Key Takeaways
- PoS (Proof of Stake) is a blockchain consensus mechanism where validators are picked to produce new blocks and validate transactions according to the amount of cryptocurrency they own.
- PoS originated as an alternative to Proof of Work (PoW) to address its energy inefficiency.
- PoS differs from PoW as it replaces energy-intensive mining with staking, where validators lock up their coins as collateral.
- In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on their stake, and they earn rewards for their participation.
- PoS features include scalability, energy efficiency, and security through economic incentives.
- PoS Pros include energy efficiency and scalability.
- PoS cons may involve potential centralization and security concerns.
- PoS addresses monopoly problems by mitigating centralization risks through mechanisms like coin age and slashing penalties.
- PoS cyptocurrencies examples include Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, and Tezos, which use PoS for consensus.
- RedSwitches provides robust and scalable dedicated hosting solutions, ensuring validators have the high-performance and reliable infrastructure to participate effectively in Proof of Stake networks.
Proof of Stake (PoS) has emerged as a revolutionary alternative to the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) system. It has quickly gained significant traction over the past decade, with around 80 cryptocurrencies currently using PoS as the consensus mechanism. PoS’s growing popularity shows a shift towards energy-efficient and scalable blockchain solutions.
This innovative consensus algorithm provides a greener alternative by significantly reducing energy consumption and democratizing the process of participating in the blockchain network. This blog is an in-depth guide on what is Proof of Stake. It will go over its advantages, how it works, and its potential to reshape the future of digital transactions.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Proof of Stake?
- History of Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Proof-of-Work vs Proof-of-Stake
- How Does PoS Work?
- Features of Proof of Stake
- Pros and Cons of PoS
- How Proof of Stake Addresses Monopoly Problems
- Proof of Stake Cryptocurrencies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Proof of Stake?
Credits: FreePik
So, what does proof of stake (PoS) mean in crypto?
PoS (Proof of Stake) is a blockchain consensus mechanism where validators are picked to produce new blocks and validate transactions according to the amount of cryptocurrency they own. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which uses a great deal of energy to solve complicated mathematical problems, PoS establishes agreement more energy-efficiently.
In PoS, validators replace miners. These validators are selected to produce new blocks and verify transactions depending on the quantity of bitcoin they own and are prepared to “stake” as collateral. The central premise is that the more cryptocurrencies you own and are prepared to hold, the more likely you will be picked as a validator. This is due to a higher stake.
The top benefits of Proof of Stake include energy efficiency, as it removes the need for energy-intensive mining activities. It also encourages greater network security and lowers the risk of centralization, as the barriers to entry are lower than PoW. PoS allows anybody with cryptocurrency to potentially participate in the validation process, making it more inclusive. In Proof of Stake (PoS), dedicated servers are pivotal in securing the network.
Also Read: Stake Crypto And Earn! Dive Into Crypto Staking Basics.
History of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Here is a brief look at how Proof of Stake came about:
The Dawn of Digital Currency: Pre-PoS Era
Before the birth of Proof of Stake (PoS), the digital currency landscape was dominated by Proof of Work (PoW), a consensus mechanism introduced by Bitcoin in 2009. To validate transactions and produce new blocks under PoW, miners must solve complicated mathematical problems. While secure, this method used a large amount of energy, raising issues about sustainability and scalability.
The Birth of Proof of Stake: Conceptual Foundations
The concept of Proof of Stake first emerged in 2012 as a response to PoW’s energy-intensive nature. Early discussions on forums like Bitcointalk introduced the idea of a staking mechanism, where the creation of blocks and the network’s security would depend on the ownership of the currency itself rather than computing power.
Peercoin: The Pioneer of PoS
Peercoin made history in 2012 as the first cryptocurrency to use a hybrid PoW/PoS mechanism. This breakthrough was a notable point in the history of digital currencies, proving that safe and energy-efficient consensus mechanisms were feasible. In Peercoin’s concept, PoS coexisted with PoW, with staking progressively taking over as the primary method of network security.
The Evolution and Refinement of PoS
Following Peercoin, other cryptocurrencies started to research and embrace different forms of PoS. Each added improvements and new features. For example, Nxt, launched in 2013, was among the first to implement a pure PoS system, completely removing the PoW component and reducing energy consumption.
Ethereum’s Shift: A Major Milestone
Initially launched with a PoW consensus mechanism, Ethereum announced plans early on to transition to PoS. This shift, Ethereum 2.0 or the Serenity upgrade, was highly anticipated. It promised to enhance scalability, security, and energy efficiency. The gradual transition to PoS culminated in the successful Merge event in September 2022. This marked a significant milestone in the history of blockchain technology.
The Maturation of PoS: Advancements and Innovations
Proof of Stake has progressed and changed, with advancements like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Liquid Proof of Stake (LPoS), and Sharding. These advancements have addressed various issues, including governance, scalability, and user engagement. Cardano, Tezos, and Polkadot are at the forefront of these innovations, each offering distinct answers to the changing PoS scenario.
The Future of PoS: Trends and Prospects
The future of Proof of Stake is bright, with continued research and development aimed at increasing its efficiency, security, and decentralization. The rising concern about environmental sustainability drives the adoption of PoS, making it an important component in the future of blockchain and digital currencies.
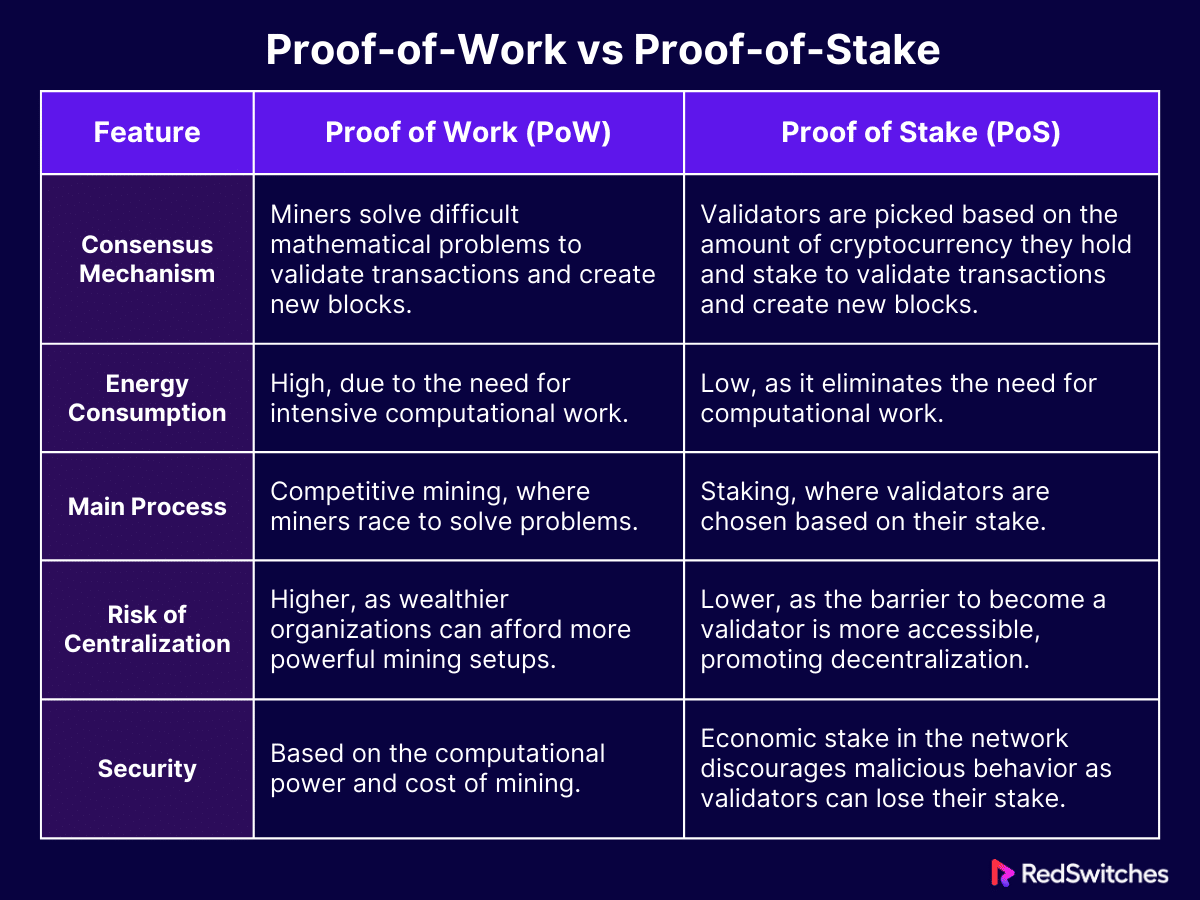
Proof-of-Work vs Proof-of-Stake
Credits: FreePik
Proof of Stake (PoS) vs. Proof of Work (PoW) are two different mechanisms blockchain networks use to gain consensus or agreement on the validity of transactions and the creation of new blocks. Understanding how these two methods differ is important to appreciate their impact on the functionality and protection of blockchain technologies.
Proof of Work (PoW)
As stated above, Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism numerous reknown cryptocurrencies use. In PoW, miners compete to achieve solutions to difficult mathematical problems via high-powered computers. The first miner to get to the solution can add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is awarded with cryptocurrency. This process is energy-intensive, requiring noteworthy electricity and computational power.
Key characteristics of PoW include:
- High Energy Consumption: Miners use substantial electricity to run their computers and cool their equipment.
- Competitive Mining: Miners compete against each other. Only the first to solve the problem gets the reward.
- Security through Work: The cost and efforts of mining act as a deterrent against fraudulent actions, as rewriting the blockchain would demand ample computational power.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake is an alternative to manage some of the limitations of PoW, mainly its high energy consumption. PoS comes with validators instead of miners who are picked to develop new blocks and validate transactions based on the cryptocurrency amount they hold and are ready to lock or “stake” as collateral.
Key characteristics in PoS include:
- Energy Efficiency: PoS eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining, greatly decreasing the blockchain’s overall energy usage.
- Staking Instead of Mining: The likelihood of being picked to validate transactions and produce new blocks is proportional to the amount of cryptocurrency invested. This means that the higher your stake, the more your likelihood of being selected as a validator.
- Less Risk of Centralization: In PoW, wealthy groups may buy more powerful mining sets, leading to centralization. PoS has a lower barrier to being a validator, allowing for a more decentralized and democratic process.
- Economic Security: PoS offers security through economic means. Validators have a financial stake in the network, preventing malicious conduct as they can lose their stake for deception or attacks.
Also Read: Guide To Types Of Crypto Staking: Risks, And Platforms 2024.
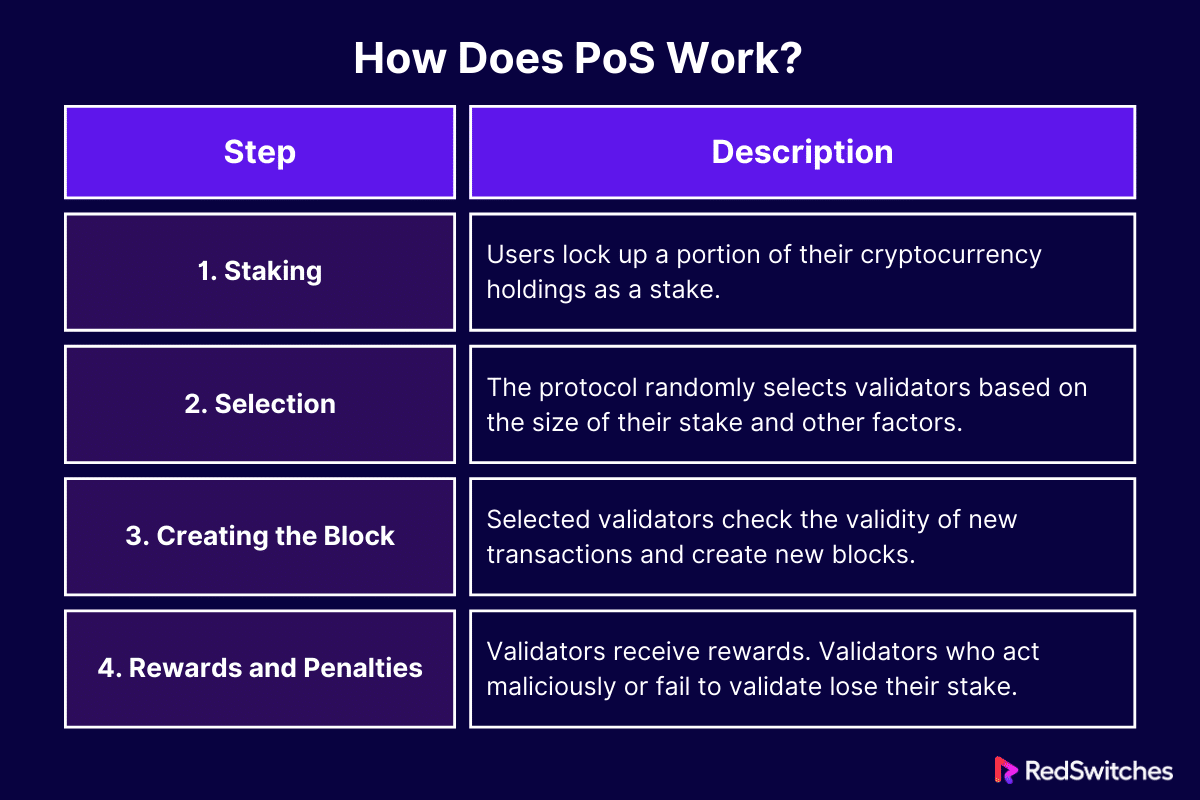
How Does PoS Work?
Credits: FreePik
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism certain blockchain networks use to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Here’s how it works:
Staking
PoS features validators instead of miners. These validators take part in the network by locking some of their own cryptocurrency as a stake. This stake acts like a security deposit. The validators have something to lose if they act dishonestly. A dedicated server ensures continuous uptime for validators participating in the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism.
Selection of Validators
When a new block has to be added to the blockchain, the protocol assigns a validator to produce and propose the new block. This pick is not random; it is influenced by the quantity of cryptocurrency staked by the validator (the more you stake, the better your chances) and the length of time they have staked it. Some networks use techniques like Randomized Block Selection or Coin Age Selection to choose validators.
- Randomized Block Selection: Validators with considerable stakes are more likely to be selected to validate the subsequent block.
- Coin Age Selection: The selection depends on the product of the stake amount and the measurement of the time it has been staked. After a validator forms a block, their coin age is reset to zero, keeping them from dominating the block creation process.
Creating the Block
Once selected, the validator reviews the transactions’ validity, forms a block, and adds it to the blockchain. Other validators must verify the new block. It only gets added to the blockchain if it’s valid.
Rewards and Penalties
Validators receive incentives for adding new blocks to the blockchain. These incentives are derived from transaction fees or newly created coins. If a validator acts maliciously, like attempting to approve fraudulent transactions or creating forks in the blockchain, they may lose some or all of their stake, a process known as slashing.
Security and Decentralization
The PoS mechanism promotes decentralization by letting more individuals become validators without requiring expensive computing resources, compared to Proof of Work (PoW). The possibility of losing staked coins due to dishonest activity is a powerful preventative measure against network attacks.
To add more depth to the understanding of PoS:
- Network Participation and Governance: Proof of Stake frequently includes mechanisms for network governance, allowing stakeholders to engage in decision-making processes about the network’s future. This might involve voting on ideas for protocol upgrades or improvements, demonstrating a more democratic and participatory approach to network growth.
- Multi-layered Staking and Delegation: Certain PoS systems allow token holders to delegate their staking rights to others. This allows people to contribute to network security and decision-making without becoming active validators. This results in a more layered and adaptable staking environment where users may receive rewards passively while contributing to the network’s resiliency.
- Adaptive Consensus Mechanisms: In some PoS models, the consensus process can change depending on network conditions. For example, the validator selection criteria may alter to promote more decentralized and equitable participation or the economic model may be adjusted as the network expands.
- Improved Efficiency: PoS is praised for its capacity to increase the efficiency of blockchain transaction processing dramatically. Without the processing overhead of PoW, PoS networks can manage more transactions at a lower cost, opening the path for more widespread use of blockchain technology in various industries.
Also Read: Ultimate Guide To Node Staking On Dedicated Servers.
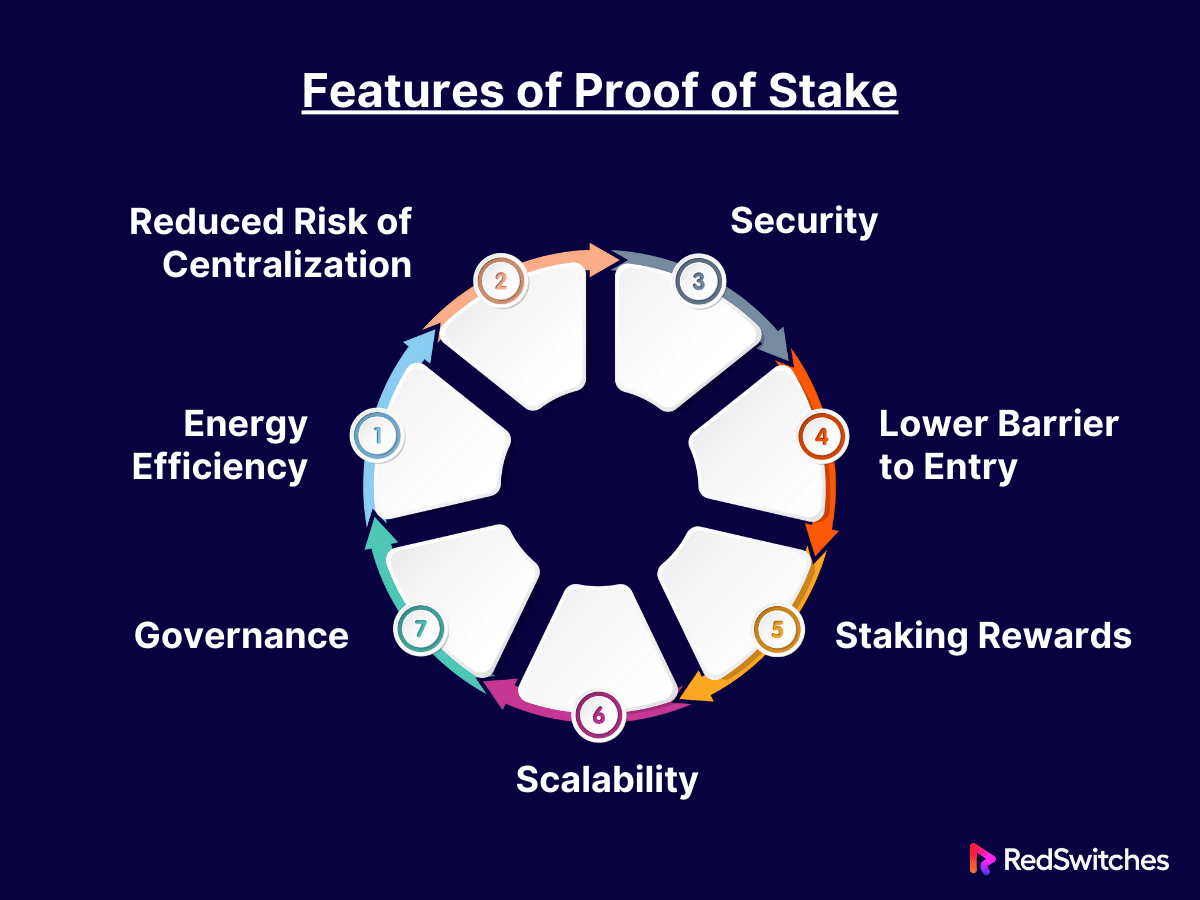
Features of Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake (PoS) offers several features that contribute to its rising popularity as a consensus mechanism in the blockchain space. Here are some of the key features:
Energy Efficiency
One of the most celebrated features of Proof of Stake is its energy efficiency. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which demands considerable computational power and energy to mine new blocks, PoS accomplishes consensus without ample electricity usage. Validators are assigned to produce new blocks based on the quantity of cryptocurrencies they own. They are willing to stake, not on their computer capacity, resulting in a substantial decrease in energy use.
Reduced Risk of Centralization
In PoW systems, the entities with the most computational power (often big mining pools) may control the mining process, resulting in centralization. PoS works differently. It democratizes the validation process. Since the selection of validators is based on their stake and not on mining power, it decreases the chance that a few participants will dominate the network.
Security
PoS increases network security through the staking process. Validators have a financial stake in the network, which they stand to lose if they allow fraudulent transactions. This financial commitment discourages harmful activity and provides an additional degree of security. With a dedicated server, validators can efficiently process transactions and contribute to the security and decentralization of the network.
Lower Barrier to Entry
Unlike PoW, which needs a considerable investment in hardware and power to begin mining, PoS allows users to join as validators without the use of expensive equipment. This reduced entrance barrier enhances network accessibility and validator decentralization.
Staking Rewards
In PoS, validators get rewards for creating new blocks and verifying transactions. These rewards come from the network’s transaction fees. They may also come from newly created tokens. The prospect of earning staking rewards motivates participants to hold and stake their coins, adding to the network’s stability and security.
Scalability
Proof of Stake can manage more transactions at an accelerated rate than Proof of Work. This expanded scalability is crucial for the across-the-board adoption of blockchain technology. It enables the network to accommodate growing numbers of transactions without a corresponding growth in power consumption or delays.
Governance
PoS often has governance mechanisms enabling stakeholders to vote on important issues, including network upgrades and policy changes. Since stakeholders are incentivized to act in the network’s best interest (because of their financial stake), this voting process helps ensure that decisions are favorable to the blockchain’s long-term health and development.
Also Read: Automated Staking Scripts and Tools for Server-based Nodes
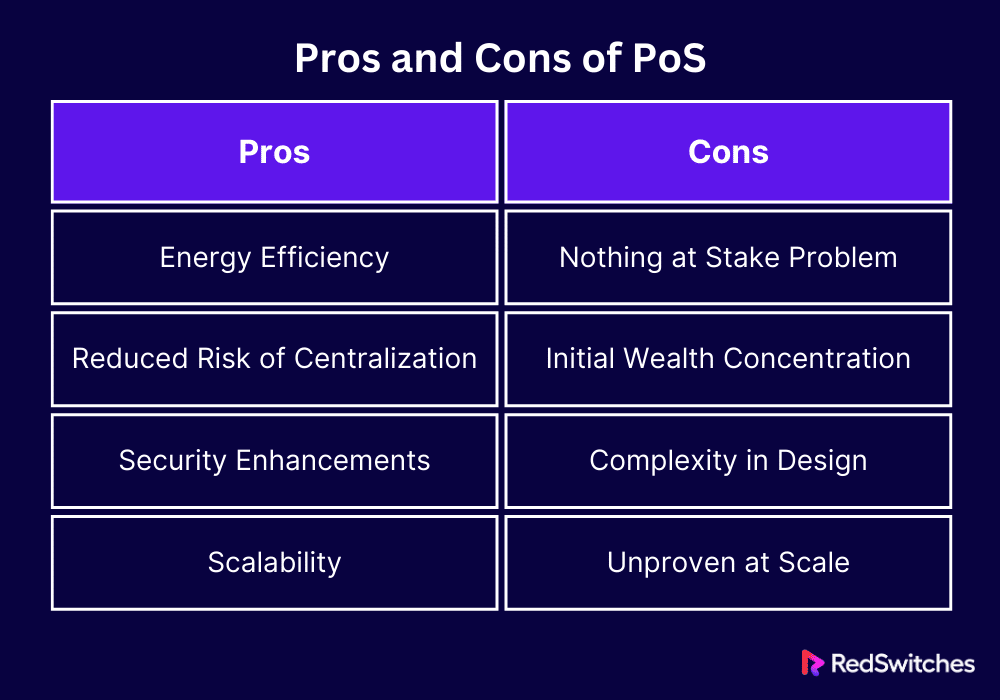
Pros and Cons of PoS
Understanding the pros and cons of PoS can help investors, developers, and users make informed decisions in terms of which blockchain technologies to invest in, support, or develop. Here are the top pros and cons of PoS:
Pros of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Let’s discuss the pros first.
- Energy Efficiency: PoS comes with the benefit of low energy consumption. Since it does not demand extensive computational work, it’s much better for the environment and sustainable in the long run.
- Reduced Risk of Centralization: The concentration of mining power is less of an issue in PoS since the creation of new blocks doesn’t rely on cutting-edge and expensive hardware.
- Security Enhancements: PoS systems can offer advanced security features. The requirement to stake a high amount of currency to participate as a validator means there’s a financial disincentive for fraudulent acts.
- Scalability: PoS can potentially manage greater transactions, making blockchain networks faster and more scalable.
Cons of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Now, let’s take a look at the cons of PoS.
- Nothing at Stake Problem: In PoS, there’s a theoretical problem called the “nothing at stake” problem, where validators might support several blockchain versions at the same time to maximize their rewards, potentially creating security vulnerabilities.
- Initial Wealth Concentration: If a small group of people hold a notable portion of the cryptocurrency, they could control the validation process. This may result in centralization and control, which contradicts the decentralized spirit of blockchain.
- Complexity in Design: Implementing a PoS system can be complex, with intricate mechanisms to ensure network security and prevent manipulation. This can make development and maintenance more challenging.
- Unproven at Scale: While PoS has been successfully deployed in a range of blockchains, its capacity to protect a network as large and valuable as Bitcoin’s, for example, is largely unknown, prompting discussion over its long-term viability.
Also Read: The Connection: Dedicated Servers In Crypto Staking.
How Proof of Stake Addresses Monopoly Problems
Proof of Stake (PoS) offers a unique approach to addressing monopoly problems in blockchain networks, especially those seen in Proof of Work (PoW) systems. Here’s how PoS helps manage these issues:
Democratizing Network Participation
In PoW, the chance of winning rewards is greatly affected by the processing capability that a participant possesses. This sometimes leads to the formation of mining pools, in which individuals pool their resources to compete more efficiently, sometimes resulting in a few pools dominating the network.
PoS levels the playing field by providing network validation possibilities depending on how much cryptocurrency an investor has and is prepared to stake. This implies that as long as you have a stake, you may contribute to the consensus process, lowering the possibility of a monopoly.
Lowering Entry Barriers
Proof of Stake (PoS) systems greatly minimize the entry barriers seen in Proof of Work (PoW) systems. PoW necessitates users to invest in high-end processing hardware and use plenty of power to mine new blocks, which might be too costly.
This financial constraint limits participation to those who can afford the significant investment, frequently resulting in a concentration of power among wealthy people or groups.
PoS eliminates the requirement for such a large hardware configuration and the resulting energy expenses. Instead, the capacity to participate in and validate transactions is determined by the quantity of cryptocurrency a user has and is open to stake.
This change indicates that those with less financial resources can contribute to and participate in the network’s consensus process. It facilitates a more diverse and inclusive validator base.
Stake-Based Incentives
PoS system design includes features that oppose centralization and encourage a fair distribution of control. Stake-based incentives play an important part in this. Participant risks and possible rewards in proof of stake (PoS) increase with the amount of cryptocurrency staked.
Participants with considerable funds invested in the network are prone to act in their best interests to safeguard their investment. This alignment of interests contributes to the network’s integrity and fairness.
It also assures that individuals with a higher stake, who may have more power over the network, remain dedicated to its health and longevity, avoiding monopolistic tendencies and ensuring a safer and stable blockchain ecosystem.
Penalties for Misconduct
Slashing is used in PoS to punish validators who violate network rules or engage in misconduct. Slashing is the withdrawal of a portion of the validator’s stake if they are determined to be behaving maliciously or failing to fulfill their validation tasks properly.
This penal approach is a major disincentive to destructive actions, such as efforts to dominate the network or influence consensus procedures. PoS assures that validators remain watchful and act responsibly by imposing severe financial penalties for misconduct, thus protecting the network against centralization and abuse.
Encouraging Decentralization
PoS systems promote a more decentralized network structure. Given that the ability to validate transactions and produce new blocks is not reliant on processing capacity, as in PoW, but rather on the amount of staked cryptocurrency, greater numbers of people can participate in the network’s consensus mechanism.
This widespread involvement distributes network control among a larger number of validators, minimizing the possibility of any single entity or group dominating the network. Increased decentralization reduces monopolistic concerns while increasing network resilience and security.
Also Read: 7 Best GPUs For Mining In 2024.
Proof of Stake Cryptocurrencies
Proof of Stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies represent a major shift in the blockchain world, focusing on energy efficiency and stake-based consensus to validate transactions. Here are a few leading proof of stake cryptocurrencies:
Ethereum 2.0
Credits: Ethereum
The Ethereum proof-of-stake system was introduced in September 2022. This shift aimed to enhance the network’s scalability and lower its carbon footprint. In Ethereum 2.0, validators are chosen to develop new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and want to “stake” as collateral.
Cardano
Credits: Cardano
Cardano is noted for its research-driven methodology, as well as its distinctive two-layered architecture. This design separates the ledger of account values from the reason why values are transferred from one account to another. This split provides more flexibility and speedier transactions. Cardano’s PoS mechanism, Ouroboros, is intended to be more secure and energy efficient.
Tezos
Credits: Tezos
Tezos provides a unique approach to governance by allowing stakeholders to vote on protocol modifications that can be deployed without hard to fork network. This capability has established Tezos as a self-amending blockchain platform.
Its proof-of-stake method promotes a more energy-efficient procedure while incentivizing user engagement in network improvements and decision-making, resulting in a more democratic and dynamic blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion
Proof of Stake is a game-changing approach to blockchain that promises increased scalability, security, and energy efficiency for cryptocurrency systems. As we accept this development, the need for dependable and strong digital infrastructure becomes important. Using dedicated servers in Proof of Stake aligns to create a sustainable and robust blockchain ecosystem.
RedSwitches facilitates this transformation. We provide robust and scalable dedicated hosting solutions, ensuring validators have the high-performance and reliable infrastructure needed to participate effectively in Proof of Stake networks.
Our secure and always-on dedicated server validators can maintain a constant presence on the network, reducing the risk of missed opportunities for block validation and ensuring a steady flow of rewards.
So what are you waiting for? Contact Us to learn more.
FAQs
Q. What is proof-of-stake in simple terms?
Proof of stake is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks where validators are selected to form new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they own and want to “stake” as collateral.
Q. Is proof-of-stake better?
Whether proof-of-stake is better depends on the context. PoS is considered more energy-efficient and better for the environment than PoW since it demands less computational power. However, it may result in centralization, as those with more coins have greater control.
Q. How does proof of work differ from proof of stake?
Proof of work and proof of stake are consensus algorithms in blockchain, but they differ in how new blocks are validated and added to the blockchain. Proof of work relies on computations and energy consumption, while proof of stake selects validators based on their stake in the network.
Q. What is a blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that securely records transactions via a network of computers. It is the fundamental technology that powers cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Q. What is a validator in a blockchain network?
A validator participates in a blockchain network responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. Validators play a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of the network.
Q. How do staking pools work?
Staking pools are collective groups where multiple users combine resources to increase their chances of being selected as validators in a proof-of-stake network. Rewards earned from validating transactions are then distributed among the pool members.
Q. Is cryptocurrency mining still profitable in 2022?
Cryptocurrency mining profitability in 2022 depends on factors like the value of the cryptocurrency being mined, energy costs, and the mining hardware used. Miners must stay informed about market trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Q. How does decentralization benefit blockchain networks?
Decentralization in blockchain networks ensures that no single entity controls the entire network, boosting security, transparency, and censorship resistance. Decentralization also encourages inclusivity and autonomy among network participants.
Q. What role do tokens play in blockchain ecosystems?
Tokens represent assets or utilities on a blockchain and can serve various purposes, such as facilitating transactions, accessing services, or participating in governance within the ecosystem. Different blockchain networks may have their token standards and uses.