Key Takeaways
- With managed hosting, you can concentrate on your business and content by contracting with a provider to handle your servers.
- Managed hosting has three main parts. They are proactive server care, security upgrades, and technical help.
- There are several types of managed hosting. These include managed WordPress hosting, cloud hosting, and dedicated server hosting.
- Managed hosting has benefits: convenience, professional support, and increased security. But, it has drawbacks too. These could include higher expenses and less control.
- Users that use unmanaged hosting must separately manage security, configurations, and server maintenance.
- With unmanaged hosting, users have full control. They can install software, set server options, and customize it.
- While uncontrolled hosting necessitates complete user interaction, managed hosting offers hands-off provider support.
- To decide between managed and unmanaged hosting, consider aspects like skill, money, and time.
Today’s digital world demands the right hosting for your website. It’s as crucial as the content you present. Managed and unmanaged hosting are two key options. Each serves different needs and expertise levels. This guide is comprehensive. It will cover the pros, cons, and features of both. It will highlight 10 key differences to help you make an informed choice.
Why does this matter to you? Managing hosting could be your go-to choice if you value time and ease over control. It offers a hassle-free experience with expert support. But, if you have the skills and want control over your hosting, unmanaged hosting may be for you.
Understanding managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting is key. It helps you align your hosting with your website’s needs. It also matches your technical capabilities. Let’s uncover which hosting solution fits your unique digital footprint.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Managed Hosting?
- Key Features of Managed Hosting
- Types of Managed Hosting
- Pros and Cons of Managed Hosting
- What is Unmanaged Hosting?
- Key Features of Unmanaged Hosting
- Types of Unmanaged Hosting
- Pros and Cons of Unmanaged Hosting
- Key Differences: Managed Hosting vs Unmanaged Hosting
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Managed and Unmanaged Hosting
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Managed Hosting?
Credits: Freepik
Managed hosting is a web server hosting model. In it, a single customer leases servers and related hardware. They lease from a service provider. The provider then maintains the systems for the customer.
Customers can rent hardware in this model. It includes operating systems, system software, storage, network resources, and dedicated server. Each set of equipment serves only one client. In single-tenancy architecture, the client is a “tenant.” They often have admin access to their leased systems. But, they usually prefer to use a web interface.
With this setup, the host takes care of many admin duties. It frees website owners to focus on their content and business. They can avoid learning the complexities of server management.
One essential component of managed hosting is dedicated servers. This ensures that one client exclusively uses the rented equipment. This hosting is single-tenant. It allows for a more tailored and well-managed environment.
Key Features of Managed Hosting
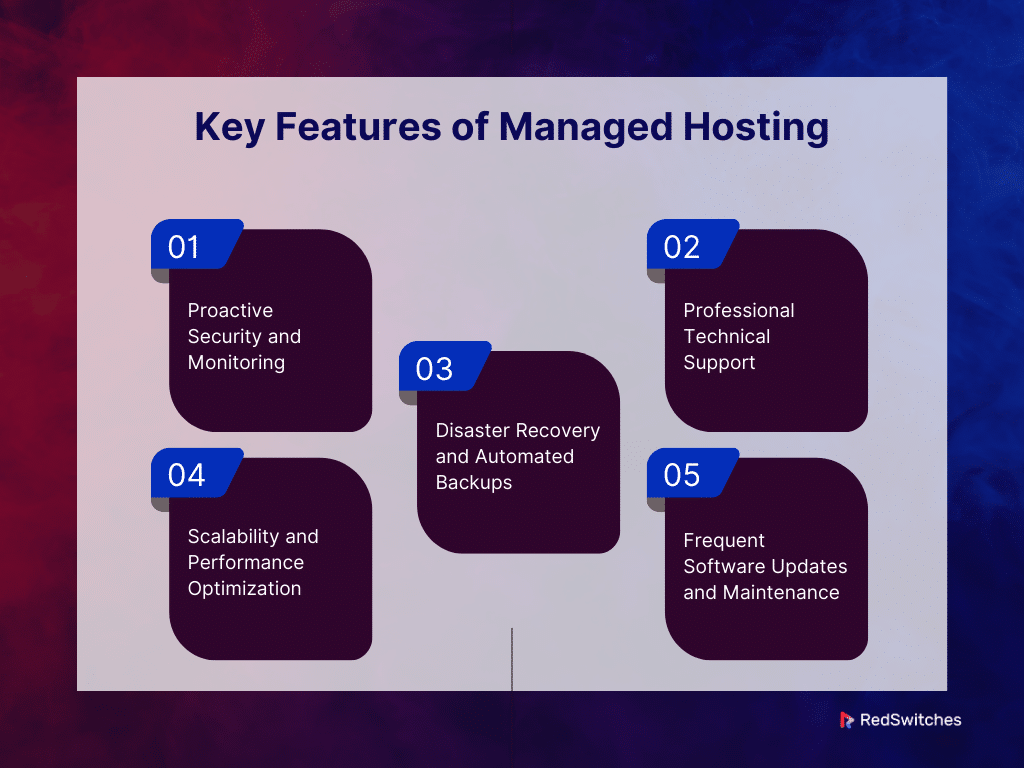
Managed Hosting gives businesses a streamlined and efficient solution. It meets their web hosting needs. It offers a range of services managed by the hosting provider. Now, let’s understand the key features of managed hosting.
Proactive Security and Monitoring
Managed hosting services often include strong monitoring systems. The systems track server performance, security risks, and possible problems. Providers use high-security methods. They use them to protect websites and data from attacks. The methods include firewalls, virus scans, and intrusion detection. This preventative measure guarantees a stable and safe hosting environment.
Professional Technical Support
Having a dedicated support staff is one of managed hosting’s best qualities. Customers gain from the experience of experts who can quickly resolve technological issues. The support staff is vital for keeping a website operating well. They handle server problems, aid with software, and give advice on optimization.
Disaster Recovery and Automated Backups
Managed hosting services often come with automated backup options. They ensure that the website’s data gets reliable and consistent backups. The backups are done automatically, without humans. These backups can be promptly restored in case of data loss or system failure. This function is vital when used with disaster recovery plans. It gives data an extra layer of security.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
Proactive steps are taken by managed hosting companies to maximize server performance. This could entail installing caching methods, optimizing software, and adjusting server configurations. Also, managed hosting packages often include scalability features. These features let websites quickly handle rising traffic and resource needs without downtime.
Frequent Software Updates and Maintenance
Keeping the operating system, applications, and server software current is essential. It is important for security and efficiency. Patching and updating these components regularly is the responsibility of managed hosting services. Managed hosting keeps customers safe and reliable. It does this by staying up-to-date with the latest software releases. It also gets the latest security fixes.
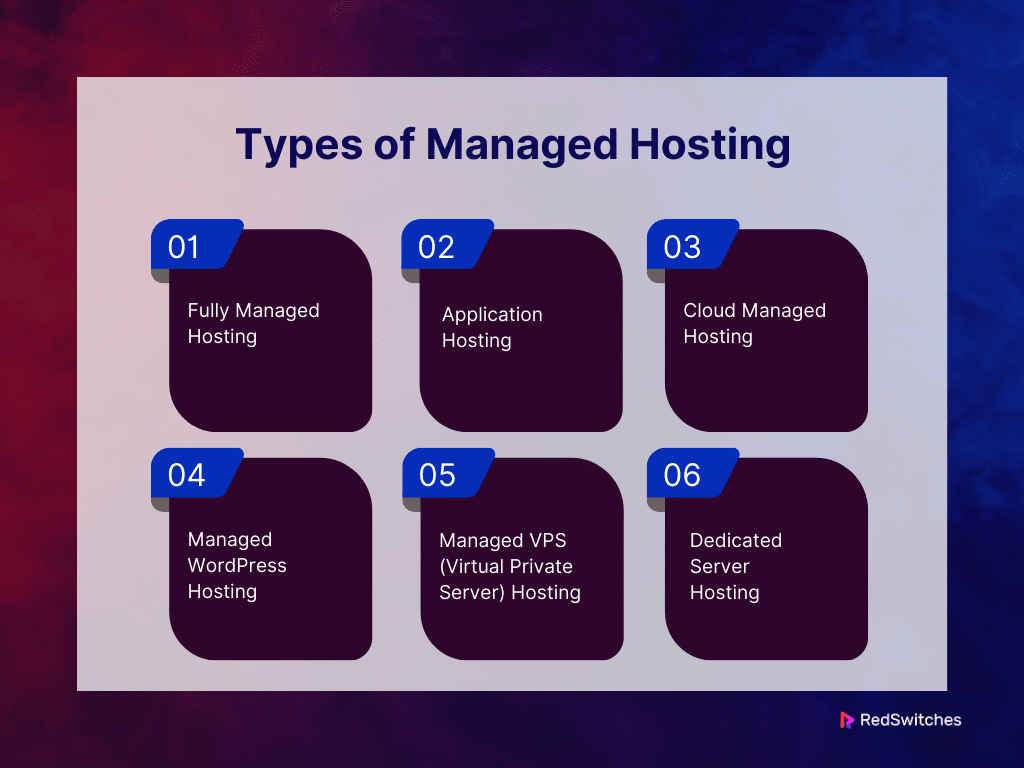
Types of Managed Hosting
Managed hosting involves a service provider. Taking care of the hardware, software, and technical services required to run websites or applications. The client essentially leases the equipment and gets support from the hosting provider. There are various types of managed hosting, each tailored to different needs and scales.
After discussing the features, let’s understand the types of managed hosting.
Fully Managed Hosting
This all-inclusive managed hosting involves the provider handling all aspects of server management. They handle configuration, setup, security, monitoring, upkeep, and tech support. Clients can focus on their website and business goals. They are not involved in day-to-day operations.
Application Hosting
It is called application-specific hosting. It is managed hosting tailored to the specific needs of individual software applications. This category includes e-commerce platforms like Magento. It also includes content management systems (CMS) like WordPress and other specialized software. To ensure the app runs smoothly, the host optimizes the server.
Cloud Managed Hosting
Cloud-managed hosting offers scalability, flexibility, and reliability by utilizing cloud infrastructure. Providers manage the cloud infrastructure. They guarantee that clients can add or remove resources. Businesses looking for a cheaper option may find this managed hosting helpful. It can also scale well. It’s also great for those with varying workloads.
Check out this article to learn in detail what Google Cloud is.
Managed WordPress Hosting
This hosting is designed for WordPress websites. It is enhanced for WordPress security and performance. Providers frequently provide automatic updates, frequent backups, and expert assistance for WordPress-related problems. It is a great option for people and companies. They rely heavily on the WordPress content management system.
Managed VPS (Virtual Private Server) Hosting
A virtualized piece of a server is assigned to clients. This happens in a managed VPS hosting environment. The hosting provider controls the virtual server’s management. This includes keeping up the hardware and security and providing technical assistance. This is for websites with moderate to high traffic. It gives more control than shared hosting.
Dedicated Server Hosting
Clients that use dedicated server hosting can rent an entire physical server. The hosting company manages all parts of server administration. They ensure peak functionality, safety, and upkeep. Websites or apps need more performance and dedicated resources. They can benefit from dedicated server hosting.
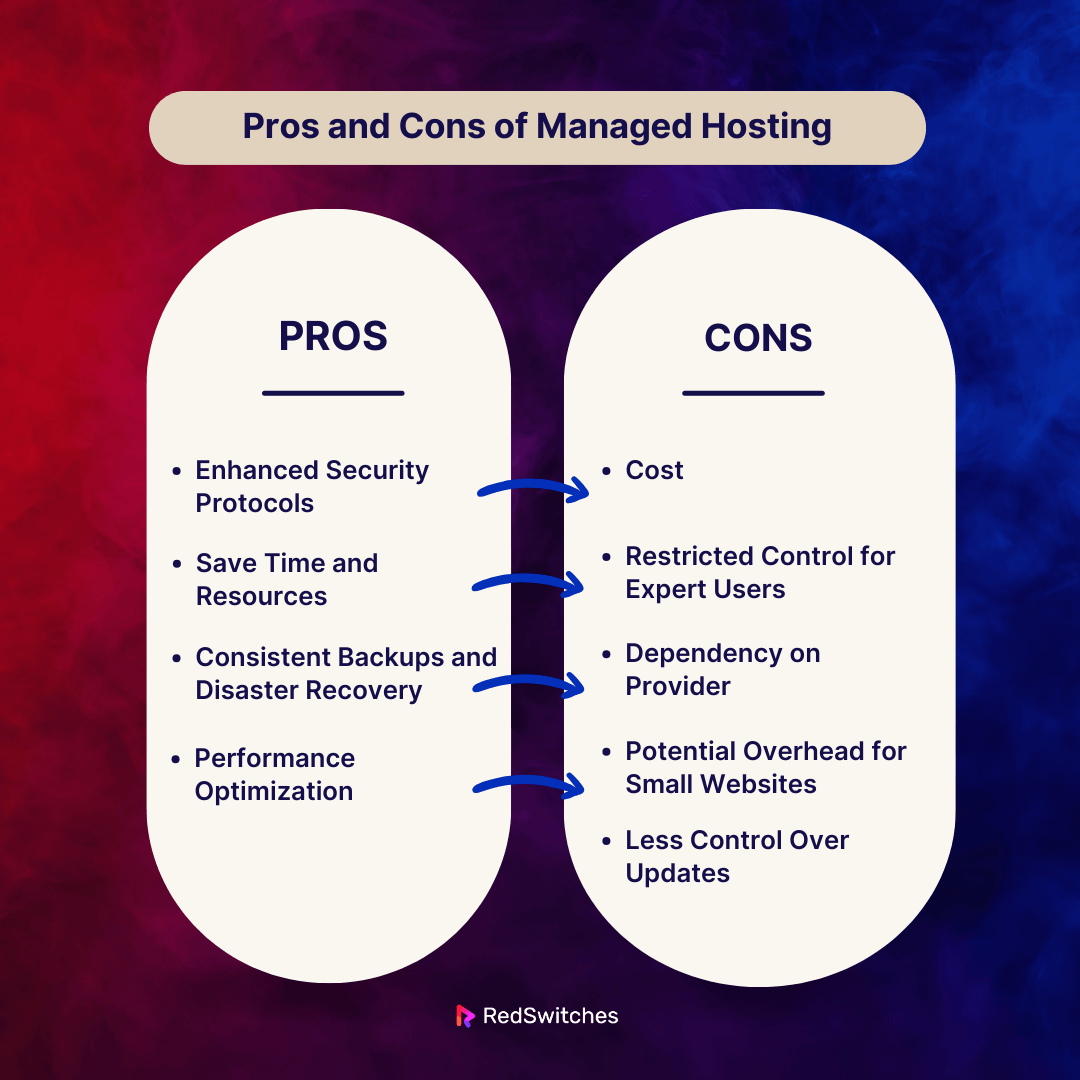
Pros and Cons of Managed Hosting
Credits: Freepik
Managed hosting is a service where the hosting provider handles the setup, administration, management, and support of a server or servers and their associated infrastructure. Here are the pros and cons of choosing managed hosting:
Pros
Enhanced Security Protocols
These services often include strong security features. They have intrusion detection, virus scanning, and firewalls. By watching for and guarding against threats, providers lower the chance of breaches.
Save Time and Resources
When the host handles server management, clients save time and resources. They would otherwise be used for routine maintenance, upgrades, and troubleshooting. This enables companies and people to concentrate more on their primary goals.
Consistent Backups and Disaster Recovery
Automated backup solutions ensure regular website data backups. They are commonly included with managed hosting. These backups can be promptly restored in the case of data loss or system failure, which adds to the dependability of a disaster recovery plan.
Performance Optimization
Managed hosting companies use caching, software optimization, and server configuration changes. They do this to improve performance. This enhances the responsiveness and speed of the website.
Cons
Cost
Managed hosting includes more services and support from the hosting company. So, it is usually more expensive than unmanaged hosting. This expense may be a barrier for people on a limited budget or small businesses.
Restricted Control for Expert Users
Managed hosting may not be ideal for tech-savvy users. They want more control over their server settings. Unmanaged hosting can better fit those who need more freedom. They can customize and configure their technology to their specific needs.
Dependency on Provider
Managed hosting customers rely on the hosting company for some server administration services. This dependency could be hard if there are problems with the provider. Or, if clients want to make custom setups outside the managed services’ scope.
Potential Overhead for Small Websites
Managed hosting offers many services. They could be seen as overkill for tiny, low-traffic websites with simple needs. The extra features and support might not be used fully in these cases. So, unmanaged hosting might be a more affordable option.
Less Control Over Updates
Managed hosting companies handle updates often. But, some customers might want more say over when and how updates are applied. The scheduled updates of managed hosting are automated. They could not match specific business needs or preferences.
What is Unmanaged Hosting?
Credits: Freepik
Unmanaged hosting is a web hosting service. It lets customers control their server’s technical and administration parts. It is also known as self-managed or bare-metal hosting.
The client handles the rest of the server management in this hosting model. The service provider provides the server, network access, and the first OS installation.
Clients who use an unmanaged hosting environment have full control over their servers. They can install software. They can adjust settings and add security to fit their needs. This level of control will especially interest advanced users. It will also interest system administrators and companies with technical needs. They want to operate their server architecture directly.
Unmanaged hosting is like dedicated servers. Clients usually lease a complete physical server. This exclusivity guarantees that the client’s requirements get the only attention from the server.
When used with unmanaged hosting, dedicated servers give the user total control over the server. They are the best option for users who want the highest level of customization and direct management.
Here’s our ultimate guide to Linux list users, and it covers essential commands and techniques.
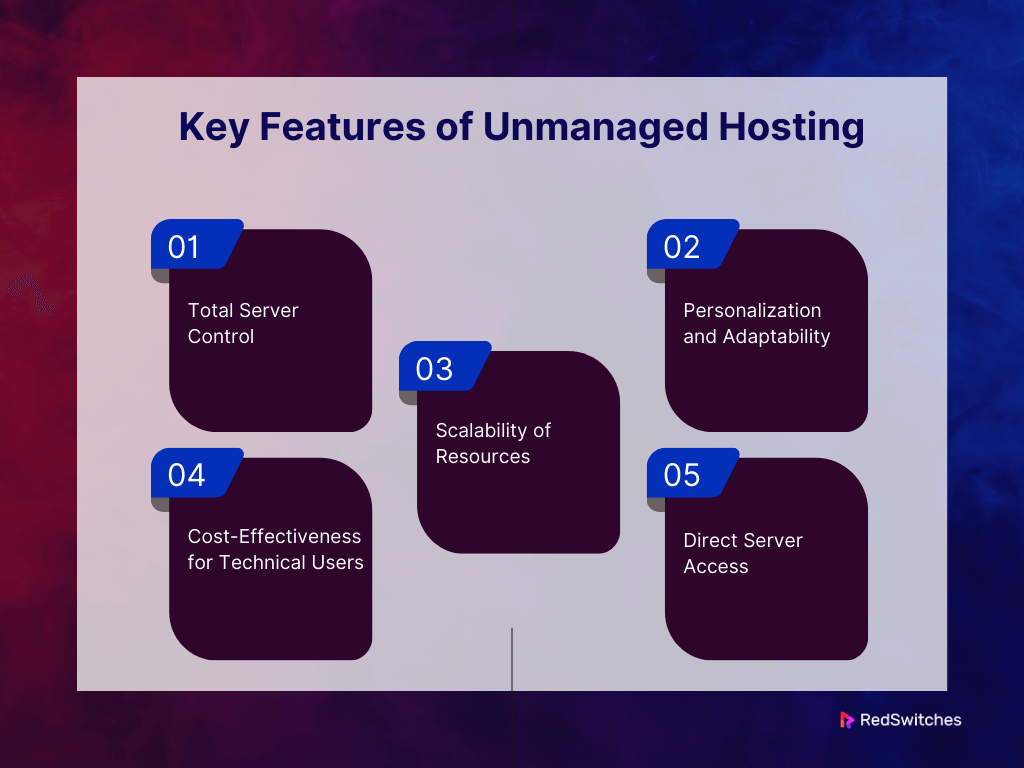
Key Features of Unmanaged Hosting
Unmanaged hosting, often chosen by tech-savvy users who want complete control over their server environment, comes with distinctive features:
Total Server Control
Clients using unmanaged hosting have total command over their server setup. Users are free to set up the server, install and alter applications, and control every operating system element to suit their needs.
Personalization and Adaptability
Unmanaged hosting customers benefit from unmatched personalization and adaptability. Users can pick the operating system, software stack, and settings they need. Businesses have specific tech needs. Advanced users will find this flexibility fitting.
Scalability of Resources
Unmanaged hosting frequently makes scaling resources like CPU, RAM, and storage simple. Users can modify these resources in response to changing needs. This makes them good for websites or apps with different traffic or resource needs.
Cost-Effectiveness for Technical Users
Unmanaged hosting is a budget-friendly choice for those with strong technical skills. It’s cheaper because clients handle server management themselves. They save money on fully managed services.
Direct Server Access
The file system and configuration files on an unmanaged server are directly accessible. This much access is essential for customers. They need it to boost performance, make precise server-level changes, or fix issues directly. They should not have to depend on help.
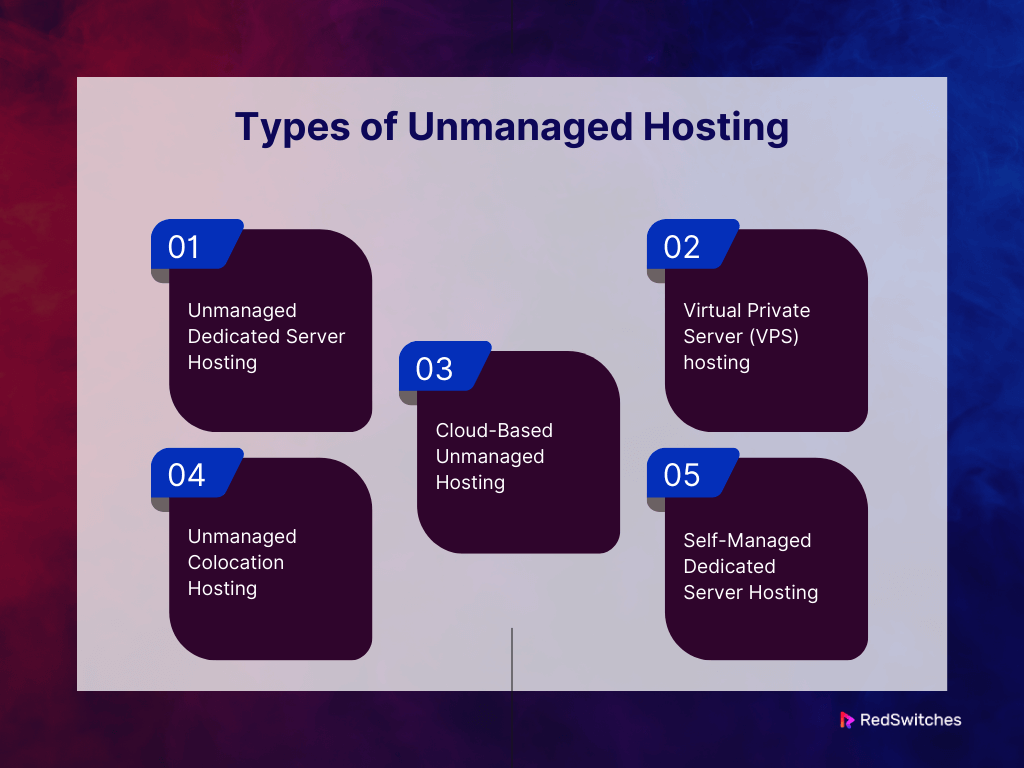
Types of Unmanaged Hosting
Unmanaged hosting, in contrast to managed hosting, provides minimal support and services from the hosting provider. The client is responsible for managing, maintaining, and securing their server. Types of unmanaged hosting include:
Unmanaged Dedicated Server Hosting
This type of hosting gives customers total control over a physical server. They oversee all aspects of server management. This includes software installs, hardware upkeep, security setups, and continuous maintenance.
Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting
Unmanaged Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting gives clients access to a virtualized server. It offers more control than shared hosting. However, clients must manage the server. This includes tasks like installing software, updating security, and boosting performance.
Cloud-Based Unmanaged Hosting
Cloud-based unmanaged hosting lets users use cloud infrastructure. They use it to set up and control virtual servers in a cloud. Customers can set and manage server resources. They can do this as needed because they have full control over their cloud servers.
Unmanaged Colocation Hosting
In colocation hosting, users house their physical servers in a data center that the hosting business provides. Users own the hardware. But, they must operate the server. This includes security, upgrades, and maintenance.
Self-Managed Dedicated Server Hosting
This kind of hosting is like unmanaged server hosting. Customers rent a whole physical server and maintain it on their own. Users are in charge of every facet of server administration and have total control over server configurations.
Credits: Freepik
Pros and Cons of Unmanaged Hosting
Before moving towards the ultimate managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate, we will review the pros and cons of unmanaged hosting.
Pros
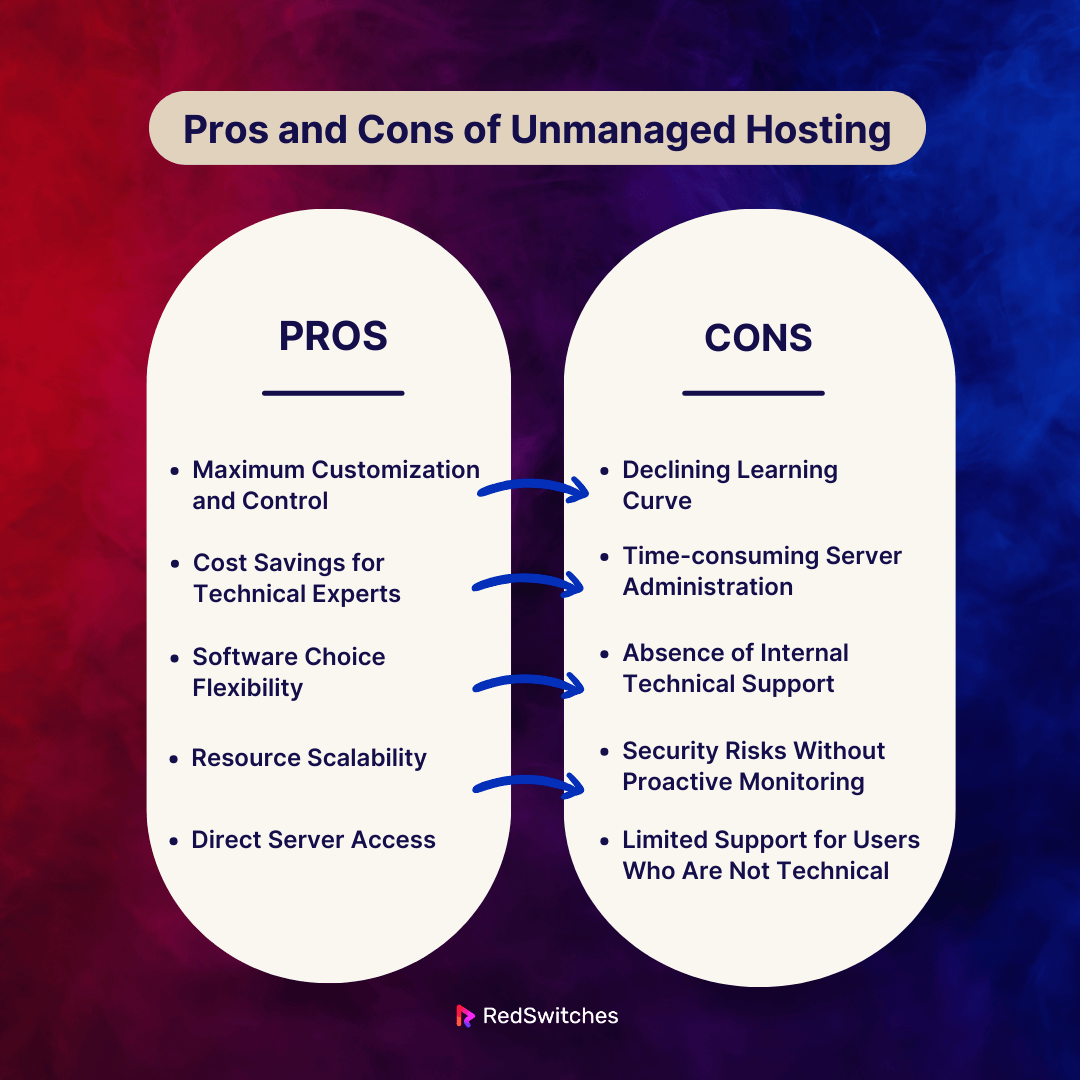
Maximum Customization and Control
Users who choose unmanaged hosting have full control. They can install programs, configure servers, and make customizations. Businesses have special technical requirements. Advanced users would benefit greatly from this level of autonomy.
Cost Savings for Technical Experts
Unmanaged hosting can be more affordable for individuals possessing extensive technical expertise. Since clients handle most of the server work themselves, they don’t have to pay for full-service management.
Software Choice Flexibility
Users using unmanaged hosting can pick the operating system, software stack, and other components. This flexibility is vital. It is for people who need specific software for their websites or applications.
Resource Scalability
Users may quickly adjust CPU, RAM, and storage capacity in response to shifting needs. Unmanaged hosting is for websites or apps. They have varying traffic volumes and resource needs. This is due to its scalability.
Direct Server Access
Direct access to the file system and server configuration files is possible with unmanaged hosting. This access level is needed for users who need to actively fix problems, improve performance, or make server-level changes.
Cons
Declining Learning Curve
Unmanaged hosting necessitates a high degree of technical know-how. Users must have strong technical skills. They need these skills in server administration, security, and troubleshooting. But, these skills may be hard for people without such a background.
Time-consuming Server Administration
The clients handle all server administration tasks. These include upgrades, security setups, and troubleshooting. This can take a lot of time, and users will have to put in a lot of work on continuous upkeep.
Let’s explore the difference between data privacy vs data security.
Absence of Internal Technical Support
Unmanaged hosting doesn’t come with the technical support you get in managed hosting. Users have to handle any issues themselves or seek help elsewhere, which can be challenging for complex problems.
Security Risks Without Proactive Monitoring
Users using unmanaged hosting must maintain security measures. They must keep them current. Without proactive monitoring and support, security flaws are more likely to occur. This is especially true when users lack knowledge of security best practices.
Limited Support for Users Who Are Not Technical
Users without technical experience should not utilize unmanaged hosting. Without support staff to help with server management, non-technical users could find it hard to use and fix problems.
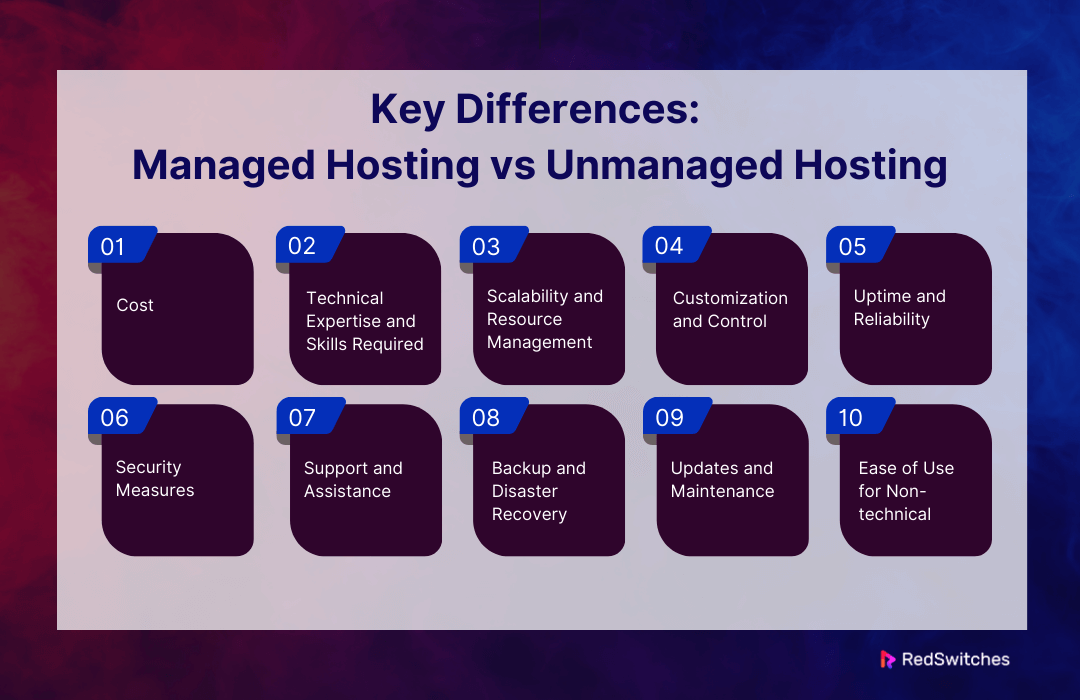
Key Differences: Managed Hosting vs Unmanaged Hosting
Managed hosting and unmanaged hosting differ significantly in the level of service and responsibility assumed by the provider and the client. Here are the key differences, we will discuss the core part of our blog i.e. managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting, in detail.
1. Cost
In the first section of the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate, we will compare the cost of both.
Managed Hosting
Generally speaking, managed hosting is more expensive upfront than unmanaged hosting. This is because managed hosting companies provide many services. These include: regular maintenance, skilled support, security monitoring, and server setup.
The higher cost of the premium service is justified by the convenience of having a team of experts manage the server daily. This lets clients focus their time and resources on their primary business operations.
Unmanaged Hosting
Unmanaged hosting is cheaper. It’s known for this. It’s especially so for those with technical skill. Clients can save money upfront by running their servers themselves. They avoid paying for the extra services managed hosting offers.
It’s very tempting for people good at server management. Unmanaged hosting lets them personalize their server. They don’t need continuous help from a professional.
2. Technical Expertise and Skills Required
This section is about managed hosting vs. unmanaged hosting. It will cover the comparison of technical expertise and skill.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting exists to serve users. They have different levels of technical skill. Its main benefit is that it lessens the clients’ technical burden considerably.
Users may manage their hosting without needing server skills. They have access to a support team. The hosting company handles routine maintenance, security monitoring, server setup, and configuration.
Unmanaged Hosting
Users requiring unmanaged hosting must possess greater technical proficiency. Clients are responsible for all server maintenance under this hosting model. This includes software installations, server setup, security, upgrades, and troubleshooting.
Users need to know using command-line interfaces. They also need to manage servers and understand their chosen operating system and software stack.
3. Scalability and Resource Management
In this section of the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate, we will compare Scalability and Resource Management.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting services often have great scalability. They can support the growth of websites and apps. Hosting companies usually offer tiered plans. These plans have set resource amounts. They make it easy to upgrade or downgrade in response to changing user needs. Managed hosting includes CPU, RAM, and storage. It also includes load balancing and traffic management.
Unmanaged Hosting
Unmanaged hosting is highly flexible. It lets customers adjust and expand their resources based on their needs.
However, users are entirely in charge of managing scalability. With root access, users can control server settings. They can install needed applications, adjust resources, and boost server performance.
4. Customization and Control
Now, let’s compare the customization and control for the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting argument.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting provides many services and support options. But, it has specific limits on management and customization. Usually, the hosting provider configures the server environment. They do this to meet general requirements and security standards. Limits are in place to protect the stability and security of the server system. Even so, users can customize parts of their hosting.
Unmanaged Hosting
Unmanaged hosting stands out for its high level of control and customization. Users have almost complete freedom over the hosting setup. They can install programs, set up the server, and more. With root access, users can tailor the server to their needs. They can choose their preferred software stacks, operating systems, and configurations.
5. Uptime and Reliability
We will now focus on the uptime and reliability of both concerning the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting argument.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting providers often prioritize uptime and dependability. These are part of their essential services. Hosting companies invest in great infrastructure. They also invest in redundant systems and fancy tools. They do this to guarantee ideal server performance. The support staff is committed. They keep a close eye on server health, respond fast to problems, and take action to reduce downtime.
Unmanaged Hosting
In unmanaged hosting, uptime, and dependability depend on the user. They must monitor and manage the server well. Users can personalize their server. But, they must also put in place reliable settings, do regular maintenance, and quickly resolve any problems.
Credits: Freepik
6. Security Measures
Security is crucial for any organization. Let’s compare it in the managed vs. unmanaged hosting debate.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting services provide strong security. They protect client data and server architecture well. Typically, hosting companies use a thorough security approach. It includes firewalls, proactive monitoring, intrusion detection, and virus screening.
Being proactive lowers the chance of breaches. It finds and contains risks before they get worse. They keep up with recent security trends and flaws. This helps the committed security teams at managed hosting companies. They ensure the hosting environment is safe from new threats.
Unmanaged Hosting
Users are solely responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures using unmanaged hosting. Clients have full control over security in an unmanaged hosting environment. They can tailor settings to meet their unique needs. However, users must also follow security best practices. These practices safeguard their server infrastructure due to this autonomy.
Also, explore these essential server monitoring tools that every system administrator should know.
7. Support and Assistance
How about support and assistance? Let’s compare both in the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting battle.
Managed Hosting
Hosting companies’ committed support and help is one of the main benefits of managed hosting. Clients that use managed hosting have access to a qualified support staff. The staff handles many parts of server administration.
Help with server configuration, debugging, and technical issues is included in this support. Customers can contact managed hosting companies anytime for help. They offer 24/7 customer support.
Unmanaged Hosting
But, unmanaged hosting has no built-in help or support from the hosting company. Users manage every part of server administration in an unmanaged hosting environment. This includes setup, configuration, and problem-solving.
They often lack access to a dedicated support team for continuous help. Some hosting providers offer basic support for hardware or network issues.
8. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Let’s compare the backup and disaster recovery for both concerning our managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting providers often offer strong backup and disaster recovery options. They use automated systems to regularly save copies of website data, understanding the importance of data safety. Backups are done at set times. They ensure there’s always a recent, reliable copy of the data. This is in case of data loss, accidental deletions, or system failures.
Unmanaged Hosting
Users alone must set up and keep backups in unmanaged hosting. They must also handle disaster recovery. Certain hosts may offer basic backups. But, users must set up and manage the backups. This is to ensure that backups are made regularly. Users must create and stick to reliable backups. They are fully responsible for how often the backups work.
9. Updates and Maintenance
Now, Let’s focus on the Updates and Maintenance concerning the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting argument.
Managed Hosting
Managed hosting services let clients maintain server security and up-to-date easily. They can do this without worrying about upgrades or maintenance.
The hosting companies often handle tasks like installing software updates and security patches. They also oversee the upkeep of the server system. The support teams are committed. They ensure the server is secure, optimized, and meets recent industry standards.
Unmanaged Hosting
Users are responsible for updates and maintenance in unmanaged hosting setups. This involves keeping the server’s operating system up to date. It also involves adding security updates and updating software. This level of control allows more customization. But, users need more technical skill.
10. Ease of Use for Non-technical Users
Now, let’s focus on the Ease of Use for Non-technical Users aspects in the debate between managed and unmanaged hosting.
Managed Hosting
Because of its incredibly user-friendly design, managed hosting is the best option for people who are not technical. Hosts in managed hosting models handle most server maintenance. They highly value simplicity and usability. This covers regular maintenance, security monitoring, server setup, and configuration.
Unmanaged Hosting
Although unmanaged hosting gives you much control, non-technical people may find operating difficult. Users must install security measures. They also configure the server and do regular maintenance. This is in an unmanaged hosting environment.
You may need a good grasp of server management and technical know-how to reach this level. This might be a hurdle for non-technical people.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Managed and Unmanaged Hosting
Credits: Freepik
After discussing the core topic of the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate, we will understand certain factors before choosing any.
We will discuss the core of the managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting debate. Then, we will understand some factors to consider before choosing either.
Technical Ability
Managed Hosting: Perfect for users with limited technology experience. Managed hosting companies manage server setup. They also handle upkeep and troubleshooting. This lets customers concentrate on their main business.
Unmanaged Hosting: Best suited for knowledgeable users or companies with in-house tech support. Users must handle all technical aspects alone. But, they have full control over server settings.
Costs
Managed Hosting: Because of the extra services and support, this type of hosting usually has a higher initial fee. Businesses that value expert management and convenience may justify this expense.
Unmanaged hosting is usually cheaper. It’s a good option for anyone who wants to cut costs and is comfortable maintaining their servers.
Server Management Duties
Managed Hosting: Providers handle monthly server maintenance. This includes backups, security, and updates. Users assign these tasks to the support staff of the hosting company.
Unmanaged Hosting puts users in charge of servers. They must do backups, set up security, and do upgrades. Although it requires active user participation, this option gives the user more power.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between managed and unmanaged hosting depends on evaluating each person’s needs. It also depends on their skills and goals. We examined each hosting model’s definitions, salient features, and advantages and disadvantages.
The ten key differences highlight the balance. They pit the independence of unmanaged hosting against the convenience of managed services. Consider your technical skills and budget. Also, consider your need for customization and desired support level when choosing.
Managed hosting offers a complete solution. It is for individuals seeking professionally managed, hassle-free hosting. However, unmanaged hosting offers great control for those with strong technical skills.
Notably, key factors in this decision-making process include security, scalability, and ease of use. Redswitches dedicated servers could offer the best of both worlds. They are a smooth transition to a dedicated infrastructure with the control of unmanaged hosting. The dependability and help of a reputable provider support this.
FAQs
Q. Managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting: What is the difference between both?
Managed hosting is a more complete and hands-off option. Unmanaged hosting usually only offers server space. Managed hosting also includes extra services like server management, security, and support. Here, the web host handles all the technical aspects of running a website. Unmanaged hosting requires the website owner to handle all the technical aspects themselves.
Q. Should I choose managed or unmanaged VPS hosting?
Unmanaged VPS hosting is reasonably priced if you have technical know-how and hands-on management. Choose managed VPS hosting if you want pro-management. It is easy to use and has support. You don’t need much tech knowledge.
Q. Who needs VPS hosting?
VPS hosting is for companies or people with busy websites. It does not need a dedicated server. But, it needs more resources and customization than shared hosting.
Q. Managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting: What are the key differences between both?
The main differences include control level, tech support, security, server management, and cost.
Q. What is managed hosting?
Managed hosting is a hosting plan. The web host provides full support. It also takes care of server maintenance and security.
Q. What is unmanaged hosting?
Unmanaged hosting is a hosting option. The website owner is responsible for all server maintenance, security, and management tasks.
Q. Which type of hosting plan is suitable for beginners?
For beginners, managed hosting is recommended. It offers more help in managing hosting’s technical parts.
Q. Managed Hosting vs Unmanaged Hosting: What are the benefits of managed hosting compared to unmanaged hosting?
Managed hosting usually has better support, security, and ease of use. It is a preferred choice for many website owners over unmanaged hosting.
Q. Managed Hosting vs Unmanaged Hosting: Is unmanaged hosting cheaper than managed hosting?
Yes, unmanaged hosting is cheaper than managed hosting. The website owner must manage the server, which cuts the web host’s cost.
Q. What is the difference between managed VPS and unmanaged VPS?
Managed VPS hosting includes support and server management by the web host. Unmanaged VPS hosting requires the website owner to handle all server tasks.
Q. What factors should I consider when choosing between managed hosting vs unmanaged hosting?
Consider your expertise, budget, and needed control. Use these to choose between managed and unmanaged hosting. Also, think about the specific needs of your website.