Key Takeaways
- The answer to what is staking in legal terms is that it is the process by which individuals lock their digital currency to support the operations of a blockchain network.
- Server-based staking is a mechanism in the digital currencies domain. It involves people or entities delegating their digital currency holdings to a server known as a validator node.
- Several legal frameworks and regulations affect server-based staking. These include data protection and privacy, financial regulations, consumer protection laws, etc.
- Compliance requirements in server-based staking include tax compliance, operational compliance, reporting obligations, etc.
- Reporting and record-keeping requirements for server-based staking include transaction reporting, customer identity verification, etc.
- Risks involved in server-based staking include operational, compliance, and security risks.
- Effective mitigation strategies can be implemented to tackle the risks in server-based staking.
Did you know that the cryptocurrency market faced significant challenges in 2023? During this time, global regulators intensified their scrutiny of digital assets. Among those affected was Binance. The cryptocurrency exchange encountered a significant setback after agreeing to a USD 4 billion settlement with U.S. regulatory bodies. This marked one of the largest corporate fines in US history.
With increasing regulatory pressure and the continuous evolution of laws governing the crypto sphere, understanding the compliance and legal considerations involved is more important than ever. This blog will help you navigate the complex legal domain of server-based staking and discuss what is staking in legal terms.
Let’s get started!
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Staking in Legal Terms?
- Understanding Server-Based Staking
- Common Legal Frameworks and Regulations Affecting Server-Based Staking
- Jurisdiction-Specific Regulations in Server-based Staking
- Other Compliance Requirements in Server-based Staking
- Licensing Requirements for Operating Staking Services
- Risk Management in Server-based Staking
- How Staking Platforms Can Prepare for Future Compliance Challenges?
- Conclusion – What is Staking in Legal Terms
- FAQs
What is Staking in Legal Terms?
Credits: FreePik
So, “what is Staking In legal terms?” Staking within the context of blockchain and digital currency refers to the process by which individuals lock their digital currency to support the operations of a blockchain network. Here’s a clearer breakdown of the process involved:
- Participation
Staking requires individuals to commit cryptocurrency tokens to a blockchain network. This step contributes to the network’s security and operational efficiency. Stakeholders are often compensated with extra tokens or fees gained from transaction processing. - Supporting Network Integrity
Staking tokens contributes to the Proof of Stake consensus process. This helps maintain network integrity. This approach is crucial for confirming transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. It helps achieve this without requiring considerable computing labor. This is also evident in systems such as Proof of Work (PoW).
Now that we have gone over what is staking in legal terms, let’s discuss server-based staking in detail.
Understanding Server-Based Staking
Credits: FreePik
Server-based staking is a mechanism in the digital currencies domain. It involves people or entities delegating their digital currency holdings to a server known as a validator node.
Staking depends on validators to verify transactions and generate new blocks. Server-based staking involves validators running specialized software on powerful servers to keep the network safe. These servers are also known as staking nodes. They require a solid infrastructure to operate reliably. Validators are encouraged to operate honestly and in the network’s best interests. They receive incentives in the form of extra cryptocurrency tokens for verifying transactions.
Individuals can earn rewards without requiring expensive hardware or technical skills by delegating their cryptocurrency holdings to a trustworthy validator via server-based staking. However, conducting thorough research and picking reliable validators is necessary. Doing so helps reduce the danger of potential loss or security breaches.
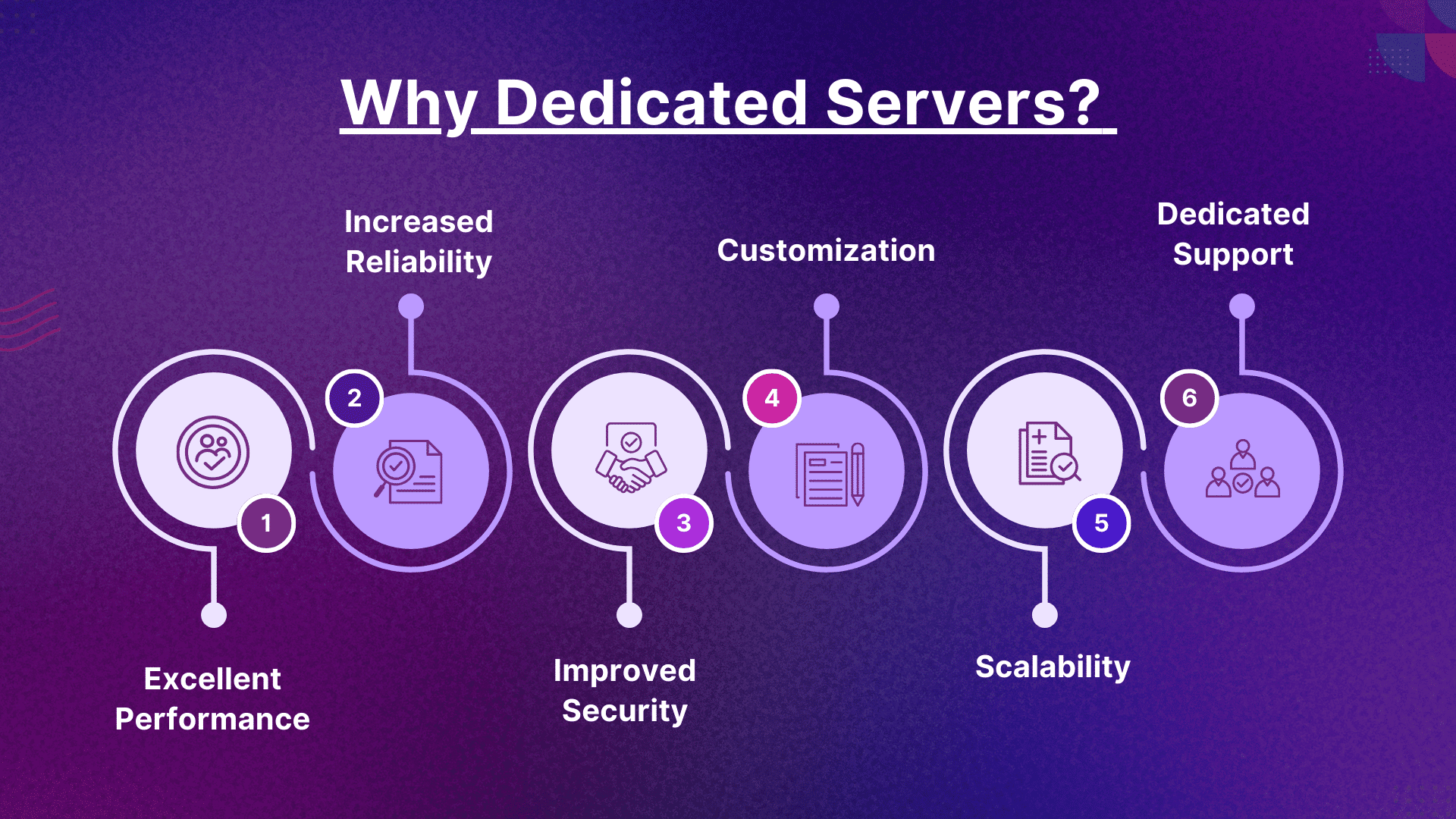
Why Dedicated Servers?
Dedicated servers are usually recommended for server-based staking. Here are a few reasons why:
- Excellent Performance: Dedicated servers offer exclusive access to computing resources. They ensure consistent and quality performance for staking operations.
- Increased Reliability: Dedicated servers lower the risk of resource contention from other users. They reduce downtime and boost uptime.
- Improved Security: Dedicated servers offer increased control of security. They protect staking data from unauthorized access or interference.
- Customization: Users can alter software/hardware configurations to fit their blockchain network’s demands.
- Scalability: Dedicated servers can conveniently scale with the evolving demands of staking operations. This ensures you can accommodate increased transaction volumes and network activity.
- Dedicated Support: Many dedicated server providers offer dedicated support services. They ensure quick problem-solving and assistance for staking-related issues.
Also Read: The Connection: Dedicated Servers In Crypto Staking.
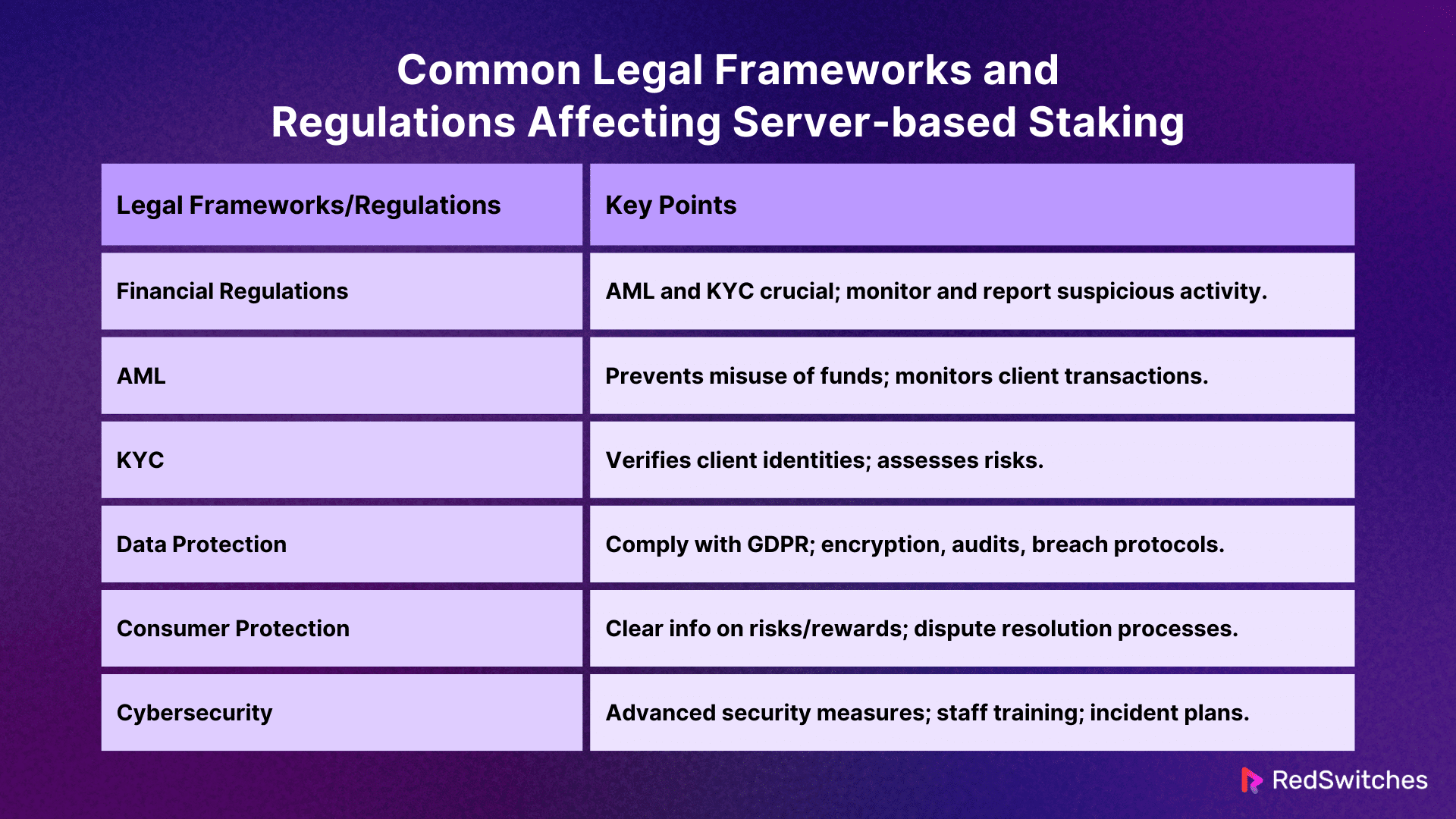
Common Legal Frameworks and Regulations Affecting Server-Based Staking
Here are a few important legal frameworks and regulations anyone engaging in server-based staking must know:
Financial Regulations
Financial monitoring is especially critical in server-based staking. This is because staking and financial services are closely related. Financial regulations include compliance with AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer). These involve finding and validating clients’ identities. It also includes monitoring transactions to find and report suspicious behaviors as soon as they occur. Here is more information on these regulatory frameworks:
AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
AML is a set of regulations and processes stopping individuals and companies from misrepresenting unlawfully obtained funds as legitimate revenue. These rules compel banking institutions and regulated businesses to track client transactions. This helps them:
- Detect suspicious behavior.
- Report large transactions.
- Take precautions to avoid helping or profiting from financial crimes.
These steps are critical in the battle against corruption, drug trafficking, and other organized crime.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
KYC is a part of AML. It involves verifying clients’ identities and determining their eligibility. It also involves assessing the potential risks of criminal intent in the business connection. The KYC process includes gathering and confirming personal information like:
- Addresses.
- Names.
- Date of birth.
KYC rules are critical for banks, insurance firms, and other financial institutions. They assure proper service use and fraud prevention.
These frameworks are critical in reducing the use of finance systems for terrorist funding or money laundering. Financial regulatory authorities across different jurisdictions implement these limits. They demand staking service providers to submit reports and audits to ensure compliance.
Several countries may also require staking platforms to maintain a specified capital reserve. This helps them ensure financial stability and protect consumer assets.
Data Protection and Privacy
Due to their nature as digital platforms, server-based staking operations manage large personal data volumes. This requires compliance with data protection requirements like the GDPR. These rules specify how personal data should be:
- Gathered.
- Handled.
- Protected from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data controllers must implement protections, including:
- Encryption.
- Regular security audits.
- Breach notification protocols.
Individuals’ right to access, correct, or delete personal data must be supported. This ensures their privacy and offers added control over their information.
Also Read: Guide To Types Of Crypto Staking: Risks, And Platforms 2024.
Consumer Protection
Consumer protection regulations guarantee that participants in staking platforms are informed about the services they use. This involves providing accurate and detailed information about:
- Potential risks.
- Terms and services.
- Rewards.
These regulations aim to protect customers against misleading activities. They provide settlement in the event of a disagreement. Regulators may require staking platforms to follow fair contractual procedures and have processes for resolving complaints and arbitration.
Cybersecurity
Credits: FreePik
There has been an increased focus on cybersecurity in the last decade due to the increasing risks of running online financial services like staking. Infrastructure protection involves adopting advanced security solutions and following network security best practices, such as frequent upgrades and vulnerability checks.
Cybersecurity legislation could require service providers to have plans for responding to incidents. They may also make it mandatory for providers to offer periodic safety instructions to their staff to lower the risks of internal threats and external attacks.
Do you want to learn how crypto staking works? Read our in-depth piece, ‘Stake Crypto And Earn! Dive Into Crypto Staking Basics.’
Jurisdiction-Specific Regulations in Server-based Staking
The regulations surrounding server-based crypto staking can vary depending on jurisdiction to jurisdiction. Here is information on the different regulations surrounding server-based staking based on different jurisdictions:
United States
The US presents a complex regulatory environment for crypto staking due to the interplay of federal and state-level laws. Key areas to consider include:
Securities Laws
The SEC researches cryptocurrency-related activity to see if they may be classed as securities transactions by the Howey test. This test determines if an agreement includes an investment of funds in a joint venture with a reasonable expectation of gains from the efforts of others.
State Laws
Regulations can also differ by state, adding another degree of complication. For example, New York’s BitLicense establishes a legal framework that is especially geared to digital currency activities in the state, affecting firms who engage in staking.
European Union
The EU is moving towards a more harmonized regulatory approach to crypto assets, but the landscape remains complex, with both overarching regulations and country-specific nuances. Here are the key areas to consider:
MiCA Regulations
The MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) laws are part of the EU’s larger effort to create a consistent legal framework for digital assets. This includes strict criteria for accountability, openness, and consumer protection in crypto-asset transactions.
Data Protection
GDPR requires that any company, including staking platforms, that handles EU individuals’ data have strong levels of data protection. This includes:
- Obtaining consent for data processing.
- Permitting data deletion.
- Facilitating data transfer.
All of these substantially impact how platforms manage personal data.
Asia
Asia presents a highly diverse regulatory landscape for crypto staking, with approaches ranging from strictly restrictive to innovation-friendly. Here’s a general overview:
Varied Regulatory Landscape
Digital currency regulation methods in Asia differ greatly between countries. For example, South Korea has unique legislation governing the operation of blockchain and crypto-related businesses. The country maintains a strong emphasis on user safety and market stability.
Innovation-Friendly Frameworks
Singapore is noted for regulatory innovation. It provides a favorable environment for blockchain technology under the Payment Services Act. This act establishes the standards for payment service providers, including those involved in digital payments and cryptocurrencies. It requires them to operate within a regulated framework that supports growth while maintaining system security and consumer safety.
Also Read: Crypto Rewards: How Long Does Crypto Staking Take?
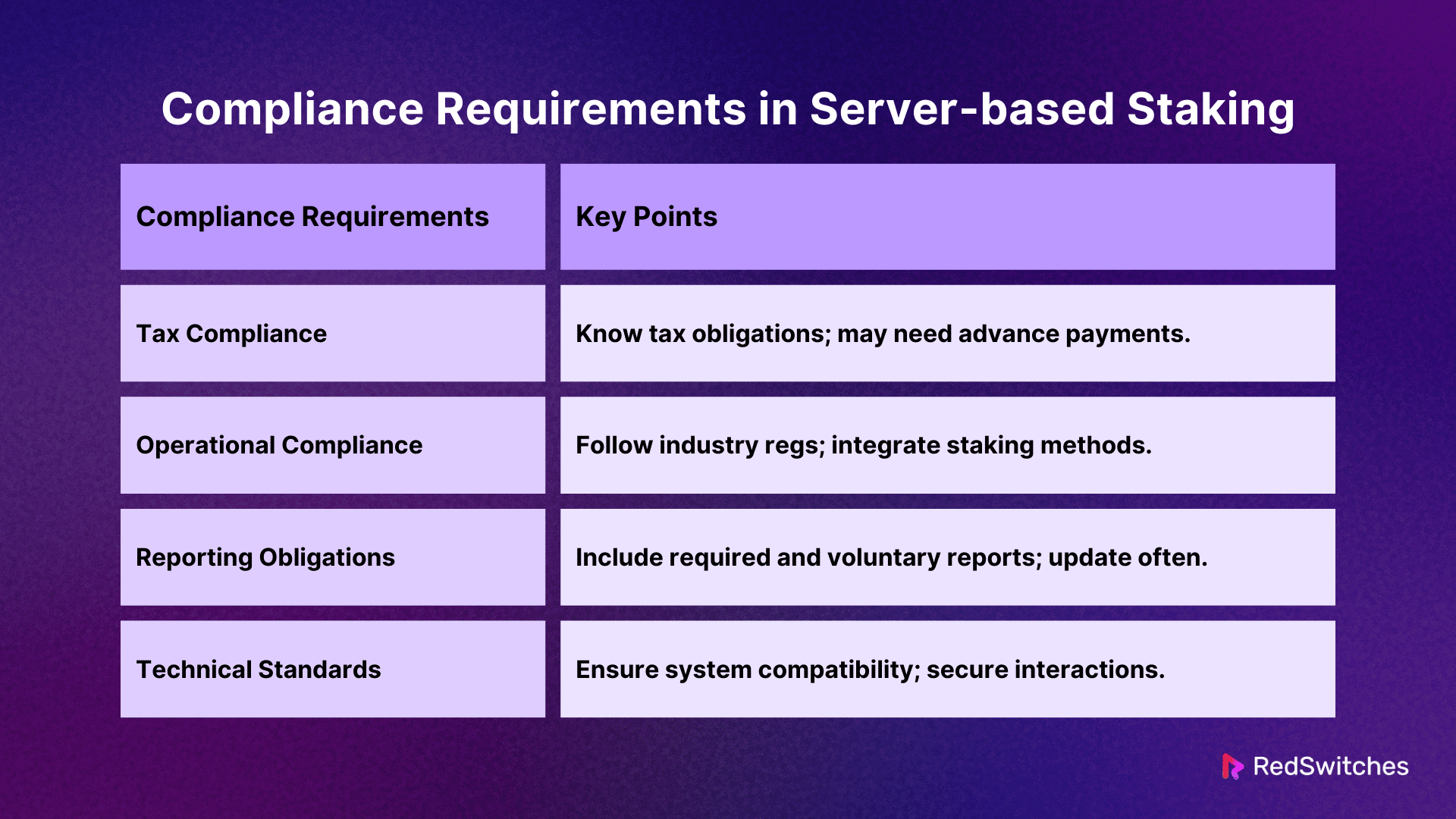
Other Compliance Requirements in Server-based Staking
Wondering what are the compliances for crypto staking? Here is detailed information on compliance requirements in server-based staking:
Tax Compliance
The taxation of staking incentives is an important problem that varies from country to country. Stakers must know their tax obligations, including reporting staking incentives as investment returns or income.
Tax rates and filing procedures might also vary greatly. In some situations, stakeholders may need to make recurring advance tax payments according to expected earnings. The inability to follow tax regulations may result in fines, interest on unpaid taxes, and legal action.
Operational Compliance
Operational compliance for server-based staking also demands businesses follow certain industry regulations. This may involve integrating with blockchain systems that allow multiple staking methods.
Compliance with electronic contract standards and ensuring these agreements are reviewed by credible third parties to minimize maliciously exploitable flaws are key components of operational integrity.
Reporting Obligations
Effective reporting must include both what is required by regulatory agencies and any other voluntary declarations of transparency. This could include:
- Management changes.
- Frequent security audits.
- System updates.
- Operational practices that may affect stakeholders.
Some regions may mandate more frequent reporting during severe volatility or market hardship. This is done to maintain compliance and financial stability.
Technical Standards
Compliance with technical guidelines also ensures compatibility among various systems and technologies. Platforms should protect their systems for server-based staking and ensure secure interactions with:
- Blockchains.
- Wallets.
- Third-party services.
This is especially critical for avoiding loss due to transfer failures or compatibility concerns.
Licensing Requirements for Operating Staking Services
Many jurisdictions require proving their ability to protect assets against fraud and hackers before they offer permits to operate with digital assets. This may involve:
- Proving the strength of security procedures and cryptographic protections.
- Physical safety precautions for servers and other key infrastructure.
Compliance with international standards, like ISO/IEC 2700, may also be necessary to acquire or renew a license.
Are you confused about the difference between crypto staking and mining? Read our informative blog, ‘Understanding Key Differences: Staking Vs Mining, ‘ to clear up all confusion.
Reporting and Record-keeping Requirements for Server-based Staking
Here is a list of the important reporting and record-keeping requirements that businesses or individuals involved in server-based staking must follow:
Transaction Reporting
Staking platforms must track and flag suspicious transactions. This covers noteworthy transactions that may hint toward money laundering or other illegal conduct. The criteria for what makes a reportable transaction vary by jurisdiction.
However, they often include transactions that exceed certain limits. They may also include transactions that do not correspond to the customer’s regular pattern of behavior.
Customer Identity Verification
Credits: FreePik
According to the KYC requirements, staking platforms must gather and verify in-depth customer information. This includes:
- Complete name and address.
- Nationality.
- DOB (Date of birth).
- Proof of address (bank statement, utility bill).
- Photographic identification (passport, driving license).
The purpose is to identify individuals and evaluate their risk profiles.
Record-keeping
Staking services are required to maintain precise customer data records and financial transactions. This includes:
- Records of all financial transactions (withdrawals, deposits, rewards, fees).
- System logs and user activities.
- Copies of all interactions with customers.
- Documentation of all completed AML and KYC checks.
Businesses must keep these records for several years, depending on local requirements. The average is between five and ten years.
Compliance Audits
Regular audits are necessary to guarantee that the staking platform meets all regulatory standards. These audits might be performed internally, by third-party auditors, or by external regulators. The frequency and extent of these audits are determined by the legal framework under which the platform is operating.
Risk Management in Server-based Staking
Risk management in server-based staking is integral to ensuring staking operations’ stability. Effective risk management strategies help reduce the chance of losses and maintain the integrity of the staking process. Here are a few risks involved in server-based staking and their mitigation strategies:
Security Risks
Security is the main concern in server-based staking. This includes the risk of cyber-attacks, like hacking or phishing, that target the servers where the digital currencies are staked. Proper security measures should be implemented to defend these servers against unauthorized access.
Mitigation Measures
Here are a few mitigation measures for security risks involved in server-based staking:
Advanced Security Protocols
Security protocols to improve the security framework include:
- Next-generation firewalls.
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
- Sophisticated encryption techniques.
Encryption should extend to data at rest and in transit to ensure comprehensive data protection.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
Periodic security audits help manage vulnerabilities before individuals with malicious intent exploit them. Compliance checks ensure that the staking services follow regulations and industry standards, helping improve security posture.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Strict Access Controls
Implementing MFA is a great way to reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access. Strict access controls ensure that only authorized personnel access critical systems depending on the least privilege principle.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employees should receive regular training on the latest security risks and best practices. The best way to mitigate insider risks is by:
- Phishing schemes.
- The significance of safe passwords.
- How to recognize unwanted access attempts.
Operational Risks
These involve the servers’ day-to-day operation risks, including technical failures, software bugs, or human error. Ensuring that the server hardware is robust and the software is updated and maintained is essential to mitigating these risks.
Mitigation Measures
Here are a few mitigation measures for operational risks involved in server-based staking:
Comprehensive Training Programs
It is essential to ensure that IT professionals are competent and regularly instructed on the most recent technology and security standards. Training programs keep your staff up-to-date on industry standards and practices. They allow for faster detection and resolution of server security and performance issues.
Regular Software Testing and Updates
Create a procedure for testing and upgrading all software components to reduce the likelihood of errors. This includes:
- Operating system.
- Blockchain software.
- Key programs that operate on the servers.
Automated testing technologies may spot potential problems before they create system disruptions. They help keep the staking process safe and efficient.
Disaster Recovery Plans
Credits: FreePik
It is important to have a well-documented DRP (disaster recovery plan). This strategy should detail ways to resume operations after significant occurrences like natural calamities. The DRP should be assessed and modified as needed, helping address emerging risks or shifts in the operational environment.
Compliance Risks
As discussed above, staking providers must follow regulations like anti-money laundering (AML). Failure to comply can result in legal troubles and fines. Thankfully, there are strategies available to mitigate these compliance risks.
Mitigation Measures
Here are a few mitigation measures for compliance risks involved in server-based staking:
Regulatory Compliance
Stocking suppliers must keep up with new regulatory regulations to reduce compliance concerns. They must grasp existing and upcoming regulations influencing digital currency and staking activity. Consulting with legal experts and regulatory agencies can offer insights on compliance issues.
Technological Solutions
Using technology can also help reduce compliance concerns. Automated solutions enable real-time monitoring of transactions to spot and report questionable activity. Advanced software solutions can help keep the detailed records necessary for compliance. This makes audit procedures more efficient and less prone to human mistakes.
Auditing and Reporting
Regular audits help ensure that all processes comply with regulatory standards. Audits can be undertaken internally by the company’s compliance staff or externally by independent auditors.
Clear reporting methods are also critical to retaining confidence with authorities and stakeholders. Regular reporting aids in showing compliance and developing a reputation for honesty and dependability.
Also Read: Infrastructure Requirements For Crypto Staking In 2024.
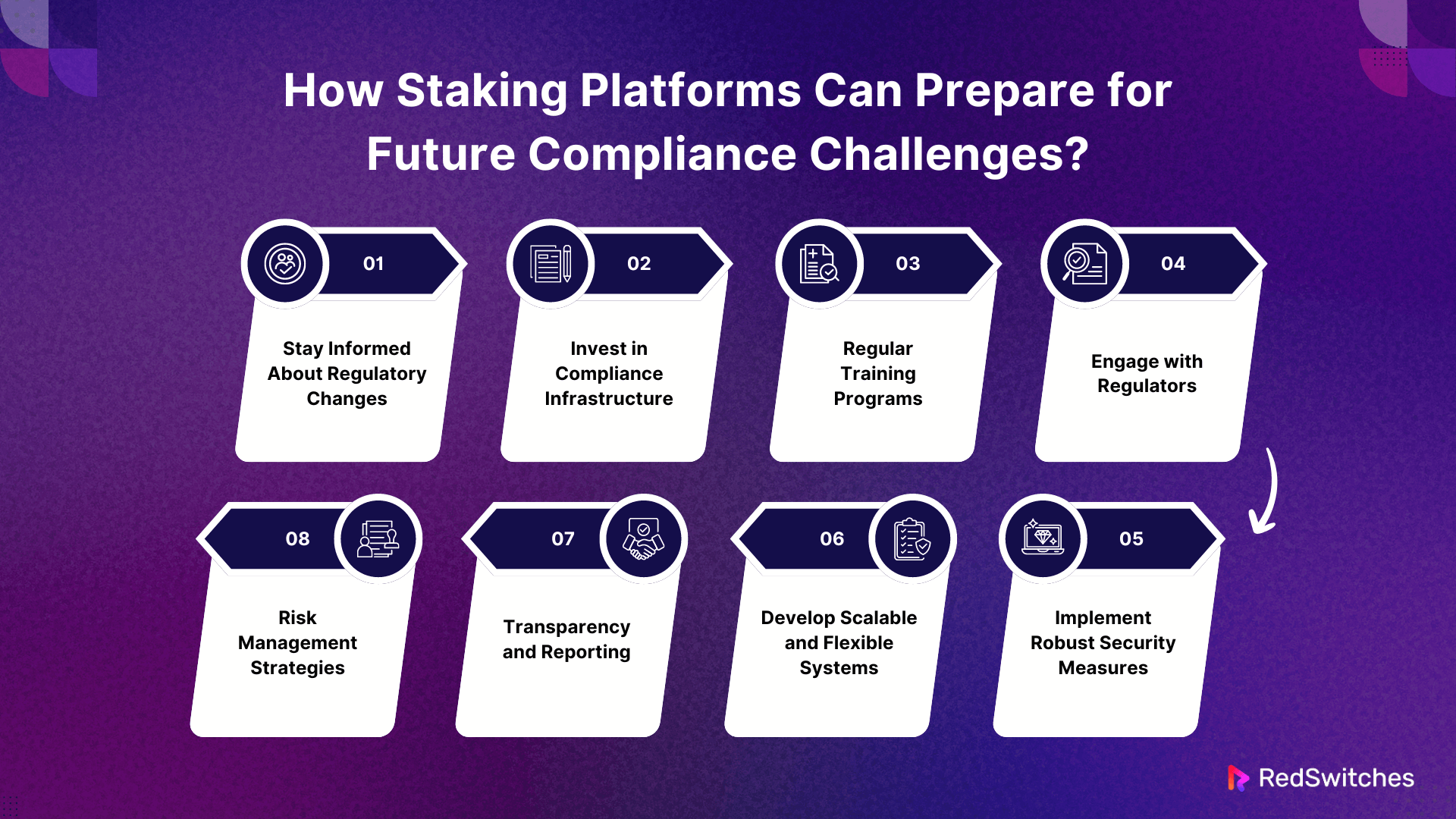
How Staking Platforms Can Prepare for Future Compliance Challenges?
Staking platforms can plan for future compliance difficulties with some proactive actions. Preparing for changing rules demands flexibility and a commitment to maintaining high compliance and security standards. Here’s how they can accomplish it:
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
Keep track of legal changes in all areas where the platform operates. This can be achieved by:
- Receiving information from financial regulatory organizations.
- Joining industry groups.
- Engaging in blockchain governance forums.
Invest in Compliance Infrastructure
Create or improve internal compliance departments or collaborate with external experts in the cryptocurrency industry’s legal and regulatory compliance. This involves using technological solutions to automate compliance procedures.
Regular Training Programs
Credits: FreePik
Provide continual employee training on current compliance processes and best practices. This ensures that the team knows the importance of compliance and is up to speed on managing regulatory needs efficiently.
Engage with Regulators
Actively interact with regulatory bodies. This might include participating in discussions and consultations on new rules. Such interactions can help shape a regulatory environment that fosters innovation and follows compliance standards.
Implement Robust Security Measures
Compliance also requires protecting consumers’ funds and data. Therefore, investing in cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions is critical. Regular security audits and changes to security policies can help defend against vulnerabilities and increase user and authority confidence.
Develop Scalable and Flexible Systems
Ensure that systems and procedures are scalable and adaptable enough to meet new regulatory needs rapidly. This includes modular solutions that allow for the easy integration of more compliance features. These solutions help achieve this without affecting existing processes.
Transparency and Reporting
Provide clear information on stakeholder actions and finances to maintain a transparent organization. Regular reporting helps:
- Meet regulatory obligations.
- Foster confidence among stakeholders.
- Promote a reputation for dependability and honesty.
Risk Management Strategies
Implement thorough risk management measures to mitigate any compliance issues. This includes detecting, analyzing, and minimizing risks associated with regulatory changes.
Conclusion – What is Staking in Legal Terms
Understanding What is Staking in Legal Terms? Complying with the compliance and legal considerations for server-based crypto staking can take time and effort. This task is even more challenging for those new to this domain. We recommend partnering with a reliable and compliant hosting provider like RedSwitches.
RedSwitches offers dedicated hosted servers tailored to the needs of blockchain applications. We help ensure your staking activities are profitable and meet all legal requirements.
Want to learn more about what is staking in legal terms and how we can support your staking ventures? Contact us today. Partnering with us will help you maximize your investment potential while ensuring compliance.
FAQs
Q. What is the legal definition of staking?
The answer to what is staking in legal terms is that it is the process of holding digital currency in a digital wallet to sustain the operations of a blockchain network. This participation is essential for validating transactions and securing the network. It often delivers incentives for the stakeholders.
Q. What is a staking requirement?
A staking requirement is the minimum quantity of digital currency to be kept in a wallet. This requirement must be met to participate in the blockchain network’s staking process. It guarantees that participants are vested in the network’s security and performance.
Q. What are staking protocols?
Staking protocols are the rules governing the staking process within a blockchain network. They define how transactions are validated, how rewards are distributed, and the penalties for malicious activities by participants. They are essential for maintaining the network’s security and efficiency.
Q. What are cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies are digital assets designed to work as a medium of exchange. They use cryptography to secure transactions, control the creation of more units, and verify the transfer of assets.
Q. How can I earn passive income with cryptocurrencies?
You can earn passive income by staking your crypto assets. Staking involves locking your crypto assets in a wallet to support a blockchain network’s operation and earn rewards.
Q. What is Ethereum and how does it relate to staking?
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows for creating and running smart contracts and decentralized applications. It helps achieve this without downtime, fraud, control, or interference from a third party. With the shift to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, Ethereum will introduce staking.
Q. Can you explain the concept of proof of stake?
Proof of stake is a consensus mechanism where the creator of the next block is chosen through different combinations of random selection and wealth or age. This system aims to achieve distributed consensus and secure a blockchain network.
Q. How does staking work and what are the risks associated with it?
Staking involves actively participating in transaction validation on a proof-of-stake blockchain network. The risks of staking crypto include the potential loss of funds due to vulnerabilities in the network or cyber-attacks.
Q. What are the benefits of staking crypto?
Some benefits of staking crypto include earning passive income through rewards and participating in securing the blockchain network. Staking crypto also allows stakers to contribute to the decentralization of the crypto ecosystem.
Q. How can I stake my crypto assets and where can I do it?
You can stake your crypto assets through staking pools or staking contracts offered by various crypto exchanges.
Q. What is staking reward?
When you offer staking, you can earn staking reward by participating in staking activities within a crypto wallet. By staking your staked tokens on platforms like Solana and Cardano, you may receive rewards in the form of additional crypto assets.
Q. How does staking differ from proof-of-work?
Staking is a way to validate transactions on a blockchain network without using the energy-intensive proof-of-work consensus mechanisms. Validators in a staking network slash their staked assets if they act maliciously, ensuring network security.
Q. What is staking in the context of cryptocurrency?
Staking is also known as staking cryptocurrency. It refers to the act of holding digital assets in a crypto wallet to support the network’s operations. Validators use staking to secure the network, validate transactions, and earn rewards.
Q. How is the legal treatment of staking handled?
The legal treatment of staking varies by jurisdiction and current legal regulations. Understanding how authorities view staking is essential to complying with related laws.
Q. What are some use cases for staking?
Staking is a versatile concept in the blockchain space. Besides securing networks, it also provides staking services and allows the staking of various assets.
Q. How does staking benefit the validator’s role?
Staking provides validators with incentives to perform their duties honestly. By staking their own tokens as collateral, validators have a financial interest in maintaining the network’s integrity and receiving incentives.