Key Takeaways
- Staking is crucial for security and governance in Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain systems.
- These are based on network security, economic considerations, and decentralization needs.
- Staking provides passive income through rewards based on the amount of cryptocurrency staked.
- Delegation allows broader participation in staking without direct node management.
- Staking involves risks like market volatility, lock-up periods, and regulatory challenges.
- The staking future looks promising, with expected innovations, increased adoption, and improved security.
- Dedicated servers, such as those from RedSwitches, enhance staking operations’ security and efficiency.
Greetings from the world of cryptocurrency staking. Even a small investment can bring large profits. Staking is an active way to contribute to the upkeep and security of blockchain networks, not merely a way to generate passive income. It might be intimidating to navigate the waters of staking regulations, though. Each cryptocurrency has its own guidelines and minimum requirements. They often leave prospective investors unsure of where to start.
This article breaks down the basics and minimum amount required for staking on different platforms. We’ll give you the info you need to explore this profitable part of cryptocurrency confidently.
Knowing these few requirements is the first step to successful Bitcoin staking. This is true no matter your experience or interest. Let’s investigate how you optimize your profits and make essential ion to the blockchain ecosystem.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Staking?
- Basic Principles of Staking
- Benefits of Staking
- Factors Influencing Minimum Amount Required For Staking
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Network Security
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Decentralization
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Economic Considerations
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Validator Performance and Network
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: User Participation Levels
- Comparison of Prices Across Popular Cryptocurrencies
- Tools and Resources For Calculating Staking Amounts
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Staking Calculators
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Cryptocurrency Wallets with Built-In Security Features
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Blockchain Explorers
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Dedicated Staking Platforms
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Community Forums and Educational Resources
- Minimum Amount Required For Staking: APIs For Developers
- Risks and Considerations
- Future of Staking
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Staking?
Credits: Freepik
Staking is a crucial idea in blockchain tech and cryptocurrencies. It’s essential in networks that use the Proof of Stake (PoS) method. PoS depends on staking for security. It aims to be more energy-efficient and accessible than the energy-intensive PoW used by networks like Bitcoin.
Staking essentially keeps a portion of cryptocurrencies locked up in a wallet to maintain a blockchain network. Participants do this to join in creating blocks and validating transactions. They are also known as validators or stakeholders. Stakeholders give up their money and risk danger. In return, they get rewards in the form of more coins or tokens. This could reduce market volatility. It encourages people to hold the currency and rewards the upkeep of the network’s security.
The idea behind the Proof of Stake (PoS) architecture says that a validator’s odds of being selected to validate transactions and create new blocks are based on the amount of cash they stake. As a result, the likelihood of being chosen as a validator increases with stake size. This system aims to keep a fair and widespread transaction verification process. It is vital to the blockchain’s strength and trust.
Staking is also very important for the governance of many blockchain networks. In addition to providing financial support for the blockchain, stakers can influence its future direction through their ability to vote on proposals that affect the network’s development and rule-setting.
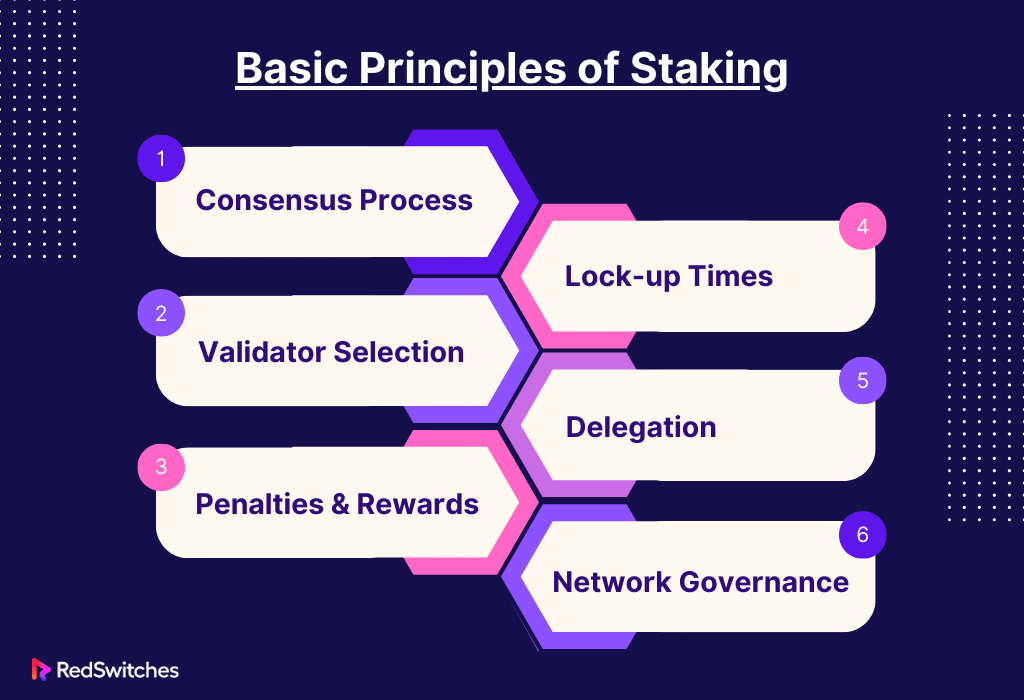
Basic Principles of Staking
In many blockchain networks, especially those that use the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus model, staking is an essential technique. Comprehending the fundamental concepts of staking is crucial for all those associated with cryptocurrency. The following are some of the fundamental ideas that support staking:
Consensus process
The PoS consensus process relies heavily on staking. Proof of Stake (PoS) selects validators according to the number of coins they pledge as stake, unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which requires miners to solve challenging mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This balances the incentives of the validators with the security and well-being of the network while also lowering the processing power and energy needed to keep it running.
Validator Selection
In proof-of-work (PoS) systems, validators are generally chosen according to the amount of coins they have staked; the more coins a validator has, the more likely they will be picked to validate transactions and build new blocks. Since validators with a more significant stake have more to lose from malicious behavior or network instability, this is believed to inspire commitment to the network’s stability.
Penalties and Rewards
In exchange for their assistance keeping the network secure, validators can receive newly minted coins or transaction fees as compensation. Validators are incentivized to act honorably and efficiently by these rewards. In contrast, proof-of-work (PoS) systems can penalize validators for dishonesty or poor performance (such as being offline), which may result in a loss of some of their staked tokens. This system of incentives and sanctions partly preserves the network’s dependability and integrity.
Also read What Is Proof of Stake?
Lock-up Times
Coins that have been staked are typically locked for a set amount of time and cannot be sold or transferred. The purpose of this lock-up time, which differs from blockchain to blockchain, is to guarantee validators’ ongoing dedication to the network’s stability. Additionally, it offers some protection from “nothing at stake” assaults, in which validators would otherwise invest in several blockchain histories to guarantee they always receive a reward.
Delegation
Coin holders who do not want to act as validators can assign their stakes to others in many Proof of Stake (PoS) systems. Delegation allows more users to participate in the staking process, even if they don’t have the means or know-how to manage a validator node. It also contributes to the more comprehensive process’s further decentralization by giving a wider range of stakeholders the authority to authenticate transactions.
Network Governance
The opportunity to influence governance choices is frequently associated with staking. Voting on ideas on protocol upgrades and governance policy changes, among other matters impacting the blockchain’s future, is available to stakeholders. Each vote has an influence that is usually correlated with the stake size of the user, so incorporating democracy into the blockchain’s functioning.
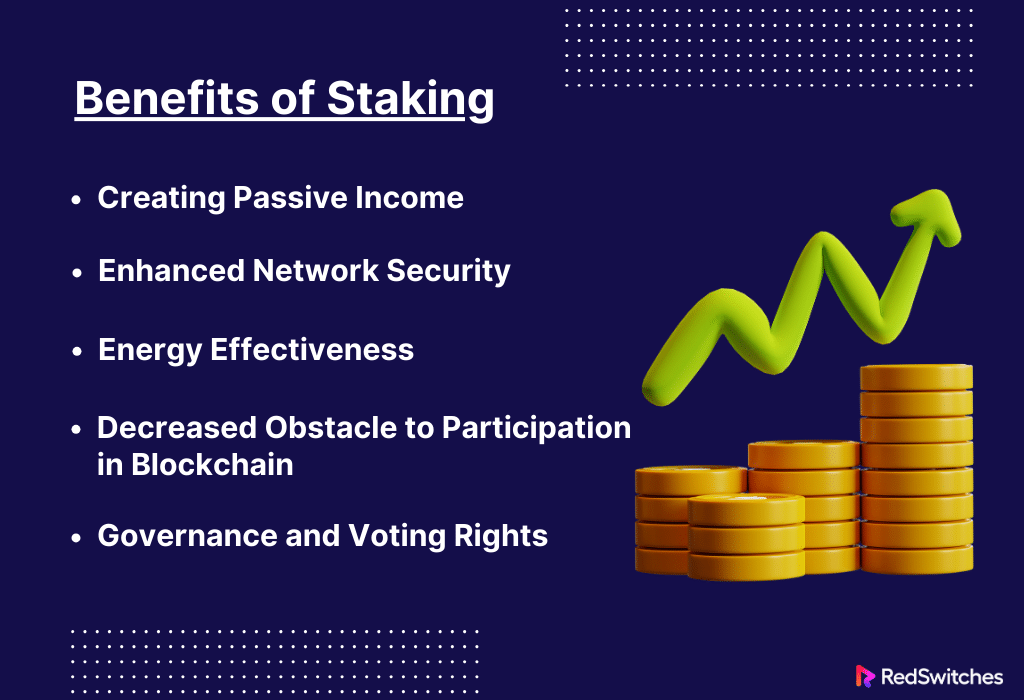
Benefits of Staking
Staking in blockchain networks has advantages. This is particularly true for those who use a Proof of Stake (PoS) paradigm. It benefits the network and its members. Here is a thorough analysis of the main advantages of staking:
Creating Passive Income
One of the most alluring advantages of staking is the potential to create passive income. Stakeholders can benefit in three ways. They can lock up coins, validate, or assign their stake to a validator. These benefits require either extra tokens or network-collected transaction fees. Yields from staking can vary greatly. This depends on the network rules, the total amount staked, and other factors. But staking usually offers a steady income over time. It is like interest on a savings account.
Enhanced Network Security
Staking helps keep the blockchain stable and secure. They have staked tokens in the network. Stakeholders in proof-of-stake (PoS) systems must maintain the network’s security. It becomes harder and more expensive for a hostile actor to obtain enough stake to undermine the network. The more tokens staked, the more secure the network.
Energy Effectiveness
Proof of Work (PoW) systems, like Bitcoin, require a lot of energy and processing capacity to mine blocks. In contrast, PoS systems use significantly less energy. PoS significantly lowers the electricity needed to run the network because it doesn’t need complex computations to mine blocks. This fits better with global concerns about energy usage and the environment.
Decreased Obstacle to Participation in Blockchain
Staking makes it easier to participate in the blockchain and governance mechanisms. Running an entire mining operation in proof-of-work (PoW) needs high technical skill and hardware. In contrast, staking can be done through a pool or wallet, making it more widely available.
Governance and Voting Rights
In many PoS networks, stakeholders get governance rights. These rights usually include voting on protocol updates, changes, and the network’s future. Allowing stakeholders to join in the decision-making process promotes a decentralized governance style. It enhances democracy and user-driven ecosystems.
Also Read: What Is the Minimum Lockup Period for Crypto Staking?
Factors Influencing Minimum Amount Required For Staking
Credits: Freepik
A variety of factors can affect the minimum amount required for staking in different blockchain networks, ensure the essential network stays decentralized, secure, and effective. While these variables differ from blockchain to blockchain, they usually consist of the following important factors:
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Network Security
It makes it cost more for validators to be wrong. The minimum stake aims to improve security. Effectively creating a financial deterrent against attacks, the network requires validators to lock up a significant proportion of tokens. Their stakes could be cut as punishment. This staking system ensures that validators have much to lose if they are dishonest. The high stakes make it costly to try any network disruption. They help balance the validators’ interests with the network’s health and security. A dedicated server must enforce high staking minimums to enhance network security, deterring validators from misconduct.
Also Read Mastering the Pillars of Blockchain: A Deep Dive into Validator Nodes and Staking
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Decentralization
The critical idea of blockchain technology is decentralization. It spreads authority across many participants. This eliminates single points of failure and control. A blockchain can set the level of decentralization. It does this by changing the minimum staking requirements. Lower minimums let more users serve as validators. This can prevent a few powerful parties from controlling the network. But very few criteria might also be dangerous. They could open the door for many small players to work together on shady projects. Establishing an ideal staking criterion is essential to preserving a safe and stable decentralized system. A dedicated server can spread authority widely by adjusting the minimum staking requirements, promoting decentralization.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Economic Considerations
A blockchain’s staking dynamics are greatly influenced by its economic structure. Key variables include the total tokens, their distribution (mining, sales, or airdrops), and the inflation rate. Networks with more tokens may have higher minimum staking requirements. This is to prevent value dilution and keep economic stability. Also, inflation might impact the return on staked assets. This could reduce the appeal of staking to possible validators. To keep a healthy balance, networks must pay validators fairly. They must also maintain the token’s value by regulating these economic aspects. Dedicated servers are crucial in managing economic stability by setting appropriate staking thresholds based on token distribution.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Validator Performance and Network
A blockchain’s ability to function correctly depends on validators performing well. High-performance standards guarantee the network’s continued speed, dependability, and security. Validators must often meet performance requirements. Staking systems set these requirements. They include minimum uptime and voting in consensus. As a sign of dedication to the position, more enormous stakes might be necessary to guarantee these requirements are fulfilled. Removing new or careless users from the network. This ensures that only the best validators handle block creation and transaction validation. Validator performance requirements, such as uptime and consensus voting, are enforced by dedicated servers to ensure network reliability.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: User Participation Levels
The level of user participation and the state of network development can impact the minimum staking requirements. Smaller or newer networks sometimes have lower staking requirements. This is to promote community development and engagement. These requirements may be raised to improve security and network performance. This will happen as the network grows and matures with more established validators. These changes make sure the network keeps evolving. It will balance resilience and openness. They will draw in a dedicated and competent set of validators.
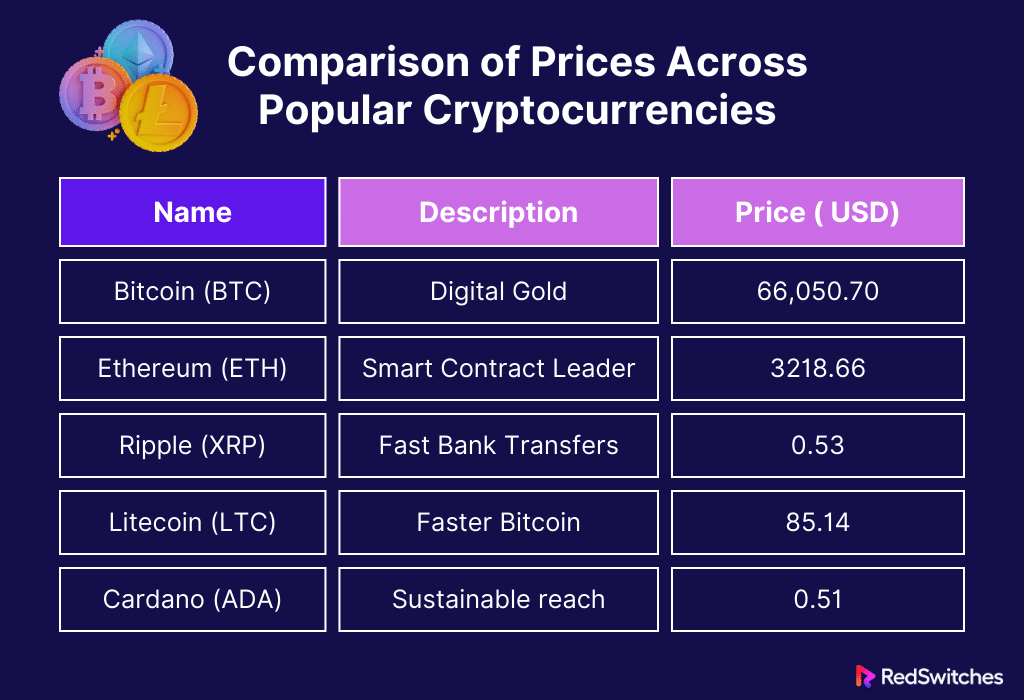
Comparison of Prices Across Popular Cryptocurrencies
Credits: Freepik
Before comparing cryptocurrency prices, learn about the most well-known cryptocurrencies in detail.
Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. It has a first-mover advantage that makes it a premium asset. Bitcoin is the digital equivalent of gold. Financial markets worldwide carefully monitor the price of Bitcoin. It is the most well-known digital currency. Its 21 million significant supply cap creates scarcity, which plays a significant role in its pricing. Institutional considerations and speculation mainly determine its price variations. Lately, its price has been influenced by the new interest from large institutional investors. They see it as a significant safe haven asset. This has made it a major part of retail and institutional portfolios.
Ethereum (ETH)
Its currency, Ether, fuels these activities. Ethereum has made itself the top for decentralized applications and smart contracts. The Ethereum development community thrives and always pushes for new ideas to broaden the platform’s use. The upgrade to Ethereum 2.0 is expected to improve the network. It will make it more scalable, less environmentally harmful, and may boost security. This will raise Ether’s market value. Ether’s market price is impacted by the growing demand for non-fungible primarily based) and decentralized finance (DeFi), based mainly on Ethereum.
Also Read How to Stake Ethereum?
Ripple (XRP)
Ripple’s XRP stands out. It is aimed at the financial sector and provides quick transactions. These are essential for international money transfers. In contrast to many other cryptocurrencies, Ripple’s value is determined more by its practical uses than by speculative trading. Relationships with large financial services firms and banks are essential to its pricing and uptake. But Ripple has also faced intense regulatory scrutiny. This has come mainly from the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). It has caused much volatility and unpredictability about Ripple’s future.
Litecoin (LTC)
With an emphasis on speedier and smaller transactions, Litecoin was intended to be the silver to Bitcoin’s gold. It can test and apply tech improvements faster than Bitcoin. This gives it a edge in cryptocurrency. For example, Litecoin was among the first to use the Lightning Network and implement the Segregated Witness (SegWit) protocol. Its acceptance by technology, as well as its perceived value as a speedier, more adaptable substitute for Bitcoin, impact its price. Litecoin is flexible and has quick transactions. These qualities may help it stay useful as cryptocurrencies gain popularity.
Cardano
Another big name in cryptocurrency is Cardano. It stands out for its dedication to sustainability and security. It also stands out for its research-driven approach. Cardano uses a scientific ethos and peer-reviewed research. Ethereum co-founders founded it. It seeks to create a very secure blockchain network. Cardano’s ADA coin is utilized within its network to make transactions and intelligent contract executions easier.
Innovations in Cardano and the broader blockchain expansion dramatically affect price. The platform’s valuation has been dramatically impacted by the incremental distribution of features, such as the smart contracts functionality included in the Albroaderupgrade, which offers increased utility and wider usage. Additionally, Cardano’s focus on environmentally sustainable operations attracts an increasing number of eco-aware investors, which could increase its demand and desirability.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
Important Note: Cryptocurrency prices are highly dynamic. These figures represent current prices and will likely change over time.
Tools and Resources For Calculating Staking Amounts
Credits: Freepik
Staking enthusiasts who are interested in investing need to know how much is the best to stake and what the possible returns are. To help with these computations, a number of tools and resources are accessible, each with unique capabilities and insights. Here’s a thorough examination of some of the most important instruments and sources for figuring out stake amounts:
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Staking Calculators
The potential returns from staking coins are often estimated using staking calculators. Users can enter the amount they want to stake and the staking reward rate. They can enter how long they want to stake and other key details. These include the network’s inflation rate. Also, the overall percentage of cryptocurrency is already staked. They can offer full projections. The projections cover the benefits and hazards of different stake amounts and times. Platforms like Staking Rewards and MyCointainer provide advanced calculators. These tools incorporate these factors into their algorithms. They help users make wise selections.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Cryptocurrency Wallets with Built-In Security Features
Staking features are integrated into the wallet software. They improve the user experience for wallets that have built-in staking. These wallets let users manage their staking right within the app, including calculating returns and starting staking transactions. They also store cryptocurrency. Stakers prefer wallets like Trust Wallet, Ledger Live, and Exodus because of their intuitive user interfaces and helpful features that simplify the staking procedure and let both novice and expert users take part in network validation efforts. By leveraging dedicated servers, cryptocurrency wallets with built-in security features provide users with a seamless and secure environment to manage staking transactions and calculate potential returns.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Blockchain Explorers
Blockchain Explorers are indispensable resources for those who wish to learn more about validator performances and staking statistics. These apps offer a clear window into the blockchain by displaying statistics on transactions, staking pools, and validator activity in real-time. Explorers like Etherscan for Ethereum, CardanoScan for Cardano, and Solscan for Solana provide comprehensive insights into the distribution of rewards, the quantity of money staked by various validators, and the general state of the staking ecosystem for users who are interested in the intricacies of staking rewards and network participation.
Also Read How To Use Blockchain as Database for Maximum Security
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Dedicated Staking Platforms
Dedicated staking platforms and pools offer specialized services for customers who want to stake their cryptocurrency but might not have enough to meet the minimum staking criteria. By combining the resources of several investors, these services create a bigger staking pool, which raises the likelihood of getting selected as a validator and earning rewards. These websites, which include Figment, Stake. Fish and Rocket Pool also provide extensive analytical tools that enable users to monitor the performance of their staked assets project returns depending on the state of the market and modify their staking plans as necessary.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: Community Forums and Educational Resources
Community Forums and Educational Resources are essential within the staking community because they provide a forum for exchanging ideas, tactics, and timely guidance. Experienced stakers who offer their knowledge and instructions on sites like Reddit’s cryptocurrency groups or BitcoinTalk can assist novices in staking. The subtleties of various staking protocols, the associated risks, and the best techniques for safeguarding and maximizing staking returns may all be understood with the help of these materials.
Minimum Amount Required For Staking: APIs For Developers
APIs for developers allow programmers and data manipulators to access more technical resources. Many blockchain initiatives offer programming interfaces (APIs) that let programmers design unique staking calculators or incorporate staking features into already-existing websites or applications. With these APIs, real-time data can be fetched straight from the blockchain, enabling exact and customized analysis of staking chances based on the network’s most recent statistics and trends.
Risks and Considerations
Credits: Freepik
Although there are many advantages to staking, there are also risks and things to keep in mind that participants should be aware of:
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies’ volatility is well-known. The principal and incentives in fiat currency are subject to significant fluctuations in the value of staked assets.
Lock-up Times: Staked funds frequently have a lock-up time that limits your ability to access and liquidate your holdings.
Slashing Risks: In certain PoS networks, validators who engage in wrongdoing or neglect the network may be subject to slashing penalties. As a result, some of the staked money may be forfeited in network security breaches or failures to validate tasks.
Technical Risks: Software and smart contracts used in staking are subject to bugs and vulnerabilities. These technical issues could lead to losses through poor processing of staking activities or outright exploitation.
Regulatory Risks: The rules governing cryptocurrencies are often changing. Changes in laws or regulations may affect the profitability or legality of staking operations, putting stakers under legal or compliance duties.
Future of Staking
Staking’s position in cryptocurrency seems bright, and as the market develops, it should see substantial change. Future staking is expected to be shaped by several significant advancements and trends in blockchain technology, including:
Growing Adoption of Proof of Stake (PoS)
The cryptocurrency community strongly pushes for a shift from energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) as environmental concerns become more widely recognized. Because Proof of Stake (PoS) uses far less energy by design, it provides a more sustainable option. With versions like Ethereum 2.0, major cryptocurrencies like Ethereum have already started the shift to Proof of Stake (PoS).
Improved Security methods
As digital assets gain in value and significance, improving PoS networks’ security methods will be essential. Subsequent staking protocols might integrate more robust, sophisticated cryptographic methods and stronger validation procedures to guarantee the network’s integrity and security. Validators can be validated using multi-factor validation procedures that use biometric information or behavioral patterns in addition to basic token ownership.
Increased Regulatory Clarity and Compliance
As staking gains popularity, international regulatory organizations will probably establish more precise rules and laws. This legislative clarification will make the staking environment more stable, attracting the attention of traditional financial institutions and institutional investors. Staking platforms must also pay close attention to compliance, which may mean implementing more advanced reporting and monitoring systems to abide by global financial standards.
Innovation in Staking Products and Services
As staking becomes popular, new innovative staking products and services may follow. Staking derivatives, staking as a service (SaaS), and pooled staking platforms are examples of financial instruments that may advance in sophistication and accessibility. These services will reduce entry barriers into staking and provide greater flexibility to both retail and institutional investors.
Decentralization and Community Governance
These two concepts will probably receive more attention as staking mechanisms develop. It will be key to empower stakeholders by giving them a bigger say in decision-making processes, from protocol improvements to governance reforms. Staking effective ecosystems will require tools and platforms that support fair and transparent governance procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anyone wishing to participate in this lucrative but intricate facet of Bitcoin investing must know the minimal amount needed for staking. In addition to providing the possibility of passive revenue, staking is essential to the security and management of blockchain networks. Every blockchain is unique, with criteria and incentive systems varying depending on user involvement, network security, and economic considerations. We have discussed the minimum amount required for staking in detail.
Those prepared to enter the staking realm can improve their experience by selecting a dependable and effective platform such as RedSwitches. We provide dedicated server solutions with the performance, security, and availability you need to keep your staking operations running smoothly. By working with us, you can ensure that your digital assets are properly managed so you can concentrate on increasing your staking profits.
FAQs
Q. What is the minimum amount required for staking?
The minimal sum, which differs for each blockchain, guarantees that users significantly contribute to the network’s efficiency and security.
Q. Is crypto staking profitable?
Staking can be successful since it offers rewards for passive income; nevertheless, profits are contingent on the state of the network and the amount staked.
Q. What are the risks of staking?
Risks include fluctuations in the market, exposure to regulatory changes, potential penalties (slashing), and loss of liquidity due to lock-up periods.
Q. What is the Minimum amount required for staking?
The minimum amount required for staking varies greatly depending on the specific cryptocurrency and the staking platform you choose.
Q. How can I start staking my crypto?
To start staking your crypto, you can use a staking service provided by a crypto exchange or stake your tokens directly through a crypto wallet that supports staking.
Q. What happens if I stake an amount below the minimum amount required for staking?
Depending on the staking platform’s rules, if you stake an amount below the minimum required, you may not be eligible to receive staking rewards or participate in staking.
Q. Can I unstake my tokens before the staking period ends?
Yes, you can usually unstake your tokens before the staking period ends, but some platforms may have restrictions or penalties for early unstaking.
Q. How do I receive staking rewards?
You can receive staking rewards by staking your crypto assets and actively participating in the staking process as a validator or delegator.
Q. What is the significance of the amount of stake in staking?
Your stake in staking determines your chances of being chosen as a validator to validate transactions and earn rewards in a proof-of-stake network.
Q. Where can I find information about staking options for a specific cryptocurrency like Ethereum or Polkadot?
You can find information about staking options for specific cryptocurrencies on their official websites, crypto exchanges that offer staking, or staking service providers.