Key Takeaways
- The “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning message is a security alert browsers display to users when they attempt to access a potentially harmful site.
- Google may think your site is dangerous due to malware, phishing, unusual behavior, etc.
- You can confirm a website has been flagged by using Google’s safe browsing transparency report, checking search engine notifications, etc.
- Use security services like Seahawk’s WordPress Security Scanner, WordFence, All In One WP Security & Firewall, or Sucuri to fix the deceptive site ahead warning.
- Fixing the deceptive site ahead warning also involves Verifying SSL certificate and requesting a review from Google Safe Browsing.
- You can reduce your site’s likelihood of being marked as deceptive by implementing preventive measures like regular backups, web application firewall, monitoring, robust hosting security, etc.
Encountering critical warnings like “Deceptive Site Ahead” on their website may feel like the end of the world for website owners. Such alerts not only deter visitors but can also tarnish your website’s reputation. When faced with such issues, instead of panicking, it is essential to understand why your site has been marked as defective and follow the appropriate steps to fix the issue before the damage is done.
This guide will demystify warnings like “Deceptive Site Ahead,” explain their causes, and, more importantly, provide step-by-step solutions to resolve them.
Let’s begin!
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is the Deceptive Site Ahead Warning Message?
- Why Does Google Think Your Site is Dangerous?
- How to Confirm a Website Has Been Flagged as “Deceptive”
- How Long Has Your Site Been Listed as “Deceptive?”
- Other Website Warning Messages and What They Mean
- How to Fix a Deceptive Site Warning on Your Website
- Preventive Website Security Measures
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is the Deceptive Site Ahead Warning Message?
The “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning message is a security alert that browsers display to users when they attempt to navigate to a website that could potentially be harmful. This warning is a part of Google’s Safe Browsing initiative, which aims to protect users from sites that may engage in phishing or host malware.
When a site is flagged with this warning, it indicates that Google has detected suspicious or malicious content, suggesting that it could deceive visitors, steal personal information, or install harmful software. The message serves as a precaution, advising users to proceed cautiously or avoid the site altogether to protect their security and personal data. Websites receiving this warning must address the underlying security issues to have the warning removed and restore user trust and access.
Are you looking to learn the difference between SSL vs TLS? Read our informative blog, ‘Difference Between SSL vs TLS: 2024’s Best Internet Security Protocol‘ for answers.
Why Does Google Think Your Site is Dangerous?
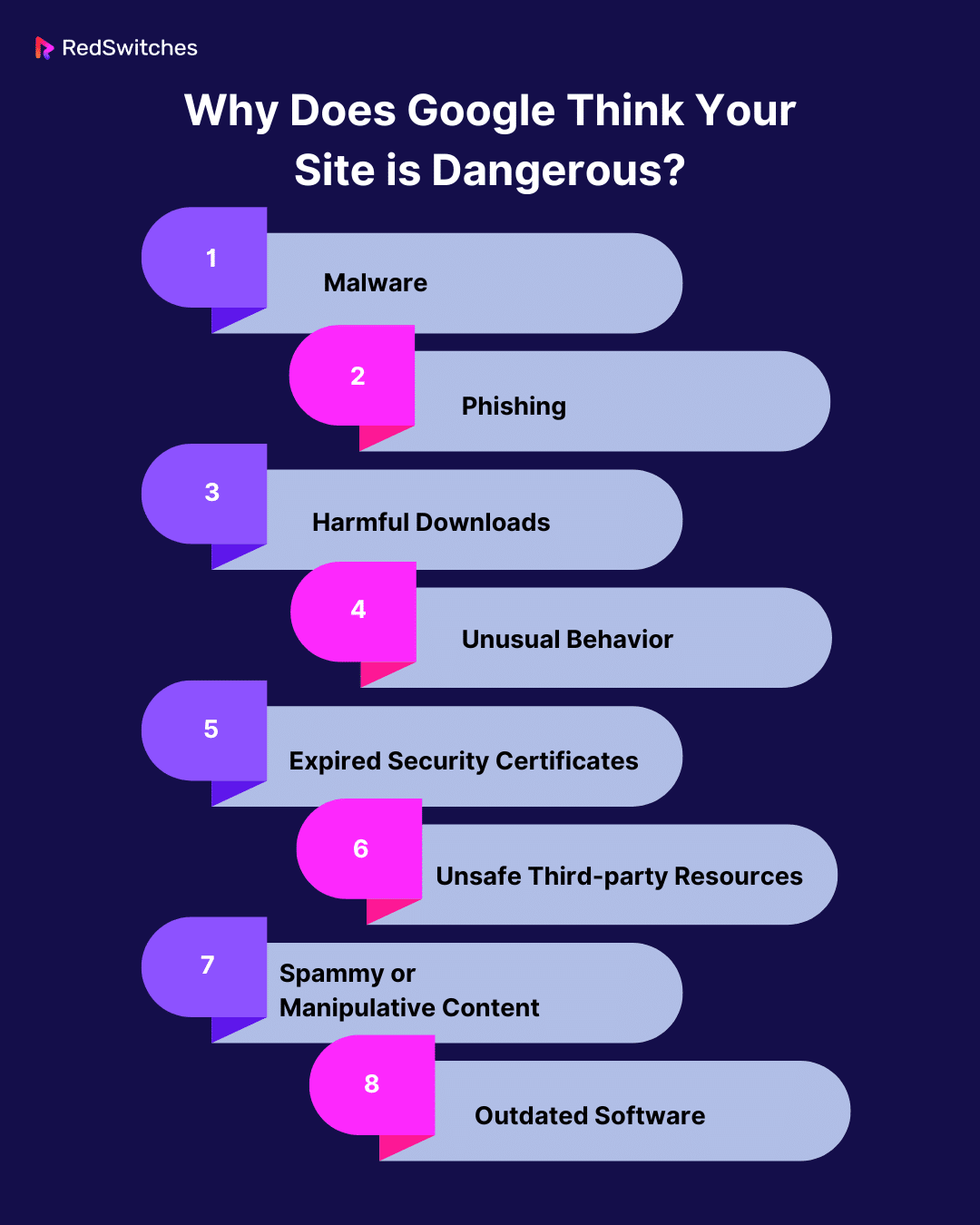
When Google displays the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning, it clearly indicates that the website may pose a risk to its visitors. This flagging by Google can be attributed to various factors that classify a website as potentially dangerous. Below are a few common factors that contribute to Google displaying the deceptive website warning on your site:
-
Malware
Malware is one of the primary reasons for a site to display the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning. Google’s algorithms will detect if your website has been hacked or compromised to host or distribute malware. Malware includes various forms of harmful software designed to damage or disable computers and can also be used to steal personal information from users. Google aims to protect internet users by preventing access to sites that could infect their devices with such malicious software.
-
Phishing
Google takes a strong stance against phishing websites. These are sites designed to fraudulently acquire sensitive information by masquerading as trustworthy entities. If your website, intentionally or unintentionally, mimics a legitimate site to trick visitors into entering their personal information, including credit card details, passwords, or social security numbers, it will be flagged. Phishing is a significant threat to online security, and Google’s warning safeguards users from potential identity theft or financial fraud.
-
Harmful Downloads
If your site provides downloads that Google identifies as dangerous, it will trigger the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning. This includes deceptive software or content that may compromise user security. These downloads might appear legitimate but can be laced with malware or other harmful code designed to exploit user system vulnerabilities.
-
Unusual Behavior
Websites that exhibit unexpected or suspicious behavior, like unauthorized redirects to malicious sites or the inclusion of suspicious code, are red warning flags for Google’s security algorithms. Such behaviors often suggest that the site has been compromised or engages in potentially harmful activities.
-
Expired Security Certificates
Websites with expired SSL/TLS certificates, especially those dealing with personal or sensitive data, are often deemed insecure by Google. SSL certificates ensure secure, encrypted communication between the user’s browser and the web server. Without SSL, sensitive data like login credentials and payment information can be intercepted by malicious actors, triggering deceptive site warnings. An expired certificate can indicate neglect in maintaining the website’s security standards, making it potentially unsafe for users to transmit sensitive data, leading to a “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning.
- Unsafe Third-party Resources
Sometimes, even if your primary website content is safe, loading resources from other domains flagged as dangerous can lead to your site being flagged. These resources can include ads, images, scripts, or other elements sourced from external sites that pose security risks.
- Spammy or Manipulative Content
Websites containing spammy content or those that engage in manipulative practices, such as misleading information or deceptive links, can also encounter the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning. This type of content can negatively impact user experience, erode a site’s trustworthiness, and be harmful to users.
- Outdated Software
Using outdated content management systems (CMS), plugins, or themes can expose your website to known security vulnerabilities. Hackers often leverage these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access or distribute malware. Google’s flagging in such cases serves as a deterrent to prevent users from visiting sites that could be compromised.
Are you looking for answers to how to check whether a site is legitimate? Read our blog ‘How to Check if a Website is Legit: 8 Ways to Check.’
How to Confirm a Website Has Been Flagged as “Deceptive”
You can use several methods to confirm whether a website has been marked as “deceptive.” Below are the top ways to check whether your site has been marked as a deceptive site:
- Use Google’s Safe Browsing Transparency Report
Google offers a valuable tool called the Safe Browsing Transparency Report. You can access this tool at https://transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/search. Here, you simply input the website URL you are concerned about. The tool will then inform you if the website has been reported as unsafe. This feature of Google is part of its broader effort to maintain internet safety and provides a quick and easy way to verify the security status of a website.
- Search Engine Notifications
Major search engines, like Google, are proactive in safeguarding users against deceptive websites. They often display warning messages underneath the website’s listing in search results, indicating that the site could be deceptive. These notifications are an additional layer of security, informing users right at the search engine level before they even click on the website link.
- Use Security Plugins or Services
For website administrators looking to ensure their site’s integrity, using security plugins or online services is an effective strategy. For instance, if your site is developed on WordPress, plugins like Sucuri or Wordfence can be instrumental. These tools scan your website for security vulnerabilities, including deceptive content or malware, and provide solutions to address any issues found.
- Review Website Security Certificates
A valid SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a hallmark of a secure website. You can check a website’s security certificate by selecting the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar. This certificate indicates that the website has a verified identity and the connection is encrypted, safeguarding against data interception and other forms of cyber intrusion.
- Check with Webmaster Tools
Using webmaster tools like Google Search Console is crucial if you own or manage a website. These tools can alert you to security issues or warnings like “Deceptive Site Ahead”, that search engines, like Google, might have detected on your site. By monitoring these tools, you can stay informed about your site’s security status and take immediate action if any issues are identified.
How Long Has Your Site Been Listed as “Deceptive?”
A multi-step approach is necessary to determine the duration your site has been listed as a deceptive website. Below are a few steps you can take to get answers:
Check Your Email Notifications
If you have registered your website with webmaster services like Google Search Console, these platforms typically send out immediate email notifications upon detecting any security concerns. If your site is flagged as deceptive, the notification will generally include the date the issue was first identified. These emails are an official record from the service that detected the issue and are a reliable source for finding out when your site was first flagged.
Review Webmaster Tools Records
As stated above Webmaster tools records can help you determine whether your site has been displaying the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning. However, besides this information, these tools often include a timeline or a date stamp indicating when the site was first listed as deceptive. By reviewing these records, you can clearly understand the timeline of events concerning your site’s security status.
Review the History of Your Security Plugins or Tools
Besides helping you confirm whether your site was marked as deceptive security plugins can also help you identify when the site was flagged as deceptive. These plugins continuously scan your website for potential security threats and keep detailed logs of their findings. This can offer a comprehensive view of your site’s security history.
Contact Your Hosting Provider
Your website’s hosting provider is another vital source of information. Hosting services typically monitor the sites they host for security issues and may have records of any alerts or flags associated with your site. You can request information on any security incidents by contacting your WordPress hosting provider, including when your site first displayed the“Deceptive Site Ahead” warning. Hosting providers can also offer insights into the nature of the security issue, which can be crucial for resolving the problem.
Check Browser Warnings
Sometimes, browser warnings alert site administrators or owners of the issue “Deceptive Site Ahead” – Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari may display these messages alerting users and administrators of potential security risks. While browser warnings do not typically provide a historical record of when the site was first listed as deceptive, they indicate that it is currently flagged.
If this is your first indication of a problem, you can correlate the timing of the warning with any recent changes or updates to your site. This could include new content additions, plugin updates, or changes in hosting services. Such correlations can help estimate the timeframe during which the issue might have arisen.
Also Read: 14 WordPress Security Issues You Don’t Have To Worry About Anymore! [Fixes Inside!].
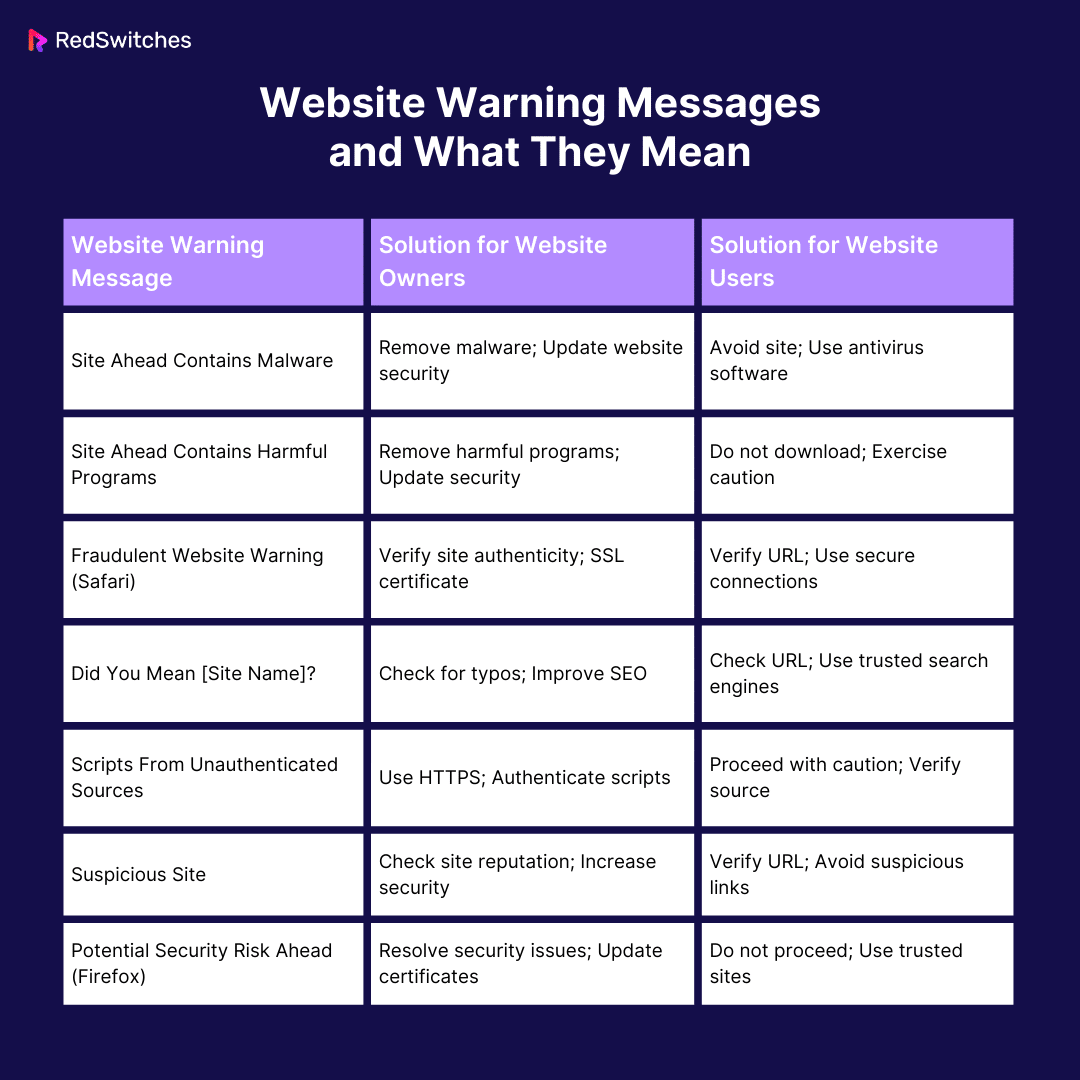
Other Website Warning Messages and What They Mean
Credits: FreePik
You may encounter several warning signs besides the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning message, all signifying different issues. Below are a few other common warnings site owners or web users may encounter and their solutions:
“Site Ahead Contains Malware”
This alarming message stating the site contains malware appears when a website is suspected of being infected with malware. For those who don’t know, malware is software designed to harm your computer, steal sensitive data, or engage in other hostile activities. Malware can include viruses, spyware, ransomware, and other harmful programs.
Solution
- For Users: It’s crucial to avoid accessing the site. Ensure your antivirus software is active and updated to protect your device from accidental malware exposure. Regularly updating your operating system and browser can provide additional security layers against malware.
- For Site Owners: Immediate action is required to secure your site and protect your site visitors. Use reputable security tools to thoroughly scan your site to identify and remove any malware. It is also important to assess your site for security vulnerabilities that might have allowed the malware to infiltrate.
“The Site Ahead Contains Harmful Programs”
The warning is triggered when a website is suspected of containing software that could threaten the user, such as adware, spyware, or other unwanted programs that might be inadvertently downloaded and installed.
Solution
- For Users: Do not proceed to the site. Consider running a comprehensive scan with your antivirus software to safeguard your device. Keep your security software and browsers updated to protect against the latest threats.
- For Site Owners: Investigate your website for any signs of unwanted software, which might be embedded in third-party ads or downloadable content. Remove any harmful elements and enhance your site’s security protocols. Once the issues are resolved, request a re-evaluation of your site from the search engine or web service that issued the warning. This usually requires proving that your site is now clean and free of harmful programs.
“Fraudulent Website Warning” (Safari)
Exclusive to Safari browser users, this warning typically indicates that the site may be involved in phishing attempts – trying to trick visitors into revealing personal or financial information by pretending to be trustworthy.
Solution
- For Users: Leave the site immediately and avoid providing any personal information. If possible, report the site to help protect others. It’s also advisable to inform the legitimate entity (if the website is impersonating one) about the phishing attempt.
- For Site Owners: Conduct a detailed investigation to understand why your site is being flagged. Look for any unauthorized changes, phishing scripts, or compromised site elements. Strengthen your site’s security measures, including updating passwords and implementing stricter access controls. Once you have addressed these issues, contact the browser’s support team (Apple Support for Safari) to request a review of your site. This process may involve providing details of the actions taken to secure your site and rectifying phishing-related content.
“Did You Mean [Site Name]?”
This message is a common feature in search engines, designed to assist users who may have made a typographical error while typing a website address. It’s essentially a helpful prompt that suggests the correct or more popular site based on the search engine’s algorithm. This feature is particularly useful in directing users to the intended website, especially when the typo is subtle.
Solution
- For Users: If you see this message from a site when browsing the internet, you can simply resolve it by clicking on the suggested link if it matches your intended destination.
- For Site Owners: Encountering this message about your site might indicate that your website’s name is easily mistyped or another site has a similar name. This could lead to potential visitors being directed away from your site. To address this, enhancing your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) and increasing your online presence through marketing and content strategies can help your site become more recognizable and distinct in search results. It is also important to consider the user experience aspects of your website’s name, making it simple and distinct to avoid confusion.
“This Page Is Trying to Load Scripts From Unauthenticated Sources”
This warning message is crucial for maintaining secure web browsing. It appears when a webpage, which is secured with HTTPS (indicating a secure connection), is trying to load scripts from sources that are not secure (HTTP). This scenario, known as mixed content, presents significant security risks because the unsecure scripts can be easily tampered with or used to transmit personal data securely.
Solution
- For Users: Proceeding cautiously when encountering this warning is advisable. Loading these scripts can compromise your data’s security, making it vulnerable to interception or malicious attacks.
- For Site Owners: Resolving this issue involves ensuring that all elements on the website – scripts, images, and links – are loaded over HTTPS. This can be done by meticulously updating all the URLs to use HTTPS and configuring the web hosting server to default to HTTPS, thereby securing all data transmissions to and from your website. Regularly auditing your website for mixed content can prevent such warnings from appearing to your visitors.
“Suspicious Site”
The “Suspicious Site” warning is a broader alert that encompasses various types of potentially harmful online behavior. This includes websites that might be involved in scams, disseminating malware, or other forms of deceptive practices. Such sites may install harmful software, trick visitors into revealing personal information, or engage in malicious activities.
Solution
- For Users: Visitors should practice caution and avoid interacting with these sites since they can introduce trojans, viruses, or other forms of malware into your devices.
- For Site Owners: Website owners who find their site flagged under this category must conduct a comprehensive security audit. This can involve using specialized security plugins, such as those available for WordPress, or enlisting the help of professional cybersecurity services. It’s crucial to identify the root cause – whether it’s outdated software, vulnerable plugins, or compromised site files. Regular updates and vigilant monitoring for unusual site activities can prevent future flags. Once the issues are rectified, reaching out to the browser or security service that issued the warning for a review is necessary to lift the flag.
“Potential Security Risk Ahead” (Firefox)
Firefox displays this warning when it detects issues with your site, mainly its SSL certificate. It may also display it if your site’s connection is not securely encrypted. SSL certificates ensure a secure connection between a browser and a web server, safeguarding any data transfer from eavesdropping or tampering. Issues might include expired certificates, certificates not issued by a trusted authority, or a misconfiguration in the site’s encryption setup.
Solution
- For Users: The advice is not to proceed to the site, especially if it requires entering sensitive information.
- For Site Owners: Site owners should immediately check their SSL certificates. This includes verifying that the certificate is up to date, correctly installed, and issued by a reputable certificate authority. Problems with the site’s encryption protocols must also be addressed, which may require consultation with web hosting providers or cybersecurity professionals. Correcting these issues will not only secure the site and protect user data but also lead to removing the browser warning, as modern browsers periodically recheck sites and update their security status accordingly.
Also Read: Checking Domain Name History In 3 Easy Steps | RedSwitches.
How to Fix a Deceptive Site Warning on Your Website
Looking for a deceptive site ahead fix? Below are the tried and tested ways to fix a “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning:
Method 1: Use a Security Service to Eliminate Malware
Dealing with a “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning can be daunting. Thankfully, there are ways to resolve this issue. The first and easiest method to resolve “Deceptive Site Ahead” is to use a reliable security service or plugin to scan for and remove malware from your site. Here are some recommended tools:
Seahawk’s WordPress Security Scanner
Credits: Seahawk
Seahawk’s WordPress Security Scanner is an exceptional tool that offers an in-depth scan of your WordPress site. It meticulously searches for malicious code, uncovers security vulnerabilities, and identifies compromised files.
This scanner is particularly effective in pinpointing the specific issues contributing to the ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ warning, allowing you to take targeted actions to rectify these problems. With its detailed reporting, you can gain valuable insights into the security status of your site.
WordFence Security Plugin
Credits: WordPress Website
WordFence is a widely recognized WordPress security plugin renowned for its robust firewall and comprehensive malware scanner. It diligently scans your site for many known threats and vulnerabilities.
By identifying and helping you remove malicious content, WordFence plays a pivotal role in securing your site against future attacks. Its real-time threat intelligence feed also safeguards your site against the latest known vulnerabilities and attacks.
Astra Security Suite
Credits: Astra Security Suite
The Astra Security Suite is a powerhouse in WordPress security designed to offer end-to-end protection. It goes beyond malware scanning. Instead, it includes a web application firewall that shields your site from ongoing threats, real-time threat defense mechanisms to prevent attacks as they happen, and malware cleanup functionalities. This comprehensive approach ensures your site is cleaned and fortified against various security threats.
All In One WP Security & Firewall
Credits: WordPress Website
All In One WP Security & Firewall is a robust plugin that adopts an all-encompassing strategy for WordPress security. This plugin rigorously checks for vulnerabilities and implements many of the latest recommended WordPress security practices and techniques. From enforcing strong passwords to protecting against brute force attacks, it provides many security features that help maintain your site’s integrity and safety.
Sucuri Security
Credits: WordPress Website
Sucuri Security has established a reputation for its high efficacy in monitoring and safeguarding websites from various security threats. Among its myriad features, Sucuri offers thorough malware scanning, detailed security activity auditing, efficient blacklist monitoring, and proactive security hardening measures. Its ability to provide a comprehensive security overview makes Sucuri an invaluable tool in detecting and addressing the issues leading to the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning.
Method 2: Clean Your Website Manually
When faced with a “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning, acting swiftly to protect your website’s reputation and visitors’ security is crucial. Besides using a security service, manually cleaning your website can be an effective solution if you prefer a hands-on approach or lack immediate access to professional services.
However, manual cleaning requires a good understanding of WordPress files and structure. If you’re not comfortable with this process, consider seeking professional help. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Take a Backup of Your Website
Before making any changes, it’s vital to back up your website. This backup acts like a safety net, allowing you to restore your site to its current state if anything goes wrong during the cleaning process. Use your hosting control panel or a WordPress plugin to create a full backup, including all files and databases.
Reinstall WordPress
Reinstalling WordPress can help remove any corrupted core files contributing to the issue. To do this:
- Download a new copy of WordPress from the official site.
- Delete the old WordPress files on your server, being careful not to remove your wp-content folder, wp-config.php file, and .htaccess file, as these contain your themes, plugins, and settings.
- Upload the new WordPress files, replacing the potentially compromised core files with clean versions.
Clean Plugin and Theme Folders
Malware often hides in the plugin and theme folders. Start by temporarily deactivating all plugins. If you believe a specific plugin or theme is the culprit, you can start by checking those. Look for recently modified files or files that seem out of place. Compare the current plugin and theme files with the originals from the WordPress repository or your recent backups. Remove any suspicious files you find.
- Plugins: Access your plugin directory (usually wp-content/plugins/). Delete the folder and reinstall a new version from the WordPress Plugin Directory if any plugin seems infected.
- Themes: Check your theme directory (wp-content/themes/). As with plugins, delete and reinstall any theme if you find suspicious or modified files.
After completing these steps, re-enable your plugins individually, checking your site for issues after each activation. This process helps ensure that none of the plugins reintroduce vulnerabilities.
Remove All Backdoors
Backdoors are hidden entry points hackers use to regain access to your site. They are often cleverly disguised in your website’s files and directories. To remove them, you must check recent file modifications, look for unfamiliar file names, and scan through code for any unusual or suspicious scripts.
This process requires a thorough understanding of your site’s codebase and structure. If you’re not confident in doing this, consider seeking help from a professional.
As an e-commerce business owner, you must know the common cybersecurity challenges and take the necessary steps to mitigate them. Read our blog, ‘15 Top Cyber Security Challenges Businesses Must Know’, to get started.
Clean Malware From the Database
Malware can also infiltrate your website’s database, injecting harmful code into your content. To clean this up, you must access your database through a tool like phpMyAdmin. Look for any recent changes or additions that seem out of place.
Common malware indicators include spammy keywords, strange links, or long strings of nonsensical text. Once identified, these malicious entries need to be carefully removed. Be sure to back up your database before making any changes, as one wrong move can cause significant issues.
Reupload Your Cleaned Files
After cleaning your files and database, you should reupload the cleaned versions to your server. This ensures that all remnants of the malware are removed. Before doing this, it’s a good idea to delete the old files from your server, except for essential configuration files like wp-config.php in WordPress, which you should manually clean and keep. Uploading fresh, clean files minimizes the risk of leaving any infected files behind.
Clear the Cache
The first step in addressing a “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning is to clear your website’s cache. Cached data can sometimes harbor malicious scripts, leading to such security warnings. By clearing the cache, you ensure that you are working with the most current version of your site, free from any cached malicious content. This process varies depending on your platform: for websites built on content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, you can use specialized cache-clearing plugins.
If your site is hosted on a custom platform, you may need to clear the cache through the hosting control panel or via FTP. Remember, clearing the cache doesn’t only remove harmful scripts. It also helps refresh your site’s content for visitors.
Check for Fake Plugins
Malware often infiltrates websites through fake or compromised plugins. This step is crucial, mainly if you use a CMS like WordPress, which relies heavily on plugins for extended functionalities. Scrutinize your list of installed plugins. Check each one for authenticity and legitimacy. Be wary of plugins you don’t recall installing or appear out of place. Immediate removal of any dubious plugins is essential.
It is also important to ensure all your plugins are up to date. Developers frequently release updates to fix security vulnerabilities, and keeping your plugins updated is a key line of defense against malware attacks.
Use a Security Scanner to Confirm That the Malware is Completely Gone
The next step after clearing the cache and auditing your plugins is to run a thorough check using a security scanner. These tools are designed to comprehensively scan your website for malware, backdoors, and other security threats.
You can find a range of security scanners online, some of which are offered as plugins for CMS platforms. They work by crawling through your website’s files and databases and searching for irregularities or known malware patterns. This step ensures that no aspect of your site remains compromised.
Method 3: Verify SSL certificate
The SSL certificate is vital for establishing a secure web server and browser connection. If there’s an issue with the SSL certificate, it could trigger security warnings, including the deceptive site alert.
To verify and fix SSL certificate issues, follow these steps:
- Check SSL Certificate Validity: First, ensure your SSL certificate is valid and has not expired. You can use online tools such as an SSL Checker to verify the validity of your certificate. An expired certificate needs to be renewed immediately.
- Ensure Proper Certificate Installation: Sometimes, SSL certificates are not installed correctly, which can cause errors. Verify that your certificate is installed correctly on your server. This can typically be checked through your hosting provider’s control panel or online tools that analyze SSL installations.
- Correct Mismatched Domain Names: Ensure the SSL certificate is issued for the correct domain name. If your certificate is for ‘www.example.com,’ but your site is accessed at ‘example.com,’ this mismatch can cause warnings. You might need a wildcard SSL or a certificate that covers your site’s www and non-www versions.
- Look for Mixed Content Issues: Mixed content occurs when a secure site (HTTPS) contains elements loaded over an insecure (HTTP) connection. Browsers may flag your site as a security risk. Tools like ‘Why No Padlock?’ can help you identify and fix these mixed content issues.
- Update to a Stronger Encryption Algorithm: Older encryption algorithms like SHA-1 are no longer considered secure. Ensure your SSL certificate uses a robust and modern algorithm like SHA-256.
- Contact Your SSL Provider: If you still face issues, contact your SSL certificate provider for assistance. They can offer guidance specific to your certificate and help resolve any underlying issues.
Request a Review from Google Safe Browsing
Once you’ve confirmed that your site is malware-free, it’s time to remove the warning. You’ll need to request a review from the security team of the web browser that is displaying the warning, such as Google’s Safe Browsing team.
This review process involves submitting your site for re-evaluation, and while it might take a few days, it is a necessary step to regain the trust of visitors and search engines. Once the review is complete and your site is deemed safe, the ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ warning will be lifted, restoring normal access to your site.
Also Read: What Is A Web Security Gateway? Understanding The Essentials.
Preventive Website Security Measures
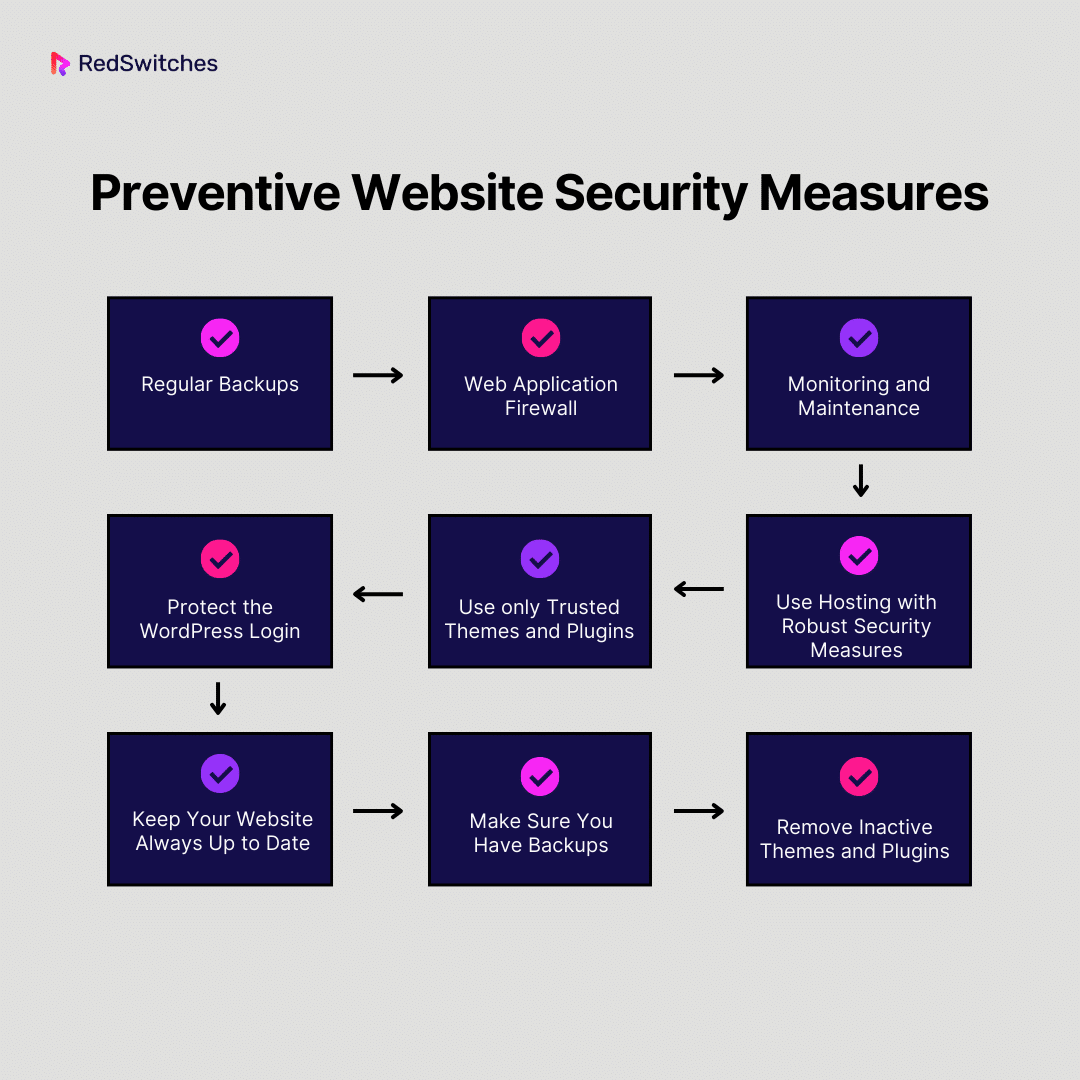
Website security has become a major concern for businesses and individuals today. With cyber threats on the rise, it’s no longer just about fixing issues as they arise – prevention is key. Taking preventative measures beforehand can also help site owners reduce the likelihood of encountering warning messages like “Deceptive Site Ahead” on their website. Below are some of the best website security measures that every site owner must take:
Regular Backups
Regular backups are one of website security’s most crucial yet often overlooked aspects. Imagine losing all your data to a cyber-attack or a technical glitch; it’s a nightmare scenario. Regular backups act as a safety net, ensuring your website can be restored quickly and efficiently, even in the worst-case scenario.
It’s essential to have an automated backup system that periodically saves all your website data, including files and databases. This system should store backups in a secure, off-site location to prevent data loss from physical damage like fire or theft. Doing so minimizes downtime and data loss, which is critical for maintaining your online presence and customer trust.
Web Application Firewall:
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is your first defense against web-based threats. It monitors, filters, and blocks malicious traffic from reaching your website. A robust WAF can protect against various attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and DDoS attacks, common tactics cybercriminals use.
A WAF ensures that only legitimate traffic reaches your site by analyzing and filtering incoming traffic. This protects your website from harm and helps maintain its performance by mitigating unwanted traffic load.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuous monitoring and regular maintenance are vital for ensuring the ongoing security of your website. This involves:
- Regularly scanning for vulnerabilities.
- Updating software and plugins.
- Checking for any unusual activity that could indicate a security breach.
Regular updates are crucial because they often include patches for security vulnerabilities that have been recently discovered. Similarly, monitoring tools can alert you to suspicious activity, allowing you to respond promptly before significant damage occurs. It’s also beneficial to conduct periodic security audits to assess your website’s overall health and security.
Use Hosting with Robust Security Measures
Selecting a hosting provider that prioritizes security is essential in safeguarding your website. Key features to look for include regular backups, which ensure that your site can be quickly restored in case of data loss. Firewalls act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access, while malware scanning helps detect and eliminate malicious software that could compromise your site.
Equally important is the presence of SSL/TLS certificates, which encrypt data transferred between your server and your users, protecting sensitive information like login credentials and personal data. A hosting service equipped with these robust security measures plays a critical role in minimizing the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches, thus maintaining the integrity and reliability of your website.
Use only Trusted Themes and Plugins
While free themes and plugins are available for website customization, it’s essential to be discerning in your choices. Using only trusted and reputable themes and plugins can significantly lower the risk of security vulnerabilities. Opt for regularly updated and maintained products, reflecting the developers’ commitment to security and functionality. Pay attention to user reviews and ratings, as these can provide insights into the reliability and performance of the themes and plugins.
By choosing trusted themes and plugins, you not only enhance the aesthetic and functionality of your site but also protect it from potential security breaches that poorly maintained extensions might introduce.
Protect the WordPress Login
The login page is often the most vulnerable part of a WordPress website, making it a frequent target for cyber attacks. Strengthening the security of this page is, therefore, crucial. Implementing two-factor authentication adds a layer of security, making it challenging for unauthorized users to get access. Using strong passwords for your WordPress account is a basic yet effective measure.
Limiting the number of login attempts can thwart brute-force attacks, where attackers try multiple password combinations to gain access. Altering the default admin login URL is another smart strategy, as it can significantly reduce the chances of automated attacks. By taking these steps, you can significantly enhance the security of your website’s backend, making it harder for attackers to compromise your site.
Keep Your Website Always Up to Date
Ensuring your website is up-to-date is critical to its security. This process involves regularly updating the core platform, such as WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal, and any themes and plugins you use. These updates are crucial because they often include patches for security vulnerabilities discovered since the last version. Developers continuously work to identify and fix these vulnerabilities, and by keeping your site updated, you benefit from their efforts.
The risks of running outdated software are significant. Hackers and cybercriminals actively look for websites using older versions with known vulnerabilities, as these are easier targets. By neglecting updates, you might inadvertently leave a door open for malicious attacks, leading to data breaches, loss of customer trust, or even legal consequences depending on the nature of the data you handle.
Make Sure You Have Backups
Backups are a critical safety mechanism for any website. In the event of a security breach, data loss, or even accidental deletion, backups are your fallback option to restore your site to a working state without significant downtime or data loss.
When setting up a backup system, it’s essential to ensure it’s comprehensive, covering all aspects of your website, including databases, files, and other critical components. The storage of these backups is equally important. It’s recommended to store them in a secure, off-site location to protect against physical disasters like floods or fires that could affect your primary website.
Also Read: Difference Between Public Vs Private Networks.
Remove Inactive Themes and Plugins
Inactive themes and plugins on your website can serve as hidden vulnerabilities. When not actively used, these components are often ignored during regular updates. This neglect can leave them susceptible to security exploits. Hackers can use these outdated and unmonitored components as a backdoor to access your website.
Regularly auditing and removing these inactive themes and plugins is crucial in safeguarding your website. This reduces the risk of security breaches and helps improve your site’s performance. Fewer components mean a lighter and faster website, which is beneficial both from a security and user experience standpoint.
Credits: FreePik
Conclusion
Dealing with warnings like ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ warning on your website can be difficult and stressful, but it’s manageable with the proper knowledge and tools. Regular website maintenance and proactive security measures are your best defense against these warnings.
If you’re looking for a reliable hosting provider that prioritizes security and offers robust support, consider RedSwitches. Our comprehensive hosting solutions ensure your website runs smoothly, securely, and free from harmful alerts, letting you focus on what you do best – growing your online presence. Visit RedSwitches today to learn more about our services and how they can help keep your website safe and successful.
FAQs
Q. How do I fix “deceptive website” warning?
To fix the “Deceptive Site Ahead” warning, review your website for any malicious content or security breaches, remove them, and then request a review from your webmaster tools.
Q. How do I turn off security warnings on my website?
Turning off security warnings like ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ isn’t recommended as they indicate underlying issues. Instead, address the security concerns that trigger these warnings. If you encounter security warnings on your website, it is best to:
- Ensure your website is secure and malware-free.
- Update SSL certificates.
- Follow web security best practices.
Q. How do I know if a website is deceptive?
To determine if a website is deceptive, look for trust indicators like SSL certificates, check for clear contact information, and verify its reputation through online reviews and security tools. Avoid sites flagged with ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ warnings.
Q. What is a Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
A Deceptive Site Ahead warning is a security alert shown by Google Chrome to inform users that the website they are trying to visit may contain harmful content, such as malware or phishing attempts. Sometimes you may get an incorrect phishing warning. To fix this, you may have to report incorrect phishing warning to Google.
Q. How can I remove the Deceptive Site Ahead warning from my WordPress site?
To remove the Deceptive Site Ahead warning from your WordPress site, you need to identify and remove any malicious content from your website, secure your site against hacking attempts, and then request a review from Google to remove the warning.
Q. What should I do if my site has been flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
If your site has been flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning, you should immediately take steps to scan your website for malware. Remove malicious content, and follow Google’s guidelines for cleaning up your site before requesting a review.
Q. How can I check if a site contains deceptive content or has been hacked?
You can use various online tools and security scanners to check if a site contains deceptive content or shows signs of a hacked WordPress site. It is also recommended to monitor your website for any suspicious activity regularly to monitor whether your site has been hacked.
Q. What are some common reasons for receiving a Deceptive Site Ahead warning on my website?
Some common reasons for receiving a Deceptive Site Ahead warning on your website include outdated software, insecure WordPress plugins, hosting vulnerabilities, or malware or phishing content.
Q. How can I protect my WordPress site from being flagged by Google for deceptive content?
To protect your WordPress site from being flagged for deceptive content, ensure that you regularly update your themes and plugins, use strong passwords, implement security measures like SSL certificates, and monitor your site for suspicious activity.
Q. What steps should I take to resubmit my site to Google after fixing the Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
The answer to how to resubmit your website to Google after getting rid of the deceptive site ahead of warning reasons is simple. You can easily request a review from Google by going to the Google Search Console, navigating to Security Issues, and submitting a review request.
Q. What is a Deceptive Site Ahead warning, and how does it affect my WordPress website?
A Deceptive Site Ahead warning is a message displayed by Google Chrome to warn users that the website they are about to visit may be deceptive or contain harmful content. If you receive this warning on your WordPress site, it can negatively impact your site’s reputation and traffic.
Q. How can I check if my WordPress site has been flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
To check if your WordPress site has been flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning, you can use Google Safe Browsing tool or simply visit your site using Google Chrome to see if the warning appears.
Q. What steps can I take to remove the Deceptive Site Ahead warning from my WordPress site?
To remove the Deceptive Site Ahead warning from your WordPress site, you must identify and address the security issue causing the warning. This may involve scanning your site for malware, fixing any vulnerabilities, and submitting a website review to Google.
Q. Are there any specific WordPress plugins that can help in fixing the Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
Yes, several WordPress plugins are available that can help improve your site’s security and remove the Deceptive Site Ahead warning. Some popular plugins include Wordfence, Sucuri Security, and MalCare.
Q. How can I resubmit my WordPress site to Google after fixing the Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
After addressing the security issues on your WordPress site, you can request a review from Google by logging into Google Search Console, selecting your property, and navigating to the Security & Manual Actions section to submit a review request.
Q. What are the common reasons for receiving a Deceptive Site Ahead warning on my WordPress site?
Common reasons for receiving a Deceptive Site Ahead warning on your WordPress site include hacked WordPress installations, presence of malware or harmful content, social engineering attempts, and Google flags indicating suspicious activity.
Q. How can I protect my WordPress site from being flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning?
To protect your WordPress site from being flagged with a Deceptive Site Ahead warning, regularly update WordPress core, themes, and plugins, use strong passwords, implement security measures such as SSL certificates, and regularly scan your site for malware.