Key Takeaways
- Staking offers a means to earn passive income through cryptocurrencies, enhancing network security and efficiency.
- Dedicated servers provide superior security, consistent performance, and control for intensive staking operations.
- Cloud servers offer scalability, reduced initial costs, and flexibility, suitable for varying staking demands.
- Security, cost, performance, scalability, control, and technical expertise requirements are critical factors in choosing between cloud and servers for staking.
- The choice between cloud and servers depends on individual staking strategy, budget, and technical capabilities.
- RedSwitches offers tailored server solutions, aligning with the needs of serious stakers seeking reliability and performance.
- Understanding the technological, financial, and operational implications is crucial for making informed decisions between cloud and server staking.
Do you need help with the convenience of cloud servers and the control of dedicated servers for your staking endeavor? Understanding the trade-offs between these technologies is crucial for success.
Staking is vital in digital finance, especially in cryptocurrencies. This process needs reliable computing solutions. Members get paid for sharing digital assets to support the network.
Network users and investors must choose between servers and cloud-based options. Each option has unique benefits and difficulties, from security and control to scalability and cost-effectiveness.
This article will dive into the core differences between cloud server vs dedicated server for staking. Helping you to make an informed decision so that you can maximize your staking rewards.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Staking?
- Advantages of Staking
- Risks Associated with Staking
- Cloud Server for Staking
- Advantages of Cloud Servers For Staking
- Limitations and Considerations of Cloud Server For Staking
- Dedicated Servers For Staking
- Advantages of Dedicated Servers For Staking
- Limitations and Considerations for Dedicated Staking
- Cloud Server vs Dedicated Server for Staking: Key Differences
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Staking?
Credits: Freepik
In cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, staking is a crucial idea that denotes a way to engage with the network and get rewards. Staking keeps money in a wallet to keep a blockchain network running. Network users contribute digital assets to maintain security and functionality. They receive rewards like coins or tokens.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a popular alternative to energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) used by networks such as Bitcoin. It serves as the basis for staking operations. A participant’s chance of validating a new block in PoS decreases as the amount of currency they stake increases. This system encourages Participants to act in the network’s best interests since the more they stake, the more likely they are to get rewards.
Staking helps investors earn passive income by locking their money for a set time. It also plays a role in network security. It is an environmentally friendly alternative because it uses much less energy than regular mining. This is a significant difference. By raising the cost of a possible assault, staking also improves network security. An attacker must buy and stake a large portion of the currency. This would be at risk if the network is breached.
Staking often grants users a say in governance and supports network functions. The extent of this influence depends on the blockchain design. Voting on proposed protocol changes will shape the network’s future direction. Voting on essential decisions will also impact the network’s future.
Advantages of Staking
There are numerous benefits to staking for individuals and the blockchain networks that depend on it. Advantages include improving network security. Stakeholders receive a passive revenue stream. Let’s examine these benefits in further detail:
Passive Income
One of the main draws of staking is the potential to generate passive income. Participants earn prizes by holding and staking digital assets. Prizes are typically more tokens or currencies. These benefits are similar to interest earnings in traditional banking but often higher rates. Investment returns vary across blockchains due to factors like total staked amount and staking methods.
Energy Efficiency
Staking requires less energy than Proof of Work. Proof of Work needs high computational power and energy for tasks like Bitcoin mining. Maintaining blockchain security uses less energy. It eliminates the need for users to solve challenging puzzles. Staking is an eco-friendly and durable way to reach agreements.
Enhanced Network Security
Staking makes blockchain networks more secure. Proof-of-stake systems depend on stakeholders who have a stake in their stability to preserve their security and integrity. There is an inherent financial disincentive against malevolent behavior since assaulting the network would reduce the value of their staked assets. The network gets more secure as more assets are staked.
Decentralization
Staking encourages more decentralization by enabling everyone interested in the network to participate in the consensus process. PoS permits greater participation than PoW, where mining power is frequently concentrated in the hands of a few influential players (due to the high cost of mining equipment and electricity). This can guarantee a more resilient and dispersed network and assist in lowering the risk of centralization.
Risks Associated with Staking
In the world of cryptocurrencies, staking offers both benefits and threats. Staking offers an unquestionable appeal for generating passive income, but there are some potential hazards that investors must be aware of to protect their money. Below is a more detailed analysis of the dangers posed by staking:
Risk Associated with Market Volatility
The value of cryptocurrencies is renowned for its extreme swings over brief periods. When assets are staked, they are frequently locked for a predetermined time, during which the market value may fluctuate dramatically. Losses could result from a sudden drop in the value of the cryptocurrency that has been staked, thereby negating any gains from staking rewards. Because of this volatility, staking must be done strategically and ideally with an eye toward long-term asset value.
Liquidity Risk
Staking frequently entails temporarily locking up a portion of one’s cryptocurrency holdings. The staked assets cannot be easily accessed or sold during this lock-up period, which could be problematic if liquidity is required or if the holder wants to take advantage of trading opportunities. Opportunity costs could result from this illiquidity, particularly in a market that is changing quickly and where agility is essential.
Slashing Risks
Certain Proof of Stake (PoS) protocols impose slashing conditions to compel participant behavior. Slashing is the practice of punishing validators for behaviors that do not serve the network’s interests, such as persistently staying offline, double-signing transactions, or attempting to compromise the network’s security by decreasing their staked tokens. Selecting a trustworthy validator becomes essential for stakeholders to reduce the possibility of fines being reduced.
Validator Performance Risk
The actions and performance of validators can significantly impact the return on investments made through staking. Validators that engage in harmful activities or ineffectively participate in consensus processes may reduce the benefits received by individuals who have staked assets under their validity. The risk highlights the importance of research before choosing reliable validators with a proven track record.
Regulatory Risk
The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrencies is undefined and differs significantly between countries. Regulations can change, affecting staking’s overall profitability as an investing strategy, as well as its legality and taxation. For example, the net returns from staking operations may be impacted if staking incentives are treated as taxable income.
Cloud Server for Staking
Credits: Freepik
A Cloud Server for Staking merges cloud computing features with Bitcoin staking methods. The new method allows people and organizations to join blockchain networks’ consensus and validation. They don’t need to purchase or upkeep hardware. It makes staking easier and cheaper for more users. Staking becomes accessible to a wider range of people. It democratizes access.
Cloud staking involves running a node for a blockchain network. This uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) or similar consensus on a virtual server in a cloud computing platform. The configuration utilizes cloud resources for a flexible staking solution. It adapts and scales easily. Renting resources on-demand helps users optimize performance and prices. They can modify resources to fit the blockchain network’s unique needs.
Advantages of Cloud Servers For Staking
Cloud server staking benefits different blockchain users. These users range from small businesses to significant investors.
The scalability, dependability, and user-friendliness of cloud computing suit blockchain staking needs. These advantages are intrinsic to cloud computing. Here are a few more details on the main benefits:
Scalability
One of the most significant advantages of staking on cloud servers is scalability. Cloud resources can be readily scaled up or down in response to changes in the blockchain network’s needs or increased staking demands. Stakeholders can adjust operations quickly without substantial financial commitments. This flexibility allows them to meet changing demands promptly. Participants are guaranteed profit and effectiveness. They can quickly adapt to network changes.
High Availability and Reliability
Cloud providers typically provide essential qualities for successful staking. Staking nodes must be online and running around the clock to maximize rewards and carry out their network functions. Cloud servers in data centers have backup networking, cooling, and power sources. Downtime danger is reduced. Cloud platforms often provide service level agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing uptime levels. This assurance ensures the efficient maintenance of blockchain networks.
Decreased Initial Investment
The initial investment needed for staking operations decreases when set up on cloud servers. Physical gear in traditional staking systems must be bought, set up, and kept, making it costly and time-consuming. Under the pay-as-you-go approach, stakeholders pay for their resources. Cloud servers eliminate upfront expenses. This concept makes it easier for new investors to join and permits more adaptability in financial planning.
Enhanced Security
Nodes must be shielded from attacks and unauthorized access to preserve the staked assets. As such, security is a top priority when it comes to staking. Cloud providers invest heavily in security processes and technologies. This protection may be rugged for individuals to achieve. This covers data encryption both in transit and at rest, network security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and physical security of the data centers. Although they still need to take precautions to secure their accounts and access to cloud resources, savers can use these cutting-edge security features to safeguard their business operations.
Accessibility and Manageability
Stakeholders benefit from the flexibility and simplicity of remotely accessing and managing cloud servers worldwide. Staking node setup and ongoing management are made more accessible by cloud platforms’ automation features and user-friendly management interfaces. No matter where they are physically located, stakeholders can more easily monitor their operations, modify resources, and react quickly to problems because of this accessibility.
Limitations and Considerations of Cloud Server For Staking
Before staking cryptocurrency on cloud servers, consider drawbacks and factors. Staking on cloud servers offers scalability and easy setup. However, there are challenges and considerations. We go into further detail about these restrictions and factors below.
Security Concerns
We have discussed that the cloud has enhanced security. On the other hand, in some cases, Cloud servers have security flaws due to their multi-tenant architecture and shared resources. Attackers might exploit these flaws to access stake activities. In the context of staking, this risk is increased when maintaining cryptographic keys is crucial. Servers offer total control over security. However, the cloud poses challenges in protecting privacy and security. There is also a higher risk of unauthorized access or breaches.
Also Read Why Is Data Privacy Important For All Stakeholders?
Cost Variability
Cloud servers with pay-as-you-go pricing may have varying costs due to computer power, storage, and network usage. Cost variability is crucial for staking due to fluctuating network activity. Demand changes can lead to unexpectedly high fees. Operating on cloud servers may be more expensive in the long run than owning and maintaining a server. Therefore, stake businesses must carefully and specifically consider their long-term cost-efficiency.
Performance and Reliability
Cloud servers are shared infrastructure. They can have inconsistent performance due to resource contention. Significant impact affects staking operations. They rely on uptime and connectivity. This is especially true for more affordable options. The shared resource model’s unpredictability may cause unexpected downtime. Many cloud service providers offer high uptime guarantees. Staking operations face risks. They rely on network participation for rewards and integrity.
Technological Restrictions
Staking operations face obstacles due to cloud server limits. Custom configurations and optimized software are affected. Cloud servers offer limited customization choices. Network latency from stakers’ distance from data centers can impact their involvement in consensus procedures. This impacts the efficacy and rewards of staking activities.
Compliance and Regulatory Issues
The cloud server situation presents compliance and regulatory problems. The main concerns include data sovereignty and regional data hosting laws. Staking operations differ by region. Not all cloud servers have the flexibility to abide by these laws simply. Proving compliance and upholding audit standards can be more difficult on a cloud server than on a server due to less physical access and control.
Dedicated Servers For Staking
Credits: Freepik
People or organizations use exclusive physical servers for validating transactions and safeguarding a blockchain network. These servers are known as servers for staking. A dedicated hosted server is a single-tenant setup instead of cloud servers, which are virtual and can be shared by numerous users. Reserve the server’s total capacity for one client. This ensures control, security, and performance. Servers are crucial for staking in PoS blockchains. They ensure safe and efficient network operation.
The performance and dependability of servers are two main benefits of employing them for staking. Stakeholders can benefit from stable network reliability. The server’s resources are not shared. This ensures consistent processing power. PoS systems need online validators to participate in consensus and collect staking rewards. This is vital for successful staking operations. Servers are dependable. Suppliers offer uptime assurances. Stakeholders can optimize involvement and earnings.
Advantages of Dedicated Servers For Staking
Dedicated servers offer benefits for blockchain staking, especially for PoS protocols. Serious investors and organizations prefer servers to enhance their gains and influence within a blockchain network. The benefits include better security, performance, control, and dependability.
Enhanced Security
A server’s higher level of security is one of the main benefits of using it for staking. One client uses a server, while cloud servers are shared among multiple tenants. The risk of cyber threats and attacks, which are more common in shared environments, is significantly decreased by this exclusivity. Stakeholders can implement strong security measures like firewalls and security protocols. This enhances protection. Total control over the physical server ensures safe cryptographic key management. This is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of staking activities.
Better Reliability and Performance
Servers are more reliable since they allocate their processing power to a single client. PoS protocols require this for staking activities to have access to power and bandwidth. This is essential for maintaining an active presence on the network. SLAs ensure servers are dependable by guaranteeing uptime. This guarantees that stakers stay online and engaged, increasing their chances of being selected to validate transactions and get rewards.
Total Control and Customization
Participants have total control and customization over servers. To meet the needs of their staking activities, they can choose the precise system specs, including CPU, RAM, and storage. They can also personalize the software environment for better performance. Operating systems, blockchain nodes, and staking apps can be optimized. Customization and control are essential for optimizing staking processes. Adapting to network changes requires scaling up resources as needed.
Lower Network Latency
By choosing the server location, stakers can place their activities near network nodes. Closeness lowers network latency, enhancing efficiency and speed for adding blocks and verifying transactions in the blockchain. Reducing latency can lead to higher payouts in the competitive PoS staking environment. Milliseconds can determine if a staker creates the next block.
Long-Term Cost Effectiveness
Dedicated servers offer better cost-effectiveness for businesses. Although initial costs may seem higher than shared or cloud options, the initial expenditure might decrease as servers perform reliably. This can improve the success rate in earning staking rewards. The stable bandwidth and fixed resource costs offer a predictable expense model, which is crucial for long-term financial planning.
Limitations and Considerations for Dedicated Staking
Servers for staking offer benefits. However, drawbacks exist too. Keep these in mind. Difficulties can influence decisions for individuals and businesses considering using servers. Understanding these issues is crucial for making informed judgments. It ensures the sustainability and profitability of staking activities.
Initial and Continuing Costs
Consider the cost when using servers for staking. Dedicated servers initially cost more because they offer exclusivity and better performance. This covers the cost of renting or buying the server. It also includes expenses for cooling, energy use, security, and hardware upkeep. Servers may be too expensive for small stakers, outweighing potential profits.
Technical Know-How
Running a server requires a certain degree of technical know-how. Participants must stock and update staking software. They should maintain server hardware configurations and ensure robust security protocols. Knowledge is crucial for starting and ongoing tasks. It helps diagnose issues. A lack of technical understanding can increase costs for inexperienced individuals. External consultants or technicians might be necessary.
Infrastructure and Physical Security
Servers offer improved cybersecurity. They need infrastructure and physical security. Servers may need more money for security, based on where they are. This safeguards against environmental hazards, theft, and damage. The server requires reliable power supplies and effective cooling to operate correctly. This can increase setup and maintenance costs.
Redundancy and Network Connectivity
A stable network is crucial for successful staking. Disruptions may lead to missed opportunities to validate transactions and earn rewards. Consider redundancy when connecting servers to reliable internet to reduce downtime. You may need to pay more for backup internet to ensure continuous connectivity. This is especially vital in areas with unreliable service.
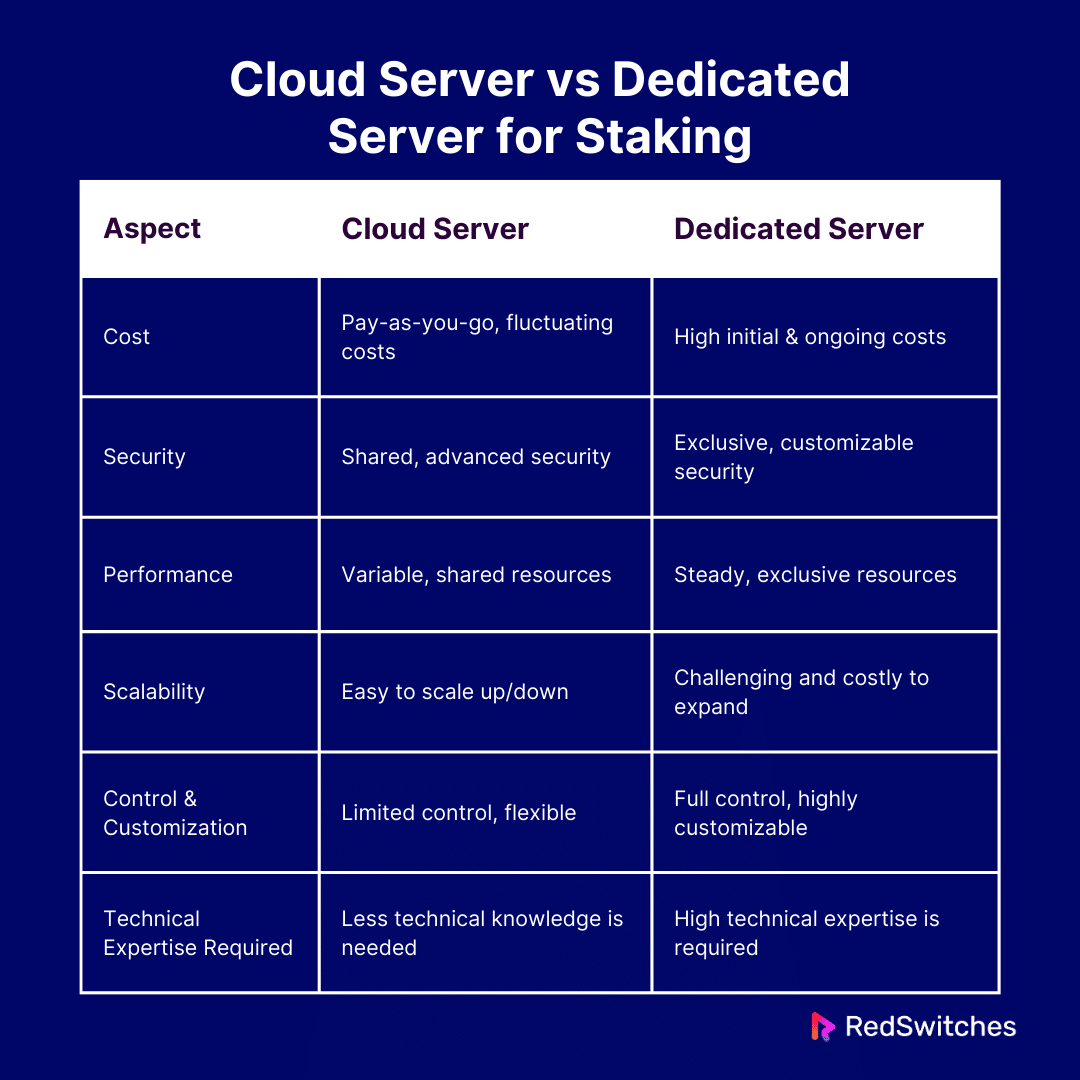
Cloud Server vs Dedicated Server for Staking: Key Differences
This section will discuss the core part of our blog, namely, the critical differences between a Cloud Server and a Dedicated Server for Staking.
Cost
The main reasons why cloud servers are appealing for staking are their affordability and adaptability. With their pay-as-you-go business model, you only pay for the resources you utilize. This may result in fluctuating expenses. They depend on how much you stake, use, need, and require. Smaller staking businesses or those with unpredictable workloads may benefit most from this model. It gives tight control over expenses without needing a large investment.
One of the server’s most important factors is its cost structure. These servers have high initial and ongoing costs, including staff, power, and maybe maintenance. These expenses are predictable and provide consistency for financial planning. However, small businesses may find them unaffordable. The cost might even itself out due to increased efficiency and potential earnings from staking.
Security
An infrastructure with cloud servers has varying degrees of security. Cloud companies deploy advanced security procedures. These benefit you. However, cloud computing’s shared nature may pose problems. The security measures taken by the provider reduce the risk of cyberattacks. However, you are still in charge of protecting access to your staking activities and controlling cryptographic keys in the cloud. It involves balancing taking advantage of advanced security measures and managing the dangers of sharing resources.
Because a server’s resources are not shared with any other user, they provide higher security benefits. Due to their exclusivity, the security measures can be highly customized. They range from advanced cybersecurity to physical precautions. These measures are adapted precisely to the requirements of the staking operation. Total control over the server environment eliminates the hazards related to sharing resources.
Performance
Cloud servers’ performance varies. Several people share resources, so the amount of processing power or network bandwidth may vary at times. Even if good cloud providers try hard to reduce these problems and maintain a high standard, staking operations may still have outages. Procedures for staking can accept some uncertainty. They are best for cloud servers.
A single staking process uses all of the server’s CPU. This ensures performance on a server is steady and reliable. This guarantees the server can handle heavy workloads and stay online. It is essential for profitable staking. Dedicated servers can provide the high performance needed for staking. Staking needs lots of processing power and network bandwidth. This is because there is no contention with other users.
Scalability
One of cloud servers’ main advantages is their ability to grow. Your resources can be easily scaled up or down in response to your staking operation’s needs. Because of their flexibility, managing demand surges or expanding your staking operations is simpler. This enables effective adaptation to changing workloads without requiring actual hardware modifications.
Scaling activities on a server can be more difficult than on cloud servers. Adding more servers or upgrading existing ones are common ways to get more resources. But they can be costly and time-consuming. Dedicated servers provide better control and performance. But growing them needs preparation and money. This is because they have fixed resources.
Control and Customization
Cloud servers provide less control and customization than servers, particularly regarding hardware and more advanced software layers. They still offer great flexibility when setting up your operating system, selecting your software stack, and adjusting your resource levels as required. The finer details of control are where there is a trade-off, and these may be limited by the alternatives offered by the cloud provider.
Dedicated servers offer unrivaled control and customization possibilities. Because users have complete control over the hardware and software environment, every part of the server can be optimized to suit the unique requirements of a staking operation. Dedicated servers are perfect for high-stakes staking operations because they offer the superior performance, security, and operational efficiency required for these activities.
Technical Expertise Required
Running a staking operation on a cloud server usually requires less technical know-how than managing a server. Numerous cloud providers provide managed services and support, which can relieve some of the technological stress. This can be a big benefit for individuals who would rather concentrate on staking methods than the finer points of server management.
Running a server requires a great deal of technical know-how. Users must be able to configure the server, oversee its operations, guarantee its security, and resolve any problems that may arise. Although the requirement for technical expertise may be a hurdle for some, it presents an opportunity to optimize the staking process to an extent difficult with cloud servers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, depending on aspects like cost, security, performance, scalability, control, and the availability of technical experience, the decision between cloud servers and servers for staking is crucial. Cloud servers are a good option for new or fluctuating stakers because they are flexible, scalable, and have fewer upfront expenditures. Conversely, servers offer unparalleled protection, steady performance, and total control—making them perfect for demanding staking operations that need dependability and customization.
When choosing the optimal infrastructure for your staking needs, it’s important to think about a provider who can give customized solutions and knows these subtleties. RedSwitches is a formidable competitor in this context, providing server options tailored to stakers’ requirements. Stakers can benefit from high performance, security, and dependability—all crucial for successful staking—as well as our professional support staff and technological help, guaranteeing seamless and effective operations.
FAQs
Q. Is the cloud cheaper than a server?
Cloud servers can be cheaper initially due to their pay-as-you-go model, but servers might offer better long-term cost efficiency for heavy, consistent workloads.
Q. Which server is the cheapest?
The cheapest server option typically depends on specific requirements; shared hosting is generally the least expensive, followed by cloud servers for small-scale operations.
Q. Why servers are expensive?
Servers are expensive due to the high-quality hardware, maintenance, security measures, and infrastructure to ensure reliable, high-performance operation.
Q. What is the difference between a cloud and a dedicated staking server?
A cloud server is a virtual server that runs in a cloud computing environment, offering scalability and flexibility. On the other hand, a server is a physical server solely for using a single organization, providing control and performance.
Q. How does server hosting differ between dedicated and cloud server hosting?
Server hosting involves leasing a physical server from a hosting provider, which offers full control over hardware and software. On the other hand, cloud server hosting involves renting virtual server space on a pay-as-you-go basis through a cloud provider.
Q. What is the significance of uptime when comparing cloud server and server hosting?
Uptime refers to the time a server is operational and accessible to users. Cloud server hosting typically offers higher uptime guarantees due to its redundancy and failover mechanisms compared to servers that rely on physical hardware.
Q. How does managed server hosting differ from a VPS hosting service?
Managed server hosting involves the hosting provider managing the server for the client, including maintenance and support. VPS hosting, or Virtual Private Server hosting, provides a virtualized server environment within a physical server, offering more control and customization options than shared hosting.
Q. What are the key resources available with cloud server hosting compared to dedicated hosting?
Cloud server hosting offers scalability, on-demand resources, and the ability to adjust server resources quickly based on demand. Server hosting provides stability, performance, and dedicated hardware resources for consistent performance.
Q. How does data loss risk vary between cloud server and server hosting?
Cloud server hosting typically includes data redundancy and backup services, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures. Servers may require manual backups and RAID configurations to mitigate data loss risks.
Q. What are the key considerations when choosing between a cloud server and a server for staking?
Factors to consider include budget, scalability needs, performance requirements, control preferences, and the level of technical expertise available for server management.