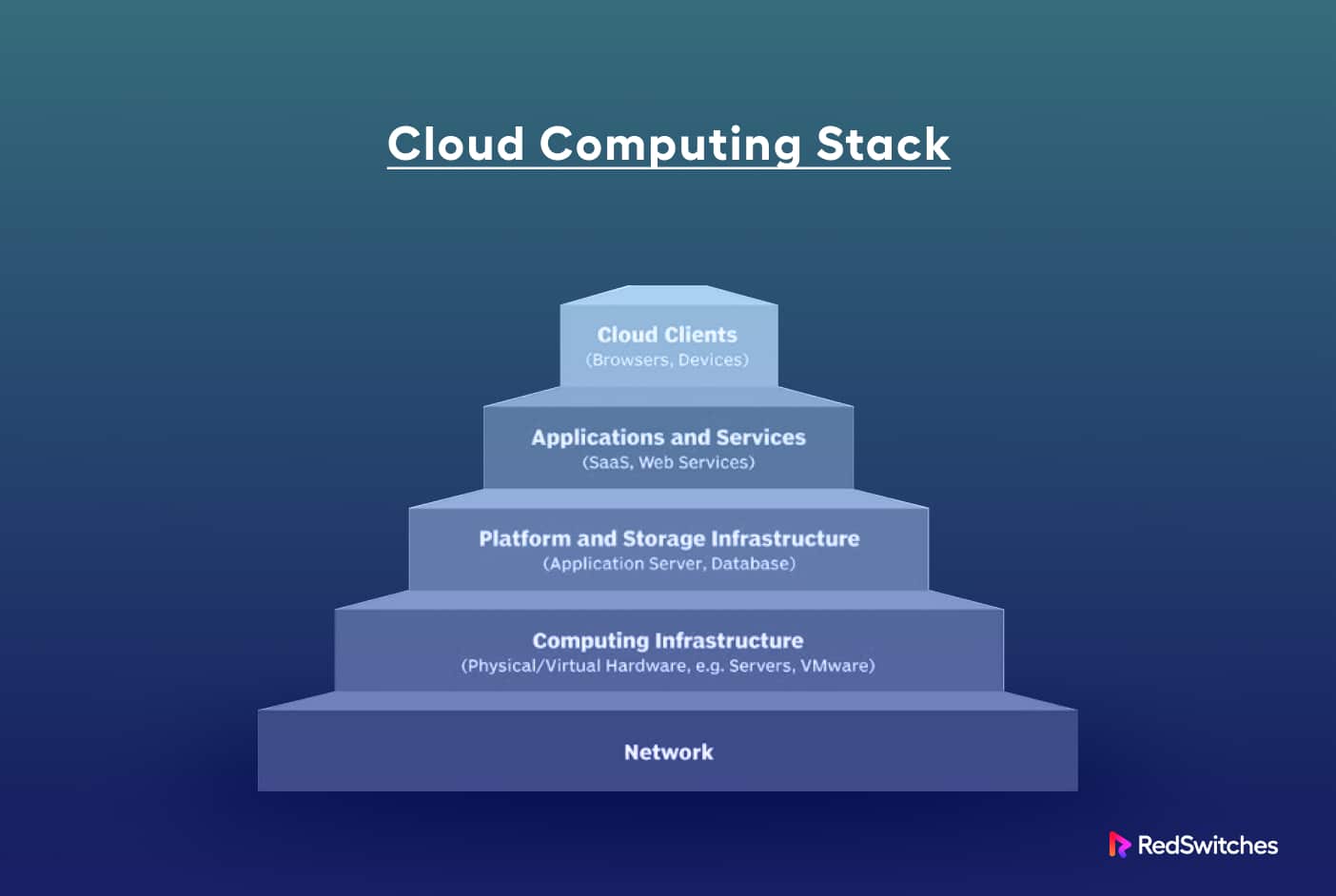
According to Gartner, ‘there is no business strategy without cloud strategy.’ The report further says that by 2025, more than 85% of organizations will adopt a cloud-first organizational design and gain business benefits from cloud computing.
You can easily observe this trend in how businesses use hosted services such as servers, databases, networks, analytics, and other functions.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses are structuring operations and service delivery. With a cloud-first approach, they design better products and analyze massive amounts of data more intelligently while strengthening customer relationships. This has led businesses to think and act faster than the competition, significantly lowering operational costs.
However, to get the full benefit of cloud computing, it is essential to know the basic workings of cloud computing infrastructure. This article covers the basics of the cloud computing infrastructure an organization needs to implement to get the ideal results.
Table Of Content
- What is Cloud Computing Infrastructure?
- Cloud Computing vs. Physical Infrastructure
- How Does Cloud Infrastructure Contribute to Cloud Computing?
- What Does Cloud Computing Infrastructure Include?
- The Difference Between Cloud Computing Infrastructure and Cloud Architecture
- Essential Requirements of Cloud Computing Infrastructure
- Comparison: Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid Cloud Computing Architecture
- What are the Various Types of Cloud Computing Delivery Models?
- The Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing Infrastructure
- Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Cloud Computing Infrastructure
- What is Cloud Computing Infrastructure Management?
- Who Leads the Cloud Computing Infrastructure Landscape?
- Conclusion
What is Cloud Computing Infrastructure?
The infrastructure in cloud computing refers to the backend technology a business needs to move operations to the cloud computing services. This includes servers, networking, storage resources, virtualization software, management tools, and services.
Cloud computing infrastructure offers numerous advantages compared to traditional physical infrastructure. The benefits of cloud computing not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive innovation and cost savings. Below are the key advantages.
Cloud Computing vs. Physical Infrastructure
Cloud computing infrastructure and physical on-premises infrastructure have the following significant differences:
Scalability
In cloud computing infrastructure, the admins can quickly scale resources up or down based on demand. In contrast, admins must invest time and resources to increase infrastructure capabilities.
Cost Efficiency
The pay-as-you-go model used in cloud infrastructure reduces the costs of maintaining the infrastructure.
Flexibility
Cloud computing infrastructure is flexible and easily adapted to the changing project requirements. In contrast, adapting physical infrastructure to new projects is often costly and takes time.
Rapid Deployment
Cloud computing infrastructure speeds up provisioning and reduces Provision resources quickly, reducing time-to-market for applications and services.
High Availability
Cloud computing infrastructure includes redundancy and failover mechanisms to reduce downtime and ensure continuous availability. Providing a similar level of availability in physical infrastructure is a costly endeavor.
Resource Usage Optimization
Cloud computing infrastructure comes with tools for monitoring and optimizing resource usage. In most cases, on-premises infrastructure often doesn’t offer this resource usage optimization.
Global Reach
Cloud computing is ideal for businesses that need multiple locations to serve customers worldwide with low latency. On-premises infrastructure to serve a similar global audience can be cost-prohibitive.
These advantages collectively make cloud computing a powerful solution for businesses seeking agility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
How Does Cloud Infrastructure Contribute to Cloud Computing?
Cloud infrastructure forms the foundation of cloud computing by breaking down the functionalities and attributes of physical hardware and software components. Subsequently, a cloud service provider, or in the case of a private cloud, the organization’s IT department, oversees these virtualized resources and dispenses them to users via the internet or a network.
These resources encompass virtual machines (VMs) and elements like servers, in-memory computing components, network switches, firewalls, load balancers, and storage. These resources frequently facilitate delivering specialized services, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
What Does Cloud Computing Infrastructure Include?
With the question of ‘what is cloud computing infrastructure’ addressed, let’s explore the composition of this infrastructure and the interaction among its components.
Cloud computing infrastructure serves as the foundation for the digital transformation of businesses worldwide. It’s a dynamic ecosystem composed of several key cloud infrastructure components, each playing a pivotal role in cloud services’ seamless functioning and delivery. Let’s dive into the details of these components to understand their significance:
Server Infrastructure
Prominent public cloud providers, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, offer services based on shared, multi-tenant servers.
This approach ensures substantial computational capabilities to manage unpredictable shifts in user requirements effectively and efficiently distribute demand across a cluster of servers. Consequently, cloud infrastructure primarily comprises high-density systems that utilize the shared capabilities of servers to deliver multi-socket and multicore services.
Storage Infrastructure
Unlike most conventional data center setups, cloud infrastructure commonly employs locally connected SSD and HDD storage solutions. These solutions often differ from the shared disk arrays within a storage area network.
These persistent storage systems are consolidated through a distributed file system (DFS) tailored explicitly for specific storage scenarios, such as big data, block storage, and objects.
The storage infrastructure brings streamlined scalability by separating storage control and management from the physical components through a distributed file system. Cloud providers can match capacity with user workloads by adding compute nodes with storage components instead of deploying large storage chassis in bulk.
Networking Infrastructure
Cloud computing relies on robust, high-bandwidth connectivity to facilitate seamless data transmission across the infrastructure. Generally, the network infrastructure comprises standard local networks based on switches and routers. Additionally, it integrates virtual networking capabilities and load-balancing mechanisms to distribute network traffic effectively.
Virtualization Infrastructure
Virtualization plays a crucial role in cloud computing. It enables the creation of virtual instances (virtual machines or VMs) on a single physical server, allowing multiple workloads to run independently.
This crucial component optimizes resource utilization, making it easier to scale resources up or down as needed. It also enhances disaster recovery capabilities by allowing quick VM backups and data migrations to new instances.
The Difference Between Cloud Computing Infrastructure and Cloud Architecture
The idea of infrastructure in cloud computing refers to all hardware and software components an enterprise needs to move and operate in the cloud. This usually includes cloud computing storage, computing power, essential services, management tools, and storage solutions.
On the other hand, cloud architecture refers to the interconnection of diverse technologies that form a cloud computing environment. This idea is implemented as a collection of components, such as hardware, networking infrastructure, operating systems, virtual resources, automation software, management utilities, and container technologies.
Essential Requirements of Cloud Computing Infrastructure
The success of a business migrating to the cloud depends entirely on the capabilities of the cloud computing infrastructure used for deployment. Since cloud computing infrastructure aims to provide a stable foundation for business processes, getting it right from the start is essential.
A cloud computing IT infrastructure needs to deliver the following to meet this standard:
Clear Service Offering
It’s crucial to define the services clearly. The documentation should outline access and usage restrictions so users can understand what to expect. This simplifies resource planning and budgeting. The businesses can add the necessary resources or scale the cloud infrastructure to accommodate increasing user requirements.
Integration With Providers
While cloud computing is entirely virtual, the business needs physical integration with the cloud infrastructure provider. Certain business functions, such as billing, deployment, and application management, require connections through proprietary APIs.
Accurate Reporting
Reporting level and accuracy are crucial for operating and maintaining cloud computing infrastructure. Tracking system performance is vital to ensuring quality customer service, billing, and compliance.
Comparison: Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud users can either have dedicated access to the cloud infrastructure or share the infrastructure with other users. However, in most cases, the infrastructure they use combines both options.
In practice, a business can opt to adopt one of the following three cloud computing architecture deployment models:
- Public Cloud: Multiple users share this multi-tenant, third-party-owned cloud environment. Public cloud services are a great way of leveraging economies of scale and lowering the cost of data storage and computing. The users generally pay for the services regularly.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud infrastructure is a single-user option with exclusive access to all resources. Usually, businesses with higher transaction volume, security, or data privacy requirements use exclusive single-tenant infrastructure offered by private cloud providers.
- Hybrid Cloud: This cloud computing infrastructure is a mix of public and private models that interact with each other through separate but interconnected systems. An enterprise may use a private cloud to maintain privacy for sensitive applications and a public cloud to expand its capacity or enhance flexibility.
What are the Various Types of Cloud Computing Delivery Models?
Cloud computing services offer three distinct cloud delivery models that reflect the varying combinations of resource access and provisioning levels.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
In the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model, organizations tap into cloud infrastructure elements as resources and services accessible via a dedicated internet connection. Businesses use the IaaS model to leverage cloud computing capabilities without spending a significant monthly budget on maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
Providers offer specialized services beyond basic cloud infrastructure, such as container infrastructure, service fabrics, serverless functions, and managed network services such as virtual private clouds, load balancers, domain name services, and firewalls.
IaaS pricing generally follows a metered approach, aligning rates with usage levels and performance benchmarks. Examples include standardized virtual CPU sizes with corresponding memory, storage options (object or block), and capacity measured by usage over time.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The lines between IaaS and Platform as a Service (PaaS) have recently blurred. PaaS builds additional layers upon infrastructure resources, introducing capabilities like load balancing, autoscaling, application development frameworks, and automated deployment mechanisms.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Unlike the IaaS and PaaS models, customers don’t directly engage with cloud infrastructure-based resources in the Software as a Service (SaaS) delivery model. Instead, the provider hosts and manages applications, typically configured within a multi-tenant architecture. Users access the service via a browser, while data related to the application can be stored locally, in the cloud, or both.
These cloud computing delivery models provide a range of options for businesses seeking to leverage cloud infrastructure’s capabilities.
The Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Link: Istock
The benefits a company gains by migrating to cloud technology are apparent. On the other hand, since not all cloud computing infrastructures are created equal, there are some drawbacks you should know before you jump on the bandwagon.
This table gives an overview of the pros and cons of the cloud computing infrastructure:
| Pros of Cloud Computing Infrastructure | Cons of Cloud Computing Infrastructure |
| Cost savings on purchasing hardware, networking equipment, and software. | Limited administrative control and backend access. |
| Pay-as-you-go model: Businesses pay for used resources only. | Dependency on Internet connectivity; outages impact access. |
| Flexibility to choose the best-fit software and hardware technologies. | Security and privacy concerns if not properly deployed. |
| Enhanced disaster recovery with managed backups and updates. | Potential security issues affecting business operations. |
| Improved security through managed security upgrades and patches. | Complexity and confusion in managing operations. |
| Seamless data access for global teams, enhancing collaboration. | Potential vendor lock-in and challenges in migration. |
| Access to resources on a variety of devices, promoting mobility. | Compliance challenges based on industry regulations. |
| Scalability to accommodate varying workloads and demands. | Technical support responsiveness might vary. |
| Reduction in physical hardware maintenance and infrastructure management. | Cost unpredictability due to changing resource demands. |
| Rapid deployment of resources for faster time-to-market. | Potential loss of direct control over physical hardware and physical resources. |
| Innovate using emerging technologies (AI, IoT) with cloud integration. | Resource allocation challenges with shared infrastructure. |
| Lower energy consumption and environmental impact due to shared resources. | Possibility of data privacy breaches and data loss. |
| Global accessibility and reduced latency for geographically dispersed teams. | Integration complexities with legacy systems. |
| Managed software updates and maintenance for improved efficiency. | Continuous reliance on cloud provider’s performance and support. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Creating an efficient and well-architecture infrastructure for getting the most benefits from cloud computing is surprisingly simple. The specifics differ from industry to industry and the particular operational requirements of a business.
The following are the basic steps in building a cloud computing infrastructure:
- Decide which virtualization and cloud computing technology works best for your business operations. Every cloud computing infrastructure type has pros and cons that will affect how the infrastructure is managed and monitored in the long run.
- Determine the delivery infrastructure to ensure scalability and efficient use of the resources. You should also determine the capacity and performance requirements of the hosted apps.
- Prepare and configure the network infrastructure with the network, storage, and hardware.
- Integrate all the pieces of the infrastructure to allow it to act on demand and automate the workflow.
What is Cloud Computing Infrastructure Management?
Cloud computing management is the overall control, administration, maintenance, and monitoring of the cloud infrastructure.
The management process is based on a consistent strategy and cohesive supporting processes to ensure that the delivery of cloud infrastructure is compatible and optimized for sustained business success.
Generally, infrastructure management involves capturing system performance metrics and a detailed analysis on a dashboard. In most cases, the business and the cloud infrastructure provider can access the dashboard. However, in some private cloud infrastructure setups, this dashboard is exclusively controlled by the in-house team.
Cloud infrastructure management services enable businesses to achieve these three key objectives:
- Facilitate Self-Service for IT Professionals: The management services deliver self-service options by allowing IT professionals to utilize cloud resources, create new instances, monitor usage and costs, and adjust resource allocations. This empowers efficient resource management and responsiveness.
- Automate Cloud Operations with Infrastructure Management: Teams can effectively manage cloud instances without requiring direct provider involvement, courtesy of workflow automation. This streamlines operations and enhances overall efficiency.
- Simplify Workload Tracking and User Experience Analysis: The process of monitoring cloud workloads and evaluating user experiences is simplified through cloud analysis. This provides valuable insights for informed decision-making and performance optimization based on data-driven perspectives.
Who Leads the Cloud Computing Infrastructure Landscape?
The cloud computing IaaS industry has several major players, each with distinctive strengths and offerings. The forefront of cloud infrastructure providers includes:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS, an industry pioneer, is a prominent player renowned for its extensive services. From computing prowess to storage, databases, IoT, analytics, and machine learning, AWS is recognized for its maturity and feature-rich portfolio.
Microsoft Azure: Representing Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure offering, Azure delivers services similar to AWS, emphasizing bolstering Microsoft-specific technologies like Windows and .NET. Furthermore, it offers robust integration with other Microsoft services such as Active Directory and Office 365.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP, the brainchild of Google, is a popular choice for hosting data analytics and machine learning projects. Its global data center network, coupled with developer-centric services like serverless computing and Kubernetes Engine, underscores its prowess.
Alibaba Cloud: Alibaba Cloud, under the Alibaba Group’s banner, commands a notable presence, particularly in Asia. Its suite of services is similar to the top providers, making it a key cloud provider.
IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud, an offering by IBM, offers a broad spectrum from computing and storage to AI, IoT, and blockchain-optimized solutions. Tailored for enterprise and hybrid deployments, IBM Cloud places a premium on security and compliance.
While these giants dominate the scene, remember that there are other players, and choosing a cloud infrastructure provider is a matter of matching the cloud provider’s capabilities with the business’s specific needs, regional presence, and objectives.
Conclusion
Cloud computing infrastructure, which includes the tools and components essential to implementing cloud computing capabilities, will continue to evolve. Businesses should understand the basics of cloud computing and get hands-on with adopting it. This will bring benefits such as optimum resource management, cost optimization, and security for critical business processes.
Explore the power of efficient cloud computing infrastructure with RedSwitches. Our proven solutions and experienced team can help you unlock the true potential of the cloud. Whether you’re looking to enhance scalability, boost performance, or ensure top-notch security, RedSwitches has you covered.
Discover RedSwitches’ Cloud Solutions and take your cloud infrastructure to the next level today!
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between public and private clouds?
Public clouds are shared by multiple organizations and managed by third-party, public cloud providers, offering scalability and cost efficiency. Private clouds are restricted to a single organization, providing higher control, security, and customization.
Q. How can businesses ensure cloud security for data in a cloud environment?
Businesses can ensure data security in the cloud through encryption, robust access controls, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards.
Q. What Are the Main Components of Cloud Computing Infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure consists of essential components such as computation servers, varied storage choices, networking elements for data transfer, resource-optimizing virtualization, automation tools, monitoring utilities, application deployment containers, security measures, backup solutions, compliance tools, and seamless service orchestration. These components work together to build an adaptable and scalable cloud environment.
Q. What are the applications of cloud computing?
A wide range of functions, including data backup, recovery, email services, terminal emulation, software programming, big data analytics, and hosting client web applications, are harnessed by businesses of all sizes, types, and sectors through cloud computing.
Q. What role does virtualization play in cloud infrastructure?
Virtualization enables multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical server, optimizing resource utilization and facilitating scalability in cloud environments.
Q. How does auto-scaling work, and why is it important?
Auto-scaling adjusts resources based on workload demands. It ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency by provisioning more resources during peak usage and scaling down during low-demand periods.
Q. What strategies can organizations employ to optimize cloud costs?
Organizations can optimize cloud costs by using reserved instances, monitoring resource utilization, leveraging cost management tools, implementing proper resource tagging, and regularly reviewing and adjusting their cloud infrastructure.