Key Takeaways
- Windows servers offer seamless integration with Microsoft products, making them ideal for businesses heavily reliant on the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Linux servers are cost-effective and highly customizable, appealing to those seeking flexibility and open-source solutions.
- Windows servers are user-friendly with a familiar GUI, lowering the learning curve for Windows users.
- Linux servers provide strong security and stability, ideal for handling sensitive data and high-demand applications.
- Due to licensing fees and resource-intensive operations, Windows dedicated servers may incur higher costs.
- Linux has a steeper learning curve, particularly for users unfamiliar with command-line interfaces.
- Both platforms have strong community and vendor support, though Linux users may rely more on community resources.
The choice between Windows and Linux servers is crucial. It matters to both enterprises and tech enthusiasts, who must adapt to the always-changing digital world. This decision affects the future scalability of your efforts and the effectiveness and reliability of your digital operations. Choosing a server might be difficult because each has different advantages and disadvantages. This thorough investigation will clarify the complex comparison of the benefits and drawbacks of Windows dedicated server vs Linux Dedicated Server.
You need to understand these subtleties to get the most out of your servers. Whether you’re an experienced IT specialist or a curious entrepreneur new to the digital world, this is true. Come along as we explore the core of this key decision-making process. We’ll help you choose one that fits your special needs and goals.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Dedicated Server?
- What is a Windows Dedicated Server?
- Pros and Cons of Windows Dedicated Server
- What is a Linux Dedicated Server?
- Pros and Cons of Linux Dedicated Server
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
With a dedicated hosted server, a customer rents the entire server, which is not shared with other users. With this setup, the client has all control over the server. They can choose the hardware, operating system, and configurations.
The server has redundant power and HVAC systems, which keep it cool and running. Servers are usually kept in data centers. Businesses and people with special hosting needs can benefit from fast, secure hosting. They can also benefit from hosting that they can customize. They get this from servers. They are more expensive and need more technical maintenance. But servers are a wise investment for sites and apps. They cannot afford to sacrifice performance, security, or control.
Servers cost more than VPS or shared hosting, but they are worth it. The cost includes the hosting provider’s support for infrastructure and the actual hardware and exclusive use of server resources.
Furthermore, a certain degree of technical know-how is needed to manage a server. Unless clients choose managed hosting, the service provider helps with these duties. Clients are in charge of maintaining, updating, and safeguarding the server.
Performance is one of the main benefits of a server. The leased server has exclusive access to resources like CPU, memory, and storage because it is not shared with other clients. This exclusivity eliminates the “noisy neighbor” effect. In this effect, one client’s server’s demands on a shared hosting platform hurt another client’s server.
As a result, servers are faster and more reliable. They are perfect for sites with heavy traffic, big databases, and complex applications that need much processing power.
What is a Windows Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
A Windows server is a kind of dedicated hosting. It uses the Windows operating system. This configuration is intended for companies and people who need server use. It gives them complete control over the server’s settings, software, and resources, all inside the Microsoft Windows ecosystem.
Choosing a Windows server is very enticing for people whose websites or apps are specifically made to run on Windows or who depend on Microsoft technologies like PowerShell scripting, Active Directory, ASP.NET, or MSSQL (Microsoft SQL Server).
Windows servers are a desirable alternative for businesses with pre-existing Microsoft-based infrastructure since they provide a recognizable Windows user interface and integration possibilities.
They improve efficiency and productivity by enabling smooth interaction with other Microsoft services and products. Businesses that run their operations using Microsoft software would particularly benefit from this, as it guarantees compatibility and makes managing their digital environment easier.
Remote desktop access makes administering a Windows server’s settings, software installations, and updates easy. It offers a graphical interface for this purpose, a significant benefit for users who would rather control their servers using a graphical interface than command-line tools.
Security on Windows servers is robust, with Microsoft consistently releasing updates and patches to protect against vulnerabilities. Users can also leverage Windows Server’s built-in security features, such as Windows Defender, to further enhance the server’s security posture.
It’s crucial to remember that because Windows Server licenses and maybe other Microsoft software licenses are required, Windows servers might have greater licensing expenses. Although this raises the total operating cost, integration, usability, and Microsoft support advantages outweigh the cost.
Pros and Cons of Windows Dedicated Server
Credits: Freepik
Windows servers have benefits and challenges. They meet specific corporate goals and technical preferences. They are popularly picked for their interoperability with Microsoft’s ecosystem.
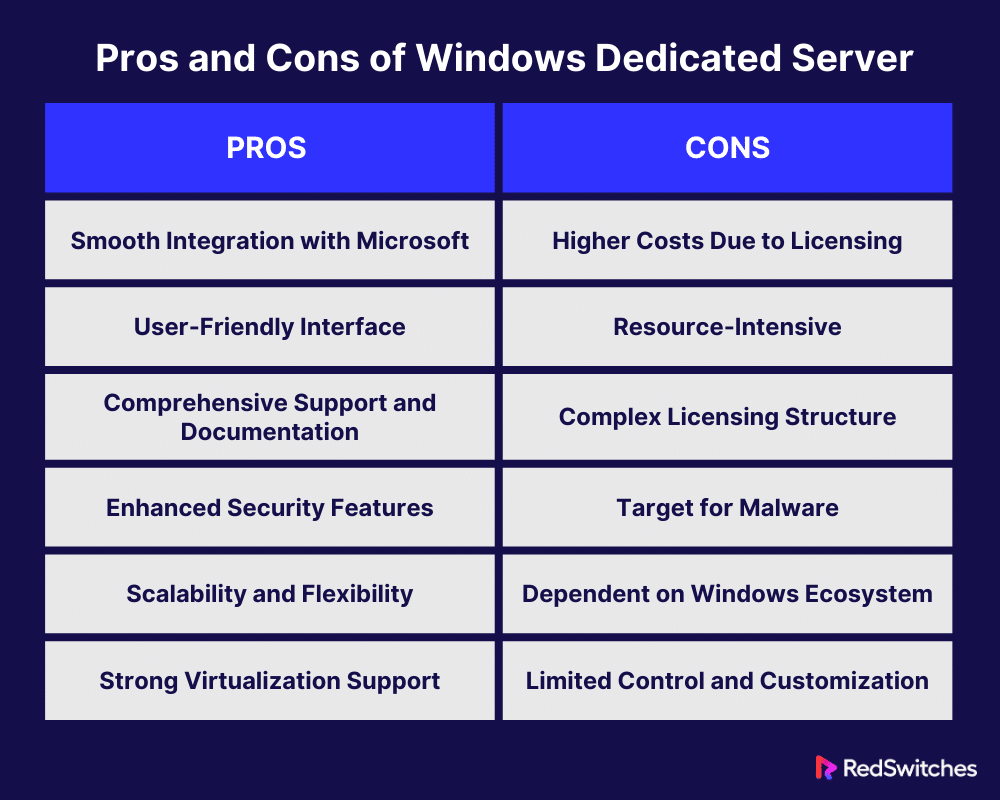
Pros
In this section, we will discuss the core part of our blog i.e. Pros and Cons of Windows Server, in detail. Let’s discuss the pros first.
Smooth Integration with Microsoft
Windows servers have a major benefit. They integrate seamlessly with Microsoft products and services. This is especially true for businesses that are heavily dependent on Microsoft. This natural compatibility reaches areas. It greatly improves operational coherence and efficiency, not just convenience. For example, developers use Microsoft SQL Server for databases.
Organizations use ASP.NET for web apps. They find that Windows servers provide the best environment for these technologies. Also, the interface works with Microsoft Exchange for email, guaranteeing a dependable and well-coordinated communication system.
Microsoft-based programs are easy to deploy, scale, and manage. Their smooth interoperability also prevents compatibility problems, which are common in non-native systems.
Interface that is easy to use
One of the main reasons Windows servers are so widely used is their intuitive user interface. The familiar Windows GUI makes switching to or managing server infrastructure less scary for many organizations.
This interface makes it easy to navigate and handle server activities. It can help with organizing files, installing apps, and adjusting networks. The learning curve is much lower for workers with prior experience with Windows.
This allows more staff to take on server management. The Windows platform includes graphical tools and utilities. Thanks to them, many simple maintenance and troubleshooting solutions are just a few clicks away.
Entire Support and Documentation
Microsoft is dedicated to supporting its products. The extensive documentation and help for Windows servers show this. Microsoft has an extensive resource library. It includes community forums, how-to manuals, and thorough documentation. It helps customers solve many problems. Each issue likely has a well-documented answer. It does not matter how complex or small the changes are. Furthermore, Microsoft’s direct support adds extra assurance. Professionals are available to help with pressing problems. This system helps IT workers solve problems quickly. It helps them grow their knowledge and improve their skills.
Extra Security Functions
Windows servers have advanced security mechanisms. They protect the servers from constantly changing cyber threats. Windows Defender has an anti-malware feature. It offers real-time defense against spyware, viruses, and other dangerous apps.
The server’s defenses will be stronger with the operating system’s advanced firewall. It has programmable rules and policies. They manage network traffic and stop unwanted access.
Another key part of Windows server security is regular security updates. They patch holes and make the system harder to break into. The improvements provide a strong security architecture. It protects sensitive data and the server environment’s integrity. It also allows role-based access control (RBAC) and encryption.
Scalability and Flexibility
Windows servers are very flexible. They can scale to meet enterprises’ changing needs. This scalability guarantees that changes in demand or growth can change the server architecture.
Windows servers support many hardware configurations. They can also easily add more resources—like RAM, CPU power, or storage—without much downtime.
Moreover, the Windows environment is versatile. Many services and apps can run on it. Windows servers are adaptable. They can change with business objectives. This is true whether an organization has to scale up, add new software, or modify resources to meet new demands.
Strong Support for Virtualization
Windows servers offer strong support for virtualization, especially for Microsoft’s hypervisor, Hyper-V. This is another important advantage. You can make and manage VMs with Hyper-V.
This lets companies run many virtualized servers on one physical server, maximizing server resources. This technology supports many operating systems. It lets us create a versatile server that can house a range of services and applications.
Hyper-V virtualization optimizes hardware use. It also improves disaster recovery. It streamlines backup and enables testing and development.
Cons
Now, let’s discuss some of the cons of Windows servers.
Cost
Beyond the basic licensing fees for Windows Server, there are extra costs for Windows servers. Additional Microsoft software and applications, which come with their licensing fees, are frequently needed for these servers to perform certain business functions.
These apps include Microsoft Exchange for email. It also has a Microsoft SQL Server for databases. This tiered pricing might make ownership much more expensive.
Open-source and Linux-based competitors do not need such licenses. Additionally, these licensing fees can increase when a firm grows and needs more servers or instances, affecting the entire budget.
Rich in Resources
Windows servers are known for using more resources. This is because of their graphical user interface (GUI) and background processes. These demand more system resources to function well. This may result in the operating system using many server resources. These could otherwise be used for programs essential to the business. More powerful technology may be needed in places where resource use is crucial.
This includes busy websites and massive data processing jobs. They need it to reach the required performance levels. Also, Windows has more overhead than lighter, command-line Linux servers. This overhead may waste server resources. This waste may require more frequent upgrades or expansions.
Complicated Licencing
Because of its complexity and range of editions, versions, and licensing models (including per-core licensing, CALs for client access licenses, and subscription-based models), Microsoft’s licensing for Windows Server and its related products can be intimidating. It can be difficult for firms to navigate this complexity and ensure they are fully compliant without getting too licensed.
Errors in licensing can result in needless spending on licenses that aren’t being used or compliance problems that can lead to fines or the requirement to buy more licenses later. Due to this intricacy, managing Windows servers is further complicated by the requirement to have a deep understanding of Microsoft’s licensing schemes or to engage with licensing professionals.
Malware’s target
Because Windows is so widely used as a desktop operating system, it is frequently the target of malware and virus attacks. This notoriety also applies to Windows servers. Because Windows servers are so widely used, hackers constantly target them to find weaknesses, even with Microsoft’s strong security measures.
Administrators must maintain vigilance in this ongoing threat by implementing a multi-layered security approach that includes frequent system upgrades, sophisticated threat detection and response tools, and maybe more third-party protection software.
When selecting their server architecture, businesses must consider these factors because the need for such extensive security measures can increase the administrative work and operating expenses of running a Windows server environment.
Reliance on the Windows ecosystem
The inherent dependence on the Windows ecosystem is one of the less well-publicized drawbacks of using Windows servers. This dependence restricts freedom regarding software and development tools and binding organizations to Microsoft’s product lifecycle, which includes planned updates and end-of-life rules.
For those who have already invested in the ecosystem, integrating with Microsoft products provides seamless operation, but there are also drawbacks.
The requirement for organizations to employ only Windows-compatible software may restrict their alternatives, perhaps limiting their access to open-source or cross-platform solutions, which are frequently more advantageous or affordable. Over time, this may increase expenses if companies are forced to buy or subscribe to more.
Minimal Control and Customization
Despite being reliable and easy to use, Windows servers give less control and customization than Linux servers. Because the Windows operating system is proprietary, there are restrictions on access to the underlying source code, which makes it more difficult to fine-tune or modify the server environment.
This might be a major disadvantage for companies with highly specialized needs or those needing extensive customization to maximize their server’s efficiency and security. On the other hand, because Linux is open-source, administrators can fully customize the operating system to meet their exact requirements.
What is a Linux Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
A Linux server is a web hosting service in which a customer rents a whole server running one of the different Linux operating systems. A server gives the client sole access to all its resources, including the CPU, memory, and storage.
Shared hosting, in contrast, gives resources to several users. This sharing guarantees better performance and dependability. Linux is open-source. It provides an adaptable and customizable hosting environment. It is suitable for many uses, including databases, application servers, websites, and email servers.
The dependability and reliability of Linux servers is one of their key characteristics. Due to its well-known dependability and uptime, Linux is a great option for companies whose online operations must be accessible 24/7. Linux is open-source. Users can use a large community of free software and apps. This makes server management and operations cheaper. Also, a global group of developers regularly updates Linux servers. They ensure the server’s software is safe and current.
Additionally very configurable, Linux servers give administrators total command over the server setup. You can customize the server. This lets you optimize its performance for the needs of the hosted website or application.
Linux offers the flexibility and features needed for fine-tuning servers. This includes installing custom software, changing kernel settings, and setting up networks. This management degree is especially useful for developers and IT experts. They can use it to maximize their server setup.
Pros and Cons of Linux Dedicated Server
Credits: Freepik
Now, let’s focus on another core section of our blog, which will discuss the pros and cons of Linux servers in detail.
Pros
First, let’s discuss the pros of Linux servers.
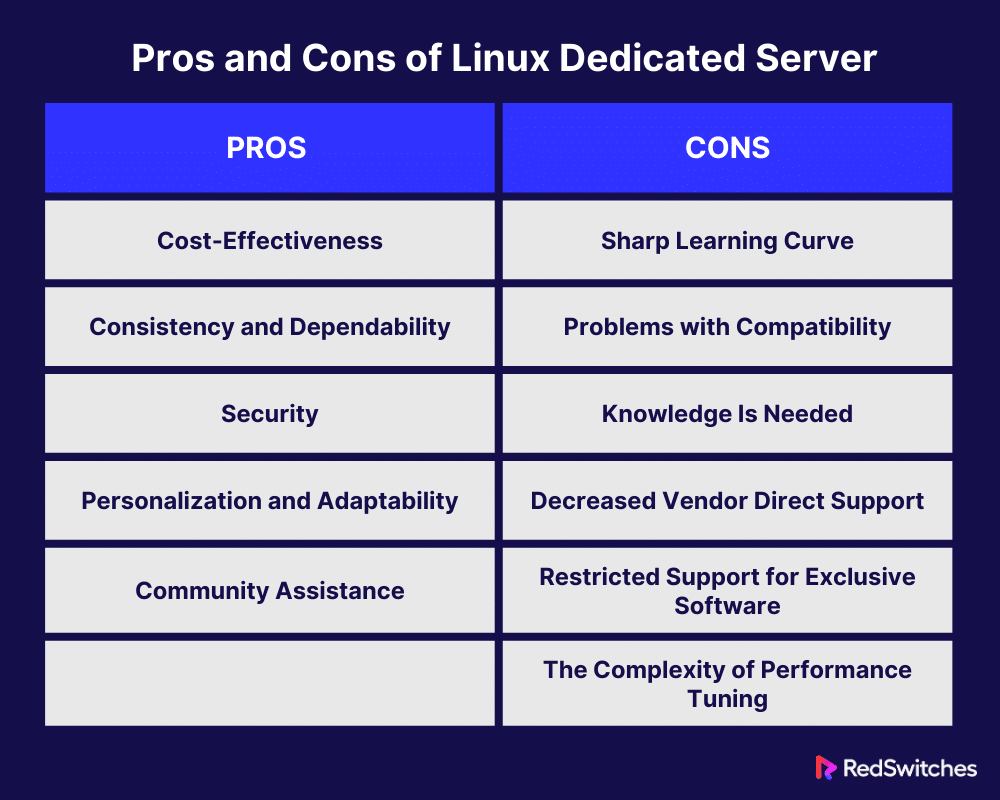
Cost-Effectiveness
Beyond not having to pay for licenses, Linux servers are quite affordable. Linux is an operating system. Companies can use its strong server capabilities without paying for proprietary software. This benefit is crucial when expanding operations. The savings go up with each server added.
Enterprises can also install many applications. These include content management systems like WordPress and web servers like Apache and Nginx. They can do this without paying more for software.
This is because of the profusion of free and open-source software in the Linux ecosystem. The company can use the savings to fund development, marketing, or expansion. This will give it a competitive edge.
Consistency and Dependability
Linux is robust. Its design and community testing provide the foundation for its stability and dependability. As a result, the platform performs well. It handles demanding applications and high-load settings with little downtime.
Businesses need their operating systems to handle pressure. Downtime means lost sales and lower client confidence. Linux is good at managing resources, which means programs keep working normally even as demands change.
It provides a steady and dependable user experience. Reliability is key for businesses. It is also vital for e-commerce sites and any online service where dependability is essential to success.
Security
Linux’s architecture has a main feature: its security model. It gives a strong framework to guard against hacking and data breaches. In addition to basic permissions, the operating system has built-in security features like SELinux.
They add an extra layer of policy-based access control, which boosts security. Linux servers have extensive security. They are the top option for sectors like banking and healthcare. These sectors have strict data protection regulations.
These sectors are suitable for managing sensitive information. The open-source community’s teamwork is key to security. They find and fix vulnerabilities quickly. They do so even faster than in proprietary systems. This keeps Linux servers at the forefront of security.
Personalization and Adaptability
Linux servers are flexible and customizable. They let companies design highly optimized server environments for their unique needs. This is unlike universal solutions. Linux lets you remove unnecessary services and apps. This reduces the attack surface and improves efficiency.
Administrators can adjust parameters at the kernel level. They do this to maximize disc I/O, memory, and network throughput. They do this based on their unique workloads. With this much control, firms can innovate and set themselves apart in the market. This is especially true for specialized applications or services that must be adjusted to work well.
Also Read Private Network vs Public Network
Community Assistance
The Linux community support system is unmatched. It is powerful and priceless. It’s a great resource for both new and expert users. The community drives this support model. It creates a collaborative environment. In it, knowledge is openly shared, and solutions are made together.
The site offers thorough documentation, lively discussion boards, and real-time chat. Users can get advice, best practices, and troubleshooting help from professionals worldwide. This international support network helps enterprises and people realize the full potential of Linux by promoting learning and skill development and expediting problem solutions.
Because of the community’s dedication to sharing information and resources, Linux users are never alone on their path, which greatly helps the platform’s success by creating a foundation of support.
Cons
Now, let’s discuss the cons of Linux servers.
Sharp Learning Curve
The command-line interface (CLI) is just one part of the steep learning curve for Linux servers. Other parts include learning the Linux filesystem. You will also have to learn about config files and the basics of Linux administration. This can mean a big change in how users interact with the server.
They are switching from systems with more graphics. Even while the CLI is useful and strong for seasoned users, learning how to use it well takes time and effort.
You must understand shell scripting. It is a key part of learning. It helps with task automation and server management. Some organizations are discouraged. This is especially true for small ones without dedicated IT staff. They may be discouraged from using the full potential of Linux servers. This is because of the initial investment needed to understand the operating system.
Problems with Compatibility
Beyond finding Windows-only app replacements. Proprietary software on Linux servers causes compatibility problems. Many industry-specific tools may lack Linux versions or similar capabilities.
This is especially true in design, engineering, and specialized business apps. This may require keeping a mix of Windows and Linux servers. This could complicate infrastructure and raise costs. Also, organizations depend on peripheral gear, such as printers and scanners. They may have difficulties due to limited support or the need for extra setup.
Knowledge Is Needed
Beyond basic administration, Linux server management requires knowledge of network configuration, Linux kernel optimization, and security best practices. To keep servers secure, Linux administrators must keep up with the most recent security alerts and patches.
They also need to comprehend advanced networking concepts to ensure the server is optimized for the unique traffic patterns and usage circumstances it will meet. This breadth of expertise is necessary to guarantee the server’s seamless, safe, and effective operation, but it may result in a dependency on a limited number of highly qualified experts.
Because of this, companies could have to pay more to hire and retain seasoned Linux administrators or to train their current workforce.
Decreased Vendor Direct Support
For Linux servers, depending on third-party vendors or the community can have its advantages and disadvantages. Although the Linux community is well known for its helpfulness and the variety of online resources, novice users may find it difficult to navigate this huge sea of knowledge. Troubleshooting complex issues may require consulting various sources and forums due to the lack of a single authorized source for support, which can be time-consuming.
If support requests are not guaranteed to be answered, it might be dangerous for firms that depend on certain applications to maintain operational continuity. While third-party vendors provide professional support services, they are chargeable extra, and suppliers’ caliber of support varies greatly.
This situation contrasts with the direct vendor support available for proprietary systems, where businesses can have more predictable support structures.
Restricted Support for Exclusive Software
Despite their strength and versatility, Linux servers can struggle with supporting proprietary software, particularly in programs with tight licensing requirements or are only meant to function on Windows or macOS. This restriction covers more than simply the software’s accessibility; it includes official vendor support and upgrades, which might not prioritize Linux compatibility.
This can present serious operational issues for companies whose core operations rely significantly on such proprietary solutions. It may not always be possible to migrate to alternative open-source software because of variations in functionality, user experience, or suitability for usage with current data and workflows.
As a result, companies may feel that the Linux software market limits their ability to use specific technologies or keep their IT infrastructure consistent. This drawback emphasizes how crucial it is for companies considering switching to Linux servers to plan thoroughly for compatibility and develop plans for adaption.
The Complexity of Performance Tuning
High levels of customization and control are provided by Linux servers, which is advantageous but also adds complexity to performance tuning and optimization.
A thorough understanding of the system’s inner workings, including kernel parameters, network configurations, and resource allocation, is frequently necessary to get optimal performance on a Linux server, in contrast to more managed or simplified server systems.
The multiplicity of distributions and the adaptability of Linux, which allows for the customization of each distribution with its own optimization strategies and configuration systems, add to this complexity.
If configurations are changed incorrectly, this intricacy might result in subpar server performance or even system instability for organizations lacking the necessary experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many factors will determine your choice. These factors include your budget, technical skills, and the unique needs of your organization and the apps you use. They will decide if you choose a dedicated Windows or Linux server. Windows servers offer seamless integration and intuitive control. But, they have higher licensing fees and resource needs.
They perform best in systems that rely largely on Microsoft’s ecosystem. But, Linux servers are known for their low cost, reliability, and security. They are popular with people who need a flexible and effective solution. But, they do have obstacles like a steep learning curve and incompatibility with proprietary software.
Navigating these options independently can be difficult, but you don’t have to. RedSwitches is committed to offering hosting solutions tailored to your needs and is aware of these nuances. We provide a selection of server options. They are meant to maximize your online operations and work well. This is true regardless of whether you prefer the smooth integration and support of Windows or the strong security and flexibility of Linux.
You can use the platform’s capabilities fully with our help. We will ensure that your infrastructure can meet your current and future needs. Let us guide you as you weigh the advantages and disadvantages of Windows vs. Linux servers, giving your company the best possible start.
FAQs
Q. Is Linux or Windows better for servers?
Linux is renowned for its cost-efficiency and flexibility, while Windows provides excellent integration with Microsoft products.
Q. Which OS is better for servers?
The better server OS depends on your application needs and technical environment; Linux is preferred for its stability and security, whereas Windows is chosen for its ease of use and support for Microsoft-centric applications.
Q. Is Linux faster than Windows servers?
Linux can be faster than Windows servers for certain tasks due to its lightweight design and efficiency in handling server-specific operations. Still, actual performance will depend on the specific use case and configuration.
Q. What is the difference between Windows Server Hosting and Linux Server Hosting?
Windows Server Hosting uses the Windows operating system, while Linux Server Hosting uses the Linux operating system.
Q. What are the key features of server hosting services?
Server hosting provides exclusive access to a physical server, ensuring high performance, security, and customization options.
Q. Is Dedicated Windows Server Hosting suitable for my website?
Windows Server Hosting is ideal for websites that require specific Windows applications or software compatibility.
Q. What are the benefits of choosing a managed server hosting?
Managed servers offer support services such as maintenance, security updates, and backups, freeing you from server management tasks.
Q. How does IP address benefit my hosting experience?
An IP address ensures that your website has a unique identity on the internet, improving security and website accessibility.
Q. Can I switch between Windows and Linux Dedicated Server Hosting plans?
Hosting providers may offer the flexibility to switch between Windows and Linux Server Hosting plans, depending on your requirements.
Q. What level of technical support can I expect with server hosting?
Server hosting often includes a support team to assist you with any technical issues or server configurations.
Q. Are there differences in pricing between Windows and Linux server hosting?
Pricing for Windows and Linux Server Hosting plans may vary based on hardware specifications, software licenses, and support services.
Q. Which operating system is more suitable for hosting game servers?
Depending on the game requirements, either Windows Server Hosting or Linux Server Hosting can be used to host game servers.