Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become a potent tool for securing online privacy and ensuring connectivity in less secure environments.
Consider a typical situation where Sarah, a corporate executive, must access confidential corporate files from her laptop during an important work trip. During the trip, she has to connect to the Internet using the hotel’s free WiFi.
Sarah turns on her VPN since hackers frequently target unsecured public WiFi networks. The VPN helps secure and encrypt the connection between her laptop and the remote corporate server, shielding her internet traffic from diversion and eavesdropping attacks.
Sarah can confidently carry out her activities, knowing that her VPN encrypts the communication to prevent unauthorized access.
Regardless of location, people and businesses rely on VPNs to securely access online locations without worrying about data theft and related issues. VPN acts as an additional security layer for the user’s devices and sets up a secure tunnel that is impossible to breach.
In this blog, we will discuss how does a VPN work, along with the popular types of VPN, associated protocols, and the benefits of using a VPN.
Let’s start with the definition.
Table Of Contents
- What is a VPN?
- How Does a VPN Work?
- Advantages of Using VPNs
- VPN Limitations and Considerations
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, creates a point-to-point tunnel between your device and a remote server owned by the VPN provider. This tunnel encrypts the data moving to and from the devices, hides the IP address, and enables users to get around content censorship and blocks.
As a result, the user’s online activities become private, safe, and protected from major cyber threats.
In practical terms, here’s how a VPN connection delivers these benefits:
-
-
- The connection is virtual because the connection process does not involve any physical cables.
- The connection remains private because no third party can access the data within the VPN tunnel or monitor the activities over the secure connection.
- A typical VPN connection heavily relies on the underlying network hoops to keep the connection open between the devices and the VPN server.
-
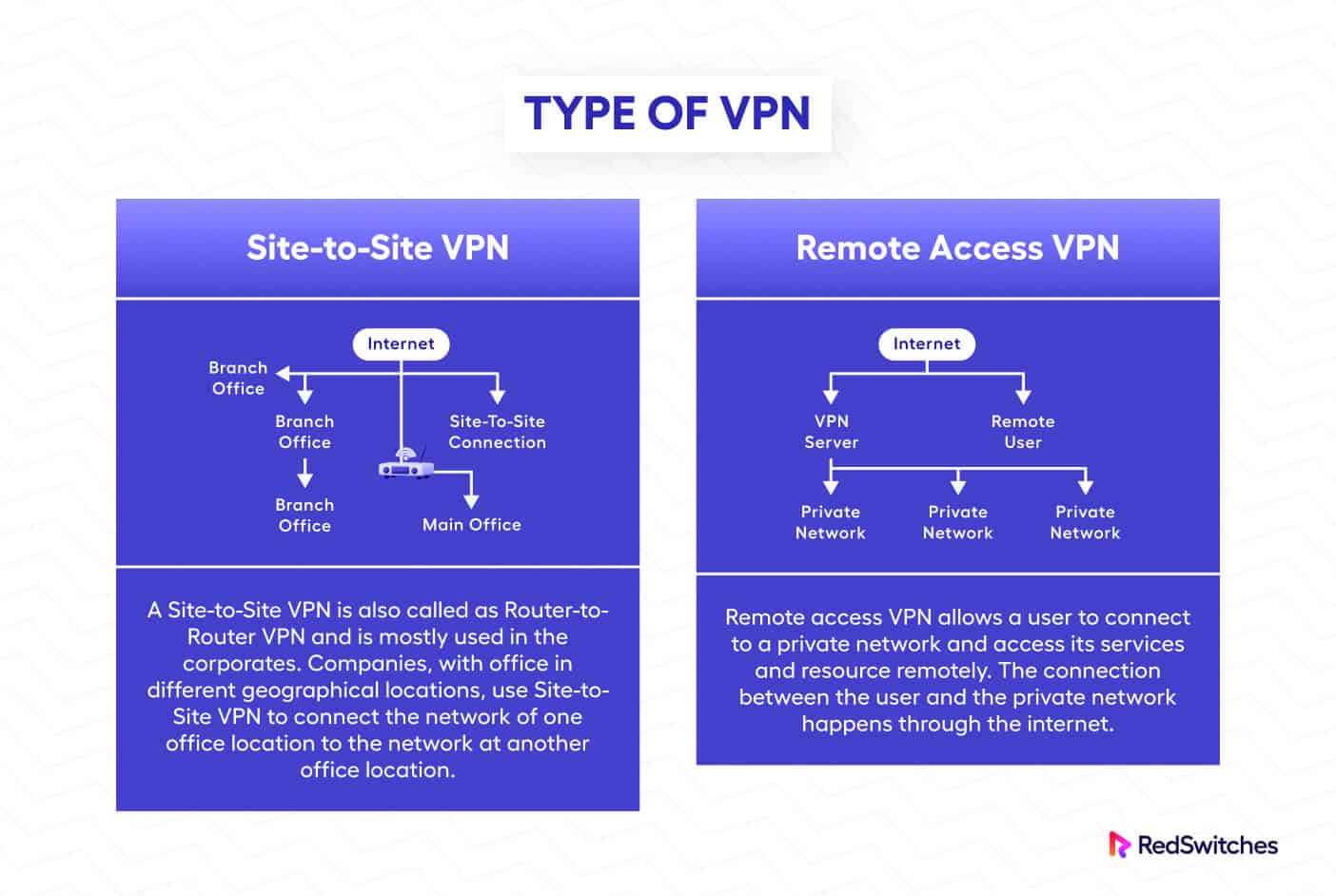
Types of VPNs
Now that you know how a VPN connection works, let’s discuss the types of VPNs you can use for your security needs.
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPN allows users to join a private network and remotely access all its resources and services. A Remote Access VPN sets up a private and secure link between the user and the private network.
Residential and commercial users can benefit from remote access VPN and connect to a private network to access files and resources remotely.
The most common use of remote access VPNs is to get around geographic Internet blocks and access prohibited websites. Users prefer to use VPNs to increase their privacy and security online.
Site-To-Site VPN
A Site-to-Site VPN, or a Router-to-Router VPN, is frequently used by businesses with multiple distributed locations. These VPNs are used to link the networks of the distributed sites into a single (or multiple) large network.
Essentially, Site-to-Site VPNs create an intranet-based virtual private network where all business locations are connected and accessible to users (depending upon access privileges).
Businesses can use these VPNs to connect third parties (other businesses or governmental entities) to their network. In this case, site-to-site VPNs are used to set up extranet-based virtual networks.
Cloud VPN
A cloud VPN enables customers to connect safely to a cloud-based infrastructure or service. It connects remote users to cloud-based resources using the internet as the primary transport medium.
Cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure frequently provide cloud VPNs as an additional service.
Businesses use cloud VPNs to ensure that the data transmitted over the VPN is secure by the same encryption and security protocols (generally, IPsec or SSL) as conventional VPNs.
Organizations frequently use cloud VPNs to safely link their on-premises resources to cloud resources, such as cloud storage or SaaS applications.
Mobile VPN
A mobile VPN enables users of mobile devices to connect to private networks, generally through cellular networks and WiFi connections. The data exchanged over the VPN connection remains protected because of the tunnel the VPN creates between the device and the target VPN server.
Users frequently use mobile VPNs to access company resources like email or internal websites while on the road, especially over public WiFi networks.
Mobile VPNs are offered as stand-alone applications or as a component of Device Management (MDM) Programs. Businesses frequently utilize these technologies to secure their mobile and remote workforce.
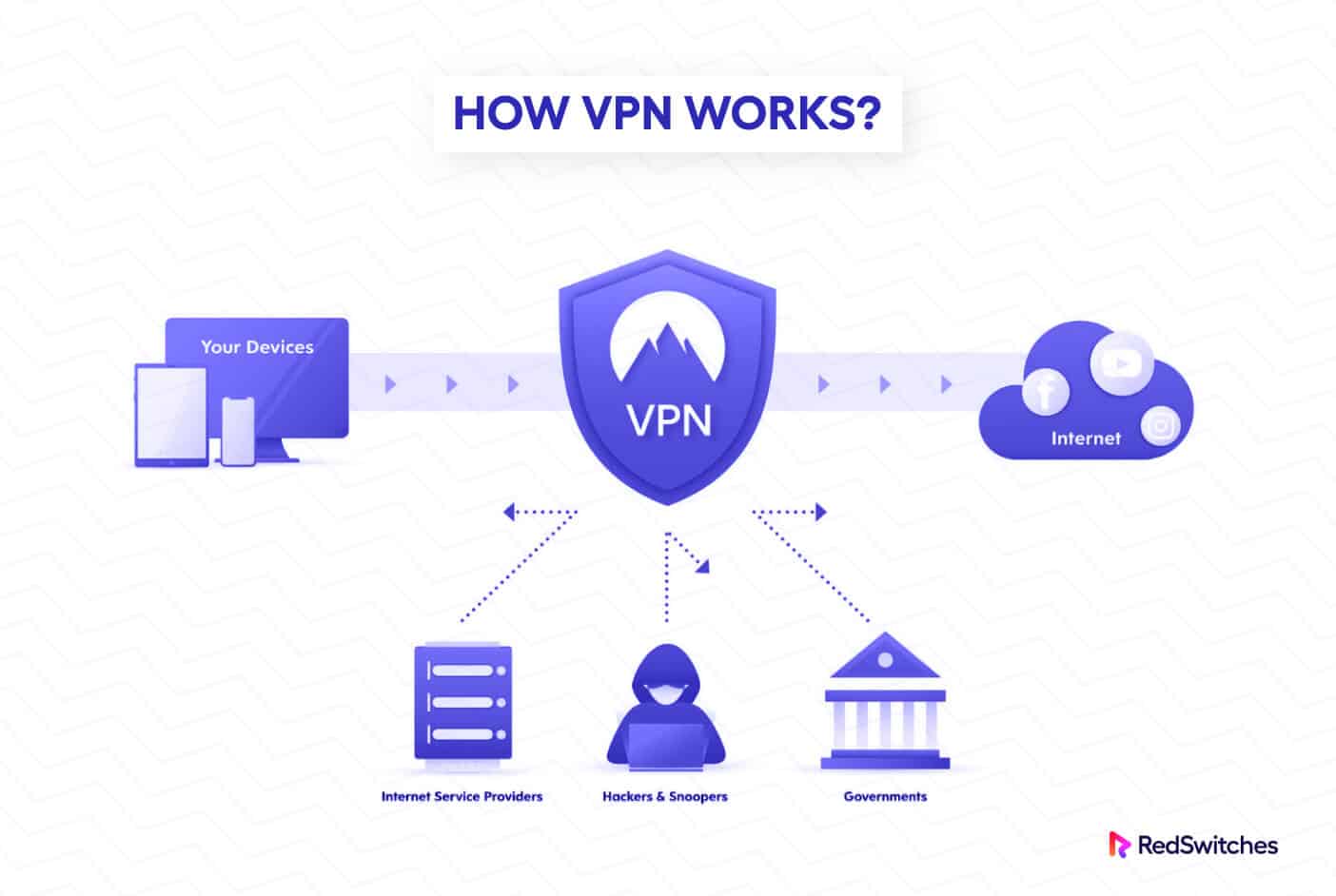
How Does a VPN Work?
At its core, A VPN uses a simple client-server model where the client (user) connects with the server (the VPN server) via a secure tunnel.
Let’s discuss the intricacies of how does a VPN work and explore these significant ideas of the client-server model, encrypted tunneling, and authentication.
The VPN Server and Client Model
The VPN connection process revolves around the VPN server that serves as the single connection point between the user’s device and the Internet. The server is also responsible for setting up and partially maintaining the secure tunnel through which data is first encrypted and transferred to the VPN server when a user establishes a VPN connection.
The data is then forwarded to its intended location on the internet after the server decrypts it and assigns a new IP address (depending on the server’s location) to the packets.
Similarly, the server encrypts data from the internet before sending it back through the secure tunnel to the user’s device.
The program or application that a user installs on their device to connect to a VPN server is known as a VPN client. The client is in charge of handling data encryption before transmission and data decryption after receipt.
Additionally, the client controls how the secure connection between the user’s device and the VPN server is created and terminated.
Encryption and Tunneling
The core purpose of a VPN is to set up a secure tunnel that protects all data transfers between the user and the VPN server. This involves two critical processes.
Encryption
Encryption is one of the most significant aspects of any VPN.
Wherever a user initiates a VPN connection, the data is encrypted and sent over the internet. This encrypted data can only be decrypted with the proper decryption key, making it impossible for any third party to access or use it, even when they manage to intercept it.
Tunneling
The tunneling process involves encapsulating data packets in a secure wrapper, thus creating a virtual tunnel through which data travels between the user’s device and the VPN server.
The method requires adding an additional layer of headers to the original data packets to make it appear as though the data is coming from the VPN server rather than the user’s device. The user’s real IP address is concealed to enhance their online privacy and mask their activities.
VPN Protocols
VPNs use various protocols for establishing and managing secure connections between the user and the VPN server. Popular VPN protocols include:
PPTP
One of the first VPN protocols, PPTP, is renowned for being simple to set up and working with most devices. However, compared to more recent options, it lacks in the security department, making it less ideal for transmitting sensitive data.
L2TP/IPsec
L2TP uses tunnels to transmit data, which offers greater security than PPTP.
L2TP becomes more secure when paired with IPsec, which provides strong encryption and authentication.
OpenVPN
An open-source VPN protocol, OpenVPN is renowned for its adaptability, robust security features, and cross-platform compatibility. It can use a variety of ports and employs the SSL/TLS encryption protocols, making it challenging to identify and stop.
Authentication and Key Exchange
Since the VPN server is directly connected to the user’s device, a VPN must use robust authentication processes to ensure proper connectivity between the authorized parties.
This involves the following two critical processes.
Authentication
Authentication procedures are used to confirm their identities when a user requests access to a VPN server. This procedure ensures that only authorized users can create a VPN connection. The authentication procedures generally use a combination of user credentials, digital certificates, and two-factor authentication (2FA) to establish user identity.
The Key Exchange
VPNs use the key exchange method to set up a secure communication channel. Sharing encryption keys between the user’s device and the VPN server is done after verifying the user’s identity.
During the VPN session, these keys are used to encrypt and decode data. VPNs use key exchange protocols like Diffie-Hellman to exchange encryption keys securely without having to send them directly over the internet. This keeps the keys private and secure from eavesdropping.
Advantages of Using VPNs
Now that you know how a VPN operates and secures the tunnel, let’s see the benefits that make VPNs an essential tool for all users.
Enhanced Data Privacy
VPNs are essential for improving data privacy since they encrypt internet traffic.
As a result, sensitive data, including login credentials, personal information, and business communications, are safeguarded against hacking and cybercrime. VPNs add a crucial degree of protection by prohibiting unauthorized access to user data, especially when utilizing public WiFi networks, which are prone to security flaws.
Protection From Public WiFi Risks
Unsecured public WiFi networks in coffee shops, airports, and hotels, are prone to eavesdropping attacks.
Hackers may be able to get usernames, passwords, and other personal data by readily intercepting data sent across these networks. VPNs are a simple yet effective way of protecting sensitive data when you’re connected to these easily-compromised networks.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions and Censorship
Users can get around geographic restrictions imposed by websites and streaming services by using VPNs. Users can access content that might be prohibited or unavailable in their present location by connecting to a VPN server in a different country. Travelers and expats who wish to access information from their own country find this especially helpful.
VPN Limitations and Considerations
Despite the advantages outlined above, VPNs require you to consider the following limitations.
Impact on Internet Speed and Performance
VPNs can worsen latency by adding extra travel time for requests and responses.
When a user initiates a request, the data packets travel to the VPN server, which could be several hops away from the user’s device. The response to this request also travels to the VPN server before reaching the user’s device.
These additional hops affect the user experience by increasing the latency of responses.
VPN Service Reliability and Trustworthiness
Reliability is a critical requirement because VPNs manage confidential data.
Simply put, they have access to all the data you want to keep hidden from prying eyes (the government, hackers, and your ISP).
You must ensure the VPN doesn’t monitor or log critical information. This assurance should be validated through a legal responsibility established through a contract between the VPN service provider and the users.
Conclusion
We outlined how does a VPN work by going into the details of the underlying processes, such as tunneling and authentication. We also discussed the benefits and limitations of VPN so that you can make an informed decision about incorporating a VPN in your business processes.
If you’re interested in setting up your VPN, RedSwitches offer dedicated VPN hosting powered by fully customizable bare metal servers. Our hosting infrastructure facilitates your VPN operations and takes care of housekeeping and maintenance of the VPN infrastructure.
Get in touch with our pre-sales teams via chat or email for a discussion about our VPN hosting services.
FAQs
1) Is it okay to use VPNs?
A) Yes, most countries permit VPNs. However, it’s critical to be aware of any potential limitations or rules about VPN usage in your current location.
2) Can a VPN give me complete online anonymity?
A) VPNs can increase your anonymity by covering your IP address and encrypting your data, but they cannot ensure total confidentiality. Governments and hackers can still track aspects of your online activities. Furthermore, even while using a VPN, some cutting-edge identifying techniques, such as browser fingerprinting, may be able to recognize people.
3) Can I access streaming services like Netflix or Hulu using a VPN?
A) Yes, you can access content from many areas by using VPNs to get around geo-restrictions on streaming services. However, not all VPNs can reliably get around these limits because streaming providers frequently block VPN connections.