Did you know that in 2023, internet users worldwide were estimated to be around 5.18 billion?
Approximately two-thirds of the world’s population is connected to the World Wide Web. With the ever-increasing need for connectivity in today’s modern world, it’s crucial to understand the differences between the available network types.
One distinction that often gets overlooked is between private and public networks. These networks serve different purposes and cater to varying needs. Understanding these intricacies can help you decide which network is most suitable for your business.
Credits: Shutterstock
This blog compares public vs private network. It dives into the differences, the applications of private networks, and how to transition from a public network to a private one.
Let’s begin!
Table of Contents
- What is Private Network?
- What is a Public Network?
- Private Network vs Public Network: What’s the Difference?
- How To Change a Public Network to Private Network
- Types of Private Network Applications
- Conclusion – Private Network vs Public Network
- FAQs
What is Private Network?
A private network is exclusive to a specific individual or organization, meaning the general public cannot access it. These networks typically use dedicated servers and equipment. They may be set up to facilitate internal communications, safeguard sensitive data, or accelerate specific organizational processes.
The global virtual private network (VPN) market amounted to $44.6 billion in 2022. Government agencies, businesses, and other institutions often use private networks that need a secure environment to communicate and transfer data. They can exist in small forms, like a home LAN, where devices communicate with one another without internet exposure, or on larger scales, such as a corporate intranet.
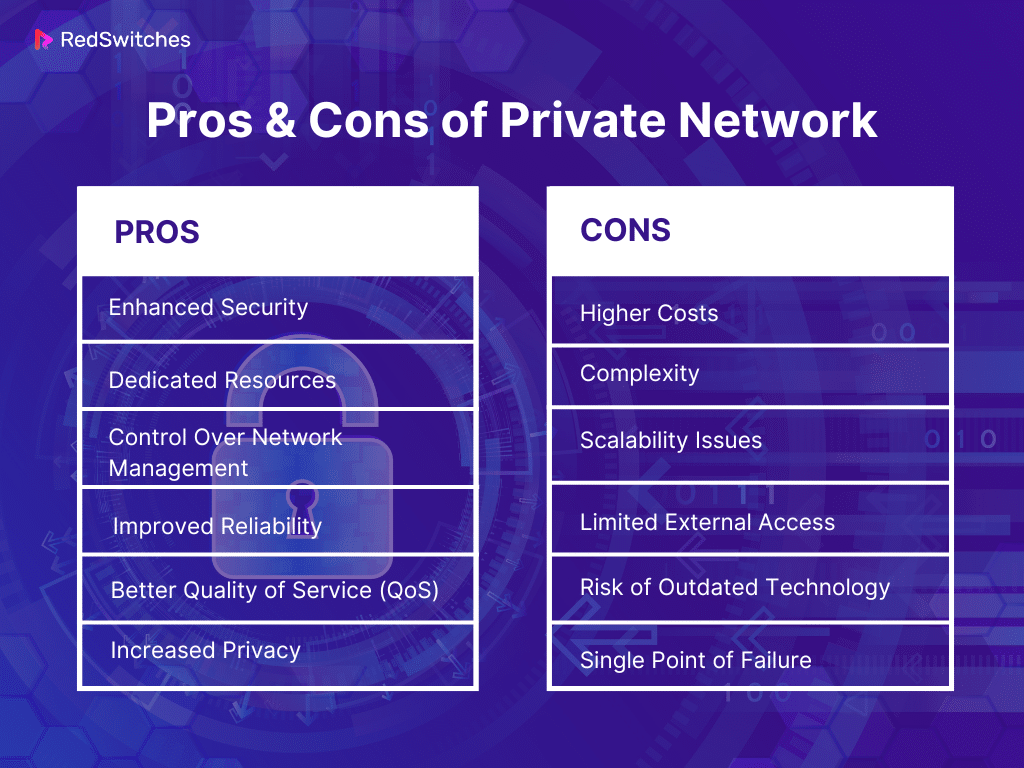
Pros & Cons of Private Network
Pros:
Enhanced Security
When comparing private network vs public network, private networks are usually safer than public ones. They’re curated to serve a specific individual or organization and are not accessible to the general public. This inherent restriction significantly lowers the risk of hacks, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks. Businesses and individuals can leverage a private network to safeguard their sensitive data.
Dedicated Resources
In a private network, resources like bandwidth are inaccessible to external users. This ensures consistent network speeds and performance, which can be particularly beneficial for businesses relying on video conferencing, real-time data transfer, or other bandwidth-intensive tasks.
Control Over Network Management
Private networks enable businesses or users to control network configurations completely. They can do everything from customizing security settings and controlling data traffic to implementing specific network policies and even deciding on the type of hardware or software to use. This level of control is typically not possible in public networks.
Improved Reliability
Since private networks are separated from the broader internet and related risks, they are usually more reliable. The risks of outages caused by significant traffic increases on the broader internet or DDoS attacks targeting public networks are much lower.
Better Quality of Service (QoS)
The control over network traffic allows businesses using private networks to ensure critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth. Whether VoIP calls, video conferences, or data backups, QoS features in private networks can ensure these tasks run seamlessly without disruptions.
Increased Privacy
A private network is isolated by its very nature, which ensures that any communication or data transfer remains confidential. This is especially important for businesses handling sensitive client data or individuals prioritizing digital privacy.
Are you wondering how does a VPN work? Read our informative blog, ‘How Does a VPN Work? A Breakdown of 4 Crucial Aspects’.
Credits: Shutterstock
Cons:
Higher Costs
Setting up and maintaining a private network can be costly. The initial investment includes software, hardware, and possibly dedicated communication lines. Over time, the expenses attached to upgrades and for professional IT staff to manage the network can add up.
Complexity
With a private network, organizations may face difficulties in its setup and configuration. Ensuring smooth communication and interconnectivity among different devices may demand expertise and in-depth knowledge of networking principles.
Scalability Issues
A business network can change as it grows. Private networks might demand significant effort and investment to scale up or down, especially if the initial setup didn’t anticipate future growth.
Limited External Access
Private networks are isolated in terms of design. This can be an issue for businesses that require external partners, clients, or remote employees to access their systems. Businesses may have to get special configurations, like VPNs, to tackle this, which can add to the complexity.
Risk of Outdated Technology
Since the organization is responsible for updating its private network, it risks staying behind in technological advancements. Over time, if not upgraded, the infrastructure may become obsolete compared to more modern solutions.
Single Point of Failure
Private networks may introduce a single point of failure depending on the design. If something critical breaks down, it could impact the entire organization’s operations, causing downtime and potential profit losses.
Is Private Network Safe?
Although private networks offer increased safety compared to public ones, they aren’t entirely risk-free. Below are a few potential threats attached to private networks:
- Internal Threats: A private network is not immune to threats from within. Unhappy employees can be as much of a threat as external hackers.
- Malware and Phishing: If a device on the network gets infected (through email phishing or malicious downloads), malware can spread within the private network.
- Outdated Hardware/Software: Private networks using outdated hardware or software can be vulnerable if they don’t undergo consistent security updates.
- Lack of Redundancy: Sometimes, private networks might not have the same backup or redundancy solutions as larger, public ones, leading to potential data loss risks.
- False Sense of Security: Assuming that a private network is inherently secure can lead to complacency and neglecting necessary precautions.
Maintaining a proactive security strategy is critical to ensure safety from these threats. Businesses must regularly update their hardware and software and educate network users about potential threats. Continuous monitoring of network activity can also add an extra layer of security from threats.
What is a Public Network?
A public network refers to any network that is open and accessible to the general public, i.e., anyone and everyone. These networks are typically unsecured, meaning users don’t have to input a password or authorization to connect. Examples include public Wi-Fi hotspots at coffee shops, airports, and hotels.
Since public networks are accessible to everyone, they are generally considered less secure. It’s advisable to use encryption and avoid accessing sensitive information when connected to a public network to prevent potential data theft or unauthorized access.
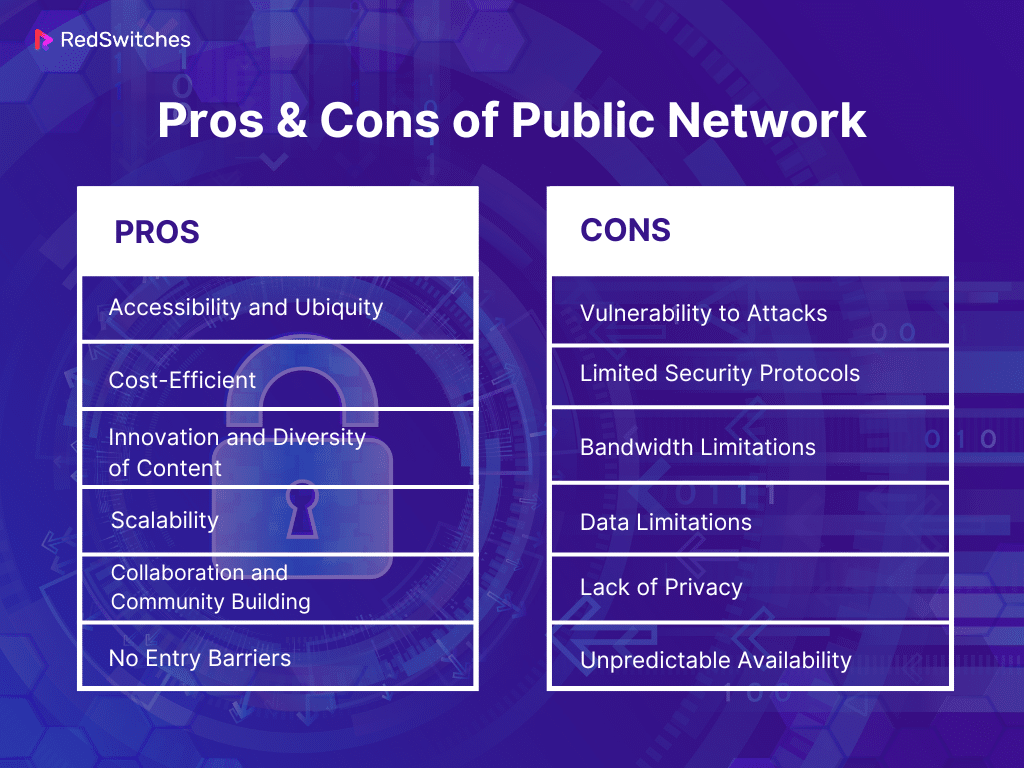
Pros & Cons of Public Network
Pros:
Accessibility and Ubiquity
Like the Internet, a public network is accessible to everyone. This universal access enables users worldwide to connect, share information, and use online resources without geographical restrictions. Its omnipresence means that individuals and businesses can communicate globally, opening up commerce, education, and social interaction opportunities.
Cost-Efficient
Setting up and maintaining a private network can be expensive. In contrast, due to its shared nature, public networks often come at a lower cost for end-users. Service providers can spread the infrastructure and maintenance costs across many users/ This helps reduce the individual costs for accessing and using the network.
Innovation and Diversity of Content
Public networks, especially the Internet, serve as a breeding ground for innovation and creativity. The unrestricted nature of public platforms allows for a diverse range of applications, content, and services. The vast content caters to varied interests and needs, from streaming services and blogs to innovative applications and platforms.
Scalability
Public networks are designed to handle many users, making them easily scalable. Service providers typically expand and upgrade their infrastructures as more users join the network. This means that as a user base or a business expands, there’s no need for overhauls or migrations, as the network is already equipped to manage the increase in traffic.
Collaboration and Community Building
The openness of public networks fosters collaboration and community building. Platforms like forums, social media sites, and collaborative wikis thrive on public networks, empowering individuals from different backgrounds and regions to connect, collaborate, share ideas, and work on projects collectively.
No Entry Barriers
Public networks eliminate the need for going through the hassle of setups, dedicated infrastructure, or specific protocols. Whether an individual or a small business, one can easily get on board without the headaches of setting up proprietary connections or systems. This democratization ensures that even individuals with limited resources can participate and benefit from the digital ecosystem.
Cons:
Vulnerability to Attacks
Public networks, especially ones without password protection, are highly susceptible to cyberattacks. Cybercriminals can easily eavesdrop on the data being transmitted, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and theft of personal information.
Limited Security Protocols
Unlike private networks with powerful security measures, public networks may lack advanced security protocols. This absence can expose users to phishing attempts, malware, and man-in-the-middle attacks, compromising their devices and data.
Bandwidth Limitations
Due to the increased percentage of users often connected to public networks, like those in malls, cafes, or airports, the available bandwidth might be limited. This can result in insufficient internet speeds, extended download times, and inefficient browsing experience.
Data Limitations
Some public networks impose limitations on data usage. This restricts the amount of data you can upload or download. This can be especially problematic for users wanting to stream videos, make video calls, or conduct other data-intensive tasks.
Lack of Privacy
Since anyone can access public networks, users have minimal privacy. Activities performed on such networks can be easily monitored, logged, or sold to third parties by unethical network providers.
Unpredictable Availability
The availability and quality of public networks can be unpredictable. Although a location may advertise free Wi-Fi, it might not always be functional or too congested with users, making reliable connections difficult.
Is Public Network Safe?
A public network, like those found in malls, airports, coffee shops, hotels, or other public places, generally isn’t considered safe for sharing sensitive or private data. Below are the reasons why:
- Eavesdropping: Malicious users can use packet sniffing tools on a public network to capture and analyze data transmitted over the network.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: In such attacks, a malicious entity intercepts the communication between two parties, captures the data, and might change it before sending it to the intended recipient.
- Rogue Hotspots: A malicious user could set up a rogue Wi-Fi hotspot with a name similar to a legitimate public Wi-Fi network to deceive users into connecting to it. Once connected, the attacker could potentially access sensitive data.
- Malware Distribution: Public networks can be used to distribute malware. Once connected, malware can be pushed to your device.
- Unencrypted Networks: Many public Wi-Fi networks are unencrypted, making it easier for attackers to intercept data.
- No Network Management: Since public networks are created for ease of access, they usually lack strong network management, making them more susceptible to cyber threats.
Now that we have discussed the definitions, pros and cons, and safety elements of private network vs public network, let’s explore the key differences between public vs private network.
It is common for new entrepreneurs to get confused between VPS and VPN. Clear the difference by reading our blog, ‘How to Choose Between VPS and VPN for Your Business Needs.’
Private Network vs Public Network: What’s the Difference?
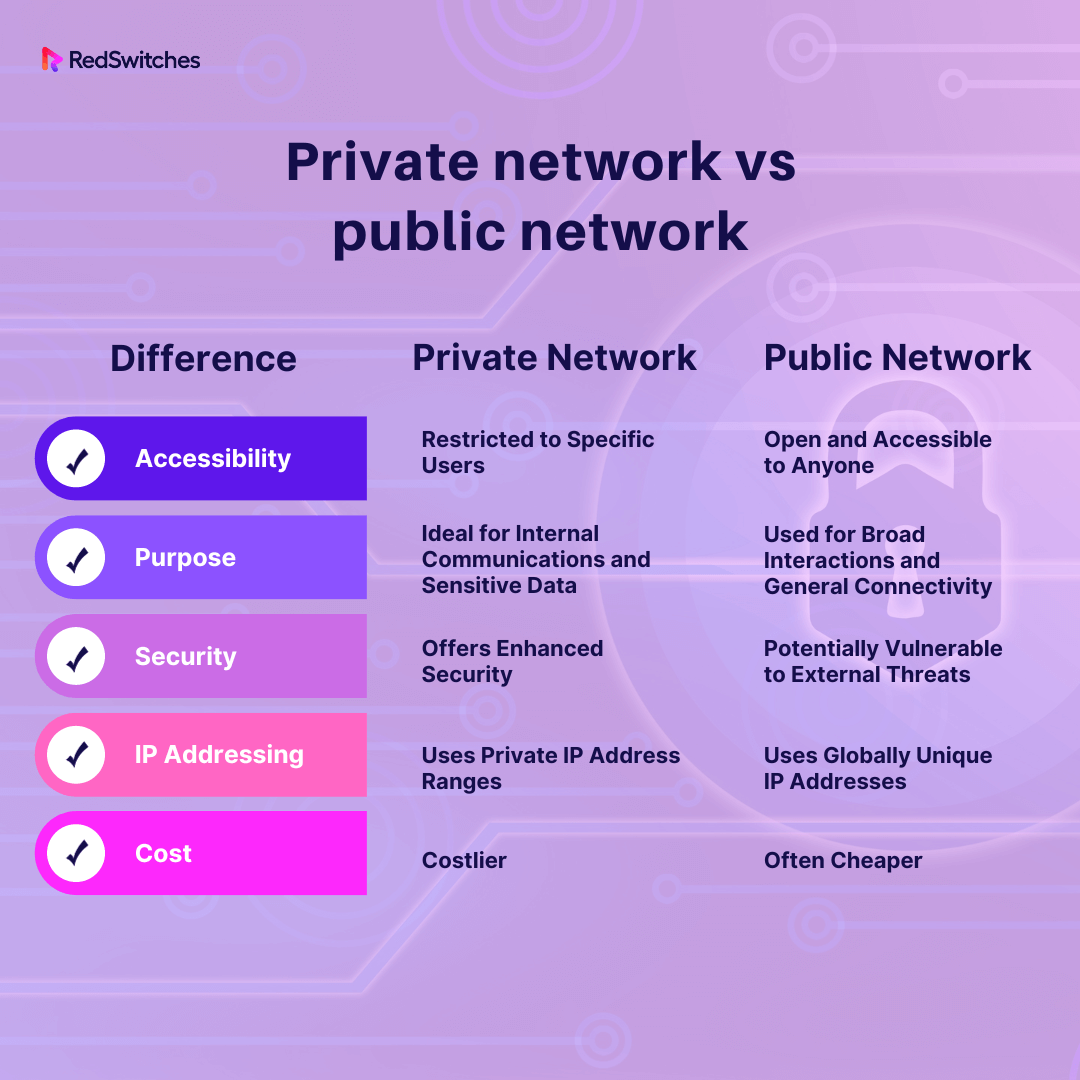
Both public and private networks play important roles in ensuring connectivity in computer networks, but they differ in terms of accessibility, purpose, cost, IP addressing, and security. Below are the distinguishing factors between private network vs public network.
Accessibility
Below are the differences between private network vs public network in terms of accessibility:
- Private Network: As the name suggests, a private network is restricted and not accessible to the general public. It’s typically used within an organization or home where the users are known and trusted. The network administrator controls access to a private network.
- Public Network: A public network is accessible to any user. The most prominent example of a public network is the Internet. There’s no restriction on who can connect unless specific access controls or paywalls are implemented.
Purpose
Below are the differences between private network vs public network in terms of purpose:
- Private Network: The primary purpose is to share resources (like printers, files, and databases) among a certain group of users without exposing those resources to the outside world.
- Public Network: It is designed to connect millions of private networks, individuals, and organizations. The main objective is information sharing and communication on a large scale.
Security
Below are the differences between private network vs public network in terms of security:
- Private Network: Private networks are more secure than public networks. They often have firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and other security appliances. Unauthorized access attempts are often detected and thwarted.
- Public Network: Due to its open nature, public networks are more vulnerable to attacks. Users must adopt individual security measures like VPNs, antiviruses, and personal firewalls to stay protected.
IP Addressing
Below are the differences between private network vs public network in terms of IP addressing:
- Private Network: A private network uses a specific range of IP addresses reserved for private use. These IP addresses are not routable on the public Internet. Examples include addresses starting with ‘192.168’ or ‘10.’.
- Public Network: Public networks use globally unique IP addresses routable in the broader Internet. Each device connected directly to the Internet will have a distinct public IP address.
Cost
Below are the differences between private network vs public network in terms of cost:
- Private Network: An initial setup cost is usually involved in establishing a private network. This includes the cost of infrastructure like switches, routers, and cabling. Internal data transfers usually don’t incur additional expenses.
- Public Network: Accessing public networks, especially the Internet, can lead to usage-based costs, depending on the service provider and the data plan in place.
Also Read: 10 Best VPN for Linux in 2023: Conquering the Digital World.
How To Change a Public Network to Private Network
Credits: Shutterstock
Connecting to a new network on your computer is usually identified as public by default for security reasons. That being said, there may be occasions where you’d want to change this public network to a private one – especially if you trust the network and need to enable device discovery or use local network features.
We’ll explore below the steps you can follow to transition from a public network to a private one.
Discovery Settings
When you’re on a private network, one major difference is the ability for your device to be discoverable by other devices. This is useful in home and business settings where you may have to share files or connect with other devices, such as printers.
Windows Settings:
- Navigate to Settings > Network and Internet.
- Select Wi-Fi or Ethernet – depending on your connection.
- Select the network you’re connected to.
- Under Network Profile, select Private. (This automatically makes your device discoverable to other devices on the same network).
Control Panel:
- Open the Control Panel and go to Network and Sharing Center.
- Click on the active network and select Home or Work Network in the popup. (Both of these are considered private network types).
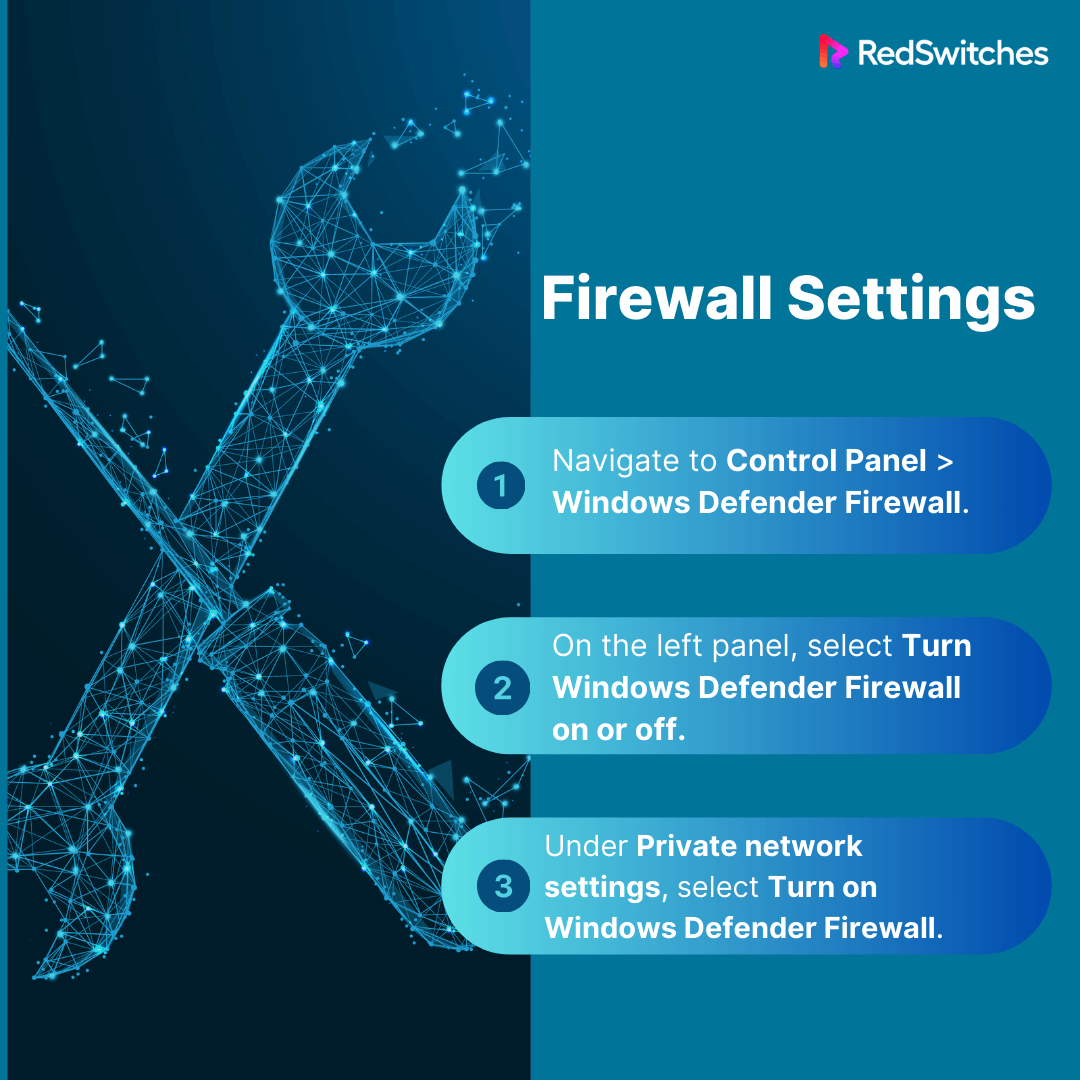
Firewall Settings
The Windows Firewall settings are essentially tied to the form of network you’re on. A public network has more robust firewall rules to protect your system, but once you transfer to a private network, these rules can become less stringent to allow for local network activities.
- Navigate to Control Panel > Windows Defender Firewall.
- On the left panel, select Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off.
- Under Private network settings, select Turn on Windows Defender Firewall. Adjust the settings as needed for your activities.
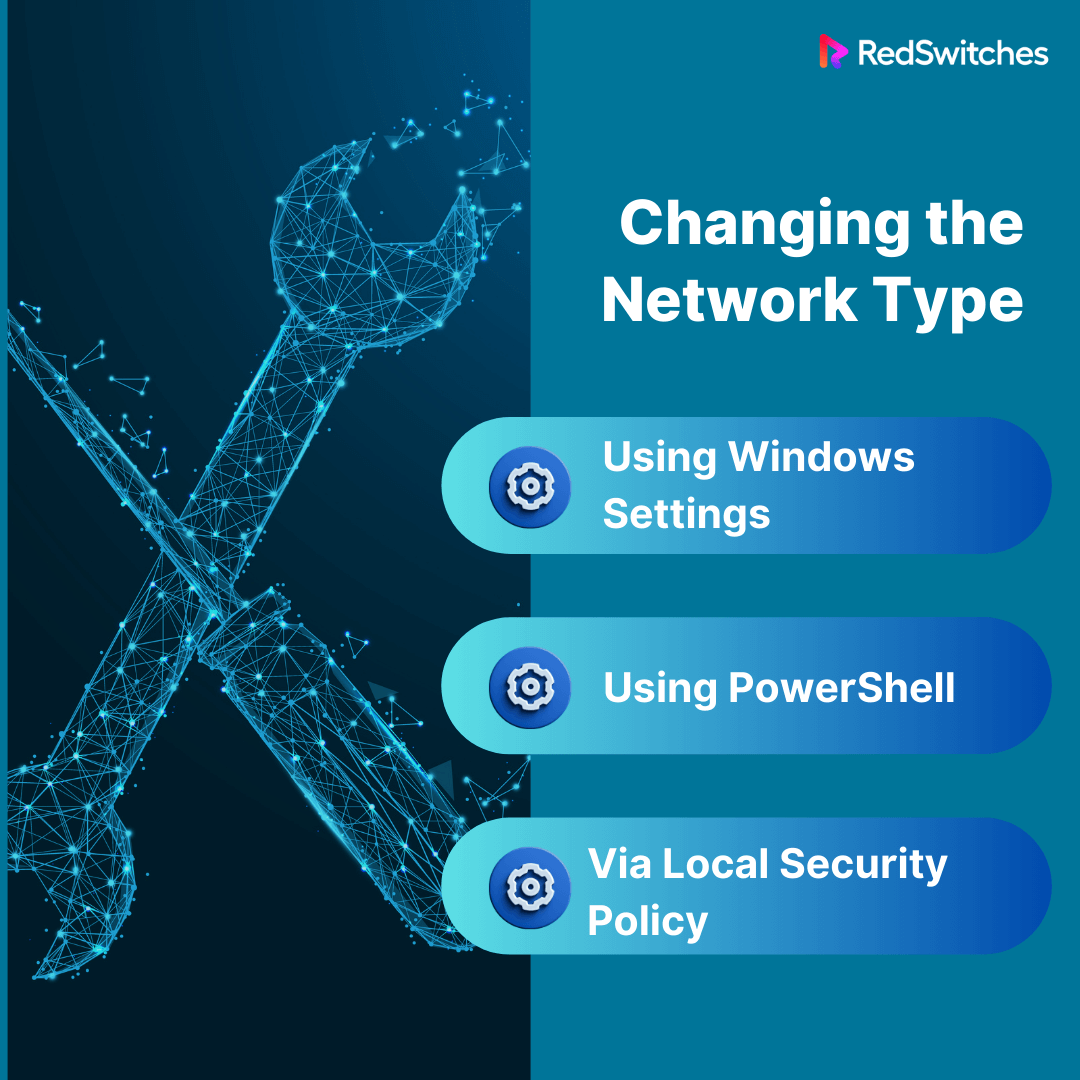
Changing the Network Type
One can change the network type through several methods, including:
Using Windows Settings:
- Navigate to Settings > Network and Internet.
- Select Wi-Fi or Ethernet, depending on your connection type.
- Select your network connection.
- Under Network Profile, transfer from Public to Private.
Using PowerShell:
- Access PowerShell as an administrator.
- Enter the command Get-NetConnectionProfile to view all networks.
- Identify the network you wish to change. Remember its Name.
- Use the command Set-NetConnectionProfile -Name “Your Network Name” -NetworkCategory Private to switch the network type.
Via Local Security Policy:
- Type secpol.msc into the Start menu and press Enter.
- Navigate to Network List Manager Policies on the left pane.
- Double-click on your network in the right pane.
- Under Network location type, select Private.
Types of Private Network Applications
Office Network
An office network, often called an enterprise network, interconnects its computing resources within a company or organization’s premises. This network type is specifically tailored to meet the requirements of enterprises, regardless of their size.
Characteristics
- Scale and Complexity: These can range from a few interconnected computers in small offices to hundreds and thousands of devices in larger enterprises.
- Hierarchical Design: Typically involves several layers like core, distribution, and access layers to manage traffic efficiently.
- Dedicated IT Team: Larger office networks often have a dedicated IT team to manage, troubleshoot, and secure the network.
- Integrated Services: Integration with services like VoIP, video conferencing, and centralized software applications.
Home Network
A home network is a private network within an individual’s residence that connects all digital devices. It’s typically set up to share internet access, files, printers, and other local resources.
Characteristics
- Simplicity: Typically consists of a router connecting various devices like PCs, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and IoT devices.
- Wi-Fi Centric: Most home networks emphasize Wi-Fi connectivity, although they might have wired connections, too.
- Limited Scale: Generally connects fewer devices than office networks.
- Consumer-grade Equipment: Uses consumer-grade routers and modems.
Conclusion – Private Network vs Public Network
In today’s interconnected world, comparing private and public networks allows users to decide which network best suits their needs and preferences.
Consider RedSwitches if you’re looking for dedicated solutions to facilitate your network requirements, primarily hosting-related. Our comprehensive services ensure your online presence is secure and efficient, regardless of the scale and nature of your operations.
So what are you waiting for? Get in touch with us now to learn more about our services.
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between a public network and a private network?
A public network is accessible to anyone and is generally open, like the Internet, whereas a private network is restricted to only a specific amount of users or devices, ensuring limited accessibility. In the debate of private network vs public network, the primary distinction lies in their levels of security and purpose.
Q. What is an example of a private and public network?
An example of a private network is a company’s intranet. An intranet is designed solely for internal use and inaccessible from the external Internet. A classic example of a public network is the Internet, which is open and accessible to everyone. When comparing private network vs public network, think of an organization’s internal communication system versus the extensive, interconnected web we use every day.
Q. What is better, a private or public network setting?
Whether a private or public network setting is better depends on the user’s needs and priorities. A private network offers improved security and privacy. This makes it ideal for sensitive data and internal communications. When looking at private network vs public network, the public network provides expansive connectivity and accessibility, suitable for broad interactions, but may require extra protection measures against potential threats.
Q. What is the difference between public and private networks?
Public networks are accessible to anyone and are often used for internet connectivity in public places like airports, coffee shops, and libraries. Private networks, on the other hand, are restricted to authorized users and are commonly found in homes, offices, and enterprise environments.
Q. How do I switch from a public to a private network in Windows 10?
In Windows 10, you can switch from a public to a private network by going to the “Network” settings, selecting the network you are connected to, and changing the network profile from public to private.
Q. What are the features of a public network?
Public networks often offer features such as network discovery, file sharing, and easy accessibility. However, they are more vulnerable to security threats compared to private networks.
Q. What are the differences between private and public networks in terms of security?
Private networks provide a more secure environment due to limited accessibility and control over user permissions. Public networks, on the other hand, are more prone to security risks and unauthorized access.
Q. Can I use public networks for sensitive activities such as online banking?
It is not recommended to use public networks for sensitive activities like online banking, as they are more susceptible to potential security breaches. It is advisable to use private networks for such purposes.
Q. How does 5G technology impact public and private networks?
5G technology enables faster and more reliable connectivity, which can benefit both public and private networks. However, it also introduces new security considerations for both types of networks.
Q. How do network discovery features differ between public and private networks?
Network discovery features are typically enabled on public networks to facilitate easy access and connectivity. In contrast, private networks may have stricter network discovery settings to enhance security and privacy.
Q. What steps can I take to enhance the security of a public network connection?
To enhance the security of a public network connection, you can disable file sharing, enable firewall protection, and avoid accessing sensitive information while connected to the public network.
Q. What type of network is a Wi-Fi network – public or private?
Wi-Fi networks can be either public or private, depending on the settings and access restrictions configured by the network administrator or user. It is essential to differentiate between public and private Wi-Fi networks for security and privacy considerations.
Q. How do I enable network discovery features for a private network in Windows?
In Windows, you can enable network discovery features for a private network by accessing the network and sharing center, selecting the network profile, and enabling network discovery and file sharing options.