In our modern, highly connected world, cloud computing has changed how businesses handle, manage, and store data. Understanding this requires a deep dive into cloud computing for small businesses and why it has become vital to continuing business processes.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify cloud computing, providing insights into its definition, applications, historical evolution, service models, and advantages. We’ll discuss critical distinctions from traditional hosting, leading service providers, emerging trends, data security considerations, and vital factors when moving to the cloud.
By the end, you’ll understand cloud computing and its pivotal role in enhancing business operations, competitiveness, and storage space in our connected world.
Let’s start with the introductions.
Table Of Content
- What is Cloud Computing?
- What is Cloud Computing Used For?
- What are the Main Cloud Service Models?
- Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Things to Consider When Moving to Cloud
- Difference Between Cloud Hosting and Traditional Web Hosting?
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing
- Final Takeaway
- FAQs
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing is a technology that allows businesses to access and utilize computing services and resources through the internet, often referred to as “the cloud.”
This represents a significant departure from conventional computing approaches that rely on local servers and devices for data processing and storage. As a result, cloud computing brings together technology, innovation, and cost-effective access to robust ICT processes.
What is Cloud Computing Used For?
The best thing about cloud computing is that various providers have implemented their idea of cloud computing services in different configurations and options across multiple industries. Here’s a brief run-through of these applications of cloud computing.
Data Storage and Backup
The cloud provides a secure location for storing and processing data, making it accessible virtually anywhere. Businesses no longer have to invest in local data storage solutions because of the speed and performance of cloud storage and recovery.
Web Hosting and Application Development
Developers leverage cloud environments to host websites and build software applications in cloud environments that closely mirror real-world scenarios. Additionally, cloud environments bring enhanced scalability and agility that help businesses achieve competitive advantage.
Big Data Analytics
Cloud computing offers businesses the right resources and capabilities to process massive datasets, extracting valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud technologies bring data redundancy and seamless recovery mechanisms to business processes. As a result, business assets are often back online with minimum outages.
Historical Evolution of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing traces its origins to the 1960s when the idea of utility computing first emerged. However, it was in the early 2000s that cloud computing, as we know it today, started to develop.
Throughout its history, cloud computing has evolved from mainframes to personal computers and data centers, driven by a constant quest for efficiency, accessibility, and innovation. These factors have collectively shaped cloud computing into a valuable asset in the contemporary business world. The most important benefit of cloud computing is the competitive edge in the form of streamlined processes and cost-effective operations.
What are the Main Cloud Service Models?
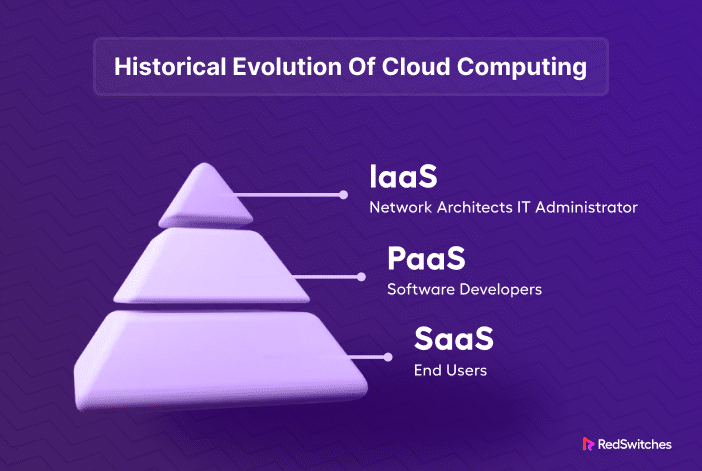
Cloud computing comes in the following three main service models to meet specific business requirements:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the basic building blocks for cloud computing, such as computing capacity, storage, and networking resources. Businesses opt for IaaS to get more control over their cloud environment. However, working with IaaS requires significant technical expertise to manage cloud computing resources.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a comprehensive environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications. PaaS takes care of the underlying infrastructure so businesses can focus on developing and deploying their applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS hosts, manages, and delivers software hosted on cloud infrastructure. SaaS is the most popular cloud computing model because it is easy to manage and helps businesses deliver software products to thousands of users.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Businesses are rapidly transitioning to cloud computing because of the many benefits that translate into a business’s competitive edge. This edge allows SMBs to operate and deliver services on par with enterprises.
Here are some of these benefits:
Cost-Effectiveness
Thanks to cloud computing, small businesses can now access on-demand computing resources and services without spending money on costly infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go billing model allows small businesses to have better control over the budget allocated to cloud services.
Scalability
If your businesses deliver services or products online, you will experience traffic spikes at your customer-facing applications and websites. Server scalability is an essential requirement for service continuity during these spikes.
Scaling cloud computing resources is almost instant and often requires no outside intervention. In most cases, the cloud vendor’s system automatically scales the core services and resources to match the volume of user traffic.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud services offer the most dependable backup and recovery options for small businesses. Every cloud provider often provides backup and recovery services that quickly restore critical business data and apps in the case of a disaster or outage.
In most cases, cloud computing services include high-tolerance systems that ensure service delivery even if some infrastructure components fail.
Security
Cloud service companies invest considerable resources in security measures to protect their clients’ data. As a result, SMEs can enjoy a similar level of security as large corporations without investing in costly in-house security systems.
Collaboration
Cloud computing can improve collaboration between employees, customers, and partners. It facilitates near instantaneous, global data transfer, making files and software available to globally distributed teams. When teams collaborate, they experience a higher output, advanced decision-making, and a strategic edge.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
SMEs considering a transition to cloud computing should consider the following challenges to avoid issues that can slow down or even break business processes.
Security Concerns
Cloud providers have a strong track record of security, but there is always the risk of a data breach. Businesses need to protect their data by using strong passwords and encryption. They should also carefully evaluate the security features of the cloud provider before they finalize their choice.
Downtime
Cloud services are highly reliable, but downtime is always possible. Businesses need to have a plan to mitigate the risk of downtime. This plan should include multiple cloud providers/servers and a backup plan. They should also monitor their cloud services closely for any signs of trouble.
Cost Management
Cloud costs can be complex and can add up quickly. Businesses need to understand their cloud costs to manage them better. This may involve using a cost-efficient cloud management platform and alerting them of unexpected resource usage that bumps these costs.
Data Transfer Speed
The data transfer speed of cloud services can vary depending on the provider, the location of the data, and the device accessing it. That’s why businesses need to consider the data transfer speeds of their cloud providers. They should also monitor their data transfer speeds to ensure they get the performance they need for smooth business operations.
Limited Control
Cloud users have limited control over the underlying infrastructure. This can affect customization options and the ability to fine-tune performance. Businesses must be aware of these limitations when deploying applications on their cloud infrastructure. In some cases, they may need to use a third-party tool or service to get the level of control they need.
Things to Consider When Moving to Cloud
As you saw, businesses can gain a lot by moving to cloud computing. However, we strongly recommend making an informed decision rather than a blind jump. For this, businesses should consider the following aspects:
Migration Costs
Data migration, employee training, and the need for new software architecture are just a few expenses that can add up when businesses move to the cloud. If you’re planning a move, include these and other related costs in the initial costs.
Future Computing Requirements
Think about your computing needs in the future before making a move to the cloud. You should check to see if your prospective cloud service provider can meet your needs now and in the future. When planning for future cloud computing requirements, remember to include the requirements for new projects.
Networking and Connectivity
Cloud computing services cannot function without constant access to high-speed internet. So, your internet provider must handle the potential increase in traffic caused by moving to the cloud. If you’re having trouble staying connected to the cloud, it may be time to talk to your cloud service provider about upgrading your network infrastructure.
Security
In migrating to the cloud, security must be a top priority. Be wary of any cloud service without adequate security options like encryption, access controls, and automatic threat alerts. You should also think about how your business-level security procedures will work alongside the security protocols used by your cloud service provider.
Compliance
Businesses must adhere to various regulations, from data privacy laws to regional legislation and industry-specific benchmarks. If you use cloud services, you must ensure your provider meets these standards and offers measures to ensure compliance.
What’s the Difference Between Cloud Hosting and Traditional Web Hosting?
After going through the benefits and specific considerations of moving to the cloud, small businesses should understand the fundamental distinction between cloud and traditional web hosting.
Traditional hosting relies on dedicated physical servers to host websites and applications. In this scenario, resources are confined to specific hardware infrastructure, limiting scalability and flexibility for business owners.
In contrast, cloud hosting distributes resources across a network of virtual servers. This results in greater scalability, redundancy, and flexibility. This dynamic allocation of resources optimizes performance and cost-efficiency, a crucial aspect of small business operations and competitiveness.
| Traditional Web Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
| Uses physical servers. | Uses virtual servers. |
| Limited scalability. | Highly scalable. |
| Risk of server downtime. | Built-in redundancy. |
| Fixed costs. | Flexible pricing. |
Popular Cloud Service Providers
Leading cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and RedSwitches offer various cloud services tailored to diverse business needs. Each provider possesses unique strengths and specialization areas, allowing business owners to choose the most suitable partner for their requirements, thereby gaining a competitive advantage.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
The cloud industry is in a perpetual evolution, with several exciting trends emerging.
Edge Computing
Edge computing extends cloud capabilities to the network’s edge, reducing latency and enabling real-time data processing for IoT devices, a game-changer for business operations and competitiveness.
Serverless Architecture
In serverless computing, you don’t have to worry about managing servers. This frees developers to concentrate solely on writing code, boosting productivity in business operations.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
More and more business owners are turning to multi-cloud and hybrid cloud approaches. This helps them spread out risk and use resources efficiently, which, in turn, makes their businesses more competitive.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud providers are integrating AI and machine learning services, empowering organizations to harness the potential of data-driven insights, a valuable asset for business competitiveness.
Security Risks to Take Into Consideration When Selecting Cloud Computing Vendors
Like all technologies, cloud computing has security threats that small businesses must weigh carefully.
Data Breaches
Cloud computing mandates using remote servers for data storage. In an attack on these data storage servers, sensitive information, such as bank records and client information, can be at risk. You should check that your cloud service provider provides multiple data security measures, including encryption, access control, and intrusion detection and prevention.
Insider Threats
There is a risk that employees of cloud service providers could gain access to customer data. Insider threats can jeopardize data security, and predicting these threats is tough. It is crucial to partner with a cloud service that adheres to stringent security procedures and data encryption ideas, such as salting, to reduce the likelihood of insider attacks.
Lack of Control
Employing cloud services may reduce a company’s ability to manage its data and systems. When this happens, monitoring and controlling security threats can become a challenge. That’s why you need to consider the level of management access and transparency the vendor provides to the users.
Businesses need to understand that these challenges should be considered carefully before opting for the cloud.
Final Takeaway
Cloud computing has transformed how small businesses run by granting them access to vast resources and capabilities previously reserved for large corporations. The benefits of cloud computing for small businesses are easy to see. However, these benefits won’t materialize until you pick the exemplary cloud service.
RedSwitches is one of the best providers offering small businesses excellent cloud computing solutions. With RedSwitches, small businesses can enjoy various services and features, such as high-speed connectivity and personalized customer service.
FAQs
Q1. What is cloud computing, and how does it function?
Cloud computing is a set of technologies that enable users to access and utilize computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and software via the Internet. These resources are hosted on remote servers and can be accessed as needed.
Q2. What are the fundamental models of cloud computing services?
Cloud computing services typically encompass Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These components provide different levels of control and management for users.
Q3. How can cloud computing benefit my business?
Cloud computing provides numerous advantages, including cost savings, scalability, accessibility from anywhere, automatic updates, and options for disaster recovery. These benefits can assist businesses in efficiently meeting their IT requirements.
Q4. Are there any disadvantages or drawbacks to using cloud computing?
Yes, there are some drawbacks, such as concerns about data security and privacy, potential downtime due to internet connectivity issues, and the need for effective cost management to avoid unexpected expenses.
Q5. What are some typical business demands that cloud-based solutions can address?
Cloud-based solutions can handle a wide range of business demands, including data storage and backup, web hosting, application development, big data analytics, and disaster recovery.
Q6. What steps should I take to select the most suitable cloud computing provider for my business?
Choosing the right cloud computing vendor requires evaluating your business requirements, financial constraints, and support prerequisites. When making your decision, consider elements like service-level agreements (SLAs), customer support, and the geographical locations of data centers.
Q7. Can you explain the difference between cloud infrastructure and traditional IT infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure relies on remote servers and virtualization technology to provide computing resources, while traditional IT infrastructure involves physical, on-premises hardware and servers. Cloud infrastructure offers greater scalability and flexibility.
Q8. Are my data and applications stored on remote servers secure?
Leading cloud providers implement stringent security measures, including encryption, access controls, and data redundancy, to safeguard your data and applications from unauthorized access and breaches.
Q9. How can I ensure cost efficiency when using cloud computing services?
To ensure cost efficiency, develop a comprehensive cost strategy, monitor and optimize cloud spending, understand pricing models, consider reserved instances, and implement cost-tracking tools.
Q10. What trends are emerging in cloud computing, and how can they benefit my business?
Emerging trends in cloud computing, such as edge computing, serverless architecture, and AI integration, can enhance business operations, productivity, and competitiveness. Stay updated on these trends to leverage their potential.