the actual physical device that filters your network traffic. It’s made up of things like processors, memory, and ports. You might find firewall hardware as a separate appliance. Or, it could be part of something else, like a router. The type of hardware you choose is essential. It affects performance and what extra features you can have. Companies like Cisco and Juniper offer good options.
Firewall Software
Credit: Freepik
Then, there’s the software. This includes types of operating systems (OS) and other applications. They’re installed on the firewall hardware. The software lets you set up and manage your firewall. You can create rules and control access with it.
Also Read What is a Network Firewall? Exploring Server Security and How Firewalls Work in 2024
Operating System (OS)
Credit: Freepik
For software-based firewalls, you need an OS. This could be a common one, like Linux. Or, it could be something made just for firewalls, like pfSense.
Network Interfaces
Source: Freepik
Network interfaces connect the firewall to your network. They also help monitor network traffic. These interfaces can be part of the firewall hardware. Or, they might be on a dedicated server running the firewall software. The number you need depends on your network’s design.
Firewall Rules
Credit: Freepik
You have to make rules for your firewall. These rules decide what traffic to allow or block for your dedicated server. Understanding your network’s security needs is critical here. You’ll create rules that match your policies. This could include content filtering or VPN enforcement.
Network Diagram and Documentation
Having a network diagram is vital. It shows how your network is set up. This helps spot security risks. It’s also helpful in auditing your firewall. Plus, documenting your firewall’s setup is crucial. It makes troubleshooting and maintenance easier.
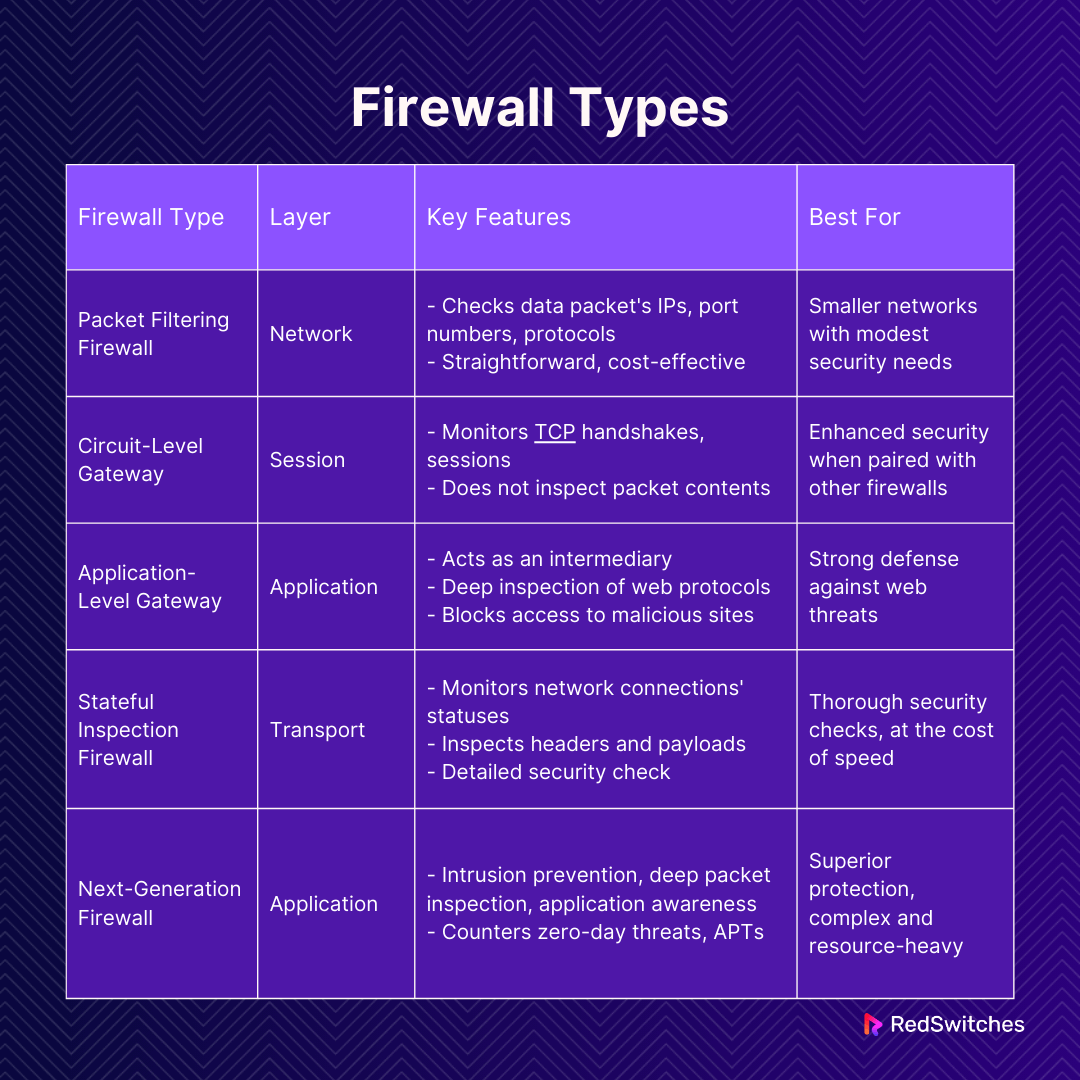
Exploring Firewall Types
Choosing the proper firewall is crucial for organizations to protect their networks. A combination of different firewall types is often necessary to achieve comprehensive security.
Packet Filtering Firewall: This basic firewall operates at the network layer and checks each data packet’s source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. It is straightforward and cost-effective but cannot inspect packets’ contents, leaving it vulnerable to specific attacks like IP spoofing. It’s a good fit for smaller networks with modest security needs.
Circuit-Level Gateway: This type focuses on monitoring the legitimacy of TCP handshakes and sessions without delving into packet contents. It is not equipped to detect malware independently and is usually paired with other firewall types for enhanced security.
Application-Level Gateway (Proxy Firewall): Acting as an intermediary, this firewall scrutinizes incoming data against security rules, particularly for web-based protocols like HTTP and FTP. It provides
- Deep inspection capabilities.
- Offering strong defense against web threats.
- Blocking access to malicious sites.
- Reducing the risk of data breaches by preventing direct external access.
Stateful Inspection Firewall: Positioned at the transport layer, this firewall keeps track of all network connections’ statuses through a state table. It examines both the headers and payloads of packets, providing a thorough security check, however, potentially slowing down network traffic due to its detailed inspections.
Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): NGFWs bring advanced features, including intrusion prevention, deep packet inspection, application awareness, and methods to counter zero-day threats and APTs. While offering superior protection, they are more complex, resource-heavy, and costly than traditional firewalls.
Each firewall type offers unique benefits and limitations, making it essential for organizations to carefully assess their specific needs and network architecture when selecting the appropriate firewall(s) for their security infrastructure.
Also read: A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of Firewalls For Your Networks
How to set up your firewall
Setting up your firewall focusing on security and efficiency is crucial for safeguarding your network against potential cyber threats. By adhering to a structured approach, such as the one recommended by Cisco, you can ensure that your firewall is a robust barrier against unauthorized access to your internal networks and resources.
Here’s an expanded guide on configuring your firewall effectively:
1. Fortify Your Firewall’s Security
Begin by reinforcing your firewall’s security foundation. This involves several key actions:
- Update your firewall to the latest firmware recommended by the manufacturer, ensuring you have all the current security patches and features.
- Remove or rename any default user accounts with the firewall, as attackers can easily target these. Replace default passwords with strong, complex passwords that are difficult to crack.
- Restrict administrative privileges strictly to users who require them to perform their duties, minimizing the risk of unauthorized changes to the firewall settings.
2. Structure Your Network with Firewall Zones
Organize your network’s assets into clearly defined zones based on their importance and function. This segmentation enhances security by controlling traffic flow between different parts of your network. For instance:
- Designate areas like your email, web, and dedicated servers for VPN to a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), which is specially configured to limit inbound traffic to only what’s necessary.
- Develop a coherent IP address scheme for these zones, assigning them to appropriate firewall interfaces and subinterfaces. For IPv4 networks, use private, non-routable IP addresses defined in RFC 1918 and set up NAT to enable internal devices to communicate with the internet.
3. Implement Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs are the core rules that govern traffic flow through your firewall, determining what’s allowed or blocked across your network’s zones. Apply these rules with precision:
- Attach ACLs to each interface or subinterface of your firewall, crafting inbound ACLs to regulate incoming traffic and outbound ACLs to manage what leaves your network.
- Make your ACLs specific, clearly defining allowed source and destination IP addresses, and port numbers, thereby enhancing the security and efficiency of traffic management.
4. Enable Essential Firewall Services and Logging
Besides basic traffic management, your firewall can support additional functionalities contributing to network security and efficiency.
- Activate services such as DHCP for dynamic IP address allocation, Intrusion Prevention for real-time threat mitigation, and NTP for accurate timekeeping across network devices.
- Turn off any non-essential services to reduce potential attack surfaces.
- Configure your firewall to integrate with logging services, especially if you must comply with standards like the PCI DSS, ensuring you have detailed records of network activities for security audits.
5. Rigorously Test Your Firewall Configuration
Before fully deploying your firewall, verifying that it performs as expected is essential.
- Conduct comprehensive tests, including vulnerability scans and penetration testing, to identify and rectify any weaknesses.
- Maintain a secure backup of your firewall configuration to quickly restore functionality in case of a configuration error or system failure.
6. Ongoing Firewall Maintenance
The initial setup of your firewall is just the beginning. Continuous management is critical to maintaining its effectiveness over time.
- Regularly update the firewall’s firmware to ensure it has the latest security enhancements.
- Periodically review system logs to monitor for any unusual activities that might indicate a security threat.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments routinely and revisit your firewall’s configuration rules, especially after making significant changes to your network infrastructure, to ensure they remain aligned with your security objectives.
By following these detailed steps, and incorporating regular reviews and updates into your firewall management practices, you can create a dynamic defense system that protects your network from current threats and adapts to meet future security challenges.
Also Read Private Network vs Public Network: A Detailed Breakdown
A Step-by-Step Guide to Firewall Configuration
Embarking on the journey of configuring a firewall can be a challenging yet rewarding task. To help you navigate this process, we’ve broken it down into simple, manageable steps. Let’s dive in!
Secure the Firewall
Credits: Freepik
The first and most crucial step is securing your firewall. This means taking specific actions to ensure only authorized individuals have access. Key measures include:
- Updating the latest firmware.
- Deleting, disabling, or renaming default accounts and setting unique, strong passwords.
- Creating individual admin accounts with limited privileges for multiple administrators, avoiding shared accounts.
- Disabling or securely configuring the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
- Ensuring the firewall is only put into production with proper configurations.
Establish Firewall Zones and an IP Address Structure
Begin by identifying your network assets. Then, design a network structure that groups these assets into zones, based on their function and sensitivity level. Consider:
- Placing internet-facing dedicated servers like email and VPN servers in a DMZ (demilitarized zone).
- Assigning internal workstations and dedicated server management to their respective zones.
- Using more zones for increased security but balancing this with the management resources required.
- Employing internal IP addresses and configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) for internet communication.
Also read Strengthen Server Security With Proper Iptables Firewall Configuration
Configure Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs determine the traffic flow in and out of each zone. When setting up ACLs:
- Apply them to each interface or subinterface.
- Be specific with source/destination IP addresses and port numbers.
- Include a “deny all” rule at the end of each ACL.
- Implement both inbound and outbound ACLs for each zone.
- Disable public access to firewall administration interfaces and unencrypted management protocols.
Configure Other Firewall Services and Logging
If your firewall supports additional services like DHCP, NTP, or IPS:
- Configure only the services you need, turning off the rest.
- Set up logging to comply with standards like PCI DSS, ensuring detailed reporting.
Test the Firewall Configuration
Testing is critical to ensure your firewall operates as intended. This includes:
- Performing vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
- Verifying that the firewall blocks traffic as per your ACL configurations.
- Backing up the configuration securely after testing.
Manage Firewall Continually
- Ongoing management is critical to maintaining firewall efficacy. This involves:
- Regularly monitoring logs and performing vulnerability scans.
- Reviewing and updating rules as needed.
- Documenting processes for consistent management and protection.
Remember, this overview is a starting point. Always consult a security expert to review your configuration, ensuring optimal data protection.
Firewall Configuration Setup: Navigating the Challenges
Setting up a firewall can be complicated. You’ll likely face several challenges along the way. Let’s break them down:
Finding the Right Balance
It’s tricky to balance security with accessibility. If your firewall is too lax, your network is at risk. But make it too strict, making it a hassle for legitimate users. Aim for a middle ground that keeps your network safe without being a burden.
Choosing the Right Firewall
Hardware firewalls are great for on-site networks. For individual devices, software firewalls are the way to go. Pick a firewall that matches the types of devices you use. Ideally, get one that works well for both on-premises and cloud assets.
Deciding on Additional Services
Firewalls can have extra features like Intrusion Prevention Systems or Network Time Protocol. It’s best to start simple. Focus on the main firewall features first. Add these extras only if they enhance security.
Managing Ports
Think of open ports as open doors for hackers. Before your firewall is up and running, check all port settings. Turn off the ports you don’t need. Keep a close eye on the ones you use to catch suspicious activity.
Resolving Authentication Issues
Sometimes, unique authentication systems don’t play nice with firewalls. This can make safe traffic seem risky. Ensure your multi-factor authentication works well with your firewall.
Monitoring Outgoing Traffic
Focus on something other than incoming traffic. A good firewall also checks what’s going out. Ensure no sensitive data is slipping through. Watch for odd patterns in outgoing traffic; they might signal data theft.
Six Best Practices for Secure Network Firewall Configuration
Securing your network with a firewall isn’t just plug-and-play. It’s about setting up clever defenses that keep the bad stuff out and let the good stuff in. Here’s a simple breakdown of six top tips to make your firewall tough as nails. These steps protect your organization from malware and other cyber threats. Let’s dive in.
- Block Traffic by Default: Setting your network firewall to block unknown traffic automatically is vital. This step makes it more challenging for hackers to sneak into your network. By default, block all traffic unless it’s verified as safe.
- Adopt the Least Privilege Principle: Only some people need full access to your network. Limit each user’s access to only what they need for their job. For instance, a vendor might only need order details, not access to sensitive business data. This approach tightens your network’s security.
- Be Specific with Source IP Addresses: Sometimes, you might want everyone to access part of your network, like a public website. In such cases, set the source IP address to ANY. Otherwise, specify which IP addresses can connect. This limits access and enhances security.
- Use Specific Destination Ports: Ensure your firewall only allows connections to designated destination ports. This means setting up specific ports for different services and allowing only authorized users to access them.
- Open Expected Firewall Ports: Understand and open the ports your users expect to access. This depends on their services and your organization’s dedicated server types. Familiarize yourself with the commonly used ports for different dedicated servers.
- Set Specific IP Address Destinations: Limiting IP address destinations is critical to preventing unauthorized access. It also helps protect against DDoS attacks, which are increasingly common. This step ensures that only authorized traffic enters your network.
Following these practices will greatly enhance your network’s security and protect it from cyber threats. Remember, a well-configured firewall is a strong defense line for your organization’s digital assets.
Choose our premium dedicated servers and bare metal servers with strong security.
Also Read: Unveiling the Hidden Risks of Dedicated Servers
Mistakes To Avoid When Setting Up a Firewall
Credit: Freepik
Setting up a firewall? Watch out for these common slip-ups. They might seem small, but they can lead to big problems.
First up, broad policies. They’re a no-go. You might run into dedicated server headaches if your firewall settings are too general. Think of trouble with the Domain Name System (DNS) or even connectivity glitches. It’s like using a too wide net—you catch much more than you bargained for.
Next, remember outgoing traffic. It’s easy to focus on what’s coming in and ignore what’s going out. But overlooking outgoing traffic is like leaving the back door unlocked. You never know what might slip out, putting your network at risk.
A firewall is excellent, but it shouldn’t be your only line of defense. Relying on just one tool or using quirky authentication methods might leave gaps in your security. It’s like wearing a raincoat in a storm but forgetting the boots. You’re protected up top but still getting soaked from below.
So, when setting up your firewall, consider it part of a bigger picture. Ensure your policies are right, monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, and use various security measures. It’s all about balance and attention to detail.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our journey through the intricacies of firewall configuration, it’s clear that this task is more than just a technical necessity—it’s a strategic endeavor critical to safeguarding your organization’s digital landscape. The journey does not end with configuration. The actual test lies in the ongoing management and adaptation of your firewall setup to respond to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. It’s about striking that delicate balance between security and accessibility, ensuring your network remains protected and functional.
Configuring a firewall is about more than just setting up barriers; it’s about creating a dynamic, responsive defense system that adapts to new challenges while supporting the needs of your users. It is a testament to the fact that in the digital age, vigilance and adaptability are crucial to maintaining the security and integrity of your network.
With this knowledge and strategy, proceed with configuring your firewall as a continuous commitment to the security and robustness of your company’s network infrastructure rather than merely as a task to be finished. Don’t forget your firewall serves as your unwavering protector in the constantly evolving digital landscape and is more than just a tool in network security.
RedSwitches, experts in digital infrastructure, can help you understand and configure firewalls. We ensure that organizations have the latest protection against online threats.
Contact us for details.
FAQs
Q. What needs to be configured in a firewall?
The central aspect of configuring a firewall involves setting up firewall rules. These rules dictate the management of incoming and outgoing network traffic, specifying what is permitted or denied. They can be tailored based on various criteria, such as IP addresses, TCP/UDP ports, application identifiers, user identities, and the nature of the traffic, such as HTTP for web traffic.
Q. What can a firewall be configured to do?
Firewalls can be set up to restrict data from specific sources, such as network addresses, applications, or ports, ensuring that only essential and appropriate data is permitted. (Refer to insights on Denial-of-Service Attacks for further details.)
Q. How many firewalls do I need?
The number of firewalls needed depends on your network’s size, complexity, and specific security requirements. Small to medium-sized businesses only need one well-configured firewall at the network perimeter. Larger organizations or those with more complex network architectures might require multiple firewalls to segment and protect network parts, such as internal divisions, data centers, and cloud environments.
Q. Why is it important to configure the host firewall?
Configuring the host firewall is essential because it provides a layer of security at the individual device level, complementing the network firewall’s border protection. It can prevent unauthorized access to the device, block outgoing connections to malicious hosts, and limit the spread of malware within the network. Proper configuration ensures that necessary applications and services can communicate while blocking potentially harmful traffic.
Q. At which layer are firewalls installed and configured?
Firewalls are primarily installed and configured to operate at the Network Layer (Layer 3) and the OSI model’s Transport Layer (Layer 4). At the Network Layer, they manage traffic based on IP addresses. At the same time, they use port numbers to control and filter traffic at the Transport Layer, aligning with the network’s security policies.
Q. What are the best practices for firewall configuration?
The best practices for firewall configuration involve following a network zone structure, continuously updating the firewall, implementing proper firewall rules configuration, and using next-generation firewalls to secure the network effectively.
Q. How can I configure a firewall to enhance network security?
To configure a firewall for enhanced network security, it is essential to configure the firewall rules, regularly audit the firewall, and ensure unencrypted firewall management protocols are not used. Additionally, deploying a next-generation firewall can significantly improve network security.
Q. What are the main challenges in firewall configuration?
Some main challenges in firewall configuration include managing dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) changes, securing a firewall from external threats, and managing the firewall to align with the organization’s network security requirements.
Q. How should I manage the firewall to ensure optimal security?
Managing the firewall involves regular auditing, monitoring firewall logs, and updating the firewall to address any vulnerabilities or security gaps. It is also crucial to verify that the firewall rules are configured according to best practices for firewall configuration.
Q. What is the role of a firewall administrator in network security?
Firewall administrators play a crucial role in network security by overseeing the firewall configuration process, managing firewall rules, and ensuring that the firewall continues to meet the organization’s security standards.
Q. How can I effectively configure a regular firewall?
To effectively configure a regular firewall, it is important to follow best practices for firewall configuration, manage firewall rules, and monitor the firewall’s performance to address any security concerns.
Q. What are the key considerations when configuring a next-generation firewall?
When configuring a next-generation firewall, considerations include:
- Implementing advanced security features.
- Managing network zones effectively.
- Ensuring that the firewall adheres to the best firewall configuration and network security practices.
Q. What are the recommended audit practices for firewall management?
Recommended audit practices for firewall management include conducting regular firewall audits, reviewing firewall logs for security incidents, and verifying that the firewall rules are aligned with the organization’s security policies and requirements.
Q. How do I verify that my firewall is configured correctly?
You can verify that your firewall is configured correctly by performing regular firewall audits, monitoring firewall logs for any irregularities, and ensuring that the firewall rules align with best practices for firewall configuration and network security.
Q. What are the important considerations when updating a firewall?
When updating a firewall, it is crucial to consider the impact on network security, ensure that the update is compatible with existing firewall rules, and verify that the updated firewall continues to provide the necessary level of protection for the network.