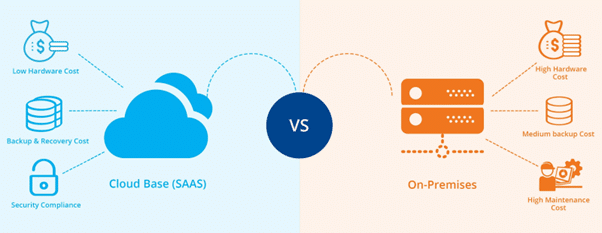
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has become indispensable for businesses to streamline their data and operations management. However, transitioning to the cloud can be daunting for many companies, especially those accustomed to traditional on-premise solutions. The decision between cloud computing vs. on-premise is not always straightforward, and here is the reason.
Each one of these models offers its own set of advantages and disadvantages. On-premise solutions provide greater control and customization, whereas cloud computing offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of both cloud computing and on-premise solutions, exploring the pros and cons of each. We will also offer practical insights and guidance for businesses seeking to make an informed decision when choosing between the two options. Whether you’re debating whether to move to the cloud or continue with on-premise solutions, you will find the knowledge you need to make a wise choice.
Table of Content
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- What is On-Premise in Cloud Computing??
- Benefits of On-Premise vs. Cloud Computing
- Differences Between Cloud Computing and On-Premise?
- Advantages of Cloud Computing and On-Premise
- Disadvantages of Cloud Computing and On-Premise
- How to Decide What to Pick?
- Moving to Cloud is Easy With RedSwitches
- Final Takeaway
- FAQ
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the supply of computing services like software, databases, analytics servers, networking, and storage through the internet. It means that you can access resources anytime via a cloud service provider rather than storing them locally.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
There are a ton of benefits of cloud computing for individuals and organizations alike. These benefits include:
- Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing allows you to scale your computing capabilities as your needs change easily. With the cloud, you can scale up your storage, computing resources, and bandwidth without purchasing hardware or installing new software.
- Cost Savings
Cloud computing can be cost-effective for businesses because it eliminates costly on-premises equipment and software requirements. Subscription models eliminate the need to invest in and maintain expensive IT infrastructure.
Since cloud computing requires less power and cooling than conventional data centers, it can also help reduce environmental impact and associated costs.
- Enhanced Mobility
You can access your files and programs from anywhere with an internet connection. It means you can collaborate with team members from different locations, even while working remotely or traveling.
- Use Cases
Businesses can tailor cloud computing to their specific requirements in several ways. For instance, companies can implement cloud storage for remote data storage, while cloud-based apps can run essential operations.
It means businesses can use cloud analytics tools to generate data-driven strategies and create apps with cloud machine learning.
Overall, cloud computing provides enterprises with many benefits and use cases that can help businesses increase their productivity and competitiveness.
What is On-Premise in Cloud Computing??
On-premises infrastructure consists of systems, hardware, and software applications. In contrast, cloud computing provides computing services via the Internet.
With an on-premises system, you can control your servers and manage their upkeep. Before the cloud computing revolution, on-premises solutions were the norm. The local storage and physical upkeep of systems are among the primary contrasts between cloud computing and on-premises.
Benefits of On-Premise vs. Cloud Computing
On-premise computing provides several benefits, including
- Greater Control and Customization
With on-premises computing, businesses own and operate all hardware, software, and data used in their operations. The ability to tailor one’s IT infrastructure to one’s requirements is invaluable, especially for businesses with unusual or specialized computing demands.
- Increased Security
Since the company is in complete charge of its data and hardware, on-premises computing is often safer than cloud computing. It’s often crucial for businesses dealing with private or personal information, such as those in the healthcare and finance sectors.
- No Internet Dependence
In the case of an Internet outage, businesses that rely on mission-critical apps and services can still run on-premise computing systems without interruption.
- Use Cases
The flexibility of on-premises computing makes it helpful in meeting a wide range of organizational requirements.
For instance, on-premises storage can store and preserve sensitive data, and on-premises apps can perform essential business activities. Industries like healthcare and finance, where compliance rules mandate local data storage, can also benefit from on-premise computing.
On-premise computing provides an impressive amount of control, security, and reliability for businesses, which could prove crucial for those with specific computing needs. Despite the popularity of cloud computing in recent years, many companies still need to rely heavily upon on-premise computing.
Differences Between Cloud Computing and On-Premise?
Image Source: Hubspot
The two primary models for overseeing data centers are cloud computing and on-premises computing. The following table compares cloud computing vs. on-premise and highlights their distinctive features.
| Feature | Cloud Computing | On-Premise |
| ● Cost | Pay-as-you-go model, minimal upfront investment. | The high upfront investment, ongoing maintenance costs. |
| ● Control | Limited control over computing resources. | Complete control over computing resources. |
| ● Compliance | Compliance requirements managed by the cloud service provider. | The organization responsible for meeting compliance requirements. |
| ● Deployment | Quick and easy deployment, accessible from anywhere. | Time-consuming deployment requires physical access to servers. |
| ● Internet Dependence | Internet connectivity is necessary for access to cloud services. | No internet connectivity is required. |
| ● Reliability | High reliability, built-in redundancy, and backup systems. | Reliability depends on the organization’s infrastructure. |
| ● Scalability | Highly scalable, can easily adjust computing resources as needed. | Limited scalability requires additional hardware and software. |
| ● Security | Security measures are provided by the cloud service provider. | The organization has complete control over security measures. |
Largely, on-premise computing provides more control, security, and compliance, whereas cloud computing provides scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Organizational requirements and available resources will determine which option is best.
Advantages of Cloud Computing and On-Premise
There are pros and cons to both cloud and on-premises computing. Here’s a table outlining the advantages of cloud computing and on-premise computing:
| Cloud Computing | On-Premise |
| ● Scalability: It allows businesses to scale up or down their computing resources as needed. It means they can easily adjust their capacity to match demand without investing in additional hardware or infrastructure. | ● Reliability: It depends on the organization’s infrastructure but eliminates the risk of internet connectivity issues disrupting resource access. |
| ● Flexibility: It enables organizations to conduct operations from any location with an internet connection, which can be helpful for mobile workforces or teams working in remote areas. | ● No internet dependence: Eliminates the need for internet connectivity to access resources, which can be important for organizations with limited or unreliable internet access. |
| ● Disaster recovery: It allows businesses to back up their data quickly and recover it in the event of a disaster. It can help ensure business continuity and prevent data loss. | ● Customization: Allows organizations to customize their infrastructure to meet their specific needs. They can choose the hardware and software they use and configure it to their liking. |
| ● Improved security: Cloud computing providers often have robust security measures to protect their clients’ data. It can be an excellent asset for SMEs who need more workforce or budget to install their security systems fully. | ● Long-term cost savings: Although on-premise computing requires a high upfront investment, it can lead to long-term cost savings as there are no ongoing cloud service fees. |
| ● Increased collaboration: It allows businesses to collaborate on projects and documents in real-time, regardless of physical location. It can improve productivity and efficiency. | ● Security: It allows organizations to have complete control over their security measures. It can be crucial for organizations that deal with sensitive data, such as healthcare providers or financial institutions. |
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing and On-Premise
While both cloud and on-premise computing have many advantages, there are also several disadvantages to consider. Here’s a table outlining their downsides:
| Cloud Computing | On-Premise Computing |
| ● Limited control: Providers maintain control over the underlying infrastructure and software, which can limit businesses’ ability to customize their systems to their specific needs. | ● Maintenance and upgrades: The systems require ongoing upgrades, which can be time-consuming and costly. |
| ● Dependence on Internet connectivity: It requires a stable and reliable Internet connection. If the internet connection is slow or disrupted, it can negatively impact the performance of cloud-based applications and services. | ● Location limitations: The systems are physically located on-site, which can limit the ability of remote teams to access data and applications. |
| ● Security concerns: It involves storing sensitive data on servers maintained by third-party providers. It can raise security concerns as businesses must trust the provider’s security measures to protect their data. There is also the risk of data breaches, which can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. | ● Disaster recovery: The systems may be more vulnerable to disasters such as fire, flood, or other natural disasters, which can result in data loss and downtime. |
How to Decide What to Pick?
There are several considerations unique to each company that you must take into account while picking between cloud computing and on-premise computing solutions. Here are some of the most important factors to think about when deciding which technology to use:
When Should You Use the Cloud?
- If your company is tight on funds and trying to avoid significant initial investments.
- If your company needs more technical expertise or resources to manage its computing systems.
- If your company plans to scale up or down its computing resources quickly.
- If your company has remote workers or workers that need to access data from several places.
When to Choose On-Premise
- If your company handles confidential information or must adhere to regulations.
- If you want to customize your IT setup to your business’s unique requirements.
- If you want to be in charge of your infrastructure and implement updates and changes whenever you see fit.
- If you need to run intensive business applications, such as video rendering or data analysis, on a powerful computer system.
While deciding between cloud and on-premise solutions, it’s essential to consider your unique business objectives and requirements. IT experts like RedSwitches can help you weigh your options and pick the most viable choice for your company.
Moving to Cloud is Easy With RedSwitches
Migrations to the cloud can be complex because of all the variables involved. Particularly in a large organization, the migration and synchronization of massive data present a formidable challenge.
Fortunately, RedSwitches cloud solutions can help simplify the migration procedure by providing tools enabling you to migrate and sync data effortlessly, rapidly, and securely. How RedSwitches can aid with cloud migration:
- Cloud Assessment
- Cloud Migration
- Cloud Hosting
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- Cloud Management
RedSwitches has the expertise to guarantee a smooth transition to the cloud and maximize your return on cloud investment.
Final Takeaway
The decision between cloud services and on-premise systems is complex and multifaceted. On-premise solutions offer greater control and customization, while cloud computing provides flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. No matter what option you take, you’ll need a dependable provider to help you make sense of the maze of today’s digital world. That’s where RedSwitches come in.
RedSwitches offers a range of solutions for cloud computing, including bare metal servers, which provide optimal performance, security, and reliability. Our servers are customizable and ideal for any cloud-based application, providing businesses with the speed and connectivity they need to succeed. Omnichannel assistance and customizable payment plans are just some things that set us apart from the competition.
No matter where your company does business, RedSwitches is a dependable cloud service provider. Check out our resources section for more information on cloud computing vs. on-premises systems and how our bare metal servers can add value to your business.
FAQ
Q: What are the key differences between on-premise and cloud?
A: The key differences between on-premise and cloud are infrastructure location, ownership responsibilities, and cost structure. On-premise refers to having physical servers and infrastructure within the organization’s premises, while cloud computing relies on remote servers and is accessible over the Internet.
Q: What is a hybrid cloud?
A: A hybrid cloud is a combination of on-premise and cloud environments. It allows organizations to keep some data and applications on-premise while leveraging the benefits of the cloud for specific functions or workloads.
Q: What is on-premise to cloud migration?
A: On-premise to cloud migration refers to the process of moving data, applications, and infrastructure from an on-premise environment to the cloud. This migration can involve transferring physical servers, virtual machines, and databases to a cloud service provider.
Q: What is a private cloud?
A: A private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization. It is usually hosted on-premise and offers more control, security, and customization options compared to public clouds.
Q: What is a public cloud?
A: A public cloud is a cloud computing environment where resources and services are shared among multiple organizations. These resources are owned and managed by a third-party cloud provider and accessed over the internet.
Q: What are the pros and cons of on-premise and cloud?
A: The pros of on-premise computing include control over infrastructure, data security, and compliance. However, it requires upfront investment ongoing maintenance, and may have limited scalability. In contrast, cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, but organizations have less control over infrastructure and data security.
Q: What is cloud software?
A: Cloud software, also known as Software as a Service (SaaS), refers to applications and software that are accessed over the internet from a cloud provider’s servers. Users do not need to install or maintain the software locally, as it is hosted in the cloud and accessed on-demand.
Q: What is cloud infrastructure?
A: Cloud infrastructure refers to the hardware and software components that are necessary to provide cloud computing services. It includes servers, storage, networking equipment, virtualization software, and management tools.
Q: What is the difference between on-premise and cloud?
A: The main difference between on-premise and cloud is the ownership and management responsibilities. With on-premise, organizations need to purchase and maintain their own physical servers and infrastructure, while in the cloud, the cloud provider is responsible for maintaining and managing the infrastructure.
Q: What are the key differences between on-premise and cloud computing?
A: The key differences between on-premise and cloud computing are the location of infrastructure, deployment model, ownership model, and resource allocation. On-premise computing refers to having infrastructure and applications running locally, while cloud computing involves accessing resources and services over the internet from a cloud provider.