Key Takeaways
- VPN provides encrypted connections over the internet, ensuring secure remote access.
- VPN creates a secure tunnel between the user and the network, safeguarding data transmission.
- VPN pros include cost-effectiveness, easy setup, and compatibility with various devices.
- VPN cons include limited scalability, potential security vulnerabilities, and performance fluctuations.
- VPN is suitable for remote workforce accessing corporate resources securely.
- VDI is a virtual desktop infrastructure that allows users to access desktop environments remotely.
- VDI hosts desktop environments on centralized servers and delivers them to user devices.
- Pros of VDI include enhanced security, centralized management, and flexible access.
- Cons of VDI include high initial VDI setup costs, hardware dependencies, and potential complexity.
- VDI is ideal for scenarios requiring consistent and controlled desktop environments.
- VDI vs VPN differences include hardware dependency, management overhead, and user experience.
Did you know that global spending on information security rapidly grew from 2017 to 2022, increasing from $100 billion to around $200 billion in 2023? Most of this spending is focused on security services, network security equipment, and infrastructure protection. Investment in security services is expected to reach approximately $90 billion by 2024.
Such statistics highlight the importance of secure and efficient remote access solutions today. This brings us to the debate between VPN vs VDI, two leading technologies enabling remote work and secure data access.
This blog aims to explore the VPN and VDI difference. It will also review the working mechanisms, pros and cons, and use cases of VPN vs VDI. At the end of this blog, you will have a comprehensive understanding of both remote access solutions and will be able to make informed decisions about remote access strategies.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What Is a VPN?
- What Is VDI?
- Difference between VPN and VDI
- VPN vs VDI: Which One For Hybrid/Remote Work
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is a VPN?
Credits: FreePik
Before we explore the VPN and VDI difference, it is important to go over the definitions of VPN vs VDI.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that forms an encrypted and secure connection over a network that may lack security, like the Internet. VPNs create a virtual point-to-point connection between your device and a server, routing your data traffic through an encrypted tunnel. This process helps shield your online activities from unauthorized access, ensuring privacy and security.
When you use a VPN, your internet traffic is redirected through a specially configured remote server run by the VPN host. This means that when you access websites while connected to a VPN, the VPN server becomes the source of your data.
This feature hides your IP address and encrypts all the data you send or receive. The encryption takes place in real-time and helps to secure your internet connection from eavesdroppers and hackers, making it an essential tool for enhancing online privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Also Read: Best VPN for Ubuntu Users in 2024.
How VPN Works
Below is a simplified explanation of the workings of VPN:
- Initiating a Connection: When you activate your VPN software, it communicates with the VPN server. Depending on the setup, you may need to enter credentials.
- Authentication: The VPN client and server verify each other’s authenticity using established protocols. This step ensures that both ends of the connection are legitimate.
- Establishing a Secure Tunnel: Once authentication is successful, the VPN establishes an encrypted tunnel between your server and device. All data passing through this tunnel is encrypted, making it incomprehensible to anyone who intercepts it.
- IP Address Assignment: The VPN server assigns your device a new IP address. This process masks your actual IP address, making your online activity harder to trace back to you.
- Data Transmission: When you access the Internet, your data requests are sent through the encrypted tunnel to the VPN server, which decrypts the requests and forwards them to the intended Internet resource (like a website).
- Receiving Data: The data from the internet resource is sent back to the VPN server, which encrypts it and sends it through the tunnel to your device. Once the data reaches your device, the VPN software decrypts it so you can use it normally.
- Maintaining the Connection: The VPN keeps the secure connection active, re-encrypting and decrypting data in real-time. It may also handle data integrity checks to ensure no data is tampered with during transmission.
- Ending the Session: When you disconnect from the VPN, the encrypted tunnel is closed, and your device returns to its regular network connection.
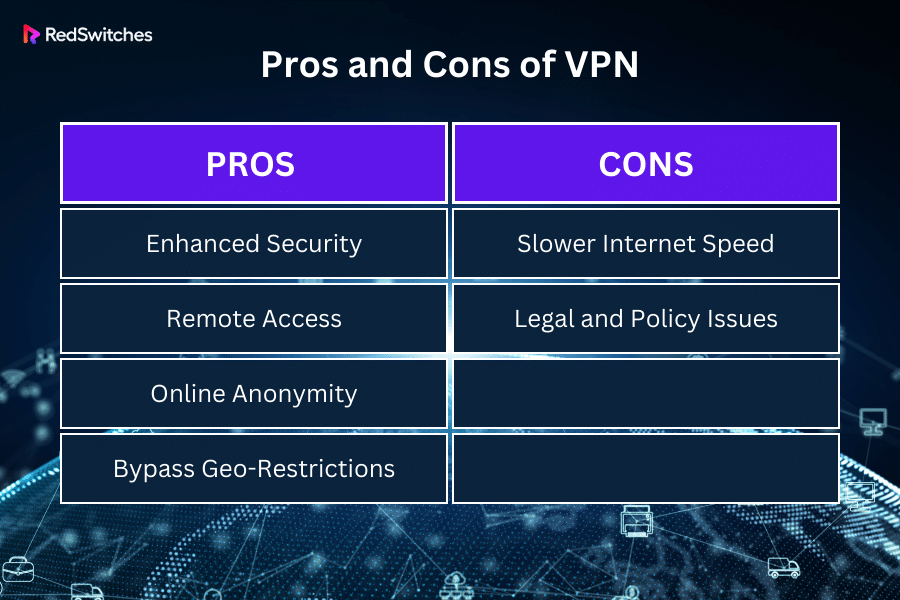
Pros and Cons of VPN
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) can greatly impact online privacy, security, and freedom. But it also comes with its own set of limitations and concerns. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of VPN.
Pros
Let’s discuss the pros first.
Enhanced Security
VPNs are important for boosting online security. They encrypt all internet traffic, making it nearly impossible for hackers and eavesdroppers to access sensitive data. This feature is particularly vital when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and prone to cyber threats. Even if a cybercriminal intercepts your data stream, the encryption of VPNs ensures they cannot decipher the data.
Remote Access
VPN technology transforms businesses. It allows for employees to access company networks from remote locations securely. This feature is invaluable for businesses with a global workforce or employees who frequently travel. Remote access via a VPN ensures that employees can work efficiently from anywhere, just as if they were in the office, without compromising the security of sensitive company data.
Online Anonymity
One of the main advantages of using a VPN is it enables you to browse the internet anonymously. With a VPN, you can hide and change your IP address and navigate the web without exposing your location or personal identity. This anonymity protects privacy in a digital age where user data is often tracked and monetized.
Bypass Geo-Restrictions
VPNs offer the unique ability to circumvent geographical internet restrictions. This feature enables users to access a broader range of online content and websites that may be blocked or restricted in their country or region. For instance, an Asian user can access services or view content only available in the United States, thus overcoming digital barriers imposed by geographical boundaries.
Cons
Now let’s take a look into the cons of VPN.
Slower Internet Speed
A notable downside of using a VPN is the potential decrease in internet speed. Encrypting data and rerouting it through VPN servers can reduce speed and increase latency. This slowdown can be particularly noticeable when using VPNs with servers located far away or low-quality VPN services that lack the infrastructure to maintain high speeds.
Legal and Policy Issues
The use of VPNs is controversial in some countries. VPNs can be restricted or heavily regulated in regions with strict internet regulations. Users need to be aware of their local laws regarding VPN usage, as there can be legal implications for using VPNs in such regions, mainly if used for illicit activities. This legal ambiguity makes it essential for users to understand and comply with the laws in their respective countries when using VPN services.
Do you want to learn more about how a VPN works? Read our blog, ‘How Does A VPN Work? A Breakdown Of 4 Crucial Aspects.’
VPN Use Cases
VPN technology has many use cases catering to individual users and organizations. Below are some primary use cases:
- Remote Work: Enables employees to securely access their company’s internal network and resources from remote locations, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data.
- Online Privacy: Protects an individual’s internet activity from being tracked or monitored by ISPs, governments, or hackers, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Secure Data Transmission: Encrypts data transmitted over the Internet, essential for sending sensitive information, such as financial data or personal identifiers.
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Allows users to access geographically restricted content by changing their apparent location. This is commonly used for streaming services, accessing region-locked websites, etc.
- Safe Online Shopping and Banking: Encrypting data transmission secures online financial transactions, particularly on public or untrusted networks.
- Avoiding Censorship: Helps users bypass government censorship in countries where internet access is heavily restricted or monitored.
- Secure VOIP Calls: This feature protects the privacy of voice-over IP calls (such as Skype or WhatsApp) that can be intercepted on unsecured networks.
- Connecting Multiple Business Sites: This process establishes secure connections between different branches of a business, creating a unified network over the Internet.
- Anonymous Research and Browsing: Allows users, like journalists or researchers, to conduct research or browse the Internet anonymously without revealing their identity or location.
- Accessing Home Network While Traveling: Enables secure access to a home network and its resources, such as personal servers or home surveillance systems, from remote locations.
- Secure File Sharing: Safeguards the transmission of files over the Internet, ensuring that sensitive information is not intercepted.
- Gaming: VPNscan can reduce ping times by connecting to servers in different regions, accessing games that are region-locked early, or protecting against DDoS attacks.
What Is VDI?
Credits: FreePik
VDI, or Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, is a technology that allows users to access and operate a desktop environment from a remote server. This means the actual computing is done on a centralized server, while users interact with their desktops through a network connection using a client device. VDI hosts desktop environments on virtual machines (VMs) and delivers them to end-users over a network.
One of the key benefits of VDI is that it centralizes management, making it easier for IT departments to deploy, update, and manage desktop environments. Users can access their desktop environments from various devices like PCs, laptops, tablets, or thin clients, regardless of location, enhancing mobility and flexibility.
VDI also offers improved security, as data is stored on servers in a data center rather than individual devices, reducing the risk of data loss or breach. This technology is beneficial in scenarios requiring high data security levels, remote work capabilities, and standardized desktop environments across a large organization.
Also Read: VDI vs VM: Understand The Differences
How VDI Works
Below is a simplified explanation of the workings of VDI:
- Virtual Desktop Provisioning: The VDI administrator creates and manages virtual desktop images, configuring them with the necessary software and settings. These images are stored on the centralized storage infrastructure.
- User Connection: When users need to access their virtual desktop, they connect to the connection broker through a client application or web browser. The connection broker authenticates the user and determines which virtual desktop they should access.
- Virtual Machine Deployment: The connection broker communicates with the hypervisor to provision a virtual machine from the appropriate virtual desktop image. The virtual machine is allocated the required CPU, memory, and storage resources.
- Desktop Session: The user’s virtual desktop is presented to them in a secure and isolated environment. Users can interact with the desktop, run applications, and access data as if using a physical computer.
- Session Management: The connection broker manages the user’s session, ensuring it remains available and responsive. Load balancing may distribute user sessions across multiple host servers for scalability.
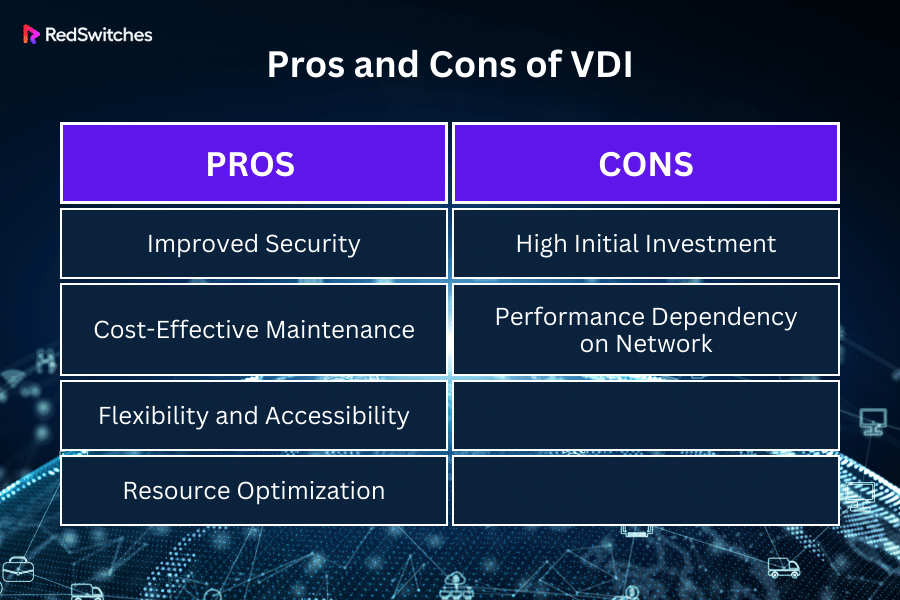
Pros and Cons of VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that hosts desktop environments on a central server and deploys them to end-users on request. This approach has several advantages and disadvantages, depending on the organizational needs, IT infrastructure, and specific use cases. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of VDI:
Pros
Let’s look into the pros first.
Improved Security
VDI allows for centralized management of data and applications, reducing the risk of data breaches on individual devices. All data is stored on servers in a data center, not local devices. This centralized approach also simplifies compliance with data protection regulations.
Cost-Effective Maintenance
With VDI, software updates, patches, and general maintenance can be performed centrally on the server, reducing the time and resources required for managing individual endpoints. This also minimizes the downtime typically associated with updating and maintaining many physical machines.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Users can access their virtual desktops from any location and on various devices, providing flexibility and convenience, especially for remote work or mobile employees. This ensures continuity of work irrespective of the user’s physical location.
Resource Optimization
VDI enables better use of hardware resources as the server infrastructure can dynamically allocate resources to virtual desktops based on demand. It also reduces the need for frequently upgrading individual user hardware, as most processing is done on the server.
Cons
Now let’s discuss the cons.
High Initial Investment
Credits: Unsplash
Setting up a VDI infrastructure can be costly due to the need for robust server hardware, virtualization software, and potential licensing costs. The total cost of ownership should be carefully considered, especially for small to medium-sized businesses.
Performance Dependency on Network
VDI’s performance heavily relies on the network connection quality. Poor connectivity can lead to latency issues, impacting user experience and productivity. This makes a reliable, high-speed network infrastructure crucial for successful VDI deployment.
Also Read: LXC Vs Docker: A Highlight Of 6 Differences.
VDI Use Cases
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) offers a range of use cases across various industries and scenarios. Below are some key examples:
- Remote Work and Mobility: VDI enables employees to access their desktop environments from any location, facilitating remote work and business travel.
- Data Security and Compliance: By centralizing data in data centers rather than on individual devices, VDI enhances data security and aids in compliance with data protection regulations.
- Cost Reduction: VDI can reduce hardware maintenance and upgrade costs, as it allows for using less powerful client machines.
- Software Management and Updates: Centralized desktop environment management makes deploying, managing, and updating software across the organization easier.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: In a disaster, VDI allows quick restoration of user desktops, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
- Flexible Work Environments: VDI supports bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies and can cater to various user needs and preferences.
- High-Performance Computing Needs: For industries requiring high computing power, like design or engineering, VDI can provide remote access to powerful computing resources.
- Education and Training: Educational institutions can use VDI to provide students access to specialized software and learning environments without needing high-end personal computers.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, VDI is used for securely accessing patient records and applications, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Call Centers: VDI allows for quick onboarding of call center agents and easy management of their desktops, improving efficiency and security.
- Seasonal Workforce Management: Organizations with fluctuating workforce needs can leverage VDI to provision quickly and de-provision desktops as needed.
- Software Development and Testing: Developers can use VDI to create and test software in different environments without requiring multiple physical machines.
- Now that we have explored what VPN vs VDI are, their mechanisms, pros and cons and use cases, let’s discover the VDI and VPN differences.
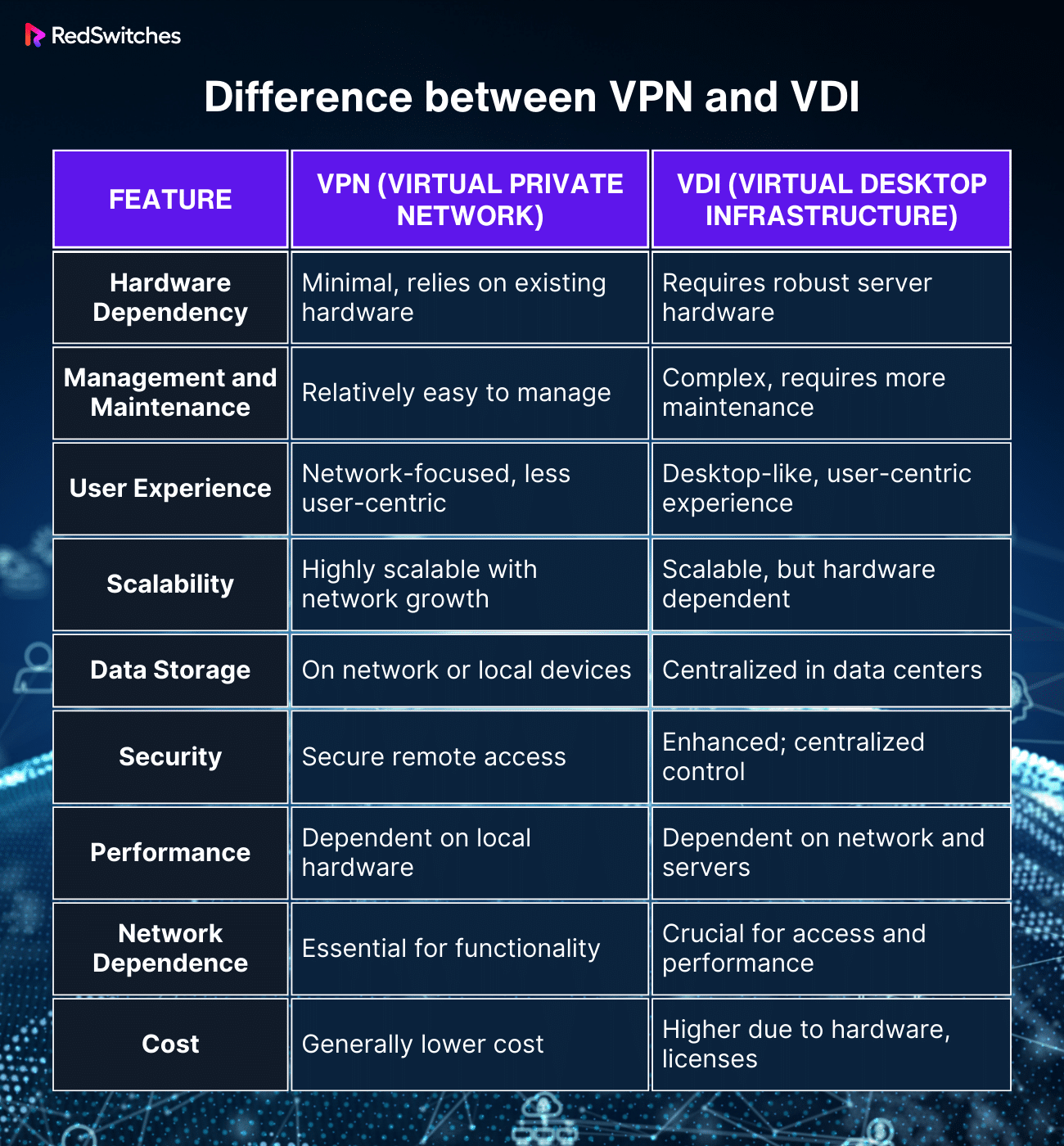
Difference between VPN and VDI
Below are the key differences between VPN vs VDN:
- Hardware Dependency
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of hardware dependency:
VPN
VPNs are designed to be lightweight in terms of hardware requirements. They typically leverage existing network infrastructure and are compatible with many client devices, from desktops to mobile phones.
This flexibility allows organizations to implement VPNs without significant hardware investments, using the existing computing power of client devices for remote access.
VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure demands robust server hardware to run the virtual desktop environments. This includes powerful servers with high processing capabilities, substantial memory, and multiple concurrent user sessions storage.
The hardware must be capable of delivering high-performance computing and graphics processing to ensure a seamless desktop experience for each user, irrespective of the client device’s capabilities.
- Management and Maintenance
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of management and maintenance:
VPN
VPN management typically revolves around configuring network settings, managing user access, and ensuring security protocols are up to date. Maintenance involves regular updates and patches to the VPN software and occasional troubleshooting of network issues. The administrative overhead is generally lower compared to VDI.
VDI
VDI management is more comprehensive. It includes network management and overseeing the virtual desktop environments – configuring user settings, managing software updates and patches, and ensuring that all virtual desktops run optimally. This requires a dedicated IT team with expertise in virtualization and desktop management.
- User Experience
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of user experience:
VPN
VPNs can sometimes compromise user experience, particularly over slow or unstable connections, where access to remote resources becomes sluggish. However, VPNs can be quite effective for simple tasks that don’t require high bandwidth or low latency.
VDI
VDI offers a more robust user experience by delivering a consistent, full-fledged desktop environment to the user, regardless of the local machine’s capabilities. This consistency is particularly beneficial in environments requiring a standardized workflow and access to specific applications.
- Scalability
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of scalability:
VPN
The scalability of VPNs also makes them suitable for rapidly evolving business environments. Since they primarily rely on software configurations, expanding a VPN setup to accommodate more users or new office locations can be achieved relatively quickly and without significant disruption to existing operations.
This scalability ensures businesses can maintain network access and security standards even as they grow or change.
VDI
Scalability is more than just adding hardware for VDI. It involves careful resource allocation planning to ensure that all users receive a consistent level of performance. This planning includes understanding the specific needs of different user groups and scaling resources accordingly.
While more complex, this scalability allows organizations to provide tailored desktop experiences, essential for roles requiring specific applications or higher computing power.
Learn about the top VPNs for Linux in our blog, ‘The 10 Best VPN For Linux.’
- Data Storage
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of data storage:
VPN
VPNs allow for flexible data storage strategies, enabling secure access to data regardless of where it is stored – whether in on-premises servers or the cloud. This flexibility is vital for organizations with a mix of legacy systems and cloud services.
VDI
The centralization of data storage can also simplify compliance with data protection regulations, as sensitive data is less dispersed and easier to monitor and control in VDI environments. This is particularly important for sectors with stringent data privacy requirements, like finance and healthcare.
- Security
Credits: Unsplash
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of security:
VPN
The security provided by VPNs ensures that remote connections to the network are as secure as internal connections, which is critical for organizations with a large remote or mobile workforce. However, organizations need to implement additional endpoint security measures to protect against threats that might originate from the user’s device.
VDI
With VDI, the centralized control over applications and user environments also allows for rapid response to security threats. For instance, if a security vulnerability is detected, updates or patches can be rolled out to all virtual desktops simultaneously, significantly reducing the exposure window.
- Performance
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of performance:
VPN
The performance of VPNs is highly contingent on the quality of the internet connection used by remote users. VPNs typically perform adequately for basic business applications like email, document editing, and light web applications.
However, VPNs might struggle to deliver optimal performance regarding bandwidth-intensive tasks such as high-definition video conferencing, large-scale data transfers, or accessing resource-heavy business applications.
This can result in slower response times and reduced productivity, especially if the remote user’s internet connection is unstable or slow. VPNs must also encrypt and decrypt data, which can introduce additional latency.
VDI
VDI environments are designed to provide a high-performance computing experience, especially for graphics or processing-intensive applications. Since the processing is done on powerful server hardware located in data centers, VDI can handle complex tasks like 3D modeling, video editing, and large-scale data analysis more efficiently than a VPN can. This server-side processing means that the user’s local device capabilities are less of a bottleneck for performance.
VDI environments can also be optimized and configured to provide the necessary computing resources for specific tasks, ensuring users have a consistent and responsive experience regardless of their local hardware.
- Network Dependence
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of network dependence:
VPN
Modern VPNs have become more efficient and reliable, even over less stable internet connections. Technologies like split tunneling, where only part of the traffic goes through the VPN, and improved encryption methods have made VPNs more resilient to variations in network quality. However, a VPN’s performance is still fundamentally linked to the user’s internet connection quality.
VDI
The reliance on VDI for network quality is significant. A stable, high-speed network connection is essential for a smooth and responsive virtual desktop experience. This requirement is critical at the data center where the VDI infrastructure is hosted and at the end-user’s location.
Latency and bandwidth limitations can significantly impact the user experience in a VDI environment, making robust network infrastructure a key consideration for VDI implementation.
- Cost
Below is a comparison of the difference between VPN vs VDN in terms of cost:
VPN
VPNs generally incur lower operational costs than VDI. They require less specialized IT expertise for day-to-day management, which can reduce the overall burden on IT departments. The costs associated with VPNs are primarily related to software licenses and network infrastructure, typically lower than those associated with managing and maintaining VDI environments.
VDI
The initial investment in VDI can be substantial, covering server hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup. However, this investment can be justified for organizations that require a high degree of control over desktop environments, need to support resource-intensive applications, or have stringent data security and compliance needs.
Over time, VDI can lead to cost savings in software licensing, reducing the need for frequent endpoint hardware upgrades and streamlining IT support and management tasks through centralized control.
Also Choose RedSwitches For Hosting CDN And VPN Apps.
VPN vs VDI: Which One For Hybrid/Remote Work
Credits: Unsplash
Are you still finding it difficult to choose between VPN vs VDI? Consider the following factors before choosing between VDI and VPN for informed decision-making:
- Assess Security Needs: VDI might be preferable for handling sensitive data due to its enhanced security features.
- Evaluate Application and Resource Accessibility: A VPN could be sufficient if users can access specific applications or resources available within the corporate network. However, if a consistent desktop experience is required regardless of the device, VDI is preferable.
- Consider Performance Requirements: VDI might offer better performance for resource-intensive tasks.
- Budget Constraints: VPNs are generally more cost-effective if budget is a limiting factor.
- User Experience: Consider the ease of use and user experience. VDI offers a more uniform experience across devices.
- IT Infrastructure and Expertise: Evaluate the existing IT infrastructure and the in-house expertise available for setup and ongoing management.
Conclusion
Remote access solutions like VPN and VDI play integral roles in remote access and data security. VPNs offer a simple and cost-effective way to access network resources remotely, while VDIs provide a more comprehensive and controlled environment, replicating the in-office experience.
The choice between VPN vs VDI largely depends on your organization’s specific needs, including factors like security requirements, budget constraints, and the nature of the workforce.
RedSwitches is a top choice for those seeking advanced, tailored remote access and data security solutions. Offering a range of services from dedicated servers to cloud hosting and advanced cybersecurity solutions, RedSwitches can enhance and secure your remote working infrastructure.
Visit our website today to dive into the world of secure and efficient remote access and discover how we can elevate your organization’s digital experience.
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between VPN vs VDI?
The difference between VPN vs VDI lies in their primary functions: VDI allows users to access and operate a desktop environment hosted on a remote server, while VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s device and a network, enabling private access to network resources from a remote location.
Q. Is remote desktop better than VPN?
Whether a remote desktop is better than a VPN depends on the specific use case: a remote desktop is ideal for accessing a specific computer or network resource remotely with a graphical interface, while a VPN is better for securely accessing a network and its services without needing direct control over a remote desktop.
Q. Is VDI and VPN the same?
When compared, VPN vs VDI are different. VDI provides a virtualized desktop experience from a remote server. VPN offers a secure tunnel to access network resources remotely without virtualizing an entire desktop environment.
Q. When should I use VDI over VPN?
You should use VDI when you need a centralized virtual environment for multiple virtual machines and secure remote access. VPN is more suitable for quick remote access to specific resources.
Q. How does VDI provide secure remote access for remote workers?
VDI creates a secure virtual desktop interface for remote and hybrid work, ensuring that data and applications are accessed in a controlled environment.
Q. Do I need to install a VPN client to use a VDI solution?
No, with VDI, users don’t need to install a VPN client as the virtual desktop interface establishes the connection.
Q. What are the benefits of using a VDI model for remote work?
VDI offers benefits such as enhanced security and access control, efficient management of remote devices, and seamless remote application usage.
Q. Is VDI performance better than VPN for remote access?
In terms of performance, VDI might be a better option for users requiring access to multiple virtual machines simultaneously, while VPN performance may vary based on connection stability.
Q. How can VPN and VDI technologies be combined for secure remote access?
Combining VPN for network security and VDI for virtual desktop infrastructure can provide a comprehensive solution for employees to work remotely while maintaining data protection.
Q. Do I need to install a VPN client for VDI access?
No, with VDI, users do not need to install a VPN client. They can connect to their virtual desktop without needing a separate VPN connection.
Q. How do VDI and VPN solutions benefit remote workers?
VDI and VPN solutions provide remote workers access to their virtual desktops and protect remote data by offering secure connections to the network.
Q. Can VDI and VPN be used together?
Yes, VDI and VPN can be used together to provide additional security and access control for remote workstations.
Q. What advantages does a cloud VDI solution offer over traditional VPN models?
A cloud VDI solution allows users to access several virtual desktops, offering more flexibility and scalability than traditional VPN models.
Q. How does a VDI connection differ from a VPN connection?
A VDI connection gives users access to a virtual desktop, while a VPN connection provides secure access to a network to access resources remotely.
Q. Is a VDI system the same as accessing resources through a VPN?
No, a VDI system provides users access to a virtual desktop environment, while a VPN allows users to access resources on a network remotely.
Q. How does a VPN protect data for remote employees?
A VPN encrypts data transmitted over the network, providing a secure connection for remote employees to access resources and protect sensitive information.