Key Takeaways
- Cloud servers offer unparalleled scalability and flexibility, ideal for fluctuating workloads.
- Dedicated Servers provide consistent performance and enhanced security for resource-intensive applications.
- Cloud servers utilize a pay-as-you-go model, offering cost efficiency for variable demands.
- Dedicated Hosted Servers allow extensive customization and control over the hardware and software environment.
- High availability and rapid deployment are key strengths of cloud servers.
- Dedicated Hosted Servers require a higher upfront investment but offer predictable monthly costs.
- Choosing between cloud and dedicated hosted servers depends on specific business needs, including performance, security, scalability, and cost.
Cloud servers vs dedicated servers are two powerful friends. Organizations can choose from them in their battle for online dominance. The battle is in the ever-changing world of digital technology. Deciding between them is hard. Each has distinct advantages. These suit various demands and goals. This is a crucial choice. It’s like picking between a powerful, custom off-road vehicle and a sporty, adaptable sports car for your next adventure. It’s not just about where you’re going; getting there quickly, securely, and saleably are all important factors.
We will delve into the core of this comparison. We would like to clarify the subtle differences between each server type and help you decide. You can then conclude in line with your company’s digital strategy. Come with us on this insightful journey. We will break down the key distinctions and may even find the best server for your business.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Cloud Server?
- How do Cloud Servers Work?
- Advantages of Cloud Servers
- What is a Dedicated Server?
- Advantages of Dedicated Server
- Key Differences: Cloud Servers vs Dedicated Servers
- Which one is better?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Cloud Server?
Credits: Freepik
A cloud server is a cloud-based virtual machine that operates in a cloud computing environment rather than a physical machine. It may be accessed remotely and is constructed, hosted, and supplied via the Internet using a cloud computing platform. Cloud servers can be accessed remotely from cloud service providers, but they have features and capabilities comparable to those of a regular physical server.
Cloud servers have substantial benefits about cost-effectiveness, scalability, and flexibility. Cloud servers can quickly scale up or down based on demand. This is unlike traditional physical servers. They have a set capacity and need an upfront hardware investment. This implies that companies won’t have to pay for capacity that isn’t being used and can adapt their resources to suit their current demands. Cloud servers are a great choice for websites and apps with varying traffic. This is because they can scale.
Moreover, cloud servers offer excellent performance and dependability. Data on cloud servers can be copied to many redundant servers in different regions. This setup improves data security and guarantees disaster recovery and business continuity. Redundancy raises uptime. It keeps services running if one server goes down.
Another important benefit of cloud servers is their cost-effectiveness. Businesses can save a lot of money. They only pay for the server resources they use in a pay-as-you-go model. This is instead of paying fixed fees for maintaining physical servers.
Additionally, the cloud service provider maintains and manages the cloud servers, reducing the burden on internal IT staff.
How do Cloud Servers Work?
Credits: Freepik
Cloud servers follow the cloud computing paradigm. This paradigm involves providing computer services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, via the Internet (“the cloud”) to achieve scale, flexible resource use, and faster innovation. Centralized resource management and virtualization are key components of cloud servers’ operation.
Virtualization
Cloud computing’s core technology is virtualization. It is revolutionizing how we use and manage IT resources. Fundamentally, virtualization generates a “virtual,” or software-based, image of a physical object, like a server, a storage device, or a network resource. A key component of virtualization software, the hypervisor, is essential to this procedure. It serves as a platform for executing virtual machines (VMs) and is positioned between the VMs and the actual hardware. As if it were its own, every virtual machine (VM) is allotted a fraction of the server’s resources, including memory, CPU, and storage. Because of this separation, several virtual servers can operate in perfect isolation alongside one physical server, preventing actions on one VM from interfering with those on another.
Enhanced Resource Pooling and Multi-tenancy
Resource pooling and multi-tenancy are key ideas in cloud computing. They make it possible to deliver services in a cheap and scalable way. Physical server resources from several data centers are combined. They are used to serve several customers or tenants. This is called resource pooling. The resources are pooled. They are allocated and redistributed based on demand. This model is efficient and adaptable. It is convenient because resources can quickly move from dormancy to support active applications or users. This maximizes utilization.
Multi-tenancy enhances resource pooling. It lets many clients, or “tenants,” share infrastructure and applications. They can do this while keeping the security and isolation of each tenant’s data.
Because of the economies of scale that come with this method, cloud providers may offer services at a cheaper cost while maximizing resource utilization. Crucially, each tenant’s service seems to utilize a dedicated resource despite the shared infrastructure, protecting each tenant’s data confidentiality and privacy.
Elasticity and Scalability Extensive Analysis
Understanding the adaptability of cloud services requires understanding the principles of scalability and elasticity within cloud computing. Businesses can adjust their IT resources to match fluctuating demand by leveraging scalability. Horizontal scaling (adding more machines) or vertical scaling (giving current machines more power) can accomplish this. Elasticity goes beyond scalability by enabling these resources to be automatically modified in a real-time, demand-driven manner. With this feature, applications can manage demand surges without manual intervention or a large over-allocation of resources.
Details of On-Demand Accessibility
A distinguishing feature of cloud computing is on-demand accessibility, which provides users with unmatched ease and flexibility. As long as they have internet connectivity, this capability enables people and organisations to access their virtual servers, data, and applications from anywhere in the world. Businesses with scattered or remote teams can benefit greatly from this global reach, allowing them to collaborate efficiently from any place. It also supports various use cases, such as dynamically deploying and expanding software development and testing environments and hosting websites and apps. On-demand access’s efficiency and convenience revolutionize corporate operations by encouraging adaptability and creativity.
Overseas Maintenance and Services Whole Perspective
Managed services and maintenance support cloud computing’s dependability and safety. Cloud service providers oversee the physical infrastructure that underpins their services, ensuring network and hardware components are secure, modern, and operating efficiently. This relieves clients of the responsibilities related to maintaining physical servers and includes routine maintenance, security patches, and updates.
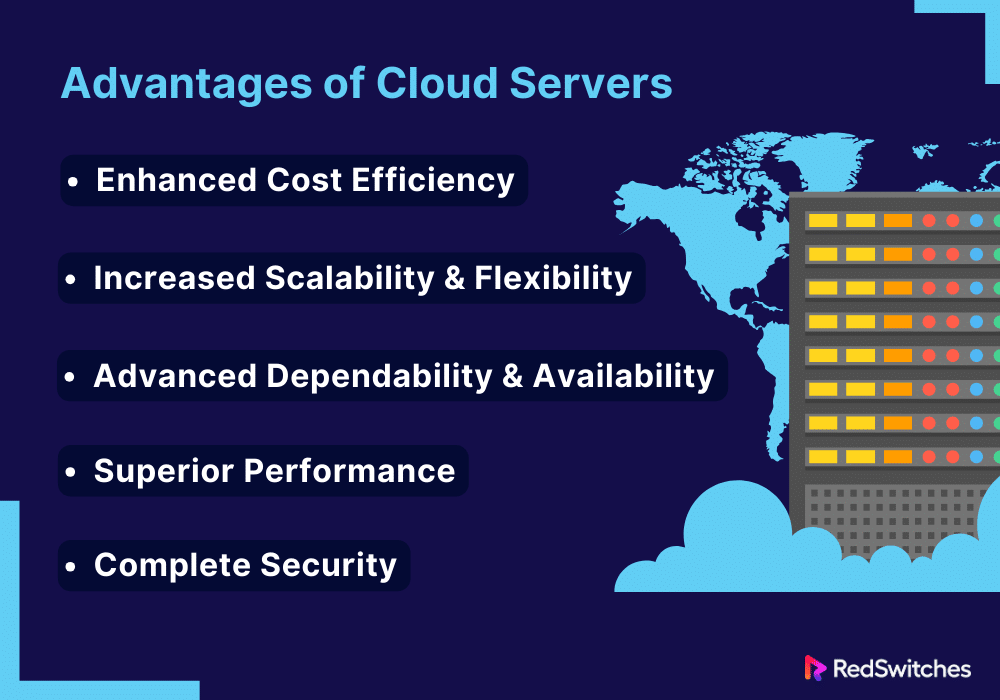
Advantages of Cloud Servers
Cloud servers have many benefits over physical servers. They are becoming increasingly popular among people and businesses. These advantages arise from the nature of cloud computing. It has qualities like the service delivery model, scalability, and virtualization. The following provides thorough justifications of the main benefits of cloud servers:
Enhanced Cost Efficiency
The advantages of cloud servers go beyond simple reductions in operating and hardware costs. Cloud changes the CapEx model to the OpEx model. This changes the financial framework for IT investment. This change gives firms more predictability and financial flexibility when creating their budgets. Also, because cloud providers are competitive, organizations can benefit from always falling prices and creative pricing strategies. These include spot pricing and reserved instances. They give more cost savings for predictable or unpredictable workloads. Cloud servers are cost-effective. They are desirable for new and established companies. These companies are trying to maximize their IT spending.
Increased Scalability and Flexibility
Credits: Freepik
Cloud servers are scalable and flexible. They go beyond just changing resources. They let companies experiment and develop with less financial risk. Developers and startups can test new concepts or applications. They can do this without making big upfront infrastructure investments. It makes it easier for businesses to quickly address client needs by expanding into new markets or launching new services. Cloud servers are adaptable. They aid agile development. They do this by enabling faster deployment and continuous integration and delivery. This speeds up the time to launch new features or goods.
Advanced Dependability and Availability
Cloud servers use advanced tech. They use load balancing, automated failover, and auto-scaling. These tools improve their dependability and availability. Auto-scaling adds or removes resources based on metrics. It ensures that applications have the resources they need to run well. Load balancing divides traffic among server instances. This prevents any one server from becoming a bottleneck. It guarantees smooth and constant application performance. Failover systems are automated. They find problems in real time and divert traffic to healthy instances. This reduces downtime. These traits and the global reach of cloud providers guarantee that companies can keep giving their users high availability worldwide.
Superior Performance
These features help a lot. They include high-speed networking, SSD storage, and access to modern computing options. These options include GPU and FPGA for specialized workloads. They all help cloud servers be faster. These properties help with workloads for machine learning. They are also useful for complex data analytics and high-performance computing (HPC). They make the workloads execute fast. Additionally, cloud providers enable configurable setups. They meet specific performance needs so that companies can optimize settings for the best results. This level of customization ensures that every app uses all of modern cloud tech. And it operates as effectively as possible.
Complete Security
In this paradigm, the customer is in charge of protecting their data in the cloud. The cloud provider oversees the security of the cloud infrastructure. This setup is key to the security benefits of cloud servers. Companies use cloud providers’ tools and services. These include identity and access management (IAM), encryption, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. They push companies to be proactive about security. These solutions help companies follow regulations. They also enforce strict access controls and constantly monitor security incidents. Also, cloud providers operate globally. They are experts on many security risks. This expertise leads to top-notch security procedures and protocols that help their clients.
What is a Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
A physical server leased or acquired by a person or organization for their exclusive usage is known as a dedicated servers. Unlike shared or cloud servers, which divide resources among several users, a dedicated server is assigned to a single client. Thanks to this exclusivity, the client has complete control over the server, including selecting the operating system, hardware setups, and program installations. Data centers provide high-speed internet access, environmental management, and physical security, which are advantageous for servers.
Performance and dependability are a server’s main advantages. Clients can anticipate steady performance because their website, application, or database will have the server’s resources. After all, it is not shared with other users. Because of this, servers are the best option for busy websites, big e-commerce platforms, and applications requiring a lot of processing power or strict security measures. Because the server is dedicated, there is also no chance other users’ actions will impact the server’s security or performance.
The significance of servers lies in their scalability. Although the actual hardware is fixed, clients can choose dedicated hosted servers based on what best meets their needs at the time and add more as needed. This may mean upgrading the CPU, increasing the RAM, or adding extra storage. These updates require physical server modifications, often handled by the hosting firm for a fee. Because the hardware on servers may be changed, they are a flexible solution that can adapt to a business’s needs.
Also Read Explore the Top 7 Elite CPU Processor Comparison of 2024
How Does It Work?
A dedicated hosted server requires several essential parts and procedures, from setup to maintenance and upkeep. Understanding how a server functions is vital for enterprises and people seeking to utilize this potent hosting option efficiently.
First Setup and Configuration
Choosing and setting up a dedicated hosted server is the first step in its journey. Clients select servers based on their unique needs, including CPU speed, RAM size, storage capacity, and network bandwidth. After the dedicated hosted server is chosen, the hosting company or data center staff physically configures it by installing the required hardware components following the client’s requirements.
The following steps are for installing the operating system (OS) and setting up the server software. Depending on the needs of their application, clients can select from various operating systems, such as Windows Server, Linux distributions (such as Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian), or other specialized OS solutions. The operating system selection determines the program environment, administrative tools, and security configurations available for the dedicated hosted server.
Also read Types of Operating Systems: Desktop, Mobile, Server OS, & More
Network Accessibility and Connectivity
After configuring, the server is linked to the data center’s network infrastructure. Thanks to this connection’s high-speed internet access, the server can provide content or offer services to users over the Internet. The server is given a static IP address to identify it on the network and enable remote access.
Typically, clients use tools like Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) for Windows servers and Secure Shell (SSH) for Linux-based servers to remotely control their servers. With the help of these tools, administrators may access the server from any location with an internet connection, apply updates, adjust configurations, and diagnose problems.
Continuous Upkeep and Improvements
To guarantee peak performance and security, a dedicated hosted server must be regularly updated and monitored. This entails updating the operating system and loaded applications with security patches, monitoring performance indicators and system health, and adjusting the system as necessary to accommodate variations in load or functionality.
Clients may also choose to upgrade the hardware components of their servers over time to meet increasing needs. Enhancements may include increasing RAM and storage space or swapping out the CPU for a more potent one. Since the hosting provider will modify the data center’s hardware, collaboration is usually necessary for these physical updates.
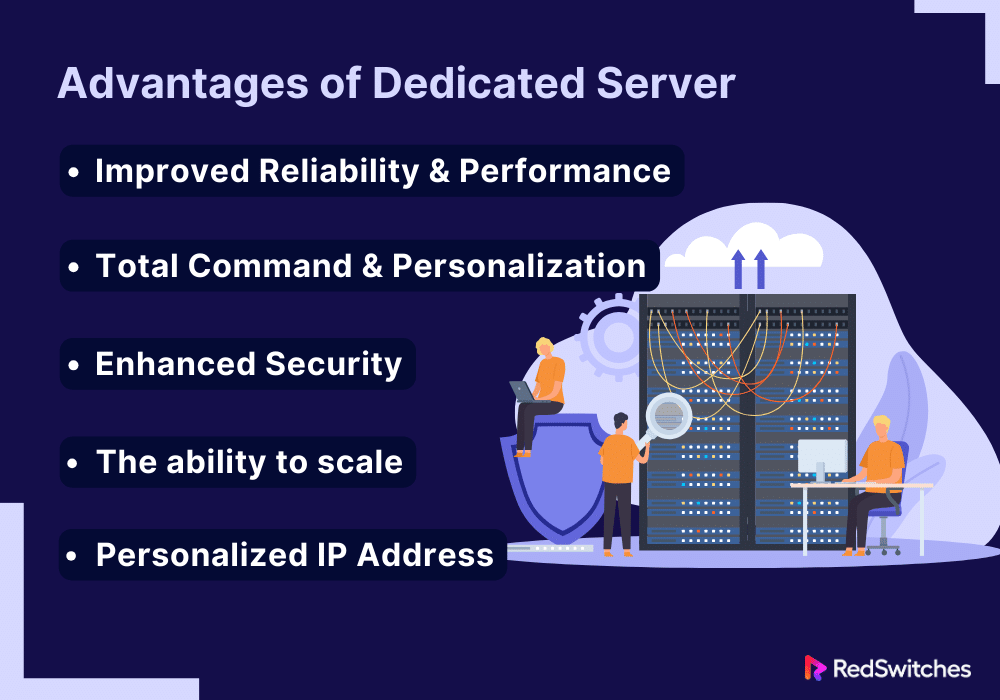
Advantages of Dedicated Server
Servers offer many benefits. They are for companies and people with specific hosting needs. Using only server resources has these benefits. They include better control, security, and performance. The following is a thorough analysis of the main advantages of selecting servers:
Improved Reliability and Performance
Dedicated hosted Servers offer unmatched performance. All the server’s resources are devoted to just one client. This gives more processing power and faster load times. It also makes a more stable environment for websites and programs. This is because CPU, RAM, and storage are not shared with other users. They benefit from this. They need fast, reliable access to resources. Additionally, organizations benefit from improved uptime and reliability when using servers. The server’s environment is managed and unaffected by other users. So there is less chance of downtime due to conflicts or overloads.
Total Command and Personalization
Credits: Freepik
Clients get root or admin access to their servers, which gives them full control over the setup and software. With this degree of access, the server environment can be fully customized to satisfy the needs of a particular application. Businesses can install specialized software, apply specific security policies, and optimize server settings, establishing a secure and optimized operating environment. Businesses have specific requirements. They must have this flexibility, especially if they must follow industry laws.
Enhanced Security
Servers do not share resources with unidentified websites or apps. These may be harmful or insecure. So, servers provide a more secure hosting environment. According to their unique security requirements, clients can deploy security measures, including intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and antivirus programs. The computers are additionally safeguarded by physical security measures in data centers, such as biometric access controls and surveillance. Due to organizations’ total control over data processing, storage, and transmission, the server’s exclusive use also makes compliance with data protection rules easier.
The Ability to Scale
Dedicated hosted Servers are limited in capacity; however, hardware modifications can make them somewhat more scalable. Customers can expand their databases or apps by upgrading components like CPUs, RAM, and storage. Thanks to this scalability, businesses can plan for growth and increase their server capacities as needed, eliminating the need for server migrations or lengthy downtime.
Personalized IP Address
Every server has a dedicated IP address, which is crucial for companies with e-commerce websites or those needing server SSL to handle credit card payments securely. By ensuring that the client has complete control over the IP address’s reputation, dedicated IP addresses mitigate the risk of sharing an IP address with spam or potentially hazardous websites, which could result in the IP address being blocked by email providers or search engines.
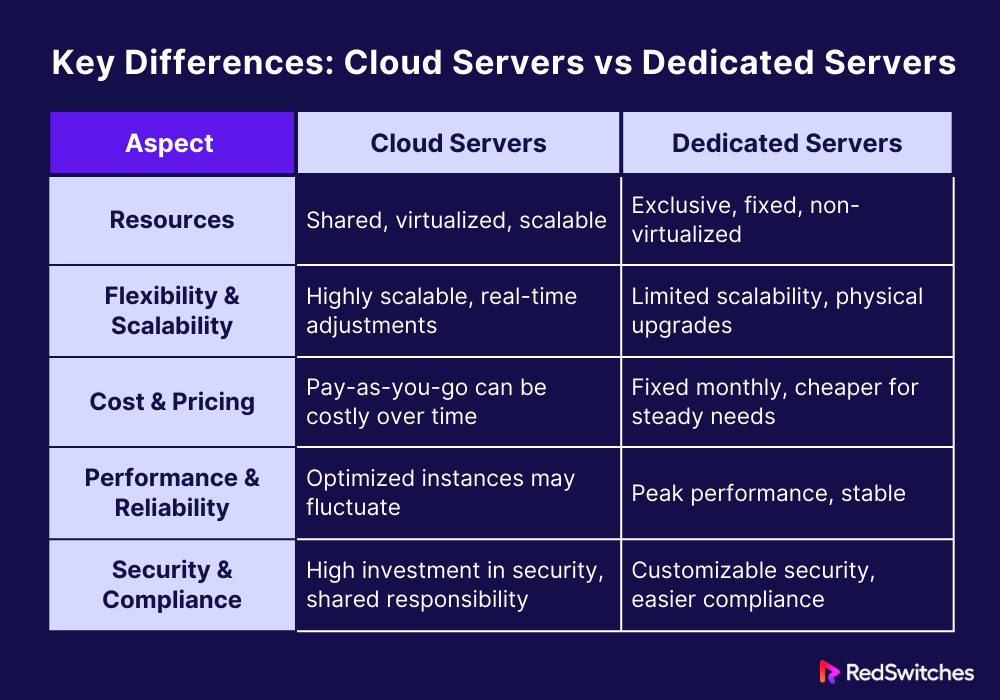
Key Differences: Cloud Servers vs Dedicated Servers
Credits: Freepik
In this section, we will discuss the core part of our blog. It is the key difference in the Cloud servers vs Dedicated servers debate.
Allocating and Sharing Resources
Cloud servers: Take advantage of a multi-tenant architecture in which the computational resources of the physical server are virtualized and distributed among several users. This method enables high resource use. Virtual machines can be quickly added or removed in response to user demand. The shared environment, however, may cause “noisy neighbor” problems. One tenant’s resource overuse hurts the performance other tenants can enjoy.
Dedicated Private Servers: Offer a secluded setting where a single tenant exclusively uses all hardware resources. Performance is steady and predictable because no rivalry exists for resources. It is best for applications that need a constant high level of processing power. It also helps those who need specific hardware. Virtualized environments can’t use it.
Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud servers: They provide remarkable scalability, facilitating horizontal and vertical scaling without needing physical intervention. This elasticity is a huge benefit for fast-growing or seasonal companies. It lets them adjust their infrastructure in real time to meet shifting needs. It prevents them from overspending on resources.
Dedicated Private Servers: Although they provide some scalability, scaling can be more difficult due to physical constraints and manual intervention requirements. Fast growth is held back by downtime. This downtime is for planning and installing hardware upgrades or expansions. Despite this, servers meet specific performance or compliance requirements. They do so by providing unmatched flexibility in hardware and software.
Model of Cost and Price
Cloud servers: Cloud servers’ adaptable pay-as-you-go pricing structure can result in considerable cost savings, particularly for companies with variable workloads. The model lets businesses cut costs and avoid expenses from underused infrastructure by modifying resources in real-time. Yet, over time, costs might mount up. This happens for workloads that have steady, predictable needs. The costs will outweigh the advantages.
Dedicated Private Servers: Due to the exclusive usage of physical resources, these servers usually have a greater upfront investment or fixed monthly charges. Their dependability helps firms, and the cost structure lets them plan their IT budgets. Servers balance performance and cost. They may be cheaper for groups with steady and predictable needs in the long run.
Effectiveness and Dependability
Cloud servers: Providers offering instances optimized for various workloads, including compute, memory, and storage-intensive applications, have significantly improved cloud server performance. Even with these changes, performance may still fluctuate. This can happen because the infrastructure is shared. The supplier’s infrastructure supports reliability by guaranteeing high availability and data integrity through automated failover and data replication.
Dedicated Private Servers are distinguished by their capacity to provide reliable, peak performance without the unpredictability of shared environments. The center’s excellence and the hardware’s quality are key. They are tied to the reliability of servers. With proper care and management, servers can have better uptime and stable performance, which is crucial for mission-critical applications.
Safety and Adherence
Cloud servers: Cloud providers provide a secure environment for various applications by significantly investing in security technologies and adhering to stringent compliance rules. According to the shared responsibility paradigm, clients must understand. They must also oversee the security of their data and apps. They do this within the cloud infrastructure. Cloud servers can offer controls and certifications. These are needed to comply with strict laws for the industries they cover.
Dedicated Private Servers: They Provide more control over security configurations, enabling companies to customize their security posture to match precise requirements. Customers can select data centers with the best server safety and physical security. Servers are segregated, so it is easier to comply with requirements unique to the business.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
Which one is better?
Credits: Freepik
Select cloud servers if
- Your business depends on scalability and flexibility. Ideal for managing demands for quick scaling and fluctuating workloads.
- Cost-effectiveness is important. It’s key if you want to pay for what you use and avoid big upfront commitments. This can be done by using a pay-as-you-go strategy.
- The priorities include disaster recovery and high availability. Data is mirrored across several sites, providing business continuity.
- We need rapid deployment and development to support agile development and testing, and they need prompt resource delivery.
- It favors easy management. It uses managed services to lessen the work of server administration and maintenance.
Select dedicated servers if
- Your applications depend on predictable performance. This is especially true if they need special hardware or are resource-intensive.
- Prioritizing security and compliance gives you more control. It covers network and physical security.
- Controlling the server environment is essential. This includes customizing particular hardware installs, settings, and setups.
- Cost predictability is crucial, and fixed pricing models provide an easy approach to set aside money for IT costs.
- You intend to make long-term IT investments. So, it makes sense to buy and maintain servers upfront.
Conclusion
The choice between cloud and dedicated servers is crucial. This choice matters in the digital arena. That’s where companies compete to be the best. It’s like deciding between a fast, versatile sports car and a sturdy, specially designed off-road vehicle for your tech expedition.
Cloud servers are a great option for enterprises with changing demands and expansion goals because of their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. On the other hand, dedicated servers are distinguished by their consistent performance, increased security, and total control, making them perfect for resource-intensive applications with particular compliance needs.
RedSwitches stands out as a beacon in rough waters. We provide custom hosting solutions that combine the best of both worlds. We are prepared to advance your digital strategy, guaranteeing that your online presence is maintained and flourishes in the constantly changing world of digital technology, regardless of your preference for the adaptability of cloud servers or the unwavering dependability of servers.
FAQs
Q. Is the cloud cheaper than a dedicated server?
Because of its pay-as-you-go concept, the cloud may be less expensive than a dedicated hosted server for fluctuating workloads; however, dedicated hosted servers may be more expensive for steady workloads in great demand.
Q. Is VPS faster than a cloud?
While virtual private servers (VPS) can provide faster-dedicated resources for some jobs, cloud environments are more scalable and flexible. They may provide better performance for a wider range of workloads.
Q. Is AWS cheaper than VPS?
Given that costs vary depending on usage patterns and unique demands, AWS may not always be less expensive than VPS. However, some customers may find AWS’s scalability and capabilities worth the additional price.
Q. What is the difference between cloud and dedicated hosted servers?
Cloud servers are virtualized servers that run on a cloud computing environment, whereas dedicated hosted servers are physical servers dedicated to a single customer.
Q. What is cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting where resources are spread across multiple servers and are scalable on demand.
Q. What are the similarities between cloud and dedicated hosted servers?
Cloud and dedicated hosted servers provide resources for hosting websites and applications but differ in infrastructure and scalability.
Q. How do I choose the right hosting option between cloud and dedicated hosted servers?
To choose between cloud and dedicated hosted servers, consider factors like your budget, scalability requirements, and control over hardware resources.
Q. What are the types of web hosting available?
Web hosting options include shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated private server hosting, and cloud hosting.