Key Takeaways
- An IP address is a unique set of characters identifying every device using the Internet to communicate over a network.
- IP addresses are important for enabling communication over the Internet, security, location tracking, etc.
- IPv4 is the original Internet protocol used since the 1980s.
- IPv6 is a 128-bit address system developed to address IPv4 exhaustion.
- IP addresses are assigned either dynamically by a DHCP server, which allocates them as devices connected to a network, or statically, where a network administrator manually sets them.
- Best practices for IP address allocation include planning an IP address scheme, using subnetting, implementing Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, having a record, etc.
- Types of IP addresses include Consumer IP addresses, Private IP addresses, Public IP addresses, etc.
- Two types of website IP addresses include shared IP addresses and dedicated IP addresses.
- When deciding between shared vs dedicated IP address, factors include SEO, security, budget, and site traffic.
- Strategies to protect your IP address include using a VPN, enabling private browsing, using public Wi-Fi with caution, etc.
With abundant new devices connecting to the internet daily, efficient IP address allocation has become critical today. According to a report, there are nearly 17.08 billion connected IoT devices in 2023. This noteworthy number shows the need for effective IP address management strategies.
Proper allocation of IP addresses is more than just a matter of operational convenience. It is critical for ensuring smooth connectivity, security, and scalability in any network infrastructure. This blog takes readers through the best practices for allocating IP addresses.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is an IP Address?
- What is the Importance of IP Address?
- What is IPv4?
- What is IPv6?
- How are IP Addresses Assigned?
- Best Practices for Allocating IP Addresses
- Challenges in IP Address Allocation and their Solutions
- Types of IP Addresses
- What are The Two Types of Website IP Addresses
- Factors to Consider: Shared vs Dedicated IP Addresses
- Strategies to Protect Your IP Address
- The Role of Dedicated Servers in IP Allocation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is an IP Address?
Credits: FreePik
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is like a home address but for your computer or device on the Internet. It’s a unique set of numbers separated by periods, like 192.168.1.1. This helps identify each device connected to the Internet.
Just as your home address lets people send you mail, an IP address lets computers send and receive information from other computers. It’s essential because it ensures that when you go online and ask to visit a website or send an email, the Internet knows where to send the website’s data or where the email needs to go.
There are two types of IP addresses. The first is IPv4, the traditional format with around four billion addresses. The second type is IPv6, a newer format created to provide many addresses as the Internet grew and more devices needed unique addresses. An IP address is an important aspect of how the Internet works, acting to identify and locate billions of devices on the vast Internet network.
Are you struggling to find your IP address in Linux? Read our informative piece, ‘How To Find Your IP Address In Linux | 4 Easy Ways,’ for answers.
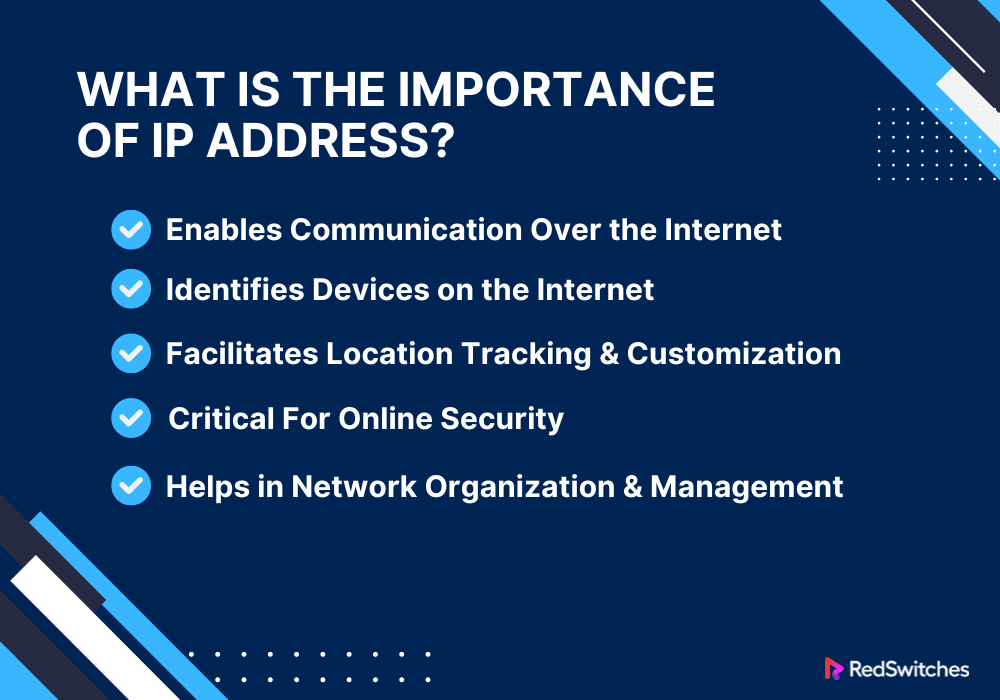
What is the Importance of IP Address?
The importance of an IP address in the digital world is multi-faceted and extends beyond the basic functionality of enabling internet connectivity. Below are factors to help you understand its significance:
-
Enables Communication Over the Internet
An IP address acts like a digital postman. Imagine you’re sending a letter. You need the correct address to reach the right person. Similarly, when you’re online and want to send an email or visit a website, your device requires the correct IP address of the recipient or website.
This address ensures your email reaches the right inbox or lands on the correct website. The internet could not function without IP addresses, as there would be no way to direct information to its proper destination.
-
Identifies Devices
The IP address is your device’s identity on the internet. Similar to how your fingerprint identifies you, your device’s IP address identifies it on the internet. This unique identification is critical, especially today, where countless devices are connected to the internet. It ensures that when you request information or a service online, your device receives it, not someone else’s.
-
Facilitates Location Tracking and Customization
Have you ever wondered how websites know what language to display or why some online services are unavailable in your region? This is where IP addresses come in. They provide an approximate location of where your device is accessing the internet.
This location-specific data is used by websites to edit their content, like showing you news relevant to your area or items that can be shipped to your location. This customization improves your online experience by making it more relevant.
-
Security
IP addresses are critical for online security. They can be used to track down devices involved in malicious activities. For instance, if a specific IP address is consistently involved in cyber attacks or spamming, it can be blocked by websites or internet service providers, acting as a defense against cyber threats. Monitoring IP addresses also helps pinpoint unusual patterns that could signal security breaches.
-
Helps in Network Organization and Management
IP addresses are crucial for network organization in multiple-device environments. Some examples include corporate offices or university campuses. They enable network administrators to find and manage devices on the network easily.
If a specific computer is causing network issues, the administrator can use its IP address to locate and address the problem. In setting up networks, assigning IP addresses to each device helps organize the network systematically, ensuring smooth operation and easy troubleshooting.
Also Read: Learn About IP Addressing Schemes And Subnet Masks.
What is IPv4?
Credits: Freepik
IPv4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4. It’s slightly comparable to postal service of the Internet, a set of rules that helps direct data to the right place. An IPv4 address is made up of four numbers separated by dots.
For instance, an IPv4 address might look like this: 189.168.1.1. Every number set can range from 0 to 255. This format offers many possible combinations. It still does have a limit on how many addresses it can form.
What Does IPv4 Do?
IPv4 is a specific version of this Internet Protocol. It’s responsible for identifying devices on a network and routing data between them. Every device linked to the Internet requires its own IP address, a series of numbers that identifies that specific device. IPv4 creates these addresses.
Why is IPv4 Important?
IPv4 is important because it’s one of the main protocols for the Internet. Sending and receiving data over the Internet would be chaotic and disorganized without IPv4. It can be compared to having a mail system without addresses or postal codes.
The Limitation of IPv4
One issue with IPv4 is that it can only create about 4 billion unique IP addresses. This may sound like a lot, but we are running out of these addresses due to the high number of devices linking to the Internet. This limitation has led to the development of a new version called IPv6. This version can create a much larger number of addresses.
How IPv4 Works in Everyday Life
IPv4 is operational in the background whenever you visit a site, play a video, or send an email. It directs the data you send and receives to the right devices. Whether using Wi-Fi at home or data on your phone, IPv4 keeps you linked to the online space.
Also Read: Add Additional IPv4 Addresses on Windows Server 2019 in 4 Simple Steps
What is IPv6?
Credits: Freepik
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6. It’s the newest Internet Protocol version. IPv6 was developed to replace IPv4, the previous version, which has existed since the Internet’s early days.
Why Do We Need IPv6?
The main reason for IPv6 is the need for more IP addresses. Think of it like phone numbers. We need more unique phone numbers as more people get phones. Similarly, we need more unique IP addresses as more and more devices link to the Internet.
IPv4, a 32-bit addressing scheme, can support about 4.3 billion addresses. That sounds like a lot, but we’ve already run out of them. IPv6, with its 128-bit addressing, can support a greater number – 340 undecillion addresses.
The Importance of IPv6
IPv6 addresses is important because of the enormous amount of IP addresses it can generate. This means we’re unlikely to run out of IP addresses anytime soon. IPv6 allows internet data to be routed more efficiently. This can lead to quicker and more reliable internet connections.
IPv6 was also designed with a focus on security. It has built-in features for encrypting data and ensuring data packets are authentic, which is not standard in IPv4. With IPv6, devices can automatically configure themselves when connected to an IPv6 network, thanks to a process called address auto-configuration.
Challenges in Adopting IPv6
The adoption of IPv6 has been slow despite its many benefits. One reason is the sheer scale of replacing or upgrading countless internet-connected devices and systems to be IPv6 compatible. Since IPv4 and IPv6 aren’t directly compatible, running them side-by-side can be complex.
IPv6 and Everyday Internet Use
The transition to IPv6 won’t be noticeable for most Internet users. It’s more of a behind-the-scenes change. It’s a necessary evolution to ensure that the Internet can keep growing and adding new devices. Over time, more websites and online services will transition to IPv6. This transition is gradual, and many systems now use both IPv4 and IPv6.
Also Read: Dedicated IP Vs Shared IP: Differences, Benefits & Their Impact.
How are IP Addresses Assigned?
Credits: Freepik
Connecting to the internet is similar to getting an entry ticket at an event. Each ticket (or IP address) lets you access the event (or network). Here is how this “ticketing” process works when devices connect to a network:
Connecting to a Network
Imagine entering a Wi-Fi network like walking into a cafe with free Wi-Fi. When you enter (connect), you ask for a ticket to use their service.
- Requesting an IP Address: As soon as your device connects to the network, it looks for an IP address. This is like asking the cafe staff for a Wi-Fi code.
DHCP Server Response
Most home and office networks have a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. This is usually part of your router.
- Assigning an IP Address: The DHCP server listens to your device’s request and gives it an IP address. This address is usually temporary (dynamic). It’s like the cafe staff giving you a Wi-Fi code that changes daily.
For Static IPs
Sometimes, a device needs a special, unchanging IP address. This is called a static IP address.
- Setting Up a Static IP: An IT professional can manually set this up on your device. Once set, this IP address doesn’t change, even if you disconnect and reconnect to the network. It’s similar to having a VIP pass to the cafe, where you have a special code that consistently works just for you.
For Public IPs
Things are slightly different when it comes to accessing the broader internet. Your Internet Service Provider plays a significant role here.
- ISP Assigning Public IPs: The ISP has several IP addresses, like a stack of tickets. When your home or business network connects to the internet, the ISP gives your network a public IP address. This address represents your entire home or business on the internet. It’s like the cafe having its unique address in the city.
Best Practices for Allocating IP Addresses
Credits: FreePik
IP address allocation is an important aspect of network management. It involves assigning unique identifiers to each device within a network, ensuring efficient communication and management.
IP address allocation can become chaotic without proper planning and practices. This can lead to IP conflicts and network inefficiency. This makes it critical for one to follow IP address allocation best practices. Here are a few best practices for allocating IP addresses:
Plan Your IP Address Scheme
- Understand Your Network’s Size and Scope: Assess the number of devices that will be connected to your network. This understanding will help guide your IP address allocation strategy.
- Choose Between IPv4 and IPv6: IPv4 is the most commonly used IP version but has few addresses. IPv6 offers a much larger address space. Choose the appropriate version depending on your network’s size and future growth.
Use Subnetting
Subnetting is dividing a network into smaller, manageable parts (subnets). This makes network management more efficient and improves security.
- Organize Network into Subnets: Divide your network logically based on departments, usage types, or geographical locations.
- Allocate IP Addresses to Subnets: Assign each subnet a range of IP addresses. Doing so helps in managing traffic and improving security.
A subnet calculator can be an invaluable tool here. It helps you divide your network logically and allocate IP ranges accordingly.
Why Use a Subnet Calculator?
- Efficiency: It automates the calculation process, reducing errors.
- Optimization: Helps in optimal utilization of IP address space.
- Simplification: A subnet calculator makes subnetting more accessible, especially for complex networks.
Implement Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP automatically allocates IP addresses to devices on a network. This automation reduces the chances of IP conflicts and eases the management burden.
- Configure DHCP Server: Set up a DHCP server to manage and automate the IP address allocation process.
- Reserve IP Addresses: For critical devices like servers and printers, reserve static IP addresses to ensure they always receive the same IP.
Maintain a Record
A detailed record of IP address allocations is essential for troubleshooting and managing the network effectively.
- Document IP Addresses: Maintain an up-to-date record of all allocated IP addresses, including static and dynamic assignments.
- Regularly Update Records: Whenever a change is made in the network or a new device is added, update the documentation accordingly.
Also Read: How To Assign Floating IP In Leaseweb With Your Subnet In New Ways.
Implement IP Address Management (IPAM) Tools
IPAM tools can automate many aspects of IP address management, making the process more efficient and less prone to errors.
- Choose an IPAM Solution: Select a tool that suits your network’s size and complexity.
- Integrate IPAM with Your Network: Ensure your IPAM tool fully integrates with your network infrastructure for optimal performance.
Regularly Review and Optimize Your IP Address Scheme
The network needs to evolve with time. Regularly review your IP address allocations to meet your network’s needs. Always be prepared to restructure your IP addressing scheme to adapt to changes in your network.
Follow Security Best Practices
Securing your IP addresses is crucial to protect your network from threats.
- Use Private IP Addresses for Internal Network: Use private IP ranges for devices within your network to enhance security.
- Implement Firewalls and Network Segmentation: Use firewalls to control traffic and segment your network to contain potential breaches.
Challenges in IP Address Allocation and their Solutions
Credits: Freepik
IP address allocation has its challenges. Below, we explore some of the top challenges linked to IP address allocation and their solutions.
Depletion of IPv4 Addresses
IPv4 addresses are limited to approximately 4.3 billion unique combinations. This number seemed plentiful when the Internet came about. However, the exponential growth in Internet users and the addition of smart devices and IoT (Internet of Things) changed this. It brought us to a situation where the availability of new IPv4 addresses became critically low.
Regional Variations
The rate of IPv4 exhaustion varies globally. Some regions have already drained their allotment, while others are quickly approaching this point. This difference can cause operational challenges and inequities in internet accessibility and growth potential across various geographical areas.
Solutions for IPv4 Depletion
Let’s discuss some possible solutions to IPv4 Problems.
Adoption of IPv6
IPv6 addresses this limitation with its 128-bit address space. It offers around 340 undecillion unique IP addresses. This enormous capacity is more than sufficient to accommodate future growth.
- Gradual Transition: The shift to IPv6 isn’t instantaneous. It requires strategic planning and investment in IPv6-compatible hardware and software.
- Benefits: IPv6 offers enhanced security features and more efficient routing besides addressing depletion.
IP Address Sharing
Network Address Translation is important in mitigating IPv4 depletion. It enables multiple devices in a private network to share the same public IPv4 address.
- Types of NAT: Solutions like Port Address Translation enable multiple internal requests to be translated into a single IP address with varying port numbers.
- Limitations: Although NAT helps conserve IP addresses, it can complicate network configurations and restrain certain services, like peer-to-peer applications.
Efficient IP Address Management
Efficient management of existing IP addresses becomes necessary as we navigate the challenges of IPv4 depletion.
IP Address Management (IPAM) Tools
These tools offer a centralized platform for locating and managing IP addresses, ensuring optimal resource use.
- Features: Advanced IPAM solutions offer automated address allocation, real-time tracking, and detailed reporting.
- Integration with DHCP and DNS: Effective integration with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and Domain Name System management is essential for streamlined operations.
Addressing Security Concerns
With the growing complexity of IP address allocation, security risks also escalate.
Enhancing Security Measures
Implementing vigorous security protocols is critical to protect against IP spoofing and hijacking dangers.
- Access Control: Implementing stringent access controls and authentication mechanisms for accessing IPAM tools and network configurations.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: Continuous monitoring for unusual activities and routine audits of IP address allocations are essential in specifying and mitigating potential security threats.
Compatibility and Transition Challenges
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is a necessary evolution in internet technology. It is, however, not without its challenges, especially regarding compatibility and infrastructure readiness. Let’s discuss these challenges and the solutions to facilitate a smoother transition.
The Complexity of Transitioning
- Technical Incompatibility: IPv4 and IPv6 are incompatible. This means devices and services created for IPv4 cannot communicate with those developed for IPv6. This is a major challenge in terms of maintaining connectivity and services during the transition period.
- Legacy Systems: Many organizations have legacy systems and infrastructure that only support IPv4. Upgrading or changing these systems can be expensive and complex. It may demand considerable planning and resources.
Solutions for Transition Challenges
Let’s discuss some possible solutions for Transition Challenges.
Dual Stacking
Dual stacking involves running IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously on the same network. This approach allows for a gradual transition by maintaining compatibility with both protocols during migration.
- Operational Flexibility: It offers flexibility, allowing network administrators to manage the transition at a pace that suits their organization’s needs.
- Challenges: Running two protocols requires careful configuration to avoid complexities and potential security vulnerabilities.
Upgrading Infrastructure
Investing in new infrastructure is critical for a complete transition to IPv6. This includes upgrading routers, switches, and servers to support IPv6 natively.
- Long-Term Investment: Although the initial cost can be high, this is a long-term investment in the network’s future scalability and security.
- Vendor Support: Choosing vendors and solutions that offer robust IPv6 support is crucial.
Want to learn more about IPv4 and IPv6? Read our blog, ‘Evolving Internet Protocols: IPV4 Vs IPV6 Compared.
Dynamic IP Address Allocation Issues
While efficient, the dynamic allocation of IP addresses introduces its own challenges.
Problems with Dynamic Allocation
- IP Conflicts and Connectivity Issues: Dynamic allocation can sometimes lead to IP conflicts, where two devices are inadvertently assigned the same IP address, leading to connectivity issues.
- Managing a Fluid Network Environment: Managing a constantly changing set of IP addresses can be challenging in dynamic environments, especially with mobile devices and IoT.
Solutions for Dynamic Allocation
Now Let’s discuss some possible solutions for Dynamic Allocation.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP is a network management protocol that automates the assignment of IP addresses.
- Efficient Management: DHCP servers assign IP addresses for a specific lease time, ensuring efficient use of an IP address pool.
- Flexibility: DHCP allows for easy reconfiguration of IP settings on the network without manual intervention.
Lease Time Management
Proper management of DHCP lease times is essential in dynamic environments.
- Optimizing Lease Times: Setting appropriate lease times can reduce the likelihood of IP conflicts and address exhaustion.
- Adapting to Network Needs: Lease times can be adjusted based on the network’s specific needs, such as shorter leases for guest networks.
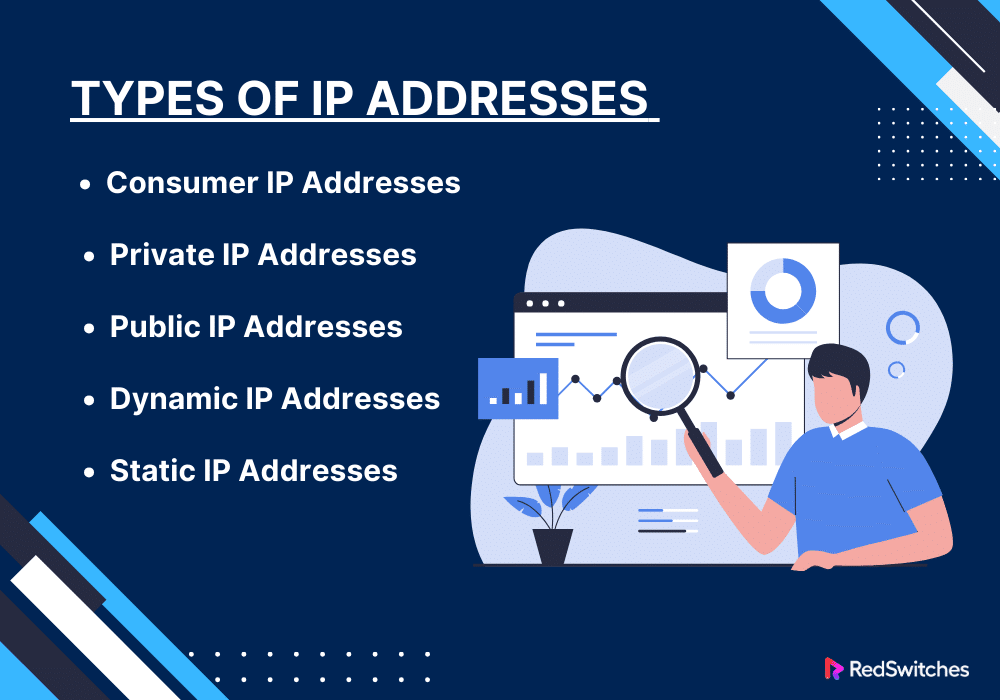
Types of IP Addresses
There are different types of IP addresses. Each serves a specific purpose. It is important to understand each IP address, its role, functionalities, etc. Here is an in-depth breakdown of the different types of IP addresses:
Consumer IP Addresses
Consumer IP addresses are IP addresses usually assigned to individuals or households by Internet Service Providers. These addresses are used for personal internet access. Consumer IPs can be dynamic or static (discussed below). The key feature of consumer IP addresses is that they are allocated for standard, non-commercial internet usage, like browsing, streaming, or gaming.
Private IP Addresses
Private IP addresses are used in a private network. They are not visible on the public internet. These are the addresses your home or office router assigns to each device on your local network. Examples include your computer, smartphone, or printer. Private IP addresses allow multiple devices in the same network to communicate.
The range of private IP addresses is defined in the IPv4 and IPv6 standards and cannot be routed through the public internet. This makes private IPs ideal for internal network security and efficiency.
Public IP Addresses
Public IP addresses are used globally and must be unique across the entire internet. These are the addresses that ISPs assign to each of their customers. When you open a website, your public IP address is how the website knows where to send the data. Public IP addresses are essential for external communication over the internet. They enable different networks worldwide to connect and interact.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Dynamic IP addresses are temporary. They are assigned to a device each time it connects to the network. A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server within the network typically manages and distributes these addresses. This includes your router or ISP.
A standout advantage of dynamic IPs is their efficiency in reusing addresses. They are ideal for consumer and business networks where devices frequently come and go. This is because they eliminate the need for manual IP configuration and reduce the risk of IP address conflicts.
Static IP Addresses
Static IP addresses are fixed. They do not change over time. These addresses are manually assigned to a device and remain constant until changed manually. Static IPs are beneficial when a device needs a constant address. For instance, a server hosting a website or a remote access system.
They provide reliable and consistent remote access. This makes them ideal for businesses with fixed network infrastructure. However, static IPs require more management and are more likely to experience security risks if not properly secured. This is because their constant nature can make them easier targets for malicious activities.
What are The Two Types of Website IP Addresses
Credits: Pexels
Website IP addresses come in two main types: shared and dedicated. Both have their unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Here is more information on the two types of website IP addresses:
Shared IP Address
A shared IP address refers to an IP address used by numerous websites or domains. This setup involves a server hosting several websites with the same IP address. This is a common practice in web hosting, especially in shared hosting environments where multiple clients’ websites are hosted on the same server infrastructure.
How Shared IP Addresses Work
Here’s how shared IP addresses work:
- Hosting Structure: Multiple websites are hosted on a single server. They share the server’s resources.
- Traffic Routing: The server uses the same IP address to route traffic to all these websites. The HTTP/HTTPS header contains the domain name. This tells the server which website the user is trying to access.
- Domain Name Resolution: The server’s software, like Apache, reads the request and serves the appropriate website content based on the domain name.
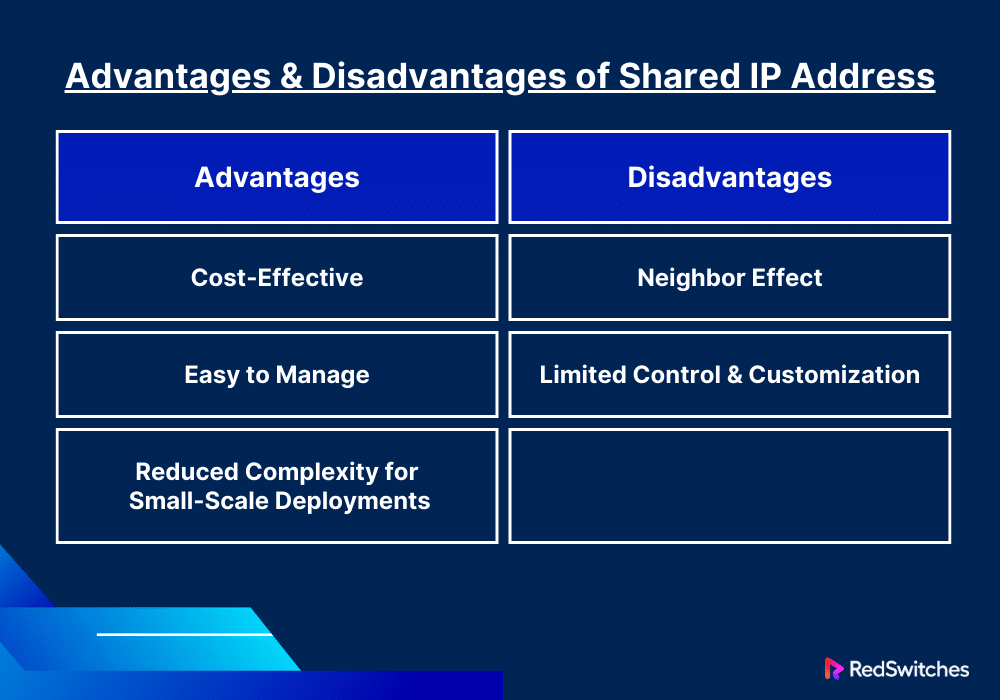
Advantages
Shared IP addresses offer several advantages in various network and web hosting scenarios:
- Cost-Effective: Shared IP addresses are generally more affordable. This makes them best for small businesses or personal websites with limited budgets.
- Easy to Manage: Shared IPs offer a seamless experience. This is mainly because the hosting provider handles the technical aspects. This includes server maintenance and software updates.
- Reduced Complexity for Small-Scale Deployments: Shared IP addresses offer a simplified setup. This is ideal for individuals or small businesses with basic website requirements. The setup eliminates the need for complex network configurations.
Disadvantages
While shared IP addresses offer advantages, they also come with some disadvantages:
- Neighbor Effect: If one website on a shared server is blacklisted by search engines or flagged for spamming, it can negatively impact all other websites sharing the IP. This is because the IP address’s reputation affects all associated domains.
- Limited Control and Customization: Users have less control over server settings and resources. For instance, installing specific software or performing custom server configurations is often not possible.
Use Cases
- Small business websites with limited traffic.
- Personal blogs or portfolio websites.
- Startups looking for cost-effective hosting solutions.
- Websites without the need for SSL certificates for online transactions.
- Users with basic hosting needs and minimal technical expertise.
Also Read: Your Ultimate Cheat Sheet To IP Transit.
Dedicated IP Address
A dedicated IP address is a distinctive Internet Protocol address exclusively assigned to a single hosting account or website, offering higher control and stability. This exclusivity distinguishes it from shared IP addresses, where multiple websites use one IP.
How Dedicated IP Addresses Work
Here’s how dedicated IP addresses work:
- Unique Assignment: Each website or hosting account is assigned a unique IP address.
- Hosting Flexibility: While typically associated with dedicated servers, a dedicated IP can also be used in a shared hosting environment, providing a unique identity to a website on a shared server.
- Direct Access: Websites with a dedicated IP can be accessed directly via the IP address, facilitating specific tasks and setups.
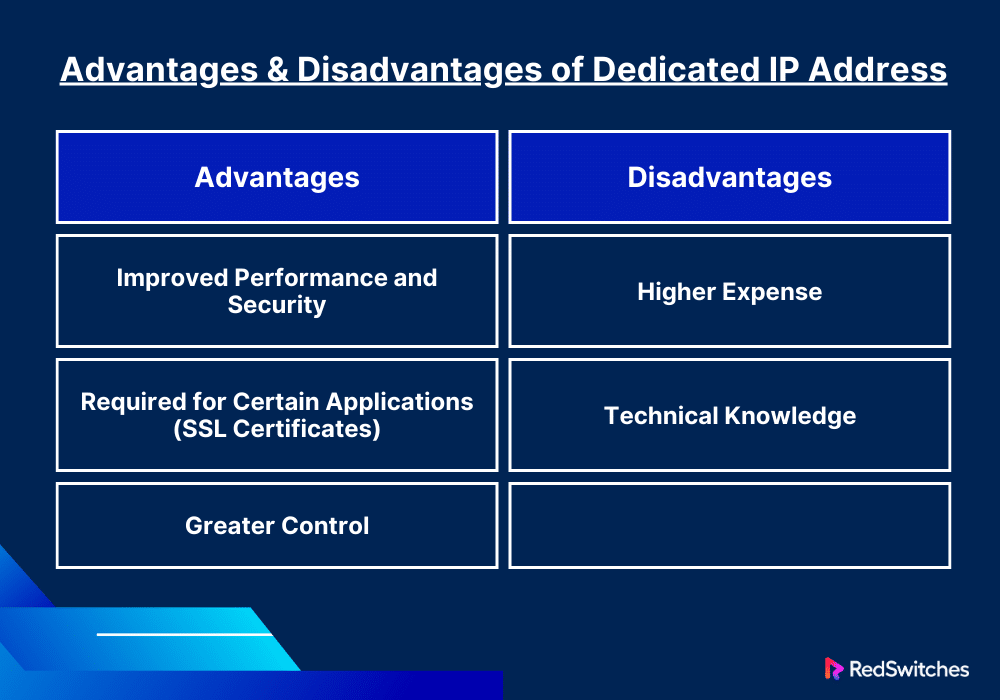
Advantages
Dedicated IP addresses offer several advantages in various network and hosting scenarios:
- Improved Performance and Security: Being the sole occupant of an IP address means the site’s performance isn’t affected by other sites’ traffic and usage patterns. Dedicated IPs also reduce the risk of IP blacklisting due to other websites’ malpractices.
- Required for Certain Applications (SSL Certificates): Essential for websites that handle sensitive transactions, such as e-commerce sites. A dedicated IP facilitates the installation of these certificates.
- Greater Control: Dedicated IPs enable more control over DNS settings. This is important for larger websites or those with specific technical requirements. They also allow for more advanced server configuration and customization options.
Disadvantages
Despite the advantages, dedicated IP addresses also come with some disadvantages:
- Higher Expense: Dedicated IPs come with additional costs. They also often require more expensive hosting plans with dedicated IP functionality. This can be major drawback for small businesses or individual users.
- Technical Knowledge: Dedicated IPs require more technical expertise to manage and configure. Users also need to be more involved in server administration. This may be stressful for those lacking technical backgrounds.
Use Cases
- E-commerce websites requiring SSL certificates for secure transactions.
- Large corporate sites with high traffic volumes.
- Websites needing specific server customizations.
- Services requiring a stable and consistent IP address (example: email servers).
- Websites under compliance regulations that demand heightened security measures.
Factors to Consider: Shared vs Dedicated IP Addresses
Several critical factors should be considered when contemplating a dedicated and a shared IP address for your website. Doing so helps ensure your choice aligns with your website’s needs and goals. Below are a few factors to consider when choosing between shared vs dedicated IP addresses:
SEO Impact
Credits: Freepik
The impact of IP addresses on SEO is a topic of much debate. Having a shared IP address does not negatively impact a website’s SEO. Search engines have become capable enough to recognize different websites on a shared IP.
If a website on a shared IP is involved in malicious activities and gets blacklisted, this can have a collateral impact on other sites sharing the IP. A dedicated IP eliminates this risk, as the IP reputation is entirely in your control.
Website Traffic and Resources
Credits: Freepik
The traffic volume your website expects to handle is a significant consideration. For high-traffic sites, a dedicated IP address can be beneficial. It offers more stability and can handle higher traffic loads without the risk of being affected by other sites’ traffic surges, a common issue with shared IPs.
A dedicated IP can provide these resources more reliably if your website requires significant resources. This includes higher bandwidth, more storage, or enhanced processing power.
Security Needs
Credits: Freepik
Security has become a need instead of a choice for websites handling sensitive transactions. This includes e-commerce sites, financial services, or any platform dealing with personal user data. A dedicated IP address offers a higher level of security.
It allows for installing SSL certificates, crucial for encrypting data and secure communication. Having a dedicated IP can help implement more stringent security measures and protocols. This might be necessary to comply with various data protection regulations.
Budget
Credits: Freepik
The website hosting and management budget is crucial for many, especially for small businesses or personal websites. Shared IP addresses are more cost-effective, as the server and IP address cost are distributed among all the websites hosted on that server.
This makes it an attractive option for those who are budget-conscious. However, weighing the cost savings against potential drawbacks, such as the ‘neighbor effect’ and limited control, is important.
Also Read: How To Check Server Location? 8 Simple Steps Guide.
Strategies to Protect Your IP Address
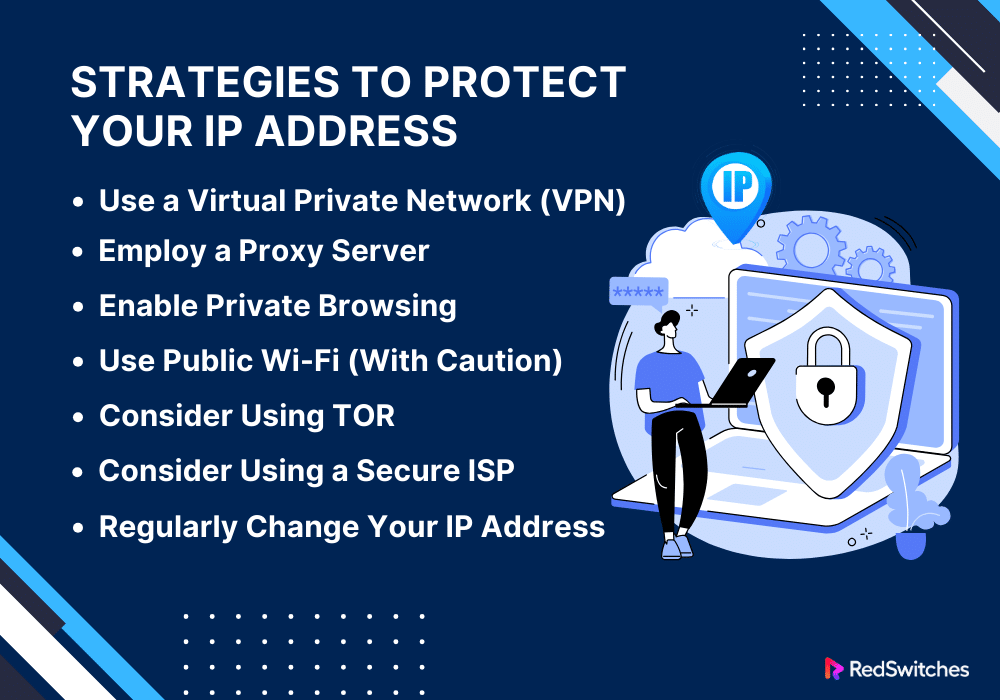
Below are a few strategies to protect your IP address:
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network is one of the best ways to protect your IP address. With a virtual private network (VPN), your internet connection is encrypted and routed via a server located wherever you choose.
This process masks your IP address and replaces it with one from the VPN server. While keeping your IP address hidden from websites and ISPs, a VPN also helps secure your data from eavesdroppers.
Employ a Proxy Server
Proxy servers function similarly to VPNs. They act as intermediaries between the internet and your device. When you use a proxy server, your internet traffic is routed through the proxy server, hiding your actual IP address.
Proxies can be helpful in bypassing geo-restrictions or for basic IP masking. However, they often lack the strong encryption VPNs offer, making them less secure.
Enable Private Browsing
Most modern web browsers offer a private browsing mode (like Incognito in Google Chrome). While private browsing doesn’t hide your IP address from external entities, it can prevent your browser from storing information about your browsing session. This includes cookies, history, or form inputs. This is particularly useful for protecting your privacy from others who might use the same device.
Use Public Wi-Fi (With Caution)
Connecting to public Wi-Fi can effectively mask your home IP address. It does, however, come with considerable security risks. Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them hotbeds for cybercriminal activity. If you choose this method, using a VPN to encrypt your connection and shield your data from potential threats is crucial.
Consider Using TOR
The TOR (Onion Router) is a free network for anonymous communication. It routes your internet traffic through several servers, encrypting it at every step. This makes tracing your IP address extremely difficult. Although TOR is a powerful tool for maintaining anonymity, it can slow down your internet connection. It is also unsuitable for data-heavy activities like streaming or downloading large files.
Consider Using a Secure ISP
Some Internet Service Providers prioritize user privacy and offer services like dynamic IP allocation. This is where your IP address constantly changes. These ISPs may also provide built-in VPN services. This makes it essential to research reliable ISPs in your area and consider switching to one that offers these privacy-boosting features.
Regularly Change Your IP Address
If you’re using a dynamic IP address common with many ISPs, you can change it by restarting your router. This might not be a foolproof method for protecting privacy. However, regularly changing your IP address can make it more challenging for someone to track your online activities over time.
Challenges and Considerations
Although the above strategies offer protection for your IP address, they also come with challenges, including:
- VPN and Tor Network: Tor and VPN sometimes slow internet connections due to the encryption process and traffic routing through several servers.
- Proxy Servers: Not all proxies are secure. Using reputable proxy services is crucial to avoid exposing your data to potentially malicious operators.
- Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi can still come with risks, even when using a VPN. This makes it essential to be cautious about the activities you perform on these networks.
Also Read: Quick Guide To Modify CentOS 7 Network Config Files.
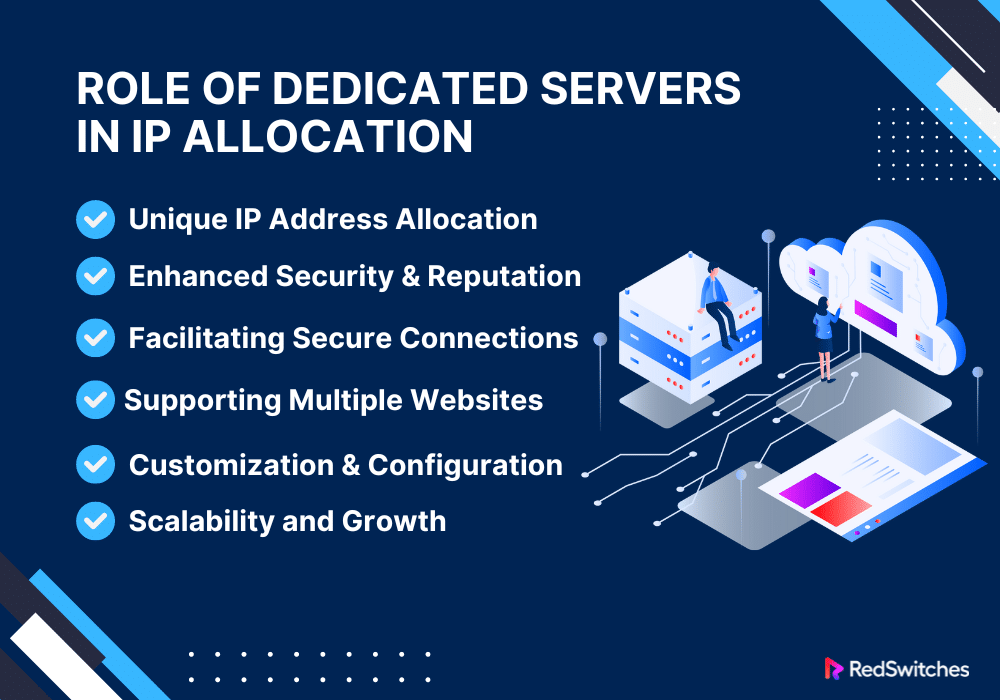
The Role of Dedicated Servers in IP Allocation
Credits: Freepik
Below, we shed light on the role of dedicated servers in IP allocation becomes crucial:
Understanding Dedicated Servers
A dedicated server is a remote server completely dedicated to an organization, individual, or application. Unlike shared servers, it is not shared with multiple users or organizations. These servers offer robust performance, security, and control over the server environment.
Key Characteristics of Dedicated Servers
Here are some key characteristics of dedicated servers:
- Exclusive Use: Dedicated servers provide exclusive resources to the user, including CPU, memory, and disk space.
- Performance and Reliability: They offer high performance and reliability since resources are not shared.
- Security and Control: Users have greater control over server configuration, enhancing security and customization.
- Cost: Dedicated servers are more costly than shared hosting solutions, reflecting enhanced capabilities.
The Role of Dedicated Servers in IP Allocation
Below are a few ways a server plays an integral role in IP allocation:
Unique IP Address Allocation
Each server is typically assigned a unique IP address. This exclusive allocation ensures that the server can be easily identified on the network. It boosts security, and lowers the risk of IP address conflicts common in shared hosting environments.
Enhanced Security and Reputation
Having a unique IP address associated with a server can improve security. It allows for more precise control over inbound and outbound traffic. A unique IP reduces the risk of being blacklisted or negatively impacted by other users’ actions, a common concern in shared IP environments.
Facilitating Secure Connections
Dedicated servers often host websites that require secure connections (HTTPS). A unique IP address is necessary for SSL certificates, which are crucial for encrypting data and ensuring secure transactions.
Supporting Multiple Websites
Organizations using servers can host multiple websites, each with a unique IP address. This setup is beneficial for SEO and helps differentiate traffic and analytics for each site.
Customization and Configuration
Organizations can customize IP address allocation with servers based on their needs. This flexibility includes setting up subnet masks, configuring gateways, and managing DNS settings, which is vital for larger organizations or those with specific network requirements.
Scalability and Growth
As organizations grow, their need for IP addresses increases. Dedicated servers allow for scalable IP allocation strategies, ensuring that businesses can expand their online presence seamlessly without the constraints of limited or shared IP resources.
Conclusion
Efficient IP address allocation is an important aspect of robust network management. Following the best practices in IP address management discussed above can offer several advantages. Some major benefits include operational efficiency, fortifying network security, and preparing the infrastructure for scalable growth.
Regarding efficient IP address allocation, the expertise and solutions offered by RedSwitches are invaluable. We are known for offering premium hosting services and providing many solutions tailored to businesses’ unique needs in managing their network resources.
RedSwitches is a reliable partner in optimizing your IP address allocation strategy. We ensure your network’s integrity and help your business in the evolving digital space. Explore our services now to discover how we can help transform your network management practices.
FAQs
Q. What is the IP address?
An IP address is a distinctive numerical designation assigned to every device linked to a computer network that communicates using the Internet Protocol. It fulfills two primary purposes. It gives the host’s location within the network and locates the host or network interface.
Q. How to find IP address?
Those wondering how to find my IP location, can follow the directions below:
- On Windows: Access Command Prompt and type ipconfig to find your IP address location under the relevant network adapter.
- On macOS: Go to System Preferences > Network. Choose the network connection, and your IP address will be visible.
- On Linux: Use the ifconfig or ip addr command in the terminal.
- On Mobile Devices: Go to your device’s network settings. Find your IP location listed under the Wi-Fi or mobile data network information.
- Online: You can also lookup an IP address using various online tools and websites specifically designed for IP address lookup.
Q. What is the IP address code?
The term IP address code is not a common term. In the context of the format of an IP address, it’s a numerical label. For IPv4, it is a 32-bit number (e.g., 192.168.1.1). For IPv6, it is a 128-bit number (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:7a2e:0380:7534).
Q. How do IP addresses work?
IP addresses work by serving as a distinctive identifier for devices on a network. This allows them to communicate with each other and exchange data.
Q. What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses?
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numerical addresses. IPv6 addresses are 128-bit hexadecimal addresses. They offer a larger address space for devices and improved security features.
Q. Why is IP address security important?
IP address security is crucial for protecting personal privacy. It prevents unauthorized access and protects against cyber threats and malicious activities.
Q. How can I hide my IP address?
You can hide your IP address using a proxy server or VPN (virtual private network). Doing so enables you to browse the internet anonymously.
Q. What is a MAC address?
A MAC address, or Media Access Control address, is a unique number linked to network interfaces so that they can communicate with one another inside a network segment.
Q. How can I find the physical location of an IP address?
You can find the physical location of an IP address using IP location tools or services available online that provide geolocation data.
Q. Why use a static IP address?
Using a static IP address ensures that the assigned address remains constant. This is beneficial for certain network configurations and applications requiring a fixed IP.
Q. What is the best way to check my IP address in Windows?
The best way to check your IP address in Windows is to use the command prompt and enter “ipconfig” to view the assigned IP address and related network information.