Key Takeaways
- Dedicated servers offer unmatched control and performance but come with various risks.
- Security measures, regular audits, and updates are critical for protecting servers.
- Scalability and maintenance require strategic planning and investment.
- Compliance with data protection laws is essential to avoid legal repercussions.
- Financial planning and cost-benefit analysis can mitigate financial risks.
- Vendor selection and clear SLAs are crucial for reliable server management.
- RedSwitches provides a solution to manage these risks with expert server management.
Dedicated servers are vital to many enterprises. Digital real estate is as crucial as its physical counterpart in this era. They run anything from high-traffic websites to vital data storage solutions. But, the threats from these tech giants are complex and wide-ranging. The threats grow as we rely on them more. Managing the server market is like piloting a ship through dangerous waters. The market has ever-changing cybersecurity risks and the chance of hardware problems that might halt operations. In this piece, we explore the dark side of server administration. We expose the hidden dangers and offer advice on protecting digital assets from unplanned disasters.
Come explore this essential subject with us. You’ll leave with practical tips and expert advice, and you’ll learn about reducing the risks of dedicated servers.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What are Dedicated Servers?
- Importance of Understanding Risks
- Technical Risks Associated with Servers
- Operational Risks With Servers
- Financial Risks With Servers
- Compliance and Legal Risks
- Mitigation Strategies to Reduce Risks
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Dedicated Servers?
Credits: Freepik
Dedicated servers are advanced and powerful hosting options. They’re for companies and people with demanding web needs. Shared hosting distributes server resources among many users.
Only one client uses a server. It is exclusive. This gives unmatched control, performance, and security. So, it’s perfect for high-traffic websites, complex applications, or those that need to protect sensitive data.
A server’s architecture is built to deliver dependable and sturdy service. Clients can design and optimize the server to fit their requirements without worrying about the limitations or demands of other users on the same server because they have full access to the server’s CPU, RAM, and storage resources. With this level of access, one may install custom software and change settings. They can manage high traffic and run data-intensive applications.
Another essential benefit of servers is security. Because the server is dedicated to a single client, the dangers associated with shared hosting setups, like cross-site infection and resource abuse by other users, are minimized.
Clients can also install security tailored to their needs to better protect sensitive data. Examples of these measures include firewalls, security protocols, and encryption.
Because servers have dedicated resources and allow for customized server environments, they also have higher stability and uptime. Dedicated servers provide reliability and uptime guarantees.
They are vital for businesses that depend on their online presence for revenue or critical activities. Service level agreements (SLAs), which guarantee a specific uptime percentage, are frequently included by service providers to remind clients that their online activities will operate without a hitch.
Importance of Understanding Risks
Knowing the risks in any endeavor or technology is critical. It’s critical for several reasons. These include strategic planning, security, and sustainability. Knowing all possible risks in the context of servers. This applies more generally to any business or technology domain. It helps people and organizations plan, take precautions, and adjust as needed to ensure success. The following are some significant justifications for why risk awareness is crucial:
Strategic Planning
Assessing risk is critical to strategic planning. It lets companies expect and navigate hazards. For organizations that depend on servers, the evaluation covers cyberattacks in the virtual world and hardware durability. Finding weaknesses lets us create a multi-layered defense strategy. It includes long-term resilience and quick repairs. Businesses are tough. They face challenges by using techniques. This includes making thorough disaster recovery plans. It also means having backup sites in different places and ensuring regional redundancy.
Security Enhancement
Building strong security requires a detailed awareness of risks. The digital ecosystem is changing rapidly. Threats are changing alarmingly and growing complex. Dedicated servers require a flexible security policy. This is due to the wealth of sensitive data and vital processes they host. This entails fostering a security-conscious culture among all stakeholders and implementing cutting-edge security technology like intrusion prevention systems, next-generation firewalls, and advanced encryption standards. Frequent awareness campaigns, security drills, and training sessions ensure that people— frequently the weakest link in security chains—become an effective first line of defense.
Compliance and Legal Protection
Credits: Freepik
Businesses face this problem, especially those using servers for sensitive data. They struggle to follow the complex web of laws about data security and privacy. Not only is compliance required by law, but it also sends a message of trust to partners and consumers. They must understand the potential consequences of non-adherence. These range from hefty fines to crippling penalties. The risks motivate establishments. They carefully evaluate their procedures for managing and safeguarding data. In addition to implementing industry-standard security measures, this calls for periodic compliance assessments and policy modifications in response to changing legal frameworks.
Financial Stability
The risks of dedicated hosted servers have financial effects. They go beyond what happens right after an event. Recovery and repair might cost less than the indirect costs. These include the loss of customer trust and brand value. They can develop financial plans that include insurance. They can also invest in cutting-edge security equipment. And, they can create emergency reserves for cyberattacks. It lessens the impact of a crisis. It also shows stakeholders that the company is dedicated to stability and dependability.
Innovation and Adaptability
Forward-thinking companies are characterized by their capacity to foresee and respond to new risks in a world where change is the only constant. A thorough awareness of the risks associated with servers creates an atmosphere where innovation is not only welcomed but also required. Businesses can quickly adapt to emerging risks by creating and implementing state-of-the-art solutions that fix existing vulnerabilities and establish new industry benchmarks.
This culture of flexibility and never-ending development guarantees that companies stay at the forefront of their respective industries, converting possible setbacks into chances for expansion and innovation.
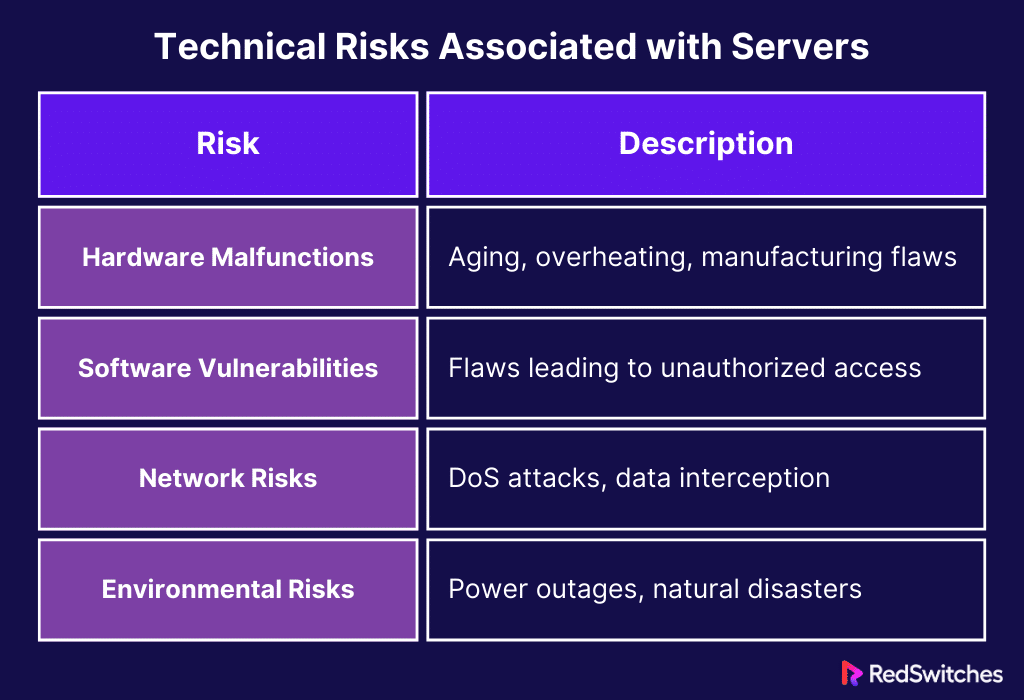
Technical Risks Associated with Servers
Credits: Freepik
Server-related technical issues can affect an organization’s IT infrastructure, data security, and operational continuity. Here, we examine these dangers in further detail:
Hardware Malfunctions
Hard drives, RAM, and power supplies are just a few of the hardware parts that make up servers. These parts can all fail due to aging, overheating, or manufacturing flaws. Such failures may cause significant data loss. This is especially true if the impacted parts hold crucial, unbacked-up data.
Also, even in redundant systems, hardware failures often cause brief outages. This is because the broken parts need to be fixed or replaced. The problem is the replacement and the costly, slow restoration of data and services.
Software Vulnerabilities
Operating systems, apps, and services are just a few of the many software layers that power servers, and each one may have flaws. Hackers use these vulnerabilities to obtain unauthorized access or interfere with server functions. Upgrades and modifications cause compatibility problems.
These problems worsen software vulnerabilities. They can interrupt and corrupt data. These dangers are made worse by out-of-date software. It exposes servers to attacks that target known but unpatched flaws. Fixing these software issues requires careful maintenance. You need to update to keep server security and integrity.
Network Risks
Servers are crucial to networks. But, threats from the network can seriously harm them. DoS and DDoS attacks can overload servers with traffic. They block access for authorized users. Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks pose another serious risk. They let attackers intercept and alter data sent between servers and clients. Strict network security standards are needed to protect servers. This is because servers with unprotected network services are prime targets for illegal access.
Also Read What Are The Security Risks Of Cloud Computing
Environmental Risks
Servers need steady conditions to work. They are sensitive to their surroundings. Servers may suddenly stop working due to power outages, which could cause data loss or corruption. Both human mistakes and physical damage from natural disasters like fires, earthquakes, or floods can seriously affect server hardware, leading to data loss and interruptions in operations.
Environmental controls in server rooms are crucial because servers must function within specific temperature and humidity ranges to prevent hardware damage or shortened lifespans.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
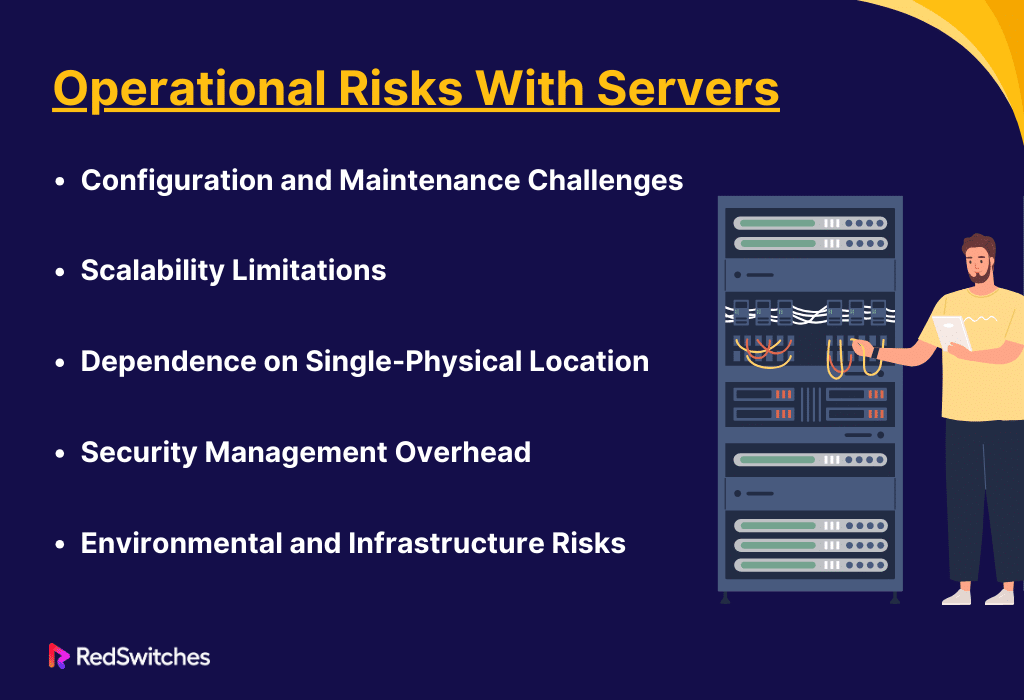
Operational Risks With Servers
Servers provide websites and apps with great power and control. But they also have many hazards. These threats may impact the IT infrastructure’s efficiency, dependability, and general efficacy. Anyone dependent on servers to support their business operations must know these risks.
Configuration and Maintenance Challenges
Understanding the specific hazards of servers is essential. They are vital to keeping a secure and effective IT system. These servers need to be set up and maintained by someone with high technical skills. So, setup and upkeep problems are significant obstacles. We must make precise changes to fit specific needs in the initial setup. This includes network settings and software installations. If we do these wrong, it might expose the system to security risks or performance problems. Frequent maintenance is also essential. It involves applying software patches and upgrades on time. This prevents security flaws and ensures peak performance. An IT staff with specialized skills is required to do these activities efficiently.
Scalability Limitations
The scalability constraints that come with servers are another critical factor. Cloud systems can scale resources dynamically. In contrast, servers are limited by their hardware. Physical upgrades or moving to a more reliable server are usually required when increasing resources like CPU, RAM, or storage. These procedures might result in significant downtime and extra expenses. This rule can be a big problem for growing companies or those facing volatile demand. Scaling up may not be as quick or smooth as they need.
Dependence on Single-Physical Location
Credits: Freepik
Servers hosted at a single physical location have hazards. These are related to disaster recovery, data sovereignty, and accessibility. High latency hurts app performance. It also hurts user satisfaction for those far from the server. Such enterprises must follow data protection rules. The location also exposes the data to the laws of that place. Also, natural disasters and power outages can harm data integrity and availability at the data center. For this reason, a thorough disaster recovery plan is crucial. It must have geographical redundancy to reduce these risks.
Security Management Overhead
Servers need strong security. They need it to fend off online dangers. These include malware, illegal access, and data breaches. The provider sometimes handles much of the security. But, the user or the organization is solely responsible for the server’s security. This includes setting up and keeping intrusion detection systems and firewalls. It also includes conducting routine security audits. Users face a heavy burden. It’s due to the complexity and changeability of cyber threats. They require ongoing attention to detail, skill, and security changes to protect sensitive data.
Environmental and Infrastructure Risks
Running servers has risks. They are from the physical environment and supporting infrastructure. Hardware can malfunction from issues like not enough cooling. Power swings can bring down servers. To reduce these hazards, data centers house servers. They must have dependable infrastructure, such as backup generators, UPSs, and advanced cooling.
Businesses that need servers must choose a data center. It must have robust infrastructure and environmental controls. The effectiveness of these safeguards can vary significantly among hosting companies.
Financial Risks With Servers
Credits: Freepik
Businesses are especially concerned about the costs and benefits of hosting options. They worry about the financial dangers of servers. Servers have apparent financial effects. They can impact a company’s budget and planning. But they offer unmatched control and performance.
High Initial Cost and Ongoing Costs
Setting up a server requires a significant initial cost, one of the most urgent financial hazards. Servers give exclusive resources to one user. Shared hosting and cloud services divide resources among many users. The price of this exclusivity includes setup, customization, hardware, and software licensing. Also, the ongoing expenses of running a server include maintenance. They also include security upgrades and technical support. These costs are in addition to the monthly or yearly leasing rates. Budgets may be strained by these accumulated expenses, particularly for startups or small- to medium-sized businesses (SMEs).
Also Read VPS vs Shared Hosting: Decoding the Best Option for Your Business
Unexpected Expenses
It might be challenging to predict when servers will experience unanticipated costs. For example, hardware breakdowns may necessitate quick replacement or repair, resulting in unanticipated expenses. Similarly, more expenditures for software updates or security measures can be required if software requirements change or new security risks surface. These erratic costs make budgeting more complex and make it difficult for companies to keep a steady IT budget.
Scalability Costs
Increasing performance or capacity usually requires a sizable capital investment, so the financial effects of scaling servers should not be taken lightly. Upgrading a server’s hardware, such as increasing RAM storage or integrating faster CPUs, necessitates a direct investment in tangible assets when a company expands or its resource requirements rise. In addition to the price of the new gear, there may be downtime during the upgrade, which could result in lost revenue.
The logistical issues associated with replacing hardware, such as compatibility checks and the actual installation, add additional layers of complexity and possible costs.
This is very different from cloud-based services, which allow users to quickly scale up or down resources, giving organizations a more affordable and adaptable way to meet changing demands. The cloud’s predictability and ease of scaling draw attention to the cost and rigidity of scaling servers.
Opportunity Costs
Investing in servers entails substantial opportunity costs that could impact a company’s long-term success and the monetary costs associated with equipment and maintenance. Money invested in physical server infrastructure may be used for marketing, hiring more people, or doing research and development, among other important strategic initiatives. Due to these lost opportunities, businesses may incur significant costs, particularly in industries with rapid innovation cycles where time-to-market is crucial.
Furthermore, managing server environments requires an operational focus that may take time and resources away from other important business goals, which could impede innovation and growth.
Depreciation and technical Obsolescence
Server hardware depreciation and obsolescence provide significant financial concerns during unrelenting technical advancement. Old hardware can soon become outdated when new technologies appear because it can’t keep up with the latest software or match changing performance requirements.
This technical obsolescence reduces recovery opportunities for the initial investment by affecting the server’s resale value and gradually decreasing its efficacy. Old gear needs to be replaced regularly to keep up with technology improvements. This is a costly cycle that can put a burden on finances and take money away from other essential investments.
Compliance and Legal Risks
Credits: Freepik
Businesses that operate online must consider the legal issues. They are related to servers. These hazards come from laws about privacy, data security, and operational integrity. Businesses rely more and more on servers. They use them to handle and store sensitive data. It’s critical to understand and reduce these risks. This is needed to stay legal and shield the company from liabilities.
Data Protection and Privacy Laws
Global focus on these issues has increased. It requires companies to manage a complex web of rules. These rules include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). They also include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and similar laws worldwide. By definition, servers hold enormous volumes of private and sensitive information. Companies must ensure that how they handle data on these servers follows the law. The law describes gathering, processing, storing, and moving data.
Risks related to intellectual property
They have IP essential to a company’s operations and competitive edge. They are often hosted on servers. Someone may steal, misuse, or violate this intellectual property. This can happen due to unauthorized access, data breaches, or poor security. Businesses must follow strict security procedures. They must also do frequent audits and pay for IP protection services. Stealing or infringing on intellectual property can have legal consequences. These include costly trials, the loss of exclusive rights, and disruptions to business and finances.
Contractual and SLA (Service Level Agreement) Obligations
These organizations use servers. They contract with hosting companies for service-level agreements (SLAs). These server SLAs specify the obligations of each party as well as the performance and uptime assurances. Not doing these tasks may lead to legal problems. It can also lead to fines and strained business ties. Also, groups must ensure that their agreements with providers follow data protection laws. These laws focus on data sovereignty. It requires data to be stored and processed only within certain legal jurisdictions.
Risks Associated with Cross-Border Data Transfers
Servers present particular difficulties for companies that conduct cross-border data transfers. Strict regulations, like the GDPR, limit the transfer of personal data outside of the EU. This requires compliance with legal frameworks like the EU-US Privacy Shield and proper security.
Businesses need to examine where to put their servers to meet these requirements. They need to do this carefully. This may mean putting servers in certain places. It may also mean adding more security for data transfers.
Mitigation Strategies to Reduce Risks
Businesses must cut the risks of using servers. This is to ensure the safety, reliability, and legal compliance of their IT infrastructure. The following are detailed approaches to reduce the many dangers of servers:
Implement Robust Security Measures
Strong security measures must be implemented to defend servers from online threats. Businesses can protect sensitive data. They do this by using thorough security processes. These processes include firewall setups, access limits, and encryption. Security levels are higher because we encrypt data in transit and at rest.
We also use multi-factor authentication for server access. Frequent vulnerability assessments and security audits help find possible vulnerabilities. Then, they can be fixed quickly. You must use tools for penetration testing. You must also use tools for ongoing security threat monitoring. These tools are vital to assessing if security measures are working.
Ensure Reliable Configuration and Maintainance
You need a standard server operating environment. It enables dependable setup and upkeep. It also ensures that servers have good performance and security. Monitoring tools examine real-time server performance, disc space, and network utilization. Scheduled maintenance and monitoring are vital. They assess server health and improve performance. Being proactive may prevent problems from worsening. It keeps operations effective and lowers downtime.
Planning For Scalability and Business Continuity
Scalability and business continuity planning are essential to meet enterprises’ changing needs. Design server architecture for scalability. It should mix servers with cloud services. This provides flexible scalability options. Creating a complete disaster recovery plan is key. It must include frequent data backups kept in many places. This ensures that business can quickly resume after an unforeseen incident. Periodically testing the disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity by confirming its efficacy in various scenarios.
Addressing Compliance and Legal Obligations
Addressing legal requirements and compliance is critical in the present regulatory landscape. You must understand and follow data protection laws like the CCPA and GDPR to reduce legal risks. Also, you must set up data governance policies. They must ensure data encryption, secure data storage, and proper handling of personal information. Frequent audits help maintain compliance with laws. Legal pros or compliance consultants can help navigate legislative changes affecting server operations.
Minimizing Financial Risks
Credits: Freepik
Minimizing financial risks necessitates a thoughtful and strategic approach to IT investments in managing servers. Before committing to server expenditures or expansions, it is imperative to perform comprehensive cost-benefit evaluations. This procedure should assess long-term operating expenses, such as maintenance, energy usage, prospective scalability requirements, and the immediate costs of purchasing and configuring gear.
By meticulously comparing these variables with the anticipated advantages, enterprises can arrive at well-informed judgments that correspond with their fiscal and functional objectives.
Examining substitute options, such as cloud services, for particular tasks can drastically reduce initial capital costs and ongoing expenses.
Vendor and Contract Management
A meticulous selection of hosting companies with a track record of dependability, security, and support is necessary for vendor and contract management. It is essential to assess suppliers’ capacity to fulfill particular requirements, such as observing data privacy regulations. Mutual understanding and accountability are ensured by negotiating explicit service-level agreements that specify roles, uptime guarantees, and corrective actions for service outages. A mutually beneficial relationship between companies and their hosting providers is made possible by routinely assessing SLAs to make sure they continue to meet industry standards and current business needs.
Conclusion
In summary, servers have a unique set of hazards that span the technical, operational, financial, compliance and legal realms yet provide unmatched performance and control. To address these threats, a complete approach incorporates strong security measures, dependable configuration and maintenance procedures, scalability planning, compliance with regulatory requirements, and responsible financial management. Enterprises can fully utilize servers to stimulate expansion and creativity by comprehending and mitigating these hazards.
Businesses may reduce many of these risks by connecting to organizations like RedSwitches. With the benefits of professional management, cutting-edge security, and adaptable scalability options, we offer servers with excellent performance and dependability.
FAQs
Q. Is it safe to host a server?
With the right security measures in place and routine maintenance, hosting on a server can be secure.
Q. Why is a server more secure?
They are more secure because servers only use their resources and have customizable security settings.
Q. Do I need a server?
You need a server if your application or website demands maximum management, security, and performance.
Q. What is server hosting?
Server hosting is a type of web hosting where a client leases an entire server for their exclusive use, providing them with full control over the server and its resources.
Q. What are the advantages of dedicated hosting?
Dedicated hosting offers greater security, reliability, and performance than shared hosting. It also provides more control over the server and the ability to customize it to meet specific needs.
Q. What are the disadvantages of server hosting?
Dedicated hosted server hosting can be more costly than shared hosting and may require technical expertise to manage effectively. Additionally, maintenance and security responsibilities fall solely on the client.
Q. How can I secure my dedicated server?
To secure your dedicated hosted server, ensure you regularly update software and security patches, use strong passwords, implement firewalls, and consider encryption methods to protect data.
Q. What are some dedicated hosted server security best practices?
Best practices for dedicated hosted server security include regularly monitoring unusual activity, encrypting sensitive data, restricting access to authorized users, and implementing intrusion detection systems.
Q. How does dedicated server security compare to shared hosting in terms of security level?
Dedicated hosted server security offers a higher level of security compared to shared hosting since resources are not shared with other users, reducing the risk of security breaches and unauthorized access.
Q. What hosting options are available as an alternative to dedicated hosting?
Some alternative hosting options include virtual private server (VPS) hosting and managed hosting, which provide varying levels of control and management based on individual needs.