Key Takeaways
- Servers offer unparalleled performance, security, and control.
- Regular updates and security audits are crucial for server maintenance.
- Virtualization and control panels enhance server efficiency and manageability.
- CDNs expand global reach and improve website load times.
- Automated backups and robust monitoring systems safeguard against data loss and security breaches.
- Systematic troubleshooting minimizes downtime and maintains operational integrity.
- RedSwitches provides scalable, secure server solutions to support advanced configurations and management.
Owning a server in the digital era is like having a solid engine propelling your online presence ahead. Setting up your own server can be a game-changer. It’s for managing demanding apps, hosting a popular website, or protecting sensitive data. This extensive manual is for anyone ready to take charge of their digital infrastructure. It is for IT enthusiasts starting to manage servers and seasoned pros looking to improve.
We will discuss hardware and software choices, learn configuring your own dedicated server, and unlock the keys to top security and performance. Join us. We will help you create a robust online base for your projects or business by navigating the complex world of servers.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What are Dedicated Servers?
- Advantages of Servers
- Initial Setup of Servers
- Network Configuration of Dedicated Servers
- Security Hardening in Dedicated Servers
- Advanced Configuration in Dedicated Servers
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting in Dedicated Servers
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Dedicated Servers?
Credits: Freepik
Dedicated servers are the ultimate in hosting. They offer unmatched security, speed, and control. They are for apps, websites, and data storage. In contrast, VPS replicates a dedicated environment within a shared server. Shared hosting splits resources among many users.
However, servers grant a single user exclusive access to all the server’s resources. Dedicated servers are unique. Their exclusivity guarantees this. The server’s memory, processing, and storage are only for one customer’s demands.
A server’s architecture is simple but effective. The system’s basis is physical hardware, like a processor (or several processors), RAM, and storage devices (HDDs or SSDs). It also includes network components. All of this hardware is stored inside a data center.
Users can customize the server configuration by choosing the hardware specs according to their needs. They can also select the environment that best fits their technical needs and skill level regarding the operating system and software.
One of the servers’ primary benefits is its performance. They have every resource. They may run websites and apps at peak performance. They can handle lots of traffic and complex processing jobs. They need not worry about other users sharing the same server overriding their needs.
Dedicated servers are the best option for companies and people. They run resource-intensive websites, big e-commerce sites, or programs that need the highest uptime and dependability.
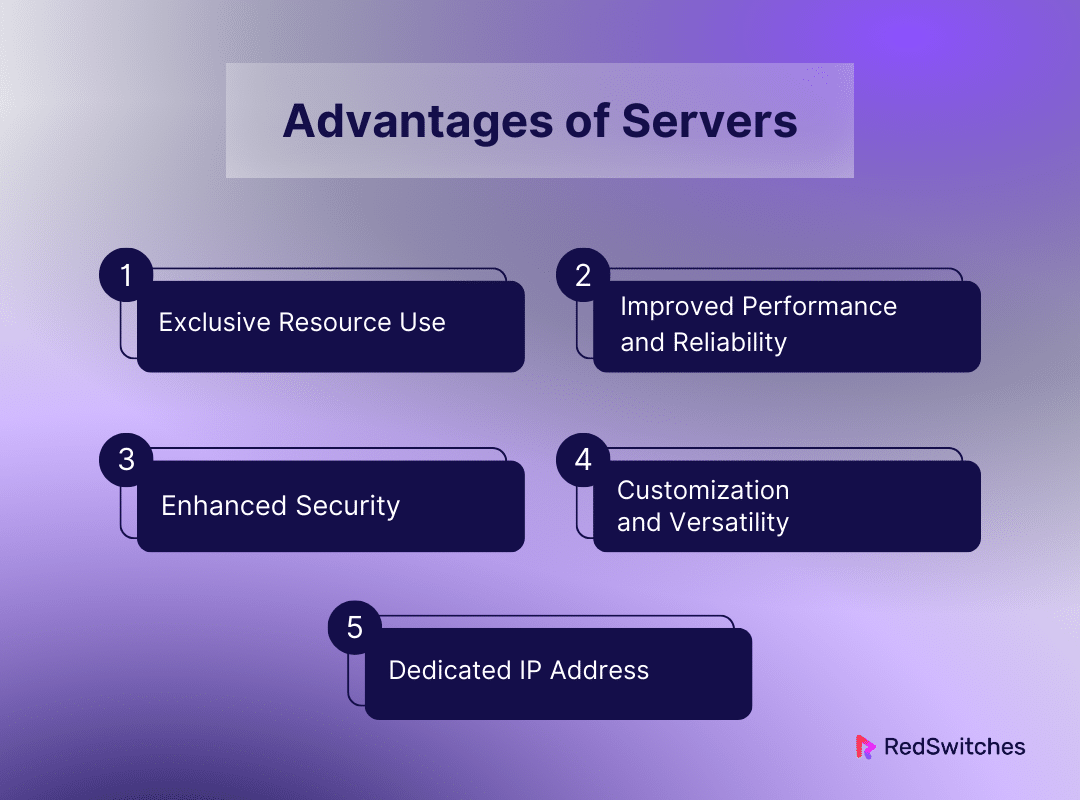
Advantages of Servers
Let’s discuss the advantages of servers in detail.
Exclusive Resource Use
It is impossible to exaggerate the advantages of solely accessing the server’s resources. Every piece of memory, bandwidth, and processing power in a server environment is yours. This ensures that busy applications do not conflict with other users’ needs. It makes things more efficient and stable.
The resources must be accessible when needed. Also, the lack of the “noisy neighbour” effect makes the server environment more predictable. This predictability allows for accurate performance tuning and planning.
Such companies rely on instant resource access and real-time data processing. This level of resource allocation is critical to keeping their competitive edge.
Improved Performance and Reliability
Dedicated servers are faster. They lead to quicker website loads and database queries. They also make applications run more seamlessly. In today’s fast-paced internet world, speed and efficiency are essential when customers expect smooth experiences and immediate responses.
Moreover, servers offer unparalleled dependability, offering a solid basis for your web presence. The capacity to withstand abrupt spikes in traffic might be the difference between success and failure during high-traffic events or sales promotions. Thus, stability is essential.
Additionally, because dedicated hardware has higher-quality components and can be customized with redundant systems to maintain continuous uptime, you are less vulnerable to hardware failures that disrupt your operations.
Enhanced Security
The degree of security customization possible in a server environment is unmatched. You can customize your security posture to suit the strictest standards by installing tailored security solutions, doing frequent security audits, and implementing hardware and software firewalls without being restricted by shared environments.
Businesses that handle sensitive financial transactions or personal data, where a breach could have severe legal and reputational repercussions, will significantly benefit from this. User isolation naturally decreases vulnerability, giving your clients peace of mind and a safe operating environment.
Customization and Versatility
Credits: Freepik
Having a blank canvas for your web hosting environment is what servers offer in terms of customization and versatility. Whether it’s a Windows server that blends in well with your current setup or a Linux distribution renowned for its stability and security, you may choose the operating system that best matches the experience of your technical staff.
By selecting the right hardware specs, you can tailor your system to the unique needs of your apps. For example, you can use SSDs to ensure quick and large amounts of storage or prioritize CPU speed.
This personalization also applies to the software layer, allowing you to install and set up web servers, database management systems, and other programs to your precise specifications without being constrained by shared hosting.
Dedicated IP Address
Having a dedicated IP address benefits your company more than simply technically. It promotes consumer trust and adherence to security regulations by making setting up SSL certificates necessary for safe transactions easier.
Additionally, since a dedicated IP prevents your site’s reputation from being damaged by perhaps spammy neighbors—a significant concern associated with shared hosting—it can have favorable SEO effects. Being on the same IP address as spammers can cause your emails to be blocked, therefore, this is very crucial for email deliverability.
Furthermore, a dedicated IP offers the stability and accessibility required to guarantee seamless operations for services needing secure access or specific network setups, such as FTPs or private databases.
Initial Setup of Servers
Credits: Freepik
A server’s initial configuration is a crucial stage that establishes the foundation for its general functionality, security, and performance. This procedure, frequently regarded as the cornerstone of server management, consists of three crucial processes: installing the operating system, adjusting the BIOS settings, and unpacking and physically setting everything up.
Below is a detailed explanation of each stage to give you a thorough grasp of the procedure.
Unpacking and Physical Setup
The initial stages of your server management adventure begin with your server’s unpacking and physical setup. When your server is delivered, carefully unpack it, being mindful of any physical damage that might have happened during transit. Verify that all parts—power cables, rack mounts, and other installation-related accessories—are present and accounted for.
Care must be taken to avoid overheating when installing the server in a rack or other designated area. Make sure it’s mounted firmly and that there’s enough airflow. To guard against power outages, connect it to a dependable power source and consider installing a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply).
Basic Configuration: BIOS Settings
When you turn on your server, you should configure the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) settings. BIOS is essential for setting up the hardware before the operating system starts. You can reach the BIOS setup during the startup phase by pressing a designated key like Delete, F2, or F10. You can change many vital parameters. This will improve security and make the server faster.
Setting the boot order in the BIOS is essential because it controls the order in which the server looks for an operating system and frequently prioritizes external devices, such as a CD/DVD drive or USB port, during the first OS installation.
Also, protecting the BIOS security settings with a password prevents unauthorized changes, keeps the BIOS setup and hardware safe, and ensures that the core settings, which control the server’s boot and hardware start, are safe and fit your security and operational needs.
Installing the Operating System
The last step in setting up your server is to install the operating system (OS). The OS you choose will depend on your needs, experience level, and the particular apps you want to use. Many people choose Windows Server because it’s user-friendly and works with Microsoft applications. Others choose Linux versions like Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian because they’re adaptable and secure.
Usually, you’ll use a bootable USB drive or a DVD with the installation media to install the operating system. Put the media in, make sure the BIOS is configured to boot from this drive, then restart the server.
The installation process involves setting network, disc, location, and user settings. You can start it by following on-screen directions. If a Linux server needs a GUI, you may need to install one. Many servers work well with just the command line.
Choose security options when installing the operating system. For example, install a firewall and make strong passwords.
Network Configuration of Dedicated Servers
Credits: Freepik
One of the most essential factors in ensuring smooth communication with the internet and other networked devices is the networking configuration of servers. Setting up IP addresses, establishing firewall configurations, and configuring DNS settings are some of the crucial tasks in this procedure. Each part is essential to the server’s capacity to handle traffic, deliver content, and defend against intrusions and online attacks.
Configuring IP Addresses
IP addresses are necessary to identify your server on a network and allow it to communicate with other devices via the Internet. Usually, the hosting company assigns one or more static IP addresses to servers. The first step is to set up these IP addresses on the server’s network interface. The operating system impacts this procedure.
The network configuration files for Linux servers must be modified to contain the static IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and, occasionally, the DNS servers. For CentOS servers, these files are typically found in /etc/network/interfaces or /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0.
By selecting the network connection, selecting Properties, and then selecting Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), you can configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway provided by your hosting provider for Windows servers using the Network and Sharing Centre.
You can ensure your server can be found and contacted from anywhere by appropriately configuring IP addresses.
Configuring DNS Settings
Setting up DNS settings is a fundamental part of server management. It ensures the smooth operation of your domain’s email and online presence. The Domain Name System (DNS) translates popular domain names into the numerical IP addresses. These addresses are needed to find and identify computer services and devices globally.
It serves as the internet’s phone book. Understanding and setting up extra DNS settings can significantly help your domain. They improve its function and security beyond A, MX, and CNAME records.
Other Types of DNS Records
TXT Record: With this record, administrators can add any text they choose to a DNS record. For instance, TXT records confirm domain ownership. They set up email security with DKIM and SPF. They give servers and admins key data.
SRV Record: This is a record of services available under a domain; it specifies the protocol being used and the port for certain services (such as VoIP, SIP, and instant messaging protocols). It is essential to operations that call for service discovery.
Nameserver records (NS Records): These are essential for assigning a domain or subdomain to a group of DNS servers.
Security Hardening in Dedicated Servers
Credits: Freepik
For servers, security hardening is vital. It reduces weaknesses and guards against intrusions. This method covers many crucial tasks. These include installing intrusion detection systems (IDS) and a firewall. They also involve routine updates and patches. Each of these parts is vital. They keep the data’s integrity and secrecy and strengthen the server’s defenses.
Continual Patches and Updates
One of the most crucial parts of security hardening is regular updates. You must apply them to the operating system and all installed applications. Developers release software updates often to fix bugs, close security holes, and boost performance. Ignoring these upgrades may make your server vulnerable to known flaws. Hackers could use them to gain unauthorized access or interfere with operations.
Operating System Updates: Make sure the operating system on your server is configured to download and install updates automatically or create a routine to search for and install these updates manually. Package managers, like yum for Red Hat and apt for Debian, automate this for Linux servers.
Software Application Patches: Your server’s applications also need to be updated. This includes any CMS, like WordPress or Joomla, and the frameworks you are using. It also includes database servers, like MySQL or PostgreSQL, and web server software, like Apache or Nginx.
Installing a Firewall
A firewall acts as a gatekeeper for your server. It regulates all traffic, inbound and outbound, by the security rules you’ve set. It serves as your initial layer of protection from unwanted access.
When configuring firewall rules, make rules that say which traffic is allowed and which is not. For example, you would block some ports and allow traffic on those used by your applications, such as web traffic on ports 80 and 443. For this, programs such as Windows Firewall on Windows Server and iptables or firewalld on Linux are used.
Monitoring and Modifying Rules: Examine firewall logs regularly to spot and look into any odd trends or efforts to get past your defenses. As your server setup changes or new threats arise, make the required adjustments to your rules.
Systems for detecting intrusions
Specialized tools called intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor system and network activity to detect malicious activity or policy violations. An IDS adds analysis and warns administrators about intrusions, enhancing a firewall.
IDS (Network-based): This type of security monitors network traffic to spot unusual activity. It analyzes network flow and volume and uses them to find patterns. The patterns suggest attacks like DDoS or unauthorized access attempts.
A host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS): Set up on each server, HIDS monitors file access and modifications, system logs, and other host activity to spot any indications of compromise. It may also inform administrators about unauthorized changes and questionable activity on the server.
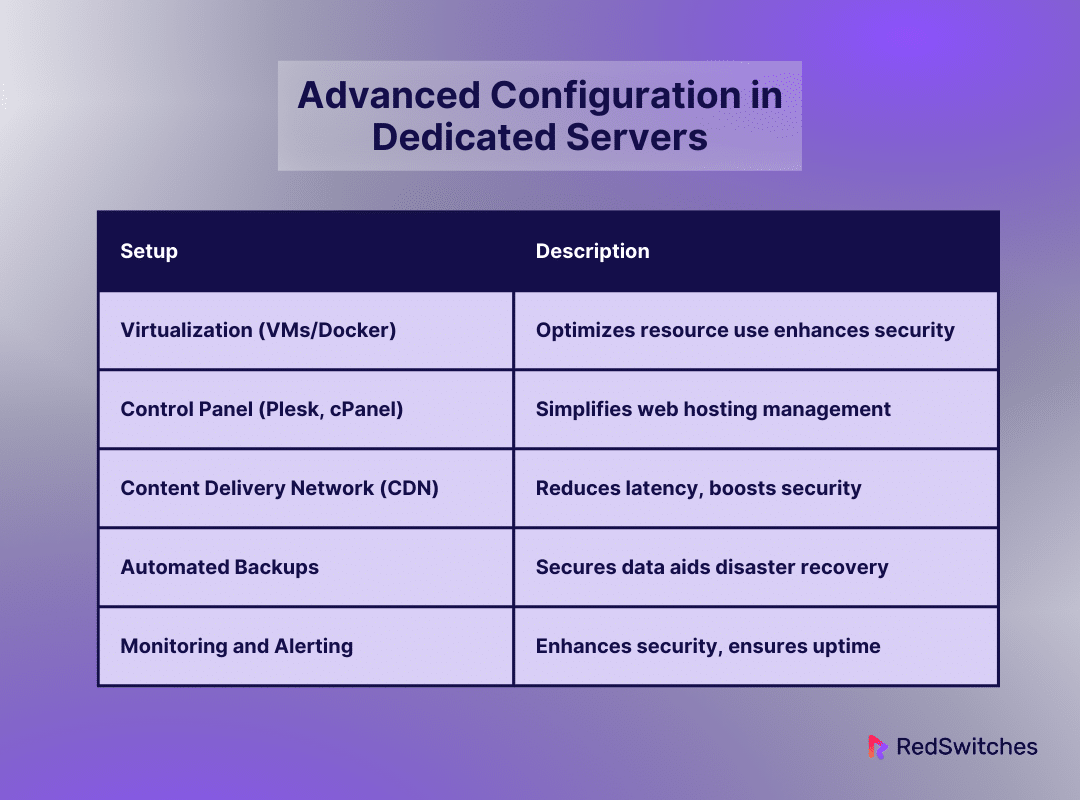
Advanced Configuration in Dedicated Servers
Complex setups on servers can significantly improve your infrastructure. They can boost its performance, manageability, and functionality. These setups address many areas of server management and optimization. They include virtualization using Docker or VMs. You set up a control panel, such as Plesk or cPanel. And you create a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for worldwide reach. Let’s examine each of these setups in more detail:
Virtualization using VMs or Docker
Docker-based virtualization is often called virtual machines or VMs. It is a game-changing technology. It changes resource management. It lets one server host many virtualized environments or dedicated resources. You can mimic whole computer systems using virtual machines. They are offered by VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, or KVM for Linux.
Each virtual machine runs its operating system and applications independently. This setup is great for testing in different places. It’s also suitable for dividing up apps to improve security. And for giving resources more effectively to particular activities. However, Docker, which focuses on containerization, offers a simplified virtualization method.
Containers share the host’s kernel but run independently. They pack an application and its dependencies into a small, portable unit. Docker has low overhead. It can be used with dynamic, microservices-based architectures for faster deployment and better scaling.
Both virtualization approaches provide reliable means of optimizing server performance, guaranteeing resource isolation, and protecting applications; nonetheless, they address slightly distinct use cases and preferences about server environment administration.
Configuring a Control Panel (Plesk, cPanel)
Credits: Freepik
Maintaining hosting systems can be pretty hard for individuals with little technical knowledge. Control panels, like Plesk and cPanel, greatly simplify this process. They provide a graphical interface that makes web hosting easy for users. cPanel is famous for its many features. It’s a mainstay in web hosting. It makes managing websites, domains, emails, and databases simple.
This increases the usefulness of cPanel by offering the backend access that admins need.
Using such control panels makes server management more accessible and manageable by eliminating the need for direct command-line interaction and improving the management of websites and server resources.
Putting a CDN in Place for Worldwide Reach
It is crucial to ensure your web content loads fast. It must load fast for users around the globe. A content delivery network (CDN) meets this requirement by distributing your material over a global network of strategically positioned servers. This reduces latency, which leads to faster load times and a more seamless user experience. It also provides scalability so that traffic spikes can be handled without problems.
CDNs are excellent at handling large amounts of traffic, spreading loads to avoid single points of failure, and keeping sites up and running even when there are problems with servers or networks. Additionally, they improve website security by protecting your site from cyberattacks with features like web application firewalls, secure sockets layer (SSL) server encryption, and DDoS protection.
Using Automated Backups to Protect Data
Data availability and safety are critical concerns in managing servers. An essential tactic that offers a failsafe against data loss due to hardware malfunctions, software defects, or security breaches is automated backups. Server administrators can ensure that recent changes are automatically maintained by setting up automated, scheduled backups that take regular snapshots of their databases, application data, and system configurations.
In disaster recovery circumstances, this procedure reduces downtime and speeds up the restoration of services to their most recent known good state. Using incremental backup programs increases efficiency even more because they only update the modifications made since the last complete backup, which lowers bandwidth and storage needs.
A strong backup plan—ideally with off-site storage options—guarantees that vital information is safe and recoverable, giving organizations and their stakeholders continual operational integrity and peace of mind.
Establishing Sturdy Monitoring and Alerting Systems
Thorough and continuous monitoring is essential to ensure performance, availability, and security in server settings. Administrators may monitor traffic patterns, resource usage, and server health in real-time by enforcing strong monitoring and alerting systems. From CPU and memory utilization to disc I/O rates and network bandwidth, these systems can monitor various parameters, spotting possible problems before they become serious malfunctions.
Furthermore, sophisticated monitoring technologies enable quick action to reduce risks by identifying unusual activity suggestive of security issues, such as suspicious outbound traffic or unauthorized access attempts.
Alerting methods configured to send administrators emails, SMS messages, or integrated dashboard notifications guarantee that issues can be addressed immediately. This proactive approach to server administration protects the apps and data it hosts by strengthening the server’s security posture against a constantly changing array of cyber threats. It also maintains optimal performance and uptime.
Let’s summarize it in tabular format.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting in Dedicated Servers
Credits: Freepik
Maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial. They are key in the life of server administration. They keep these vital systems effective, safe, and resilient to faults. Routine maintenance includes several standard procedures. They keep the server working at its best.
Maintainance
Maintaining a server entails many steps to prevent problems. The goal is to keep the systems secure, working, and providing peak performance. This approach includes many actions. They are meant to stop possible problems before they become bigger.
A key part of proper maintenance is updating the operating system and apps often. This prevents known flaws. It adds new features. They can boost productivity and security.
Administrators should do regular security audits. They will check that the server’s defenses are good for the always-changing cyber threat environment. Another key duty is to monitor the system logs. They give info about the server’s operation and point out any failures or strange activity. These can indicate deeper problems.
Watching disc space use is crucial for preventing service outages. Checksums can ensure data integrity and prevent corruption. Regular backups—ideally automated and off-site—are essential for data protection because they guarantee that the server can be promptly returned online during a data loss catastrophe. When these maintenance tasks are carried out regularly, they reduce downtime, increase server longevity, and preserve high service quality standards.
Also read Firewall Configuration for Enhanced Security
Troubleshooting
In server management, troubleshooting is reactive. It involves a methodical approach to finding and fixing problems as they appear. This method starts by trying to duplicate the issue to gain context and better understand its impact.
Server logs are vital during this stage. They provide a detailed record of system events. This record can help find the problem’s cause. These concerns are routine. They involve reviewing configurations carefully. It also means evaluating hardware for malfunctions.
And checking that firewall settings are not too restrictive. One way to address performance issues is by analyzing resource use. This shows if changes or upgrades are needed.
You need to understand the server’s setup, including the applications it hosts and the common problems seen in server environments. This understanding is key to efficient troubleshooting. Through thorough troubleshooting, administrators can quickly fix issues, limiting their impact on operations and upholding the server’s security and performance.
Conclusion
Understanding advanced server configurations can help organizations and IT professionals achieve unprecedented efficiency, security, and performance. These setups are crucial for modern server management, from the sophisticated setup of virtual environments using Docker or VMs to the streamlined management provided by control panels like Plesk and cPanel and the worldwide reach attained by CDNs.
They guarantee that your digital infrastructure can match the demands of today’s data-driven, fast-paced environment and improve the server’s capabilities.
Reliable hosting is essential for implementing these sophisticated plans, and RedSwitches is prepared to offer the dependable, scalable, and secure server solutions required to make these sophisticated configurations a reality.
FAQs
Q. What is dedicated server configuration?
A server configuration is one in which all server resources and control are given to a single client, website, or application.
Q. What are the types of servers?
Types of servers include web servers, file servers, mail servers, database servers, and application servers, each serving different functions in a network.
Q. What is the DNS server?
Browsers can load internet content when a DNS (Domain Name System) server translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses.
Q. What is a server?
A server is a type of server that is exclusively leased to a single individual or organization, hence the term “dedicated.” It gives the user complete control and customization over the server’s resources and configurations.
Q. What are the benefits of setting up a dedicated server?
Setting up a server offers advantages such as improved performance, security, customization options, and the ability to host demanding applications or websites that require more resources.
Q. How do I configure a web server on my server?
To configure a web server on your server, you can use popular server software such as Apache or Nginx and then customize the settings to suit your specific needs, such as serving web pages, handling PHP scripts, and more.
Q. What components do I need to assemble a server from scratch?
To build a server from scratch, you will need server components like a CPU, RAM, storage drives (SSD preferred for performance), motherboard, power supply unit, and a network interface card.
Q. How can I set up a MySQL database server on my server?
To set up a MySQL database server on your server, you can install MySQL software, create databases, configure user permissions, and ensure proper security measures are in place to protect your data.
Q. Can I host my website on a server?
Yes, hosting your website on a server allows you to have full control over server resources and configurations, ensuring optimal performance and security for your website.
Q. What is the recommended server operating system for a server?
Linux is a popular choice for server operating systems due to its stability, security, and open-source nature. Distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian are commonly used for server setups.
Q. How do I choose a server provider?
When selecting a server provider, consider factors such as reliability, performance guarantees, customer support, pricing, server customization options, security measures, and the provider’s reputation in the industry.