Key Takeaways
- Dedicated hosted servers offer greater security through complete control over security settings and resources. Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared, increasing vulnerability.
- Regular updates, maintenance, and backup verification are critical for keeping servers secure and operational.
- Effective access management enhances server security, including limited root access and secure SSH connections.
- Proactive threat monitoring and changing default port numbers can significantly reduce the risk of cyber-attacks.
- Optimizing server configuration by removing unused software, locking down ports, and securing databases minimizes vulnerabilities.
- Comprehensive data protection strategies, including regular backups and disaster recovery plans, safeguard against data loss.
- Enhancing connectivity security with VPNs and SSL certificates protects data in transit.
- Fully managed hosting services provide automated updates, expert monitoring, and custom security configurations for enhanced security.
- DDoS protection through traffic filtering, overprovisioning, and adaptive response mechanisms shields servers from denial-of-service attacks.
- Choosing a managed and secure dedicated hosting server, like RedSwitches, offers top-notch security, customized setups, and scalability, supporting business growth and online presence.
In today’s digital age, the safety of our online information is more crucial than ever. Every day, servers across the globe store vast amounts of data. This data can include anything from personal details to critical business information. Unfortunately, this makes servers a prime target for malicious actors constantly seeking ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Keeping this data secure for system administrators and security officers is vital and challenging.
Server security involves a set of measures designed to protect servers from all kinds of threats. These threats can range from automated attacks by bots to targeted breaches by hackers. Ensuring server security is not just about safeguarding data; it’s about maintaining its integrity, availability, and confidentiality. Moreover, a breach can severely damage a company’s reputation and lead to significant financial losses.
By implementing effective server security tips and best practices, you can minimize risks and enhance the security of your system. This article aims to guide you through the process. Providing you with essential knowledge and strategies. This is to keep your server resilient against threats. Whether you’re managing an affordable dedicated server or a shared hosting environment. The following insights will help you strengthen your server’s defenses and protect your digital assets.
Table Of Contents
-
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Server Types
- Why Dedicated Server Hosting Offers Better Security?
- How To Secure a Dedicated Server?
- Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keeping Your Server in Top Shape
- Effective Access Management: Securing Your Server
- Proactive Threat Monitoring and Management: A Strategic Approach
- Optimizing Server Configuration for Enhanced Security
- Comprehensive Data Protection for Server Security
- Enhancing Connectivity Security for Server Security
- Navigating Advanced Hosting Solutions for Optimal Security
- How Dedicated Servers Enhance Security
- The Advantages of Opting for a Managed and Secure Dedicated Hosting Server
Understanding Server Types
Credits: Freepik
When discussing the internet and websites, servers are the backbone. Think of them as the big, powerful computers that store and manage data, websites, and online services. Now, these servers mainly offer two types of hosting: dedicated and shared server hosting. Each type has its features, benefits, and drawbacks, especially regarding security. Let’s dive deeper into what makes dedicated hosted servers stand out from shared hosting, focusing on how they improve security.
Secure Dedicated Servers: A Personal Online Space
A dedicated hosted server is like having a big house. It’s all yours, including all the resources inside. This means the server’s entire CPU, memory, and storage are dedicated to your website or application. No sharing with neighbors. This exclusivity brings a lot of perks, especially in terms of security.
Firstly, because you’re not sharing the server, you have complete control over the security settings. You decide what protective measures to put in place, from firewalls and antivirus software to intrusion detection systems. This control makes it harder for malicious attacks because the security measures can be tailored specifically to your needs.
Another benefit is performance. Without other websites using up resources, your site can run faster and more efficiently. This is crucial for businesses where downtime or slow loading can mean lost customers and revenue.
Shared Hosting: The Apartment Complex
Shared hosting server, on the other hand, is like living in an apartment complex. Your website resides on a server with many others, sharing resources like CPU, memory, and storage space. This can be cost-effective, especially for starting personal sites or small businesses. However, it comes with risks.
The main issue with shared hosting is that you have little control over the server’s security measures. If one website on the server gets attacked, there’s a chance your site could be affected, too. This “bad neighbor” effect can lead to security vulnerabilities, where one site’s weakness becomes a risk for all.
Additionally, shared hosting can suffer from performance issues. If another site on the server experiences a surge in traffic, your site might slow down or become temporarily unavailable in the worst case.
Why Dedicated Server Hosting Offers Better Security?
Credits: Freepik
Choosing a satisfactory dedicated server for hosting is one of the best ways to secure your online presence. With full control over your server, you can implement numerous security measures, including vulnerability scanning and real-time server monitoring. This approach not only safeguards your server but also helps to prevent potential security breaches by ensuring that security upgrades and recent security patches are applied promptly.
Opting for a managed dedicated server adds an extra layer of protection, as many security tasks are handled by experts, reducing the risk that your server could become overwhelmed by flooding or other types of security breaches.
Best Dedicated servers are more secure because they allow administrators to use only secure connections to log in, keep unwanted user access away, and ensure that server resources are dedicated solely to safeguarding your server.
This dedicated approach to security helps avoid situations where your server is vulnerable to attacks designed to overwhelm or gain unauthorized access.
By choosing a server package that includes DDoS protection and regular security updates, you protect your server from a wide range of security threats, making servers a popular choice for those serious about the security of their dedicated online assets.
Custom Security Measures
You can install and configure the exact security software and protocols your site needs. This personalized approach to security significantly reduces the risk of attacks.
Isolated Environment
Since you’re not sharing the server, the actions of others can’t compromise your site’s security. This isolation protects against the spread of malware and the exploitation of shared vulnerabilities.
Performance Stability
A dedicated secure server ensures that your site has the resources it needs to run smoothly without the risk of being affected by the demands of other sites. Stable performance is essential for maintaining security, ensuring that security tools and software run efficiently.
Choosing between dedicated and shared hosting depends on your website’s needs, budget, and the level of control you want over security. Servers with dedicated resources offer a compelling advantage for businesses and individuals prioritizing security, performance, and control. While shared hosting can be a cost-effective solution for smaller sites, the potential security risks make servers better for those serious about protecting their online presence.
How To Secure a Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
How to Secure a Dedicated server? It is crucial for protecting your data, website, and online presence from threats. Imagine your server as a fortress. Just as a fortress needs strong walls, guards, and a smart strategy to keep invaders out, your server needs robust security measures. The good news is that you can make your server tough to crack with the right strategies. This section will guide you through essential steps to fortify your server. We’ll keep things simple, focusing on clear actions you can take on how to secure a dedicated server without needing to be a tech wizard. Let’s dive into how to shield your server from harm.
Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keeping Your Server in Top Shape
Regular updates and maintenance are the backbone of server security and performance. This is not just about keeping attackers at bay; it’s also about ensuring your server runs smoothly and efficiently. Let’s break down the essentials of keeping your server updated and well-maintained using straightforward steps and clear language.
Backup Verification: Your Safety Net
Double-check and verify your backups regularly. This could mean setting aside a few minutes each week or day to ensure everything is correctly backed up. Consider mirroring your server environment to a cloud-based virtual machine for testing. This practice is your safety net, ensuring you can bounce back quickly from any disaster.
RAID Array Checks: Avoiding Drive Failures
Many servers use a RAID (redundant array of independent disks) array to safeguard data through redundancy. A quick look at your RAID monitoring tool can alert you to potential drive issues before they become critical. This proactive step allows you to replace or rebuild drives with minimal downtime, maintaining your server’s reliability.
Storage and Resource Usage: Keeping an Eye on Capacity
Server storage can quickly fill up with log files, old emails, and unused software packages. Performance can take a hit if your disk usage exceeds 90%, especially regarding swap file operations. Similarly, monitoring memory and processor usage helps you gauge if your server is overburdened. High CPU and memory usage might indicate it’s time for an upgrade or additional resources.
Software and Control Panel Updates: Staying Current
Updating your server’s control panel, like cPanel, and the software it manages, such as Apache and PHP, is crucial. These updates can patch vulnerabilities, add features, and improve performance. Remember, updating your control panel doesn’t automatically update managed applications, so you must handle those separately.
Security Practices: A Layered Defense
Security isn’t just about software but also practices. Regularly changing passwords, installing security patches, and keeping the operating system up to date are foundational steps. Additionally, monitoring logs for network or disk errors, performing hardware firmware updates, and ensuring all current drivers are critical for catching issues early.
Monitoring and Maintenance: The Ongoing Task
Continuous server monitoring includes checking disk space, examining server logs for security alerts, and monitoring server temperature to prevent overheating. These tasks help you stay ahead of potential failures or performance bottlenecks.
Effective Access Management: Securing Your Server
Credits: Freepik
Managing access to your dedicated hosted server is critical to its security. This involves understanding root access, controlling file modifications, establishing secure connections, and wisely managing authentication methods. Let’s explore these elements to secure your server effectively.
Root Access: The Key to the Kingdom
Root access on your server is akin to having the master key to a building. It allows administrative-level changes, meaning you can alter any setting or file. While this level of control is powerful, it also poses risks if misused. Hence, managing root access responsibly is paramount.
- Limit Root Use: Use root access sparingly and for tasks that require administrative permissions only. For routine operations, utilize accounts with more limited permissions.
- Control File Permissions: You can dictate who can read or modify files and directories with root access. This control is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring only authorized users can make changes.
Secure Server Connection: SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) provides a safe path for accessing your server remotely. It’s essential for executing commands and managing the server’s settings securely.
- Firewall Configuration: Add your IP address to the firewall before connecting via SSH. This step ensures that only recognized IP addresses have access, bolstering your server’s security.
- Connection Tools: PuTTY (for Windows users) or Terminal (for Linux and macOS users) facilitate SSH connections. These tools enable secure, encrypted access to your server’s command line.
Enhancing Access Security
Beyond root access and SSH, enhancing your server’s access security involves a few additional strategies:
- SSH Keys Over Passwords: Instead of relying solely on passwords, which can be cracked or guessed, use SSH keys. This method pairs a private key with a public key, adding an extra layer of security.
- Regular Password Changes: Set a schedule for regular updates for accounts that still use passwords. Changing passwords frequently reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Managing access to your server with dedicated specs isn’t just about keeping unwanted guests out; it’s about ensuring that those within have access for their needs. You’re building a robust security posture by carefully managing root access, establishing secure SSH connections, and adopting stronger authentication methods. Remember, the goal is to maintain control over your server while keeping it open for legitimate use and administration.
Proactive Threat Monitoring and Management: A Strategic Approach
In the digital world, waiting for a threat to occur before responding is no longer sufficient. Proactive threat monitoring and management stand out as a forward-thinking defense mechanism. It’s about monitoring your network, systems, and data to spot and address potential threats before they escalate. Let’s explore how this proactive stance and strategic changes, like altering default port numbers, can significantly enhance your server’s security.
The Essence of Proactive Monitoring
Proactive monitoring is akin to having a high-tech security system for your digital estate. It provides real-time visibility into your network, allowing you to detect unusual patterns, trends, and vulnerabilities. This continuous surveillance means you can identify potential threats early and respond swiftly, minimizing the risk and impact of cyber attacks.
Countering Hackers: Beyond Standard Ports
Hackers often rely on predictability, targeting services running on well-known, standard ports. They use sophisticated tools to scan and identify open ports, and once found, they exploit them. This is where changing default port numbers comes into play. Moving services like SSH away from their default ports to less predictable numbers makes it harder for attackers to find and exploit them. This doesn’t make your services invisible but adds a layer of complexity that can deter many automated attacks.
Changing Default Port Numbers: An Effective Deterrent
Adjusting port numbers is a straightforward yet effective tactic to enhance your server’s security. The principle is simple: avoid the defaults. For services susceptible to attacks, such as SSH, changing to a random port number between 1024 and 32,767 can significantly reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access. This change acts as a disguise, making it more challenging for hackers to pinpoint your services using automated scans.
Optimizing Server Configuration for Enhanced Security
Credits: Freepik
Optimizing your server’s configuration is crucial in securing it against potential threats. This involves tuning the server for better performance and making strategic decisions to minimize vulnerabilities. Let’s explore how removing unused software, locking ports to specific IP addresses, and securing your database can fortify your server’s defenses.
Streamlining Your Server: The Minimalist Approach
One of the fundamental principles of securing a server with dedicated resources is the minimalist approach: if you don’t use it, remove it. Unused software and services consume valuable resources and open up potential entry points for attackers. You’re effectively closing off these vulnerabilities by uninstalling no longer needed software. Think of it as decluttering your digital space, leaving only what’s essential and reducing the attack surface that hackers can exploit.
Locking Down Ports: Targeted Defense
Ports are the gateways through which network communications enter and exit your server. By default, many services listen to well-known ports, which attackers can easily discover and target. Locking ports to specific IP addresses is a strategic move that significantly enhances your server’s security. This practice involves configuring your firewall to only allow connections from trusted IP addresses to sensitive ports, such as the SSH port. It’s akin to setting a combination lock on your gate, where only those with the correct code can enter.
Securing Your Database: The Data Vault
Your server’s database is often the treasure trove that attackers are after. Securing your database involves several layers of protection, from encrypting data to setting strong access controls. Ensure that your database is accessible only to those services and users that need it, and consider using database firewalls to monitor and control access. Regularly update your database software to patch any vulnerabilities and consider encrypting sensitive data to add an extra layer of security.
Comprehensive Data Protection for Server Security
Credits: Freepik
In server security, safeguarding your data is paramount. This protection involves more than just warding off cyber-attacks; it encompasses a thorough strategy for backing up your data and establishing a fail-safe disaster recovery plan. Here’s a breakdown of these essential components to ensure your server’s data is comprehensively protected.
The Backbone of Security: Regular Backups
Regular backups act as your first defense against data loss. Whether due to accidental deletion, system failure, or a security breach, having up-to-date backups means you can recover your critical data without significant downtime. Automating this process ensures backups are performed consistently and reduces the risk of human error. It’s like having a reliable safety net that catches you whenever a piece of data slips through the cracks.
Beyond Recovery: Disaster Recovery Plans
While backups are crucial, they are just one piece of the puzzle. A disaster recovery plan outlines how your organization will respond to and recover from a data loss incident. This plan should detail the steps to resume operations quickly and efficiently, minimizing the impact on your business. It involves identifying which data and systems are critical for your business operations and prioritizing their recovery. Regular drills and updates to this plan ensure that your team knows exactly what to do when disaster strikes, turning potential chaos into a structured response.
Integrating Protection Strategies
Integrating regular backups with a solid disaster recovery plan provides a comprehensive approach to data protection. This strategy ensures the preservation of your data and the continuity of your business operations in the face of unforeseen events. Testing and refining these plans are crucial. Regular drills can uncover gaps in your strategy, allowing for timely adjustments. This proactive approach secures your data and reinforces the resilience of your entire server infrastructure.
Enhancing Connectivity Security for Server Security
In the digital landscape, safeguarding data in transit is just as crucial as protecting data at rest. Two pivotal strategies for bolstering connectivity security are using Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and securing your site with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates. Let’s delve into how these technologies play a key role in securing data as it moves across the internet.
Virtual Private Networks: Creating Secure Tunnels
A VPN is a secure tunnel between your server and the internet. It encrypts data as it travels, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. This is akin to sending a letter in a locked box rather than a transparent envelope. Anyone who tries to snoop on the data in transit would find it indecipherable. A VPN is especially critical for remote server access, ensuring administrators and users can securely connect over public networks.
Secure Sockets Layer: The Standard for Web Security
SSL certificates are the backbone of secure internet communication. They encrypt data between the user’s browser and your server, ensuring that sensitive information like login credentials, personal information, and payment details remain private. When a site is secured with SSL, browsers display a padlock icon, signaling to users that their data is protected. This secures the data and builds trust with your users, an essential factor for any online service or business.
Navigating Advanced Hosting Solutions for Optimal Security
In an era where digital threats loom large, selecting a hosting solution that integrates advanced security measures is paramount. Specifically, fully managed hosting and DDoS protection are critical to safeguarding online assets. This exploration will dissect these features’ technical advantages, illuminating their significance in bolstering server security.
Fully Managed Hosting: A Closer Look
Fully managed hosting is akin to having a vigilant guardian for your digital presence. This service goes beyond hosting; it encompasses comprehensive management of your server’s security and maintenance. Here’s how it technically fortifies your defenses:
- Automated Updates and Patches: This feature ensures that your server’s software is always up-to-date with the latest security patches. Automated systems scan for updates and apply them without human intervention, closing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Expert Monitoring: Continuous monitoring by seasoned professionals means unusual activity is detected in real time. This early detection is crucial for preempting potential security breaches.
- Custom Security Configurations: Managed hosting can provide tailored security setups depending on your needs. This might include custom firewall rules, malware scanning, and intrusion detection systems (IDS), all configured to offer robust protection.
DDoS Protection: Technical Insights
DDoS protection is designed to shield your site from the flood of unwanted traffic that characterizes DDoS attacks. Here’s a technical breakdown of how it works:
- Traffic Filtering: Advanced algorithms analyze incoming traffic to distinguish between legitimate users and attack traffic. This filtering happens off-site, ensuring that only clean traffic reaches your server.
- Overprovisioning: By providing more bandwidth than you typically need, DDoS protection helps absorb the surge of traffic during an attack, keeping your site operational.
- Adaptive Response: Modern DDoS protection adapts to evolving attack patterns. It learns from each attack, enhancing its defense mechanisms over time.
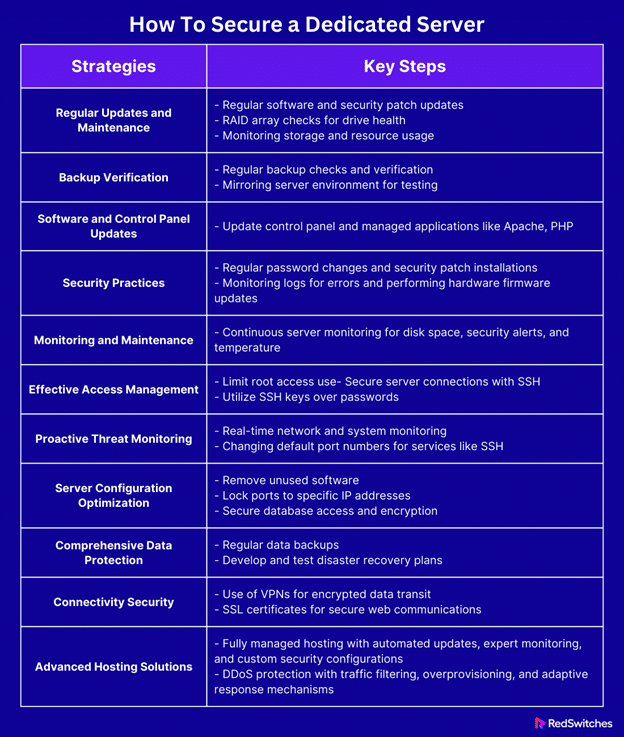
Here’s a table summarizing all the factors mentioned above:
How Dedicated Servers Enhance Security
In the hosting world, dedicated hosted servers stand out for their security benefits. These servers are like having your digital fortress. This is crucial when online threats are more common than ever. Let’s explain why servers are a top choice for those prioritizing security.
Personalized Security Measures
With a satisfactory dedicated server, you can control the security measures. It’s all in your hands. You decide on the firewalls, the antivirus software, and the monitoring systems. This customization means you can tailor your security to your business needs. It’s like building a wall around your data that meets your requirements.
No Shared Risks
One of the best things about dedicated hosted servers is that you’re not sharing space with other users. If another website is compromised on shared servers, it could also put your site at risk. But with a dedicated hosted server, you’re in your own space. This isolation greatly reduces your exposure to threats from other users.
Complete Data Control
Having a dedicated hosted server means total control over your data. You know where it is and who can access it at all times. This is not always the case with other types of hosting. With complete control, you can set up strong access measures. You can decide who gets to see or use your data. This keeps your information secure.
Enhanced Performance and Security
Dedicated hosted servers offer better performance and enhanced security. This is because they can handle more traffic and process data faster. Why does this matter for security? Well, a faster server can run security applications more effectively. It can respond to threats quicker. This means you can stop attacks before they harm.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
With a dedicated hosted server, you can keep everything up-to-date easily. This includes security patches and software updates. Staying current is a big part of staying secure. Hackers often exploit outdated software. By keeping everything updated, you close these loopholes. It’s a simple but powerful way to protect your server.
Custom Backup Solutions
Backups are a key part of any security strategy. With a server that has dedicated resources, you can set up a backup system that suits your needs perfectly. Whether it’s daily, weekly, or real-time backups, you can choose what’s best for your data. In case of data loss or a breach, you can restore your information quickly. This minimizes downtime and keeps your business running smoothly.
Servers offer a level of security that’s hard to beat. The advantages are clear, from personalized security setups to isolation from shared risks. You also get better performance, which supports your security measures. Plus, you can build a comprehensive security plan with control over updates, backups, and data access. A server with dedicated resources is a strong choice for businesses serious about protecting their online presence.
The Advantages of Opting for a Managed and Secure Dedicated Hosting Server
Choosing a managed and secure server with dedicated resources brings many benefits. This choice is crucial for any business aiming to strengthen its online presence. Let’s explore these advantages in simple terms.
Top-Notch Security
A big plus of a managed server is its strong security. The digital world is full of threats. Having a team to look after your server’s security is like having a strong guard. This team keeps the server safe. They update security settings and watch for any odd behavior. It’s like having a fortress that is always getting stronger.
All Resources Just for You
With a server that has dedicated resources, all its power and space are just for you. You don’t share with others. This means your website works better and more smoothly. It can handle many visitors at once without slowing down.
Custom Setup
Another benefit is setting up the server to meet your needs. Whether it’s special software or specific settings, you can make it perfect for what you do. This helps your server run at its best for your business.
Expert Help
When you choose managed hosting, you can access a team of experts. They can help solve problems or give advice to make your server work better. Knowing that help is just a call away is very reassuring.
Always On
These servers are watched to ensure they stay on. If something goes wrong, it gets fixed fast. This means your website is always available to your customers.
Saves Money
At first glance, managed servers might seem expensive. But they can save you money. Think about the cost of hiring your team to do this. Having the managed hosting team take care of it is much cheaper.
Grows with You
As your business grows, your server can, too. It’s easy to add more power or space as you need it. This way, your hosting can grow with your business without big changes.
Now is the moment to elevate your online presence with RedSwitches. Don’t let server management and security concerns prevent you from achieving your business goals. With RedSwitches, you can access state-of-the-art technology, expert support, and customizable solutions to your unique needs. Decide to focus on what you do best and let RedSwitches handle the rest. Get in touch with RedSwitches today and take the first step towards a more secure, reliable, and high-performing online presence for your business. Your success story starts with the right foundation. Let RedSwitches be that foundation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hosting solution plays a crucial role in the success and security of your online presence. The importance of selecting a reliable hosting provider cannot be overstated from the robust security measures offered by servers to the peace of mind provided by managed hosting solutions.
RedSwitches is a provider committed to delivering top-notch security, performance, and support. Whether you want to enhance your website’s security, improve performance, or ensure your data remains protected, RedSwitches has a solution tailored to your needs.
Ready to take your online security to the next level? Don’t wait for a security breach to happen. Click here to explore RedSwitches’ dedicated server options and discover how we can help secure your digital assets today.
FAQs
1. How do I secure my own server?
Start by updating all software to the latest versions. Then, set up strong firewalls and use antivirus programs. Don’t forget to create complex passwords and change them regularly.
2. Is it safe to host a dedicated server?
Yes, it’s safe if you take the right security steps. This includes using secure passwords, updating software, and monitoring for unusual activity.
3. How do I securely host a server?
Securely hosting a server involves a few key actions: ensuring all software is up-to-date, using encryption for data, and restricting access to only those who need it. Also, regularly back up your data.
4. How do you physically secure a server?
Physically securing a server means keeping it in a locked room or cabinet. Only let trusted people have access. Also, consider using surveillance cameras for extra security.
5. What are your first three steps when securing a server?
- Update all software and systems.
- Set up strong firewalls and antivirus protection.
- Limit access with secure passwords and user permissions.
6. What role does root access play in dedicated server security?
Root access allows complete control over your dedicated hosted server, making it crucial to use it wisely and secure it with strong passwords and access restrictions to minimize security risks.
7. What is the best way to safeguard your dedicated hosted server against unauthorized access?
The best way to secure your dedicated server involves limiting root access, using SSH keys, and implementing two-factor authentication to protect your server.
8. Why choose a managed dedicated hosted server for your web hosting needs?
Choosing a managed dedicated hosted server ensures that your hosting server benefits from expert management, including security practices, scanning, and updates, to maintain the best security posture.
9. How can you maintain the security of your dedicated hosted server over time?
Maintain the security of your dedicated server by continuously monitoring for potential security risks, applying the latest security patches, and following security best practices to prevent security breaches.
10. How can I secure my dedicated hosted server?
There are multiple ways to secure your dedicated hosted server. You can start by using a managed dedicated server, setting up strong firewalls, regularly updating software, and implementing access controls.
11. What are some best practices to protect my dedicated hosted server?
To protect your server, limit physical access, use a strong password policy, regularly backup your data, and monitor server logs for suspicious activities.
12. How can I prevent security breaches on my server?
To prevent security breaches on your server, you can install security patches promptly, use encryption for sensitive data, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct regular security audits.
13. What is the significance of having a DDoS-protected server?
Having a DDoS-protected server is crucial as it safeguards your server from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, which can overwhelm your server by flooding it with a huge amount of traffic.
14. How can I ensure that my server is safe from unauthorized access?
To ensure your server is safe from unauthorized access, you should regularly review and update user permissions, disable unused services, employ intrusion detection systems, and conduct regular vulnerability scans.
15. How can I keep malicious users away from my satisfactory dedicated server?
To keep malicious users away from your satisfactory dedicated server, you can use strong authentication methods, configure proper network segmentation, utilize encryption for data transmission, and implement robust monitoring tools.
16. What are 11 ways to secure a dedicated server effectively?
- Utilize a managed, affordable dedicated server.
- Implement strong firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Regularly update software and apply security patches.
- Use encryption for sensitive data.
- Monitor server logs for any suspicious activities.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability scans.
- Limit physical access to the server.
- Employ multi-factor authentication.
- Backup data regularly and securely.
- Utilize DDoS protection services.
- Educate staff on security best practices.