The adoption rate of cloud computing is rising, and many organizations are transitioning to cloud-based computing and storage solutions.
However, many in leadership roles consider this transition a simple exercise where the current IT infrastructure and resources could be “copied” to a cloud infrastructure. As a result, they need to invest more resources in requirement analysis and transition planning.
This oversight often leads to “bad” infrastructure design that costs the business a lot of time and resources. Worse yet, this move leaves security loopholes and related issues that continue to harm business operations.
However, there is an easy way to avoid all these issues and smoothly transition to the cloud.
This article will introduce the Cloud Maturity Model (CMM) and describe all the stages of this model. Businesses planning to move their operations to a cloud environment can use this detailed guide to assess their current situation and better plan their transition without wasting resources and time.
Let’s start with a short introduction to the Cloud Maturity Model.
Table Of Content
- What is Cloud Maturity Model
- How Businesses Can Use CMM For Cloud Adoption
- The Benefits of the Cloud Maturity Model (CMM)
- Stages of CMM
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Cloud Maturity Model
The cloud maturity model (CMM) establishes a blueprint for cloud adoption by highlighting potential gaps, suggesting suitable solutions and alternatives to consider, outlining the capabilities needed to reach particular degrees of maturity, and taking care of specific use cases.
Organizations may evaluate their level of cloud readiness using the Cloud Maturity Model methodology. It assesses the organization’s current state concerning utilizing the cloud to do business and determines where it needs to be in the context of the long-term business goals.
How Businesses Can Use CMM For Cloud Adoption
In practical terms, CMM is a roadmap businesses use to adopt the cloud for their operations.
While many see it as a theoretical model, it is a handy tool businesses can use to evaluate their current position on the cloud adoption curve. Then, when they have a baseline that aligns with a stage of the CMM, they can start planning the move to the next step.
Note that this involves considerable evaluation and planning so that the business can enhance cloud adoption in light of its objectives. The process starts with a gap analysis to identify the areas where the industry needs to work to move up the curve.
Once the gaps have been identified, the IT teams can start identifying the resources, tools, and vendors they need to fill in these gaps. The process also looks into the internal business operations and identifies areas where changes are required to implement the adoption plan.
Finally, the business can work with vendors, including a cloud infrastructure provider, to translate the requirements into an actionable plan. The plan could have a cloud migration component (often when the business is in the early stages of CMM) that the cloud infrastructure vendor helps with.
The Benefits of the Cloud Maturity Model (CMM)
CMM allows businesses to identify the gaps in their transition to cloud-based solutions. In particular, CMM offers the following benefits:
- Set objectives and create an effective cloud strategy.
- Establish desired maturity levels to implement cloud-based use cases that align with company goals.
- Follow the best practices, consider relevant risks, and prepare for the challenges businesses face in cloud adoption.
- Simplify the execution of use cases and develop a roadmap of projects that will increase the maturity levels of the businesses’ cloud optimization capabilities and domains.
- Organize priorities for infrastructure adoption for cloud-based computing solutions.
- Improve application and operations performance with the help of the cloud adoption best practices.
- Better organized planning and improved communication between all stakeholders.
- CMM ensures safer and faster adoption of the available cloud technologies.
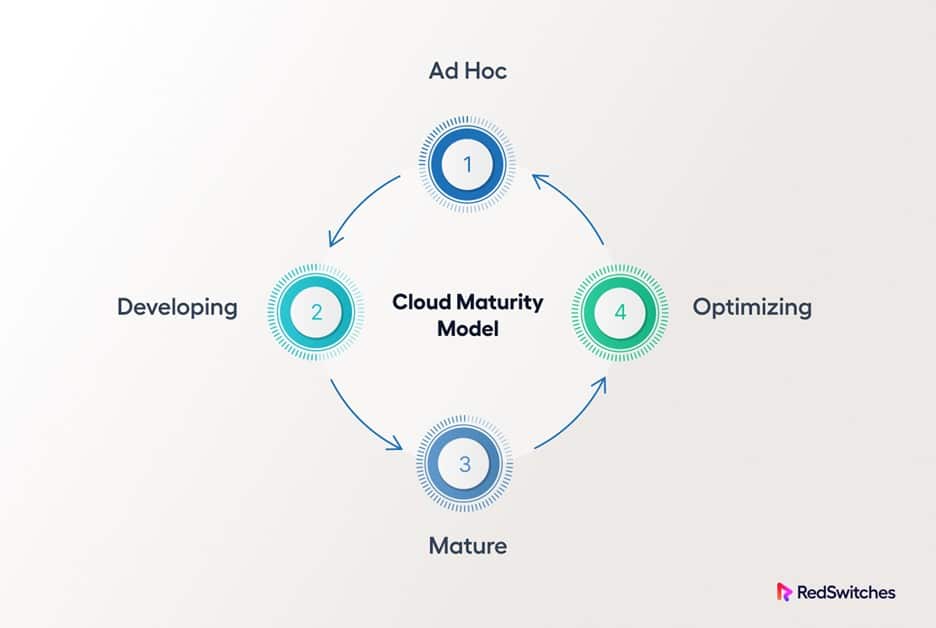
Stages of CMM
Depending on the sector and scale of the business, the teams can use the various stages and criteria of the model to increase cloud adoption.
However, the fundamental concept is always the same: a cloud maturity model depicts the development of an organization’s cloud usage through time.
This progress is mapped through a clearly defined roadmap comprising stages highlighting the digital transformation businesses typically go through.
We’ll briefly describe the CMM stages to help you assess your current position on the cloud adoption curve.
Stage 1: Project
This is the first stage of the CMM.
Here, the organization needs more cloud infrastructure in play. The management is considering adopting cloud-based services, initially for specific projects such as SaaS.
At this stage, the various teams involved in the project are making plans and evaluating resources and inventories. At this stage, the teams need to bring the management on board to get the backing for the project. The teams should also start considering the resources and timelines required for the project.
Limitations at This Stage
- Limited knowledge about the cloud.
- Limited budgets that only allow for essential services.
- The organization needs to establish procedures and rules for cloud adoption.
Outcomes of Stage 1
- Proper investment, assistance, and knowledge.
- Reliable direction, strategy, and ownership.
Stage 2: Foundation
The second stage is finalizing the planning, and detailed action plans are drafted.
The organization has a clear roadmap based on the discoveries and analyses generated in the previous stage. The teams have started the transformation process. This involves fine-tuning the initial plan and dealing with challenges as the teams move forward with the execution.
Management might have concerns about changes as the organization starts incorporating cloud-based solutions. These concerns usually revolve around compliance and security.
Experts suggest that since the organization is still in the planning mode, the teams can still plan the details, allocate additional resources, and hammer out the last-minute details.
Limitations of this Stage
- Few recorded policies.
- Lack of understanding of how the teams can use cloud systems.
- Excessive reliance on labor-intensive, manual tasks.
- Issues with scalability for cloud-enabled applications.
Outcomes of Stage 2
- The clarity in strategies about personnel, processes, and technology
- Identification of the appropriate techniques, standards, and architecture
- Allocation of resources for the organization’s cloud computing infrastructure
Stage 3: Migration
This stage is where the transition to the cloud starts.
The teams have the plans and can proceed with integration and transition to cloud services.
During the process, the organization might discover that the implementation plan needs a course correction as the teams start spinning up servers and moving data to remote servers.
As the plan progresses, the teams must update the stakeholders and continue their efforts to get the management’s support.
As the organization moves towards the finalization of this stage, the organization’s operations will have moved to the cloud, completing the organization’s digital transformation. Most of the infrastructure would be transferred to the cloud, along with most of the organization’s apps and data.
Limitations of this Stage
- Issues with environmental management.
- Challenges in the migration of all systems and applications.
- Manual tasks take up many resources.
Outcomes of Stage 3
- Transition to cloud achieved.
- Strong cloud management for all business processes
- The organization starts getting the benefit of cloud infrastructure
Stage 4: Optimization
A company’s initial digital transformation objectives have been achieved at this stage.
Now the organization transitions into a continuous cycle in which the teams plan and execute cloud infrastructure optimization to make it more effective.
The teams have well-maintained documentation, and new updates to processes and infrastructure are performed in accordance with established protocols rather than ad hoc or opportunistic procedures. This stage’s objectives are constantly reducing cloud costs and raising customer satisfaction.
In stage 4, Companies are actively utilizing cloud-based services.
Limitations of this Stage
- Cloud computing costs are the barrier to progressing to the next stage.
- Adoption of new features and options as the vendors release them.
Outcomes of Stage 4
- Optimized services and applications management.
- A practical approach for ongoing cost optimization.
- Customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
This article offers a comprehensive introduction to Cloud Maturity Model (CMM). We started with the introduction, offering a detailed overview of the framework. We then moved into benefits for a business and concluded with a look at the primary stages.
Frequently Asked Questions :
What is the Cloud Maturity Model (CMM)?
CMM is a detailed framework that measures an organization’s progress in adopting cloud services. This adoption is measured in the context of the business goals and the organizational attitudes toward technology adoption into the organization’s culture.
What are the applications of the Cloud Maturity Model?
Cloud Maturity Model is applied to all organizations working or looking to integrate cloud-based technologies.
Why is CMM important nowadays?
CMM offers organizations a simple framework for assessing cloud technology adoption. Given the rise of cloud computing, CMM has become an essential tool for streamlining cloud adoption.