Key Takeaways
- Disaster recovery is crucial for dedicated hosting resilience.
- It ensures business continuity and minimal downtime.
- Disaster Recovery Protects data integrity against natural and cyber threats.
- Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is essential.
- Disaster Recovery Offers a competitive edge by maintaining service reliability.
- Disaster Recovery Promotes innovation and adoption of new technologies.
- RedSwitches enhances Disaster Recovery strategies with robust infrastructure and expert support.
Your hosting infrastructure must be resilient to unexpected disasters. This is not just important but a lifeline in the digital age. Data is as valuable as money. Dedicated hosting has many features and resources. It is the best option for protecting your online presence. But even the most secure systems are vulnerable to the specter of impending catastrophes, including everything from natural disasters to cyberattacks.
This is where it becomes clear how important having a solid Disaster Recovery (DR) plan is. In this post, we examine the vital role of disaster recovery in dedicated hosting. It shows how it plays the unsung hero. It preserves business continuity and guards data integrity in the face of significant challenges.
Join us as we examine the protection levels dedicated hosting environments have built to ensure your digital assets survive hardships.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Disaster Recovery
- Types of Disasters in the Context of Dedicated Hosting
- The Importance of Disaster Recovery in Dedicated Hosting
- Planning for Disaster Recovery in Dedicated Hosting
- Implementing Disaster Recovery Solutions
- Testing and Maintaining Your Disaster Recovery Plan
- Future Trends in Disaster Recovery
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding Disaster Recovery
Credits: Freepik
Disaster recovery (DR) is an organization’s action to restore or maintain critical technology after a man-made or natural disaster. In dedicated hosting, disaster recovery aims to cut downtime and data loss. It does so by restoring servers, databases, networks, and data to their original state.
Disaster recovery in dedicated hosting aims to cut downtime and avoid data loss. It effectively returns networks, databases, servers, and data to their pre-disaster state. Businesses that depend on dedicated server hosting need this procedure. It guarantees ongoing operations and online visibility. These things are key to the business’s ability to withstand disruptions.
Businesses with dedicated servers may protect their vital digital assets. They can keep things running if problems occur. They do this with strong recovery plans.
Key Concepts
Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This measure establishes the upper bound on acceptable file ages that must be restored from backup storage to restore regular operations following a disaster. RPO represents the amount of data that can be lost without seriously hurting the company and is defined in time, ranging from seconds to hours or days before the disaster.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): RTO is the time frame intended to be adhered to to restore a business process following a disaster and prevent unacceptably adverse outcomes from disrupting business continuity. It is the longest time that can pass before the organization’s continued viability is jeopardized.
Business Continuity Planning (BCP): This strategy is more comprehensive than catastrophe recovery, albeit having certain similarities. It includes strategies for maintaining not just the IT parts of a company’s operations during disruptive events but all of them.
Data backup: It is the process of duplicating and preserving company data so that it may be retrieved if the data is corrupted or erased. A disaster recovery plan’s fundamental element is data backup procedures, guaranteeing copies of a company’s data are kept on multiple media or in different places.
Implementing redundancy involves creating duplicate servers, network components, or data storage instances at various physical or cloud locations. This minimizes downtime and data loss by ensuring that the backup component will take over in the event of a failure.
Types of Disasters in the Context of Dedicated Hosting
Disasters, including natural events, intentional cyber threats, and accidental errors, might harm operations, data, and business continuity in dedicated hosting. Every group has different problems and requires different approaches to disaster recovery planning.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, and fires, can cause havoc on dedicated hosting infrastructure. These events cause physical harm, ranging from destroying data centers to cutting power and networks. This shows the need for strong backups and dispersed data centers. For example, floods can cover facilities and ruin servers and gear. But earthquakes can cut vital lines and destroy buildings. Hurricanes and tornadoes bring destructive wind and flooding. These threats can harm power and telecom networks and building integrity.
Fires from natural causes, such as wildfires or facility accidents, can quickly consume hardware and data. These events demonstrate the critical need for off-site data backups and fire suppression systems.
Cyber Attacks
Ransomware, DDoS attacks, phishing, and social engineering are a few examples. So are SQL injection attacks. They are part of the always-changing threat of cyberattacks. These attacks are a danger to dedicated hosting setups. Ransomware can encrypt critical data. It can be stored on-site or off-site. This imprisons the data and disrupts corporate activities. DDoS attacks overload servers. They deprive good users of service. They may harm a company’s reputation and client base. Social engineering and phishing use human weaknesses to gain unauthorized access and compromise data. SQL injection attacks can alter or destroy databases, risking confidential data. These cyber risks show the need for comprehensive security measures. This includes regular software updates. It also means teaching staff about security best practices. And it means having robust cybersecurity systems to find and reduce threats.
Technical Failures
Technical problems are a danger to dedicated hosting operations. These include hardware failures, software flaws and bugs, power outages, and cooling system failures. Any physical component, including networking hardware and hard drives, is susceptible to hardware failures, which can cause unplanned downtime and data loss. System crashes and data corruption can be caused by software problems ranging from operating system bugs to application faults. Power outages can cause server downtime if not immediately countered by UPS activation and backup generators. Similarly, cooling system failures increase the danger of hardware damage from overheating, highlighting the importance of dependable power and environmental controls in data centers.
The Importance of Disaster Recovery in Dedicated Hosting
Credits: Freepik
Disaster recovery is vital in dedicated hosting. It matters for competitive advantage, compliance, and company resilience.
Business Continuity and Minimal Downtime
The central part of disaster recovery is to maintain business operations during disasters. It aims to cause as little service disruption as possible. A good disaster recovery strategy makes restoring essential data and systems easier. This is vital because it cuts downtime and costs. This quick recovery depends on keeping services available. It also depends on surpassing client expectations and protecting the business’s operations. The ability to sustain uninterrupted operations is critical to the company. It protects its revenue and upholds its reputation as a dependable service provider. This is vital in an era where customers are less tolerant of service interruptions. The ability of the business to maintain continuous operations on dedicated servers is essential to maintaining its income streams and enhancing its standing as a dependable service provider at a time when customers are less tolerant of service disruptions.
Data Integrity and Protection
Data is more valuable than traditional assets today. It forms the basis of competitive advantage and business intelligence in the digital world. It protects this priceless resource. Disaster recovery fortifies it. It guards against loss or corruption from disasters. Businesses may ensure that crucial data is tricky. They can make it easy to access by using thorough backup and restore protocols. This step is vital. It maintains data integrity and protects customer info. It also shields a company’s intellectual property. These things all support a business’s core values. Those values drive its operations and growth. Businesses may guarantee the security and accessibility of critical data by putting in place thorough backup and recovery procedures on dedicated servers. This stage is essential for preserving data integrity, safeguarding client information, and defending a business’s intellectual property, all of which support the basic functions and expansion of the enterprise.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Security
Data security and business continuity are crucial today. They are critical in our interconnected economy. So, rules for them are getting stricter. Firm disaster recovery plans go beyond best practices and are now required by law in many sectors of the economy. This proactive plan cuts the risk of non-compliance and the resulting financial and legal fallout. It also shows dedication to the safety and well-being of stakeholders and consumer data. In this sense, disaster recovery shows a company’s commitment to both morality and operational excellence.
Competitive Advantage
Nimble businesses can recover from setbacks quickly. They have a significant advantage over rivals. A strong disaster recovery plan is essential to a competitive strategy. This is true in industries where downtime costs money and undermines client confidence. This resilience helps the business keep its current clients despite adversity. It also makes it a top choice for new clients who value stability and dependability. In an unpredictable landscape, the focus on disaster recovery is crucial. It is critical for standing out and growing.
Risk Management and Strategic Planning
Doing disaster recovery planning requires carefully evaluating weak points. You must then strategically rank asset protection. This process dramatically helps strategic planning and risk management. It gives companies a better grasp of their environment. This procedure not only strengthens the security posture and gets ready for urgent threats, but it also promotes a culture of continuous development by highlighting areas where operational efficiency may be improved. Disaster recovery planning is a proactive approach to a business strategy that incorporates flexibility and resilience into the organization’s fabric.
Customer Trust and Loyalty
A strong disaster recovery plan directly impacts establishing and preserving customer trust and loyalty. In a time when using digital services is essential to day-to-day business, clients value security and dependability highly. Businesses convey a strong statement about their dedication to providing exceptional customer service when they show that they can react to emergencies and recover from them promptly and efficiently. When it comes to a customer’s decision to stick with a service, this dependability becomes crucial. After a successful recovery, customers are more inclined to talk about their positive experiences and act as brand ambassadors.
Innovation and Technology Adoption
Creating a disaster recovery strategy can spur an organization to embrace new technologies and creative working methods. Businesses are faced with the possibility of embracing state-of-the-art technologies that can improve their disaster recovery capabilities as they assess their vulnerabilities and develop plans to minimize possible calamities. This could involve adopting machine learning algorithms for threat detection and predictive analytics, integrating cloud-based backup solutions, or implementing advanced cybersecurity safeguards. Furthermore, as disaster recovery plans continue to advance, companies are inspired to keep ahead of technology developments and industry best practices, fostering an innovative culture.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
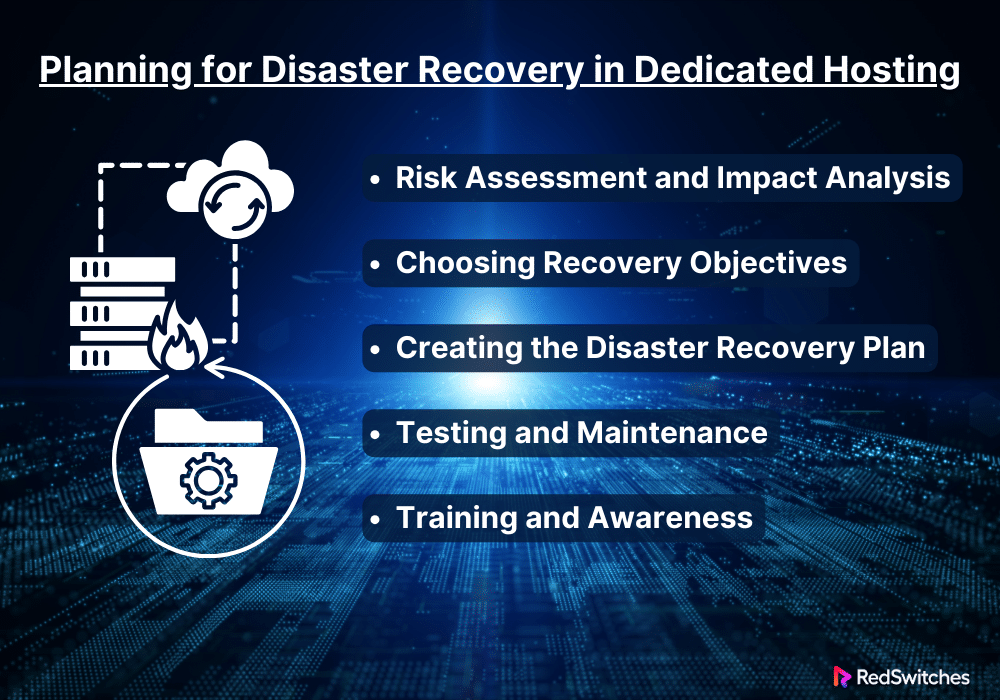
Planning for Disaster Recovery in Dedicated Hosting
In dedicated hosting, disaster recovery planning is complicated. It needs a full grasp of risks, key assets, and tactical steps. They ensure data integrity and business continuity. Businesses must plan carefully. This is key for them to recover from disasters quickly, save downtime, and prevent data loss. The main elements and factors to consider when preparing for disaster recovery in dedicated hosting are examined below.
Risk Assessment and Impact Analysis
A risk assessment and business impact analysis are essential. They are the foundation of any good disaster recovery plan. The first stage is to find hazards. These could interrupt operations, like power outages, hardware issues, and cyberattacks. After identifying a risk, we examine its likelihood and possible impact on business operations. We focus on systems and essential data hosted on dedicated servers. The analysis prioritizes risks. It focuses recovery on the most essential elements. This ensures that resources protect the company’s core operations well.
Also Read Top 15 Critical Cyber Security Challenges and How to Fix Them
Choosing Recovery Objectives
The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are key. They are vital parts of the planning process. RPO establishes the maximum age of files that must be restored from backup storage for the company to carry on with minimal losses. It calculates the maximum time the company can afford to lose data. RTO sets the deadline for fixing company operations after a disaster. It aims to prevent horrible outcomes. These goals set the scope and depth of the recovery plan. They ensure that the most vital information is restored first and quickly.
Creating the Disaster Recovery Plan
After determining the risks and recovery goals, the next stage is to create a disaster recovery plan. The plan should be extensive. It should have a plan on how to respond to different disasters. It should include step-by-step instructions for protecting and restoring systems and data. Essential elements of this strategy include:
Data backup strategies: Choosing how often and how to do backups, such as cloud-based, off-site, and on-site backups, to guarantee data availability and integrity.
Infrastructure Redundancy: Implementing redundant systems and networks, potentially spanning many geographically dispersed data centers, is called infrastructure redundancy. Its purpose is to prevent complete service disruption in the event of a breakdown in one location.
Emergency reaction Procedures: Determining the contact lists, communication strategies, and detailed reaction plans for various crisis scenarios, as well as clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of the disaster recovery team.
Testing and Maintenance
Testing the disaster recovery plan often helps find flaws. It also boosts team morale. It shows that all understand their role and can do it under duress. Full-scale drills simulate crises well. They offer priceless insights into the practical parts of the plan. By being proactive, the recovery process improves. It also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Each test presents chances to streamline the responses. The disaster recovery plan should change along with the business environment, considering new procedures, technologies, and security risks.
Training and Awareness
Not just the IT department, but all stakeholders’ readiness and awareness play a significant role in how effective a disaster recovery strategy is. Adding role-playing and simulations to training programs can help participants become even more accustomed to performing the required actions and reactions. This widespread understanding helps minimize confusion and delays by ensuring prompt, efficient, and well-coordinated responses during a crisis. Involving stakeholders in frequent updates, feedback sessions, and communications underscores the significance of disaster recovery planning and promotes collective accountability for the organization’s resilience.
Implementing Disaster Recovery Solutions
Credits: Freepik
Implementing disaster recovery solutions in a dedicated hosting environment is complex. It requires several steps. These include picking and using technologies and techniques to protect data. They also ensure system uptime and speed up recovery in an emergency. The organization has unique needs. The importance of its data and applications and any hazards it may face must be considered. This thoroughly examines the significant elements of disaster recovery solution implementation.
Choosing Disaster Recovery Solutions
When choosing disaster recovery solutions, businesses must ensure their chosen technologies can scale later. They should also support expansion without requiring a complete plan revision. Also, their ability to work with current IT is key. It is crucial for a smooth recovery. This thorough assessment guarantees that the disaster recovery solutions picked will meet current needs and be flexible enough to fit future business and tech changes.
Data Backup Plans
Good data backup plans include routine audits, tests, and checks. These verify backup integrity and restoration procedures. They ensure that data can be recovered in a usable format. Encryption and secure storage are vital. They are needed for off-site or cloud-based backups to stop unwanted access. This multi-layered approach to data backup places equal emphasis on the security and integrity of the data and its accessibility in the face of ever-changing cyber threats.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
Groups dealing with DRaaS providers should consider the location of the providers’ data centers. They should do this to ensure the centers are not at risk from the same disasters. Carefully evaluating the providers’ disaster recovery procedures and historical performance can help establish more confidence in their capacity to meet server SLAs. Creating a collaboration that strengthens the organization’s disaster recovery posture requires this thorough screening process.
Emergency Response and Communication Plans
Adding feedback loops and procedures for ongoing development can make response and communication plans more successful after disasters. They should be based on post-disaster reviews and drills. This lets businesses improve their plans gradually. They can do so in response to new information and changing risks. During a crisis, using many communication channels helps. For example, social media can increase the effectiveness and reach of outreach. It will ensure that all relevant parties know about the situation and are participating in the recovery.
Frequent Testing and Continuous Improvement
Dedication to regular testing is crucial. So is the quest for improvement. They are vital in implementing disaster recovery solutions. This requires doing planned disaster recovery exercises and simulations. Their purpose is to check the plan’s efficacy. You then look at the results to find areas that need improvement. Frequent testing validates redundancy configurations. It also checks backup systems. It checks if disaster recovery methods work. It also offers a helpful platform. It educates staff on their duties and responsibilities in a real emergency.
Testing and Maintaining Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Credits: Freepik
Testing and upkeep are critical for a disaster recovery plan. They ensure the plan stays useful. These procedures help find flaws in the disaster recovery plan. They also offer chances for improvement. They ensure every team member is ready to respond quickly and well in an absolute disaster. This article thoroughly covers testing and maintaining your disaster recovery plan. It covers doing this in a dedicated hosting environment.
Regular Testing
Validating the efficacy of the disaster recovery plan requires regular testing. Disaster scenarios are simulated to evaluate the organization’s readiness and the plan’s capacity to resume operations within the targeted Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs). Testing can happen in several ways, such as:
Tabletop Exercises: In these discussion-based exercises, the disaster recovery team reviews the plan and discusses how they would handle a fictitious situation. This highlights possible problems with the plan and aids in clarifying roles and duties.
Walkthroughs and drills entail carrying out particular steps of the disaster recovery procedures—like restoring backups or moving to redundant systems—or reviewing them in further detail step-by-step.
Full-scale testing: This type of testing is the most extensive since it simulates a disaster and the recovery process after it has occurred realistically and thoroughly. Although this kind of testing can require a lot of resources, it provides the most insightful information about the strategy’s efficacy and the team’s readiness.
Constant Enhancement
The disaster recovery plan must be updated regularly to stay effective. It is possible to accomplish continuous improvement through:
Feedback from Testing: The disaster recovery plan should be updated and improved using the knowledge gathered from testing operations. Depending on the test results, this may entail changing contact lists, recovery plans, or roles and duties.
Changes in Technology and Infrastructure: The disaster recovery plan must be updated to account for the new systems, apps, and technologies implemented as the organization’s IT environment develops. This guarantees that the plan covers every important facet of the current IT infrastructure.
Acquiring Knowledge from Real-World Events: Any real-world events or close calls should be thoroughly examined. The disaster recovery plan can be strengthened with useful information from the lessons learned from these incidents.
Changes in Regulation and Compliance: To guarantee continuous compliance, modifications to data protection and disaster recovery regulations should be tracked and included in the plan as needed.
Training and Awareness
All stakeholders, not just the IT staff, must continue to receive training and awareness campaigns to maintain a high degree of disaster recovery preparedness. This comprises:
Frequent Training Sessions: Holding training sessions frequently ensures everyone knows their responsibilities throughout the disaster recovery process. This is crucial when the disaster recovery plan is modified, or new hires are brought on board.
Awareness Campaigns: These campaigns can assist in reminding all staff members of the need for disaster recovery preparedness. Newsletters, posters, and briefings during business meetings are examples of this.
Disaster Recovery is Integrated Into Onboarding: The onboarding process of new employees should include an outline of the disaster recovery strategy and the individual’s position within it.
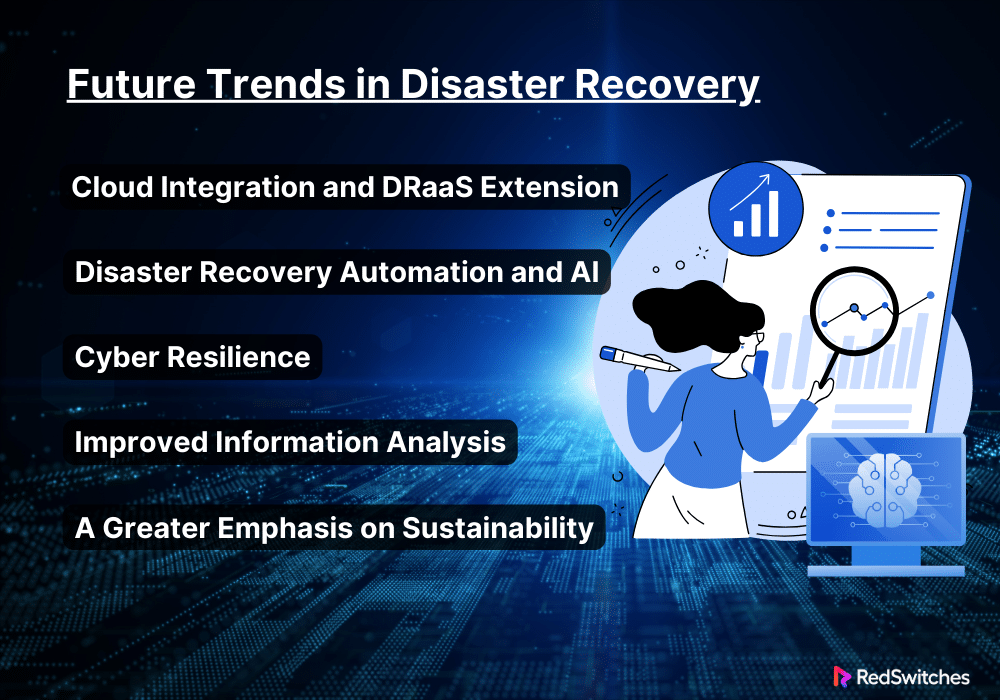
Future Trends in Disaster Recovery
This section examines the big changes that will impact disaster recovery and shows how they are expected to change resilience planning and execution.
Also read All You Need to Know About an Efficient Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud Integration and DRaaS Extension
Cloud technologies will be essential to disaster recovery in the future. Cloud services are great for disaster recovery because they are cost-effective, scalable, and adaptable. DRaaS provides enterprise-level disaster recovery. It serves enterprises of all sizes without significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. The market is predicted to grow a lot. Cloud-based solutions have better security. They link more strongly with on-premise systems. They also have more control over RTOs and RPOs. Cloud-based solutions will only get better.
Disaster Recovery Automation and AI
These two technologies are revolutionizing disaster recovery. They do so by making it more efficient and reducing the chance of human error. Automated workflows can start disaster recovery quickly when an outage is detected. This greatly minimizes downtime. AI and machine learning algorithms can predict system breakdowns. They can also spot odd patterns indicating a cyberattack. This allows for proactive action to prevent disasters. The technologies will allow more frequent and thorough disaster recovery drills. They will do this by improving testing protocols. And they will do so with fewer resources.
Cyber Resilience
Credits: Freepik
Cyber threats are growing and spreading. Disaster recovery plans will focus on cyber resilience. This means combining normal disaster recovery planning with cybersecurity best practices. This will let businesses resist and bounce back fast from cyberattacks like ransomware, phishing, and DDoS attacks.
Future disaster recovery plans should include the following:
- Frequent cybersecurity training for staff.
- More advanced encryption, endpoint security, and network segmentation.
Improved Information Analysis
Disaster recovery plans in the future will heavily rely on data analytics. By analyzing large amounts of data, organizations can identify the most important areas for security. They can also forecast the effects of disaster scenarios and gain insights into vulnerabilities. Improved data analytics skills will also allow for more precise customization of disaster recovery plans to a business’s unique requirements, maximizing resource usage and reducing possible losses.
A Greater Emphasis on Sustainability
Sustainability will be given more weight when developing disaster recovery plans. Companies will search for strategies to lessen the impact of their disaster recovery operations on the environment, such as reducing the amount of electronic trash generated, using energy-efficient data centers, and using greener cloud services. In addition to helping the environment, sustainable disaster recovery techniques can save costs and improve a company’s reputation.
Conclusion
In short, disaster recovery in dedicated hosting is vital. It is key for any company that wants to protect its digital assets, ensure business continuity, and stay ahead of the competition. A strong disaster recovery plan is key to modern corporate operations. It protects data and ensures minimal downtime while meeting regulations. Organizations can navigate the complex digital world by valuing customer trust, innovation, and proactive risk management.
By implementing these steps and collaborating with RedSwitches, businesses can use our strong infrastructure and support to implement disaster recovery plans. We are dedicated to providing exceptional hosting solutions to give companies the performance, security, and resilience needed to thrive today.
FAQs
Q. What is disaster recovery in the server?
Disaster recovery for servers refers to plans and procedures. They are for quickly resuming data and server operations after an interruption. The goal is to minimize downtime.
Q. What are disaster recovery examples?
For example, they use cloud services to keep operations running in a natural disaster. They move to redundant systems after a hardware failure.
Q. What is the goal of disaster recovery?
Disaster recovery aims to minimize disruption to services and losses by quickly restoring corporate operations and data integrity following a calamity.
Q. What is a disaster recovery plan for Dedicated Hosting?
A disaster recovery plan for Dedicated Hosting is a structured and detailed strategy that outlines the procedures and technologies involved in recovering data and restoring operations in the event of a disaster affecting the dedicated server.
Q. How does a disaster recovery plan benefit dedicated server owners?
A disaster recovery plan ensures that server owners have a reliable method for recovering their data, minimizing downtime, and swiftly resuming normal operations during an unforeseen disaster or system failure.
Q. What is the importance of backup and disaster recovery for dedicated servers?
Backup and disaster recovery are crucial for servers as they provide a means to safeguard critical data, applications, and systems, ensuring that businesses can recover swiftly and efficiently in the event of data loss or unexpected disasters.
Q. What are some common disaster recovery strategies for dedicated servers?
Dedicated servers use common disaster recovery strategies. These include regular data backups. They also include offsite storage, failover systems, and high-availability setups. And they include comprehensive recovery planning.
Q. How is the recovery point objective defined in the dedicated server disaster recovery context?
The recovery point objective (RPO) in server disaster recovery is when data must be recovered after a disaster. It determines the maximum tolerable amount of data loss during a recovery process.
Q. What is the recovery time objective in a disaster recovery plan for dedicated hosting?
The recovery time objective (RTO) is in a disaster recovery plan for dedicated hosting. It specifies the most downtime allowed for restoring operations after a disaster. It helps organizations set realistic targets and prioritize recovery tasks.
Q. Why is choosing a hosting provider offering fully managed disaster recovery services essential?
Choose a hosting provider that offers fully managed disaster recovery. They will handle the backup, recovery, and monitoring. This lets businesses focus on their core operations while keeping their data safe and available.