Key Takeaways
- Stay current with updates and patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Configure firewalls and control access to secure network traffic.
- Utilize IDS and IPS for real-time threat detection and prevention.
- Implement secure SSH and robust password policies for access management.
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
- Conduct regular security audits and comply with regulatory standards.
- Foster a culture of continuous security monitoring and user awareness.
Cyberattacks are more common now. Digital fortifications are under siege. So, server security is more than just your duty. In online business, a dedicated server is your digital fortress. It houses your most valuable assets – your website, data, and the trust of your customers. However, managing a server is no walk in the park. Security threats lurk around every corner, and a single vulnerability could compromise everything.
Come with us. We’ll guide you through the maze of server security. This article will also explain the intricacies of secure dedicated server management, empowering you to safeguard your digital kingdom.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Dedicated Server?
- Advantages of Servers
- Understanding Your Server’s Environment
- Essential Security Practices for the New Dedicated Server
- Frequent Updates and Patch Management
- Firewall Setup and Management
- Systems for detecting intrusions (IDS) and preventing intrusions (IPS)
- Safe SSH Connection
- User Account and Password Policies
- Data Encryption
- Frequent Compliance Verifications and Security Audits
- Disaster Recovery and Backup Strategies
- Access Control and Least Privilege
- Monitoring and Logging
- Security Audits and Compliance
- Implementing a Security-Focused Culture
- Implementing a Security-Focused Culture
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Dedicated Server?
Credits: Freepik
A dedicated server is a kind of remote server fully devoted to a person, group, or program. It houses the data, websites, and applications of one client. In shared hosting, many clients share the resources of a single server. Because of this exclusivity, the client controls the server. They can customize the hardware, software, and operating system. This lets them create a platform that meets their needs and tastes.
Performance is one of the main benefits of a server. One client has exclusive access to all of the server’s resources; thus, there is no rivalry for processing power, disc space, or bandwidth. This guarantees great performance and stability, which is key for high-traffic websites or programs that need power. Also, their strong architecture and dedicated hardware make servers very reliable. They often have higher uptime guarantees.
Another important advantage of having a server is security. Clients can install personalized security measures, including firewalls, protocols, and anti-malware systems, based on their unique needs. This is because they have total control over the server environment. This control provides comfort. It safeguards sensitive data by reducing data breaches and cyberattacks.
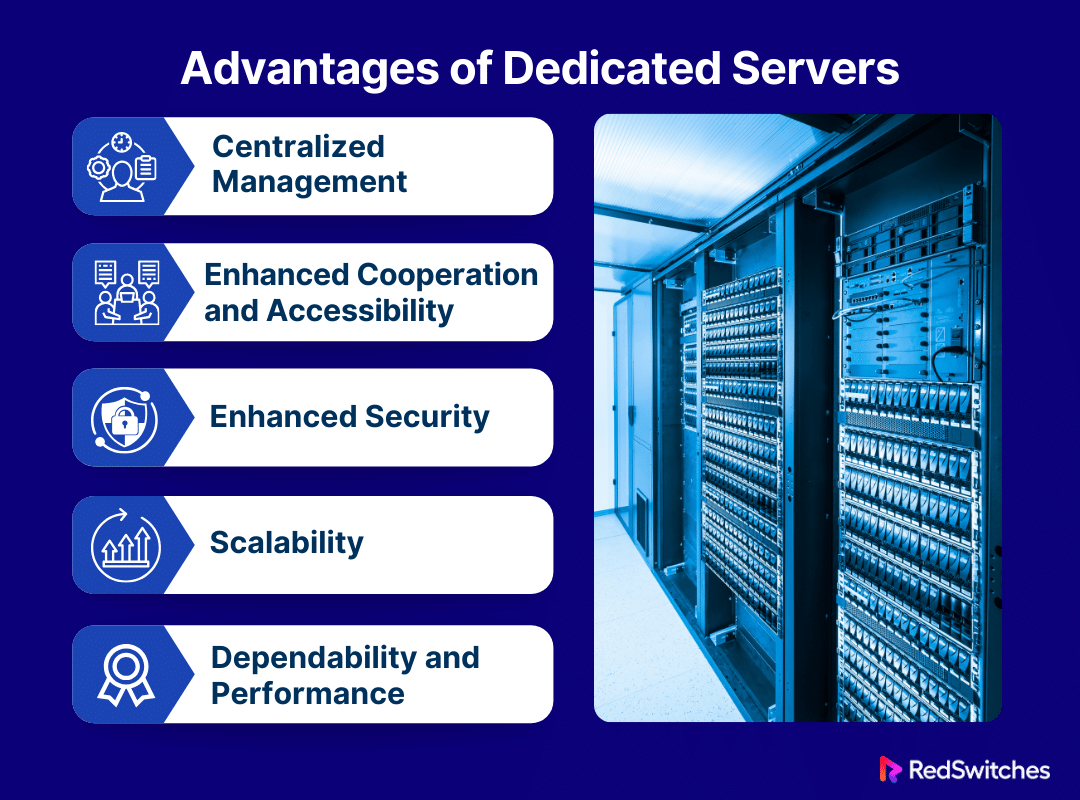
Advantages of Servers
Modern computing environments rely heavily on servers. These servers come in many forms and configurations. They are used by tiny businesses and multinational corporations. They provide several benefits, including efficiency, scalability, and security, for various purposes. Organizations may make better judgments about their digital strategy and IT infrastructure. They can do this by knowing these advantages.
Centralized Management
Credits: Freepik
Centralized management is key to the server’s advantages. It plays a big role in simplifying IT. Servers significantly cut the burden of handling lots of data and applications. They combine resources, data, and administrative chores into one central location. This hub reduces the risk of data problems. It does this by helping with updates, backups, and security. Additionally, it allows organizations to impose strict audit trails and access controls. These support data protection and strict compliance. Centralizing IT administration makes managing and improving operations easier. It also strengthens data governance and security.
Enhanced Cooperation and Accessibility
Servers offer a strong platform for file sharing. They also support synchronous and asynchronous communication and project management. They transform cooperation and accessibility. The infrastructure supports many platforms and technologies. Thanks to this, teams can easily collaborate, no matter where they are. You can access vital business data and apps from anywhere in the world. This lets you work flexibly to meet the demands of today’s workforce. That includes telecommuters and remote teams. This greater access and connection lead to more united and flexible cultures. They also lead to faster project completions and better efficiency.
Enhanced Security
Servers are essential for strengthening an organization’s defenses in cybersecurity. The deployment of multilayer security measures, including sophisticated intrusion detection and prevention systems, advanced firewalls, and strong encryption standards, is made possible by the centralized design of servers. These precautions are carefully planned to protect private data from outside dangers and unwanted access. Patches and updates are automatically applied to the entire network on a prearranged schedule, protecting the infrastructure from new threats. Furthermore, because servers are centralized, comprehensive user activity monitoring and recording is possible. This offers insightful information that can be used to spot possible security breaches and improve forensic capabilities.
Scalability
Growing companies might benefit strategically from servers’ scalability. Because dedicated private servers are built to scale, adding more storage, processing power, or network bandwidth can be done by enterprises with little trouble and minimal effort. Organizations may enhance their IT capabilities with their expansion thanks to this modular approach to infrastructure development, which spares them from the exorbitant costs and hassles of completely revamping their current systems. To maintain competitive advantage, scalability ensures that companies are flexible and responsive to market needs. It also makes it easier for new services and technology to be adopted smoothly.
Dependability and Performance
As the foundation of mission-critical operations, servers are designed to provide unmatched dependability and performance. Advanced software optimizations and enterprise-grade hardware guarantee servers can manage heavy workloads with maximum efficiency and minimum downtime. The system’s resilience is further increased by features like automated failover processes, RAID storage configurations, and redundant power sources, guarantee uninterrupted operation even during disruptions or hardware failures. The seamless running of business processes is supported by this unwavering focus on performance and dependability, which ensures that services are always available to satisfy the needs of stakeholders and customers.
Also Read: Unveiling the Hidden Risks of Dedicated Servers
Understanding Your Server’s Environment
Credits: Freepik
Understanding the server’s setup is key. It helps maximize efficiency, ensure safety, and keep dependability. This understanding covers three main topics. They are network setup basics, the operating system and software stack, and physical security.
Physical Security Measures
We need a multi-layered strategy to protect a server. It must guard against theft, unauthorized access, and environmental hazards in data centers. Data centers use advanced biometric access controls. They use fingerprint and retinal scans to stop physical contact with server hardware. This way, only authorized individuals can enter. CCTV cameras must provide constant surveillance. They monitor unauthorized activity and offer round-the-clock protection. Advanced fire suppression systems and continuous power supply guard against outages and fires. In contrast, HVAC systems regulate the air. They keep it at the ideal temperatures and humidity levels for the servers.
The systems have sensors and sirens. They detect physical intrusion. They identify any unwanted entrance or tampering with the server hardware. These physical security measures are essential. They prevent tampering with the hardware. They also guarantee the server’s integrity and dependability.
The Stack of Software and Operating Systems
A server’s operating system (OS) and the software stack built upon it play pivotal roles. They make its functionality, performance, and security possible. The operating system controls the server’s hardware. It is the main framework for all other software. People choose popular operating systems, like Windows Server, for their user-friendly interface. They also choose them for their great support for Microsoft-based applications. At the same time, Linux variants (Ubuntu, CentOS) are favored for their flexibility and robust security features. On top of this operating system layer, a carefully chosen software stack is installed to perform specific server duties. This stack has web servers, like Apache or Nginx. It also has database systems, like MySQL or PostgreSQL. It also has scripting languages and frameworks, like PHP, Python, and Ruby on Rails.
Fundamentals of Network Setup
The setup of a server’s network determines how it connects with other devices. It also determines how it communicates over the internet. This entails giving the server a distinct IP address, or a range of IP addresses, that act as its online identity and allow it to send and receive data. The firewall is a vital part of network security. It is carefully set up to control incoming and outgoing traffic according to pre-established security rules. This shields the server from intrusions and online threats.
To ensure that users are directed to the correct server, Domain Name System (DNS) settings are essential. On the other hand, carefully considered port opening and closing ensures that specific services the server provides—for example, HTTP traffic on port 80 or secured HTTPS traffic on port 443—are catered to. Just being connected is not enough for a good network. It also needs to ensure that the connection is safe, dependable, and optimized for the server’s functions and services.
Essential Security Practices for the New Dedicated Server
Let’s discuss the core part of our blog, where we will discuss the best essential practices for securing new servers.
Frequent Updates and Patch Management
Keeping a server secure needs a strict schedule. You must do regular updates and patching. This involves carefully watching, testing, and updating the server’s operating system and all its software. Software vendors regularly provide patches to improve performance, repair bugs, and address vulnerabilities. Admins can protect the server from known exploits and cyber threats. These target out-of-date software. They should do this by making these upgrades right away. Good patch management protects the operating system. It also protects any installed third-party programs, tools, and scripts on the server.
Simplifying updates with an automated system or management tools can cut the time attackers have. It also keeps the server’s integrity and performance.
Firewall Setup and Management
Firewalls control incoming and outgoing network traffic with security rules. They act as a server’s first line of defense. Clearly defined policies that permit legitimate traffic while thwarting unauthorized or suspicious attempts to reach the server are essential components of a properly configured firewall. This means defining the allowed ports and IP addresses for connections. It also means setting rules to control the data flow to and from the server. Regular rule review and management are key. They are needed to respond to changing security requirements. They also ensure the firewall reduces risks. It does this without blocking vital access or server functions.
Systems for detecting intrusions (IDS) and preventing intrusions (IPS)
The security of a server can be improved. This is done by adding intrusion prevention and detection systems (IPS and IDS). They help to find and stop hostile activity. IDS monitors system and network activity for unusual activity and security policy infractions. It logs possible threats and notifies administrators. This makes it possible to investigate and mitigate security issues promptly. However, IPS goes one step further by actively thwarting threats as soon as they are identified, stopping them from taking advantage of weaknesses. Both systems use anomaly detection to find unexpected patterns. These patterns can point to a new or developing assault. They also use signature detection to find established threats. IDS and IPS work together to provide proactive security. They greatly lower the risk of cyber attacks. They also ensure continuous monitoring and protection of the server.
Safe SSH Connection
Keeping the admin contact with the server secure requires securing SSH. SSH offers an encrypted connection path for remote administration, allowing secure communication across an unprotected network. Using key-based authentication is better than password-based authentication. It is one of the best practices to improve server SSH security. It provides a stronger defense against brute-force attacks. Also, changing the default SSH port to a non-standard port can help avoid automated assaults. They target the default settings. 2FA requires a user to have a token or a mobile device. They also need something they know, such as a password. It adds an extra layer of security.
Secure SSH access is vital to server security. It reduces entry points for attackers by regularly checking and limiting the list of users with SSH access to the server.
User Account and Password Policies
Credits: Freepik
Keeping a server secure requires an effective user account and password policies. Strong password policies ensure that all user accounts are secured. The policies require challenging passwords that are hard to guess. This covers password complexity. It includes a minimum length and the use of special characters, numerals, and both upper- and lowercase letters. This is done by reducing unauthorized access, password expiration, and account lockout. These policies block accounts after a certain number of failed logins. They also require password changes to improve security. Reducing the number of user accounts that have administrative privileges also lessens the risk of insider attacks and unintentional setup errors on the server.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a key defense against data breaches and unauthorized access. It ensures the secrecy and integrity of sensitive information. It does this while the data is in transit across networks and while it is at rest on the server. Using encrypted file systems for data storage and SSL/TLS protocols for internet traffic security are important practices. These safeguards keep sensitive data safe by encrypting it into a format that can only be viewed with the corresponding decryption key. Additionally, rotating encryption keys and renewing digital certificates improves security by lowering the risks associated with key disclosure or compromise.
Frequent Compliance Verifications and Security Audits
Finding weaknesses that an attacker could exploit and guaranteeing compliance with industry and regulatory standards require comprehensive and frequent security audits and compliance checks. This proactive strategy entails a thorough analysis of the server’s security configuration, which includes determining user access permissions, verifying the status of software updates, and assessing encryption solutions. The effectiveness of security audits can be greatly increased by utilizing automated tools and services, which offer detailed insights into the security posture of the server and specific recommendations for improvement.
In addition to protecting sensitive data, maintaining compliance with pertinent standards—like PCI DSS for payment processing or HIPAA for healthcare information—fosters confidence with stakeholders and customers by showcasing a dedication to security and privacy.
Disaster Recovery and Backup Strategies
Having well-organized strategies in place is essential to guaranteeing business continuity during cyberattacks, system failures, or data loss. To prevent loss from physical disasters or server compromises, a strong approach comprises routine and methodical backups of critical data, programs, and system settings stored securely off-site or in the cloud. These plans should include explicit data restoration and system recovery protocols, covering a spectrum of circumstances from small data damage to total system outages. Testing these recovery methods regularly is essential to confirming their efficacy and guaranteeing that the company can quickly recover from an incident with the least delay and data loss.
Access Control and Least Privilege
Credits: Freepik
Enforcing strict access control procedures and adhering to the least privilege principle is essential for lowering the possibility of unwanted access and narrowing the server’s attack surface. By carefully controlling user rights, this method greatly lowers the possibility of malicious action or unintentional data exposure by ensuring that users may access only the resources required for their responsibilities. Ensuring access privileges accurately represent current roles and responsibilities is easier by adopting role-based access control (RBAC) systems and conducting regular user accounts and permissions audits.
Monitoring and Logging
To monitor system operations and spot possible security risks, thorough and ongoing monitoring and logging of all server activity is essential. This procedure includes monitoring user activity, system and application logs, network traffic, and unusual or suspicious behavior that can point to a security event. It also involves promptly alerting administrators to these activities. The prompt detection and investigation of security issues are made possible by the effective correlation and analysis of log data made possible by the use of sophisticated log management and analysis systems. Keeping thorough logs also helps with forensic investigations and acts as an audit trail for security occurrences, which is essential for adhering to regulatory standards.
Security Audits and Compliance
Credits: Freepik
Lets understand the security audits and Compliance in Servers.
Conducting Frequent Security Audits
Frequent security audits are crucial for locating holes and weak points in the security architecture of servers. During these thorough assessments, the hardware, software, network configurations, access restrictions, and server security policies are examined in detail to look for any anomalies that could leave the system vulnerable to attacks. To reduce the server’s attack surface, the audit process usually includes a detailed review of system configurations, ensuring that security settings are optimized and that superfluous services or ports are removed. Furthermore, security audits evaluate the efficacy of implementing security mechanisms, like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and data encryption techniques, to ensure they are operating as intended and have the most recent security patches applied.
By routinely conducting these assessments, organizations may improve their defenses against new cyber threats and vulnerabilities, proactively repair security holes, and maintain a strong security posture.
Respecting Compliance Guidelines and Rules
In addition to being required by law for many organizations, adhering to established security standards and regulations is essential to a well-rounded security plan. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for payment processing, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare information, and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data protection and privacy in the European Union are a few examples of these standards, which differ by industry and location.
Implementing particular security controls, upholding strict data protection procedures, and ensuring that sensitive information is handled under the rules are all necessary to comply with these criteria. Compliance ensures that an organization’s security practices meet or exceed the minimum requirements set by regulatory bodies, thereby protecting customer data, maintaining user trust, and avoiding potential legal penalties and reputational damage.
Tools and Services for Security Auditing
Various tools and services that offer automated scanning, vulnerability assessment, and compliance monitoring capabilities are available to make conducting security audits and maintaining compliance easier. With real-time insights into the server environment’s security state, these solutions are intended to expedite the audit process. Organizations can identify and evaluate the severity of vulnerabilities in their systems using vulnerability scanners like Nessus and OpenVAS. Compliance management systems, on the other hand, make compliance verification easier by providing templates and frameworks to help match security policies with certain regulatory needs.
The ability of an organization to carry out comprehensive security audits, spot possible vulnerabilities, and uphold compliance with pertinent standards and laws can all be greatly improved by using these tools and services, which will strengthen the server environment’s overall security.
Implementing a Security-Focused Culture
Credits: Freepik
Lets understand the security audits and Compliance in Servers.
Conducting Frequent Security Audits
Frequent security audits are crucial for locating holes and weak points in the security architecture of servers. These assessments are thorough. They look at the hardware, software, networks, access rules, and server security. They search for any anomalies that could make the system vulnerable. The audit reduces the server’s attack surface. It includes a detailed review of system settings. The review ensures that security settings are optimized. It also ensures that unneeded services or ports are removed. Furthermore, audits evaluate if security mechanisms are working well. These include intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption. They also check if the mechanisms have the latest security patches.
By conducting these assessments often, organizations can improve their defenses against new cyber threats and vulnerabilities, proactively fix security holes, and maintain a strong security posture.
Respecting Compliance Guidelines and Rules
In addition to being required by law for many organizations, adhering to established security standards and regulations is essential to a well-rounded security plan. PCI DSS is for payment processing. HIPAA is for healthcare. GDPR is for data protection and privacy in the EU. These standards, which differ by industry and location, are a few examples. You need to implement specific security controls. You must uphold strict data protection procedures. Also, you must ensure that sensitive information is handled under the rules. All of these actions are necessary to comply with these criteria. Compliance ensures an organization’s security practices meet the minimum requirements. Regulatory bodies set the requirements, and the practices must meet or exceed them. This protects customer data, keeps user trust, and avoids legal penalties and reputational damage.
Tools and Services for Security Auditing
Many tools and services offer automated scanning, vulnerability assessment, and compliance monitoring. They make security audits and compliance easier. They provide real-time insights into the server’s security. They aim to speed up audits. Organizations can find and rate the seriousness of vulnerabilities in their systems. They do this using scanners like Nessus and OpenVAS. Compliance management systems make compliance verification easier. They do this by providing templates and frameworks to help match security policies with specific laws.
These tools and services can greatly improve an organization’s ability to do security audits, find vulnerabilities, and uphold compliance with standards and laws. They will strengthen the server environment’s security.
Implementing a Security-Focused Culture
Credits: Freepik
So, how do we implement a Security culture, Let’s understand.
Education and Consciousness for Every User
The first step is to have thorough training and awareness programs for all users. This includes administrators, staff, and anyone with access to the organization’s systems. These programs aim to inform users about recent cybersecurity risks. They also cover the importance of following security best practices. These practices play unique roles in protecting the company’s digital assets. Training covers many subjects. These include spotting phishing and handling passwords safely. They also include understanding data protection laws and the consequences of breaking them. They engage participants and reinforce learning. They also keep training materials relevant. This is key in the fast-changing cybersecurity field.
Security Policies and Procedures’ Function
The core of any organization’s cybersecurity architecture is its security policies and procedures. They provide a detailed plan for implementing and managing security measures. The rules in these documents are essential. They protect the company’s IT assets, including its servers. Security policies define explicit expectations for behavior and spell out the penalties for breaking them. They cover many topics. These include data encryption, incident response, remote work, and access control. Procedures are detailed guidance on specific security tasks. They ensure uniformity and compliance company-wide. We must ensure the efficacy and coherence of these policies. We will do this through their development, upkeep, and periodic revision. We will do this in collaboration with various stakeholders throughout the enterprise.
Constant observation and development
Static security methods are inadequate for long-term protection in an environment where cyber threats constantly evolve and adapt. A constant observation and development culture must be implemented if server security is to be maintained and potential threats are to be anticipated. This method entails routinely examining network traffic, system performance statistics, and security logs to spot oddities or patterns that might point to a security risk. Rapid security incident detection and mitigation can be facilitated by utilizing proactive incident response teams and automated monitoring solutions. Another aspect of continuous improvement is regularly assessing and upgrading security policies, processes, and controls in light of the results of security audits, compliance examinations, and incident analysis.
By prioritizing ongoing monitoring and development, organizations may strengthen their defenses against cyberattacks and maintain a security-focused culture that supports their long-term goals and safeguards their priceless digital assets.
Conclusion
As we navigate the challenges of server security, we’ve looked at basic procedures and cutting-edge tactics crucial for protecting your digital assets from the always-changing world of cyberattacks. Ensuring your server’s security involves a complex web of preventive measures and ongoing monitoring, from essential updates and patch management to the strong deployment of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. Furthermore, maintaining compliance requirements and cultivating a security-focused culture are essential to bolstering your server’s defenses.
In this journey towards securing your server, RedSwitches stands as a reliable partner, offering a suite of managed hosting solutions that integrate these security best practices. With us, you gain access to top-tier server environments designed with security, performance, and reliability at their core. Let us be the guardian of your digital presence, allowing you to focus on scaling your business with confidence, knowing that your server security is in expert hands.
FAQs
Q. What is a secure server?
A secure server is a server configured to protect data exchanges, using encryption to ensure that data transmitted is not intercepted or tampered with.
Q. Is SSL a secure server?
Secure Sockets Layer, or SSL, is a security protocol that encrypts data sent between a web server and a browser, thereby enhancing server security. It is not a server itself.
Q. Are dedicated servers more secure?
Because servers offer exclusive resources and control, enabling customized security measures, they may be more secure than shared hosting.
Q. What are the best practices to securing your best dedicated server?
The best practices for server security include regularly updating software, using strong passwords, implementing firewall rules, enabling DDoS protection, and restricting access to only necessary services.
Q. How can I secure affordable dedicated server hosting?
You can secure your affordable dedicated server hosting by installing security patches promptly, encrypting data in transit, setting up intrusion detection systems, and regularly auditing server logs for any suspicious activity.
Q. What are the advantages of Best dedicated servers in terms of security?
Best Dedicated servers offer enhanced security compared to shared hosting as you have full control over server settings, can install customized security measures, and reduce the risk of security threats from other users sharing the same server.
Q. What is the importance of real-time server monitoring for dedicated server security?
Real-time server monitoring is crucial for server security. It allows you to detect potential security breaches promptly, identify unusual behavior, and take immediate action to mitigate security threats.
Q. How can vulnerability scanning help in securing a dedicated server?
Vulnerability scanning can help secure a server by identifying weaknesses in the server’s configuration, software, or settings that attackers could exploit. Addressing these vulnerabilities can enhance your server’s overall security posture.