The conflict between data security and privacy is a significant issue in today’s digital world, where we live online. Our private and sensitive information becomes the battlefield where data security—the safeguards against breaches and unauthorized access—and data privacy—the preservation of our data’s confidentiality—confront as we navigate the complex web.
This blog post explores the critical differences in the data privacy vs data security debate and explains the intricate interactions between these two crucial ideas. Come along as we rethink our online privacy and security parameters while delving into the crucial subtleties that mold our digital relationships. In this article, we are going for the data privacy vs data security debate.
First, let’s start with the basics of data privacy and data security.
Table Of Contents
- What Is Data Privacy?
- What Is Data Security?
- What Is Data Protection?
- Data Privacy vs Data Security: Key Differences
- Steps for Achieving Data Privacy
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is Data Privacy?
Credits: Freepik
To comply with regulatory requirements and safeguard the confidentiality and immutability of the data, data privacy—also sometimes referred to as information privacy—relates to the appropriate handling of sensitive data, including, primarily, personal data as well as other confidential data, such as specific financial data and intellectual property data.
Traditional data protection (such as backup and restoration copies), data security, and data privacy are three significant areas of data protection. The ultimate goal of the best data protection and security practices is to ensure the continuous availability and immutability of vital business data. Thus, the best practices can also be seen as protecting sensitive and personal data.
Data Privacy Laws
If you run a company with an online presence, you have undoubtedly heard about the several recent global data privacy rules.
Examples of regulations that attempt to safeguard consumers’ internet privacy when sharing data include the following:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union.
- Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
- The CalOPPA or The California Online Privacy Protection Act
- The CCPA, or California Consumer Privacy Act
- The UCPA, or Utah Consumer Privacy Act
How Data Security Affects Data Privacy
Credits: Freepik
Before the data privacy vs security debate, first, let’s understand how Data security affects Data privacy.
Most websites and online businesses gather personal information, including email addresses, phone numbers, credit card numbers, and log-in information. These organizations should ideally not retain information for longer than it is necessary.
However, it is impossible to operationalize data privacy without guaranteeing data security.
For instance, if you don’t shield users’ credit card information from hackers, they may be able to sell it on the dark web. As a result, data privacy requires data security.
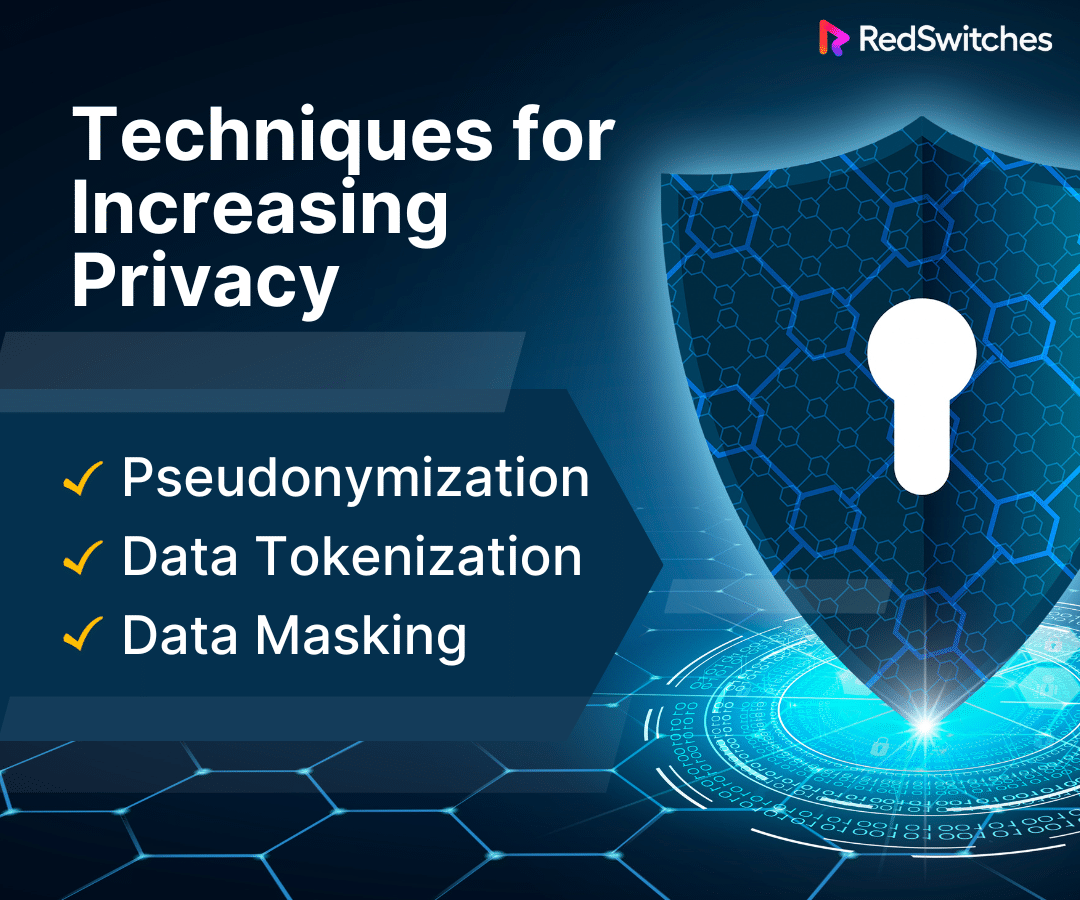
Techniques for Increasing Data Privacy
Before moving on to the core topic of our blog, i.e., data privacy vs data security, let’s discuss some techniques for increasing data privacy.
Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization is a data masking technique that guarantees that personal information cannot be linked to a particular individual without using additional information subject to security controls. The EU General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, has multiple recitals defining how and when data should be pseudonymized, including this as a critical component.
Information about a specific person, referred to as a data subject, is personal data. Data subjects can be identified by specific identifying elements, such as an individual’s physical, genetic, physiological, mental, cultural, economic, or social features, or by attributes like their name, ID number, or location.
Data Tokenization
Tokenization procedures substitute confidential data with an arbitrary token value that facilitates access to the original data. Tokens can be used once to boost the security level of data, but they are unrelated to the original data.
Additionally, tokens help organizations reduce the sensitive information they can access and the associated liability.
Data Masking
Data masking is using random characters or other data to conceal significant or distinctive portions of the information. Data masking makes it possible to identify data without changing real identity. The credit card number 5100-0000-0000-0005, for instance, can be saved as “XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-0005”.
What Is Data Security?
Credits: Freepik
The process of preventing digital information from being corrupted, stolen, or accessed by unauthorized parties is known as data security. Everything is covered, including administrative and access controls, user and storage device hardware, software, and policies and procedures of the organization.
Technologies and techniques that improve data visibility and usage inside an organization are utilized in data security. By using techniques like data masking, encryption, and the redaction of sensitive information, these tools help safeguard data. Organizations can comply with stricter data protection rules and streamline their auditing operations with the help of this approach.
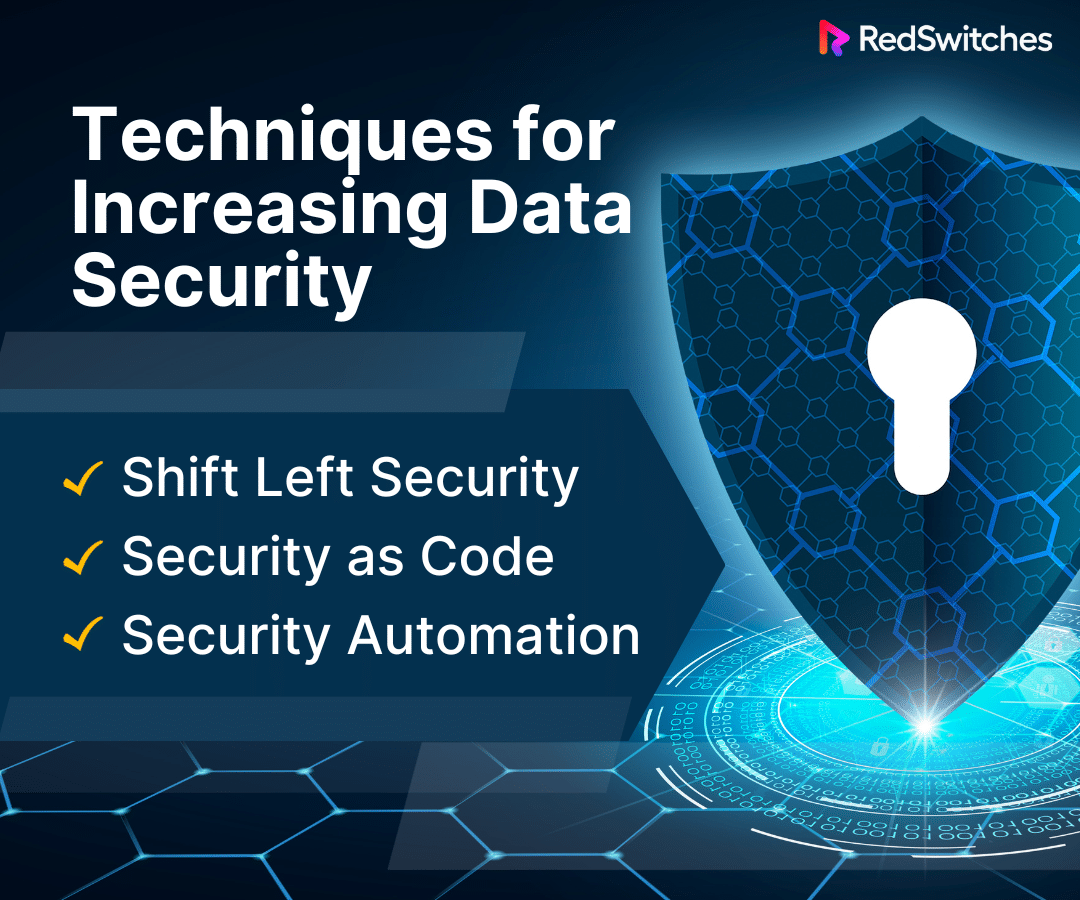
Techniques for Increasing Data Security
After discussing the techniques for increasing data privacy, we will move on to the techniques for enhancing our data security.
Shift Left Security
The goal of shift left security is to include testing and security as early in the development process as feasible.
The four steps of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) are Development, Build, Test, and Deployment.
Since developers are positioned at the left end of the cycle, everything that is moved in their direction will shift left.
But shifting security left requires more than just giving developers a list of problems to solve or a tool made for the security team.
Developers require developer-friendly tools and continuous security team help for successful deployment.
Security as Code
The discipline of incorporating security into DevOps tools and processes by figuring out where to integrate security checks, tests, and gates without increasing costs or delaying the process of making changes to infrastructure and code is known as security as code, or SaC.
Developers can define infrastructure platforms and configurations by writing code for the task. We need to consider adopting SaC to bring DevOps agility and velocity to security. SaC will drive the future of application security.
Security Automation
Automation of security tasks, encompassing incident detection and response as well as administrative responsibilities, is known as security automation. Security teams can scale to meet increasing workloads thanks to security automation, which offers several benefits to the organization.
Zero trust security was developed to help manage enterprise cyber risk as cyber attacks grow in quantity and sophistication. Zero trust security, based on role-based access controls (RBACs), authorizes or rejects access requests individually instead of implicitly trusting internal individuals and systems.
Although a zero-trust architecture offers granular security, it has many advantages and drawbacks. Developing a zero-trust strategy that is safe, scalable, and long-lasting requires security automation.
What Is Data Protection?
Credits: Freepik
People tend to forget data protection in the debate of data privacy vs data security, so we will first start with the definition.
The process of protecting sensitive data from loss, alteration, or corruption is known as data protection.
Data protection is becoming increasingly critical since data is being created and stored at previously unheard-of speeds. Additionally, there isn’t much room for downtime that could prevent access to crucial data.
Therefore, ensuring that data can be promptly restored following any corruption or loss constitutes a significant portion of a data protection plan. Other essential data protection elements include guaranteeing data privacy and shielding data from compromise.
What Are Data Protection Regulations?
Before moving into the core topic of our blog, i.e., data privacy vs data security, Let’s discuss the Data Protection Regulations.
A legislative framework known as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) establishes rules for gathering and using personal data from people inside and outside the European Union (EU). The GDPR was approved in 2016 and went into full force two years later.
By making businesses accountable for managing and treating personal data, it seeks to give customers control over their personal information. Websites that draw users from Europe must comply with the rule applicable regardless of their location, even if they don’t advertise directly to EU citizens.
Key Components of GDPR
Before moving on to our ultimate data privacy vs data security comparison, let’s discuss the critical components of GDPR.
Consent and Transparency
To acquire personal data about an individual, organizations are required by GDPR to get the subject’s clear and explicit consent. Transparency is crucial; businesses must tell people how their data will be used by sending them simple and understandable privacy statements.
Individual Rights
Under the GDPR, people have several rights, such as the ability to view their personal information, ask for changes, object to processing, and even delete their data (the right to be forgotten). These rights provide people the ability to decide how their data is used.
Data Security and Accountability
Organizations must put strong data security measures in place to guard against breaches and unauthorized access to personal data. Furthermore, companies must designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to supervise GDPR adherence and serve as an intermediary between the company, data subjects, and regulatory bodies.
Data Portability and Right to Erasure
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) granted people the power to ask for their data to be transferred in a machine-readable manner. Furthermore, the right to erasure guarantees that people may ask for the removal of their personal information in certain situations.
International Data Transfers
Organisations must ensure that the target countries offer appropriate data protection when transferring personal data outside of the EU. Secure foreign data transfers require sufficient protections, such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs).
Impact and Adoption of GDPR Principles Worldwide
Despite being a European rule, GDPR has an international effect. Businesses that operate internationally or target European consumers must abide by the GDPR regardless of their physical location. There are severe penalties for noncompliance, emphasizing the importance of comprehending and following data privacy laws.
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Key Differences
We will go through our core debate topic in detail: Data Privacy vs Data Security.
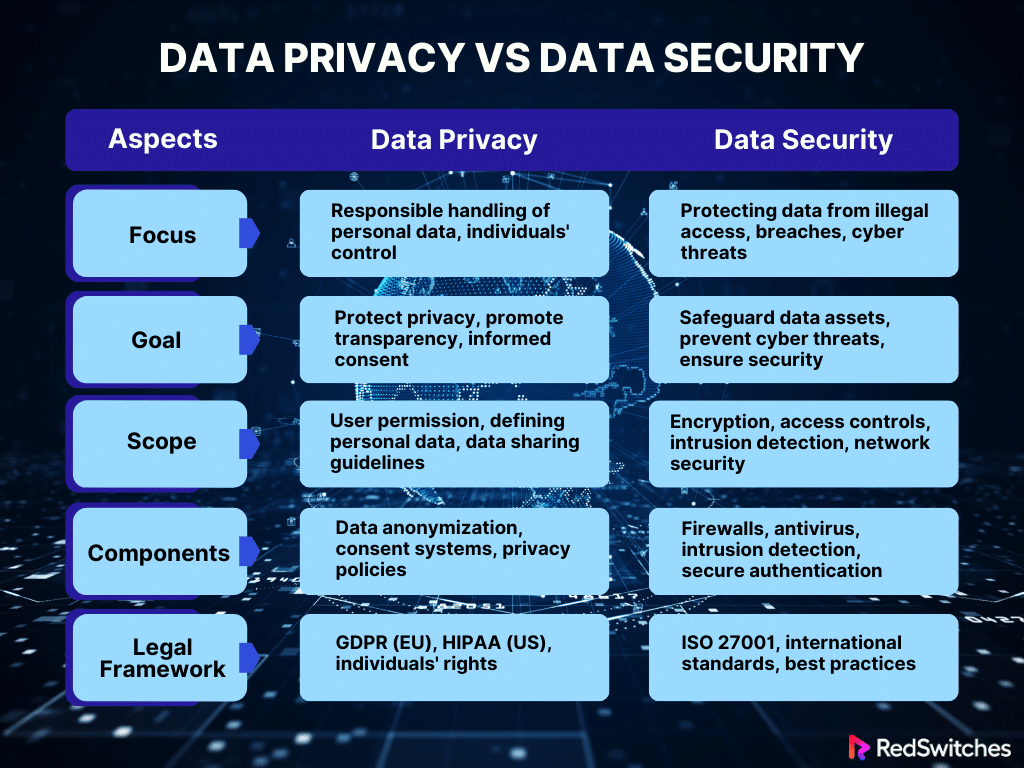
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Focus
First, we will elaborate on the data privacy vs data security aspect of Focus.
Data Privacy
Data privacy’s primary focus is treating personal data responsibly, highlighting people’s power over the information they provide and how it is gathered, used, and shared.
Fundamentally, data privacy is about preserving people’s right to control their personal data. It highlights the appropriate management of data, emphasizing the gathering, processing, sharing, and using of information. Individuals have the right to know what data is being collected, why it is being gathered, and how it will be used. This is known as data privacy.
Data Security
Data security focuses on protecting data from illegal access, breaches, or cyber threats, guaranteeing the confidentiality and integrity of individual and organizational data.
Protecting data assets against various risks, such as unauthorized access, breaches, cyberattacks, and data manipulation, is the focus of data security.
It includes putting organizational, procedural, and technical safeguards in place to ensure that data is accurate, dependable, and unaffected. Additionally, data security ensures data confidentiality by limiting access to sensitive information to authorized users or systems only.
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Goal
Now, we will discuss Data Privacy vs Data Security concerning the Goal of each.
Data Privacy
Protecting people’s right to privacy while advancing openness, informed consent, and moral data use is the aim of data privacy.
Safeguarding people’s fundamental right to privacy is the main objective of data privacy. It encourages transparency, informed consent, and moral handling of data. Data privacy helps people and organizations trust each other by granting individuals control over their data.
To achieve data privacy, transparent data practices, unambiguous privacy regulations, and avenues for people to exercise their rights—such as access, amend, or remove their data—are all necessary.
Data security
Data security seeks to safeguard data assets by implementing procedural and technical safeguards, fending off possible cyberattacks, and guaranteeing that the data is secure and unaltered.
Data protection is primarily concerned with protecting data from potential threats and weaknesses. Organizations strive to establish a strong defense against cyber threats by using security procedures such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, access controls, and encryption. Data security procedures also include vulnerability testing, incident response strategies, and routine security assessments to lessen any security breaches’ effects quickly.
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Scope
So, how does the data privacy vs data security argument take place with respect to the scope? Let’s understand each scope one by one.
Data Privacy
Personal Information: Any information that may be used to identify a specific person, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and even more private information like medical records, is called personal information.
Legal Compliance: Complies with laws and rules controlling how personal data is handled, such as the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
Consent and Transparency: Demands that organizations get people’s express consent before gathering and using personal data, as well as being open and honest about the data’s intended purpose.
Data Security
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA): refers to the goals of protecting data’s privacy, ensuring its integrity by avoiding unauthorised alterations, and ensuring its accessibility to those who require it.
Cybersecurity measures: To safeguard data against cyber threats like malware, phishing assaults, and hacking, technological measures like encryption, firewalls, and access restrictions are implemented.
Physical security: It goes beyond digital defenses and includes safe data centers, facility access controls, and safe physical data storage.
Credits: Freepik
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Components
Data Privacy
Here are the components of Data Privacy:
Personal Information: Your name, address, phone number, and even more private information like your medical or financial records are examples of personal information.
Consent: A business or organization must obtain your consent before collecting your personal data. We refer to this as consent. They ought to describe how they plan to use your information as well.
Transparency: Businesses should be open and honest about the data they gather, why, and how they plan to utilize it. It gives you an idea of what to anticipate.
Data Security
The following are the components of Data Security:
Confidentiality: Maintaining data privacy and ensuring that only those with permission can access it are examples of confidentiality. It’s comparable to having a code that only authorized individuals know.
Integrity: Integrity is the assurance that no one who shouldn’t be able to change the data does so. Consider that you have a diary and want to ensure that nothing is added or taken out without your knowledge.
Availability: Making certain the information is accessible when required. It’s similar to making sure your preferred application or game is always available when you need it.
Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is the process of securing your data from online threats by using tools and strategies including firewalls, encryption, secret codes, and antivirus software.
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Legal and Regulatory Framework
Legal and Regulatory frameworks are also critical in the data privacy vs data security argument.
Data Privacy
Protecting people’s personal information is the main goal of data privacy, which is demonstrated by laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These regulations, which strongly emphasize openness, permission, and individual rights, specify how businesses must gather, use, and preserve data.
Data Security
Data security operates in a distinct legal environment with standards like ISO/IEC 27001 and laws like the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Not just for personal data, these frameworks are intended to guarantee the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of all kinds of data.
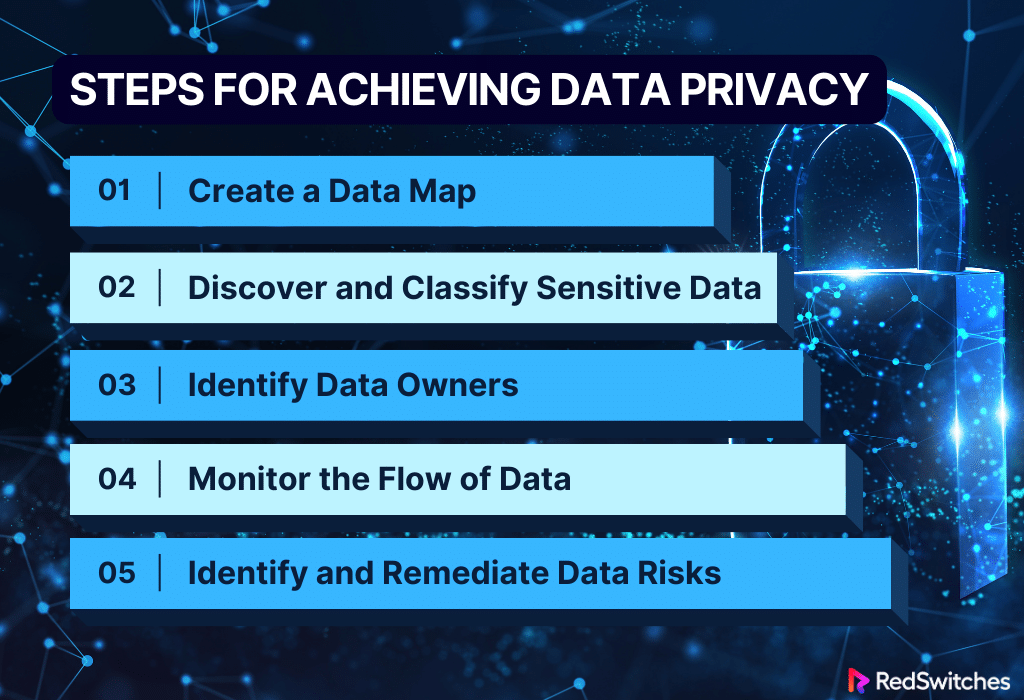
Steps for Achieving Data Privacy
After learning the key differences between Privacy and Security, another critical question that comes to the user’s mind is how Data Privacy is achieved. This section will explain the step-by-step method of achieving Data Privacy.
Step # 1: Create a Data Map
Do: Start by creating a comprehensive data map that outlines all the types of data your organization collects and processes. Include information on where it is stored, how it is used, and who has access to it.
Don’t: Overlook any data sources or repositories. A thorough data map is the foundation for effective data privacy management.
Step # 2: Discover and Classify Sensitive Data
The organization must then classify its data to identify the different kinds of information it possesses. This aids them in setting security priorities for repositories that hold the most crucial, strictly regulated, or otherwise extremely risky corporate information.
Sensitive data must be identified and categorized for targeted protection. Using automated technologies, sensitive information can be found in databases, files, and repositories.
Data should be categorized according to its level of sensitivity as soon as it is found. Classifications like restricted, private, internal, and public are frequently used. Manual inspection and validation are frequently required to guarantee appropriate classification, particularly for unstructured material like emails and documents.
Do: Implement tools and processes to discover and classify sensitive data within your organization. Clearly label and categorize data based on sensitivity, ensuring everyone understands which information requires special protection.
Don’t: Underestimate the importance of identifying sensitive data. Accurate classification is crucial for applying appropriate privacy measures.
Step # 3: Identify Data Owners
The people who control the data are the ones who know the most about its purposes and the appropriate users for it. They will be in charge of verifying and controlling who has access to the data they own.
Data owners must be assigned for efficient data administration and accountability. These are people or groups in charge of particular data sets. They are responsible for usage guidelines, data lifecycle management, and access permissions.
Determining the data owner guarantees accountability and makes it easier to communicate about data privacy policies. Establishing and implementing data protection policies should be done in concert with IT, security, and compliance teams by data owners.
Do: Assign ownership to different sets of data. Clearly define responsibilities for those who manage and oversee specific data sets. Establish communication channels between data owners and other stakeholders.
Don’t: Assume data ownership is a one-size-fits-all concept. Differentiate responsibilities based on the nature and sensitivity of the data.
Step # 4: Monitor the Flow of Data
To guarantee that suitable security measures and access controls always safeguard sensitive data, it is essential to understand how data flows between repositories or geographical locations.
Furthermore, data cannot be moved outside designated nations or regions due to various national and municipal restrictions. For example, the GDPR prohibits data transfers outside the EU unless there is a legitimate reason.
For threat detection and real-time visibility, data flow monitoring is crucial. By using data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, businesses can keep an eye on and manage data transfers happening inside and outside the network.
DLP tools can stop illegal transfers and identify trends that point to sensitive data, such as social security or credit card numbers. Sensitive data protection is ensured via continuous monitoring, which makes it possible to respond quickly to possible breaches.
Do: Implement monitoring tools and processes to track data flow within your organization. Regularly audit data access and usage to identify anomalies or potential privacy breaches.
Don’t: Neglect ongoing monitoring. Data flows can change, and continuous oversight is crucial for maintaining a proactive stance on data privacy.
Step # 5: Identify and Remediate Data Risks
The company should be able to identify its most significant data risks by evaluating the information gathered in the earlier phases. At this point, it should begin developing and implementing plans to protect data privacy. For identifying and addressing data risks, standard methods and security tools include:
- Finding and classifying data
- Encryption
- Tokenization
- Masking
- Privileged access management (PAM)
- Data access governance (DAG)
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
Proactive steps to reduce vulnerabilities and possible threats are necessary to identify and correct data hazards. Frequent vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and risk assessments aid in locating security holes and flaws in the data security infrastructure.
Organizations can rank remediation actions according to the hazards’ severity after they have been discovered. These actions could entail using encryption techniques, improving access controls, or correcting software vulnerabilities. Engaging in ongoing risk assessment and remediation is imperative to adjusting to changing security threats.
Do: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential threats to data privacy. Develop and implement strategies to remediate any identified risks promptly.
Don’t: Delay addressing identified risks. Timely action is essential to prevent privacy incidents and maintain the integrity of your data privacy framework.
Conclusion
We have uncovered the critical differences between two crucial facets of the digital environment by researching the complex debate of Data Privacy vs Data Security. As we’ve learned, data security is all about defending this data against cyberattacks and unauthorized access, while data privacy is about ensuring that personal information is treated sensibly, ethically, and openly.
By comprehending these distinctions, we can practice efficient tactics, including encryption and safe authentication techniques, to accomplish complete data privacy and security. The difference between data privacy and data security was explained comprehensively in our blog.
As we end our trip, we must acknowledge the critical role dependable partners like RedSwitches play in this space. Our state-of-the-art technology and steadfast dedication to data security enable individuals and organizations to confidently traverse the problematic world of data privacy and security.
FAQs
Q. What is the critical difference between data privacy and data security?
Data security emphasizes protecting data from unauthorized access, whereas privacy focuses on protecting personal information.
Q. What is the difference between data security and data privacy in big data?
Privacy in big data refers to the preservation of private data inside large datasets, while security in big data is preserving the confidentiality and integrity of the entire dataset.
Q. Why are data security and data privacy important?
Protecting sensitive information, upholding user confidence, adhering to legal requirements, preventing unauthorized access, and guaranteeing the integrity and confidentiality of data all depend on data privacy and security.
Q. How can companies ensure they follow data privacy laws like the CCPA and GDPR?
Strict data access controls, frequent audits, and the consultation of a data protection officer to supervise GDPR and CCPA compliance are ways businesses can guarantee compliance.
Q. How can people improve the security and privacy of their personal data online?
People can improve their privacy and security by creating solid and one-of-a-kind passwords, turning on two-factor authentication, and exercising caution when disclosing personal information online.
Q. What is the difference between data privacy and data security?
Data privacy refers to the proper handling of data in a way that respects individuals’ privacy concerns, while data security refers to the measures put in place to protect data from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Q. How can organizations ensure data privacy and security?
Organizations can ensure data privacy and security by implementing best practices for ensuring data privacy, following privacy regulations, and implementing layers of security to protect personal and sensitive data.
Q. What are some common privacy regulations related to data protection?
Common privacy regulations related to data protection include GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
Q. What are the best practices for ensuring data privacy and security?
Best practices for ensuring data privacy and security include implementing strong data security policies, using data security tools, and ensuring that data is protected from malicious threats.
Q. How does data security protect against data breaches?
Data security protects against data breaches by implementing measures such as encryption, access controls, and monitoring to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Q. Why is it important to protect personal data?
It is important to protect personal data to prevent privacy concerns, data theft, and to comply with privacy laws and regulations.
Q. What are some key elements of data protection and privacy?
Key elements of data protection and privacy include data collection, data management, and storage with built-in data protection measures.
Q. What is the significance of data security in today’s digital world?
Data security is significant in today’s digital world to protect data from digital threats, ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data, and maintain trust in digital transactions.
Q. How does data privacy and security contribute to overall business success?
Data privacy and security contribute to overall business success by building customer trust, complying with privacy laws, and safeguarding sensitive business information.
Q. What is the role of data privacy and security in ensuring ethical data practices?
Data privacy and security play a crucial role in ensuring ethical data practices by maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of certain data, while allowing for legitimate access and use of data.