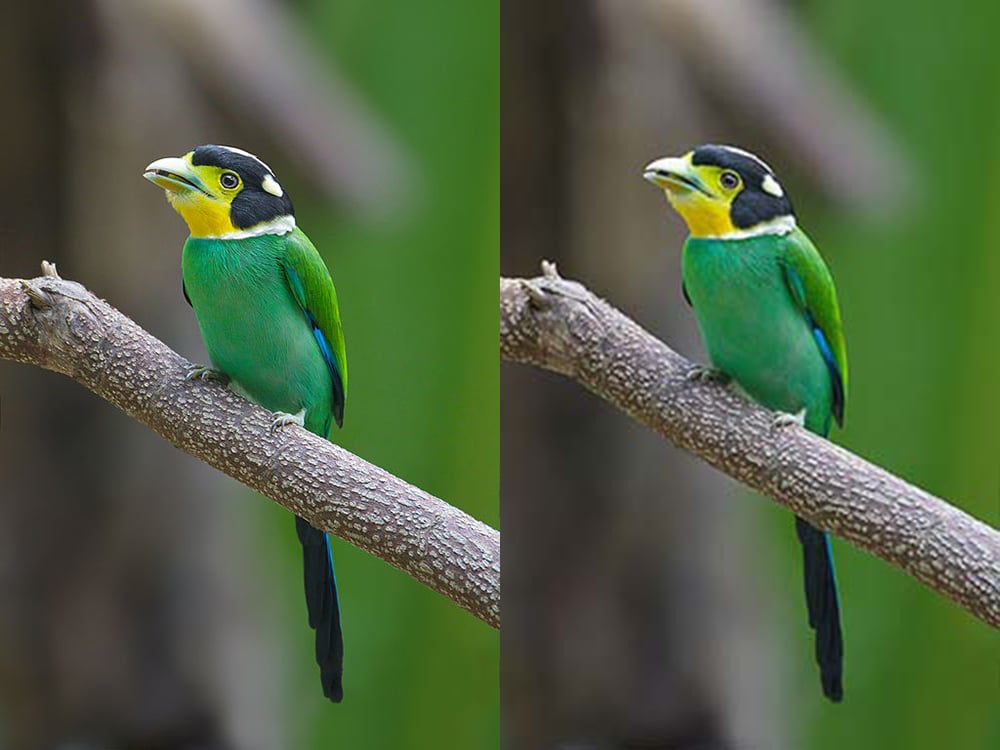
Key Takeaways
- Compression is key for managing digital files, making them easier to store and send.
- Lossy compression shrinks files by removing some data, trading off some quality for size.
- Lossless compression keeps every detail, making files smaller without losing quality.
- For quick streaming and downloads, lossy compression is the way to go due to smaller file sizes.
- Choose lossless compression when every detail counts, like in medical images or high-quality audio.
- Lossy formats, like JPEG and MP3, are great for everyday use and are supported everywhere.
- Lossless formats, such as PNG and FLAC, are perfect for preserving quality in professional fields.
- Repeatedly editing lossy files can lower their quality over time, a process called “generation loss.”
- Choosing between lossy and lossless depends on your quality, speed, and file size needs.
- RedSwitches offers hosting solutions that support both compression types for various digital projects.
Today, knowing about “lossy vs lossless” compression is important. It affects how we enjoy videos and music online. Did you know? Almost 92.3% of people worldwide watch videos on the internet every week. This includes music videos, tutorials, and lots more. That shows how much we love streaming and why knowing about compression is key. It helps us get the best quality without too much storage or internet data.
As we delve deeper into digital media, the nuances of “lossy vs lossless” compression become crucial in understanding why some videos stream flawlessly while others stutter or why specific music files sound crystal clear instead of others that are noticeably different. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a digital content creator, or someone who loves streaming media, unlocking the secrets of “lossy vs lossless” compression is your key to a richer, more informed digital experience.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is File Compression?
- What Is Lossy Compression?
- What Is Lossless Compression?
- What’s the Difference Between Lossy and Lossless Compression?
- Quality Preservation: Lossy vs Lossless
- File Size: Lossy vs Lossless
- Usage in Professional Fields: Lossy vs Lossless
- Recompression Impact: Lossy vs Lossless
- Data Retrieval: Lossy vs Lossless
- Bandwidth and Storage Requirements: Lossy vs Lossless
- Examples of File Formats: Lossy vs Lossless
- Editability and Archiving: Lossy vs Lossless
- Real-time Streaming and Loading: Lossy vs Lossless
- Complexity and Processing Power: Lossy vs Lossless
- Lossy vs Lossless: Which One Is Better?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is File Compression?
Credits: Wikimedia
At its core, file compression is a method used to reduce the size of a file, making it easier and faster to store, transmit, and manage. It’s a cornerstone technology in our digital world, where handling large amounts of data efficiently is paramount. File compression works by eliminating redundancies and optimizing data representation.
Imagine a book where some phrases are repeated hundreds of times. If we replace these repeated phrases with shorter symbols and provide a key to understanding these symbols, the book becomes much shorter. Similarly, file compression algorithms identify patterns and redundancies in data and replace them with more efficient representations.
There are two main types of file compression: lossy and lossless. Each serves different purposes and is chosen based on the specific data storage and transmission needs.
- Lossy Compression: This method significantly reduces file size by permanently eliminating certain information, particularly details that are less noticeable to the human senses. It’s widely used in audio, video, and image files where a slight loss in quality is acceptable for a substantial size reduction.
- Lossless Compression: As the name suggests, this method compresses data without any loss of information. It is essential in applications where even minor data loss, such as text files or particular image and audio formats, is unacceptable.
Understanding file compression, especially the differences and applications of “lossy vs lossless” compression, is crucial in various fields, from web development and digital art to data science and everyday digital media use.
What Is Lossy Compression?
Lossy compression is a data reduction method pivotal in interacting with digital media. This type of compression works by removing parts of the data deemed less critical, significantly reducing file size. However, this comes at the cost of a decrease in the quality of the compressed file.
To understand lossy compression, think of it as a skilled artist who creates a simplified sketch of a detailed scene. The artist retains the essential elements that define the scene but omits finer, less noticeable details. Similarly, lossy compression algorithms analyze data and discard elements less critical to human perception.
Also, Read How to Zip a File in Linux
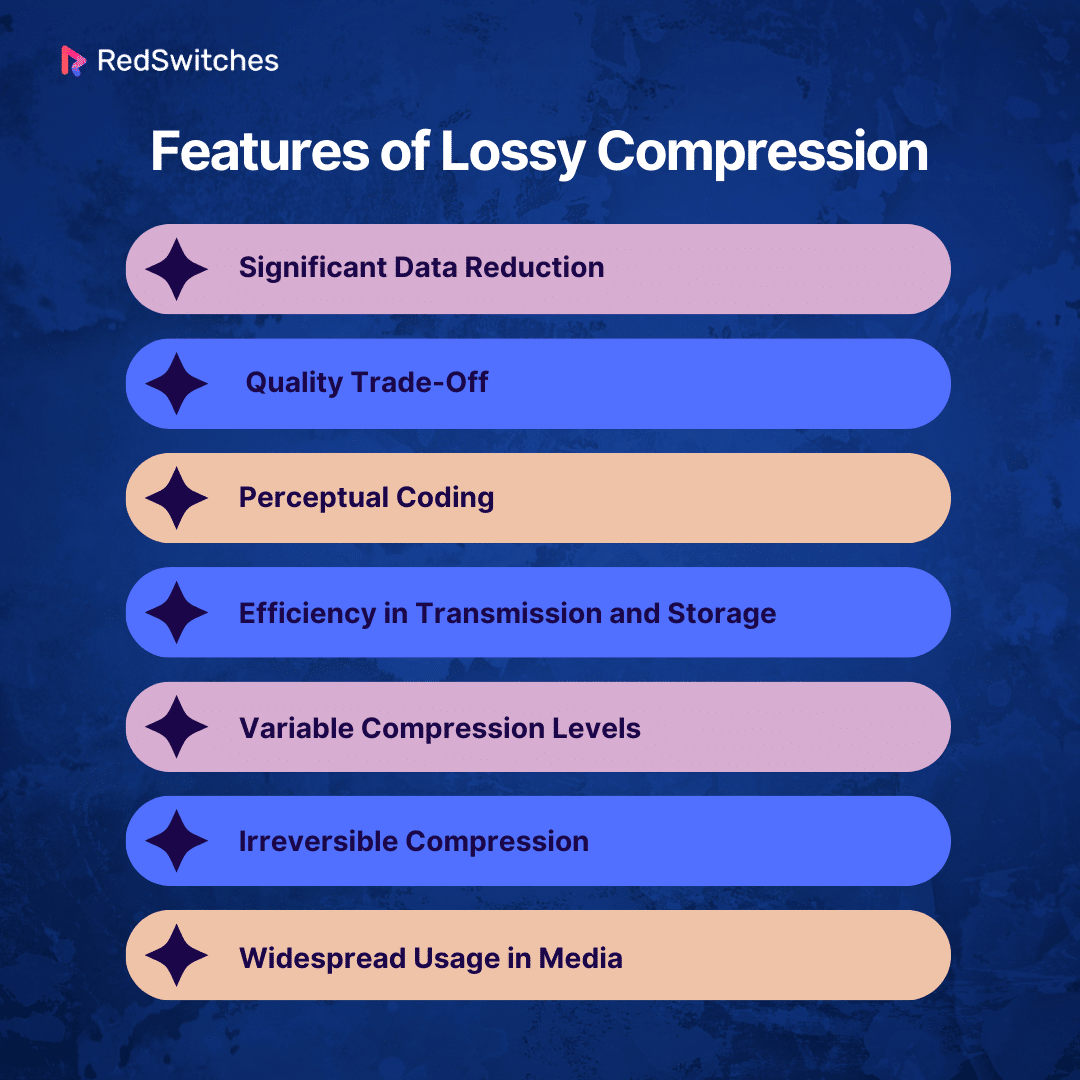
Features of Lossy Compression
When discussing “lossy vs lossless” compression, it’s essential to understand the distinctive features of lossy compression. These features define its functionality and suitability for various applications in the digital world:
- Significant Data Reduction: Lossy compression can shrink down file sizes. It does this by eliminating parts of the data that seem less important. This helps save space.
- Quality Trade-Off: There’s a trade-off between how small the file gets and how good it looks or sounds. More compression makes files smaller but might lower their quality. Finding the right balance is key.
- Perceptual Coding: This compression uses smart tricks to determine what data to drop based on what humans can’t easily see or hear. For example, it might remove sounds too high or low for us to hear.
- Efficiency in Transmission and Storage: With smaller files, sending data over the internet is easier and faster than storing lots on a hard drive or phone.
- Variable Compression Levels: You can choose how much to compress a file, depending on what you need for quality and size.
- Irreversible Compression: Once you compress a file with lossy, you can’t regain the removed data. It’s a permanent change.
- Widespread Usage in Medi This compression is popular for things like photos (JPEG), music (MP3), and videos (MPEG). Because it keeps them at a good enough quality while making them easier to share and store.
Knowing these points helps when you need to decide on how to compress and save files. Especially when trying to balance quality with how much space they take. Whether to use lossy or lossless compression depends on what’s more important for your situation: size or quality.
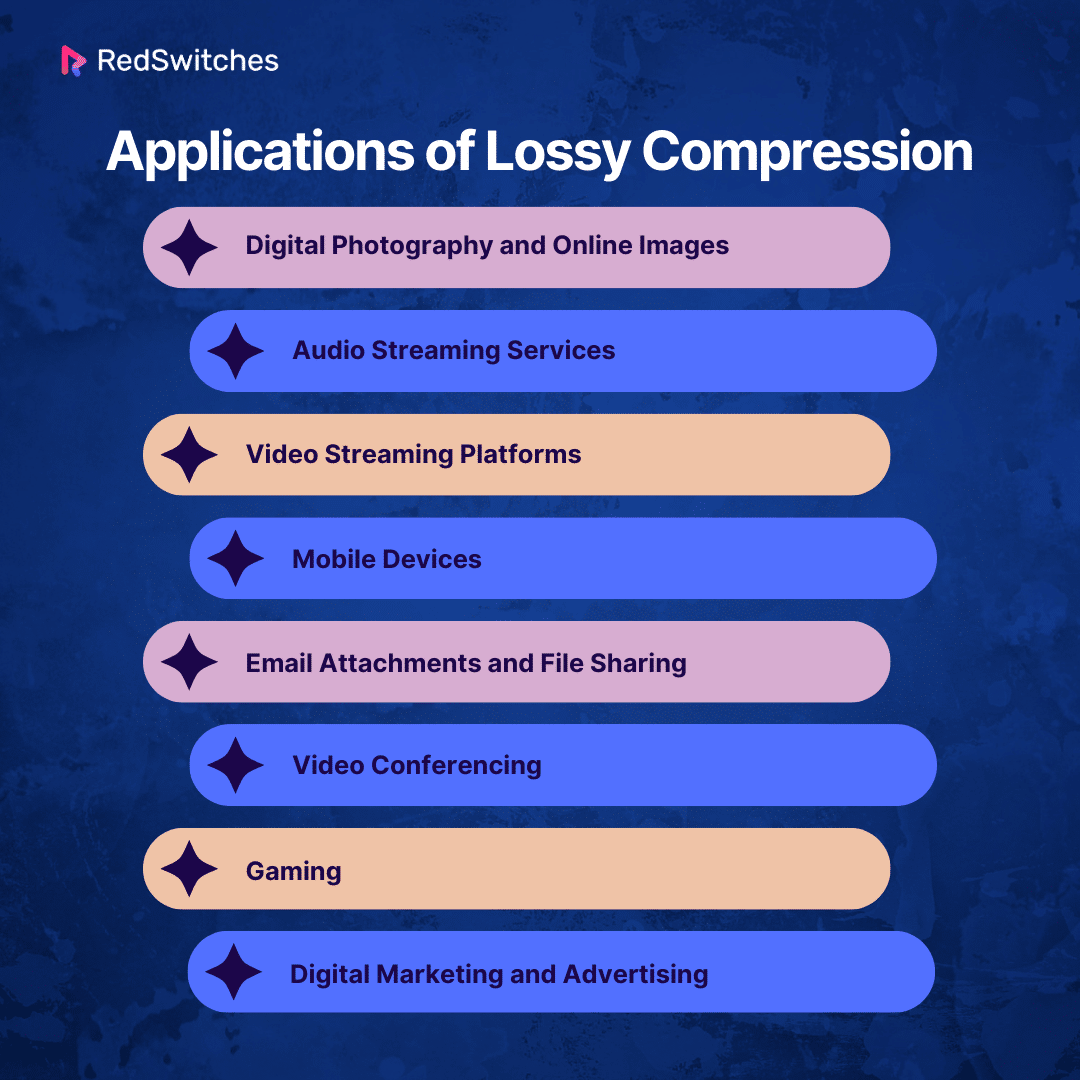
Applications of Lossy Compression
Lossless compression is super important when you need to keep all the original details and quality of your data. Here’s where it’s really useful:
Medical Imaging:
Doctors need everything clear in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans for accurate health checks. Lossless compression keeps these pictures perfect.
Professional Photography and Graphics:
Artists and designers use formats like TIFF or PNG. This way, their work stays sharp and clear for editing, printing, and saving.
Audio Production:
Music lovers and pros prefer formats like FLAC and ALAC to keep songs sounding great, just like the original recordings.
Data Archiving:
Libraries and schools must save documents without losing any information. Lossless compression helps with this.
Software Development:
Coders compress their work to share without messing up anything. ZIP is a go-to format for this. Formats like ZIP are commonly used for compressing software files and making them easier to distribute.
Scientific Research:
Researchers in space, earth sciences, and weather studies need their data intact for accurate analysis. Lossless keeps it real and reliable.
Legal and Financial Documents:
In law and finance, every word matters. Lossless compression keeps documents complete and unchanged
Internet and Web Development:
PNG is the top choice for sharp and clear website graphics, like logos with see-through backgrounds.
Keeping data just as it was originally is key in all these areas. That’s why lossless compression is chosen for its ability to save things perfectly, even if it means the files stay a bit bigger.
Pros and Cons of Lossy Compression
In the “lossy vs lossless” compression debate. Understanding the advantages and drawbacks of lossy compression is crucial. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons:
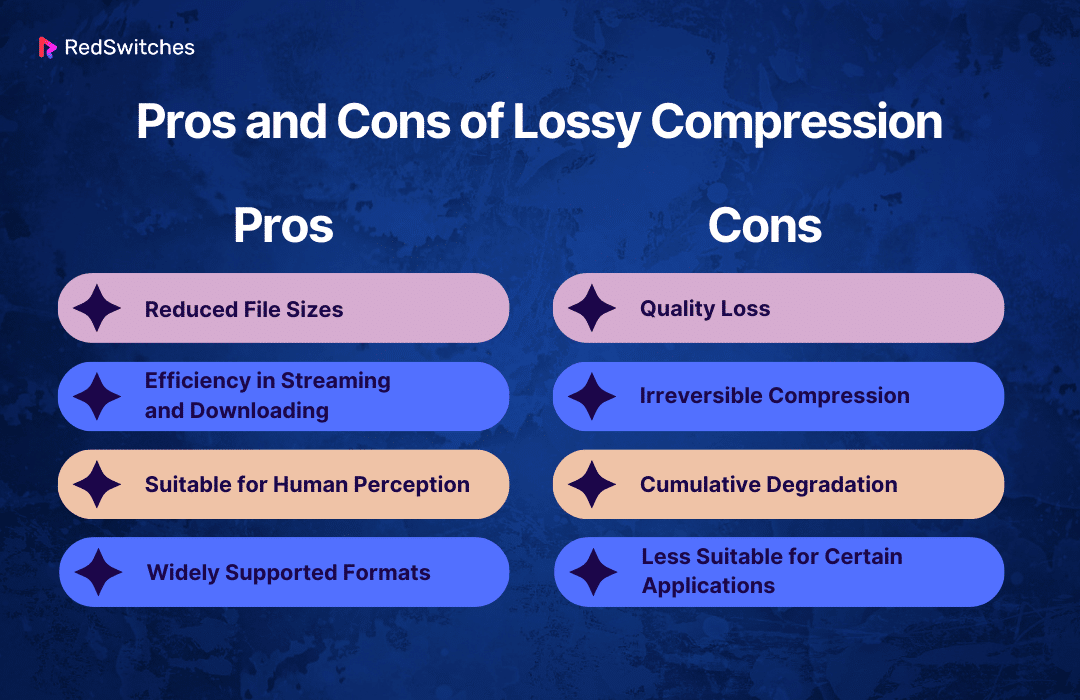
Pros of Lossy Compression:
- Reduced File Sizes: The most significant advantage of lossy compression is its ability to reduce file sizes. It drastically facilitates more accessible storage and faster transmission.
- Efficiency in Streaming and Downloading: Lossy compressed files are ideal for streaming and downloading content. This is used over the internet due to their smaller size, which requires less bandwidth.
- Suitable for Human Perception: Since lossy compression algorithms remove data less likely to be perceived by human senses. The quality loss is often unnoticeable or acceptable to the average user, particularly in audio and visual media.
- Widely Supported Formats: Lossy formats like JPEG for images and MP3 for audio are universally supported across devices and platforms, making them highly versatile.
Cons of Lossy Compression:
- Quality Loss: The most evident drawback is the loss of quality. This loss can become noticeable and potentially problematic in high compression ratios, especially for professional photography and audio production use.
- Irreversible Compression: A lossy method cannot recover the discarded data once a file is compressed. This irreversible process means original quality can never be restored if needed.
- Cumulative Degradation: Repeated editing and saving of lossy compressed files lead to cumulative quality degradation, often called “generation loss.”
- Less Suitable for Certain Applications: For applications requiring precise data integrity (like medical imaging or scientific data), lossy compression is unsuitable due to inherent data loss.
Understanding these pros and cons is essential when deciding whether to use lossy compression. The decision often hinges on balancing the need for reduced file size and the acceptable level of quality loss for the intended use.
Also, Read The unzip Command in Linux
What Is Lossless Compression?
In the context of “lossy vs lossless” compression, lossless compression stands out for its ability to reduce file sizes without sacrificing data quality. This method is vital in scenarios where preserving the original data is crucial. Unlike lossy compression, lossless compression ensures that the original data can be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data.
Lossless compression efficiently encodes data, eliminating redundancies without discarding any part of the content. Think of it like a complex puzzle where every piece is essential; lossless compression finds a more compact way to arrange these pieces without losing or altering them.
Features of Lossless Compression
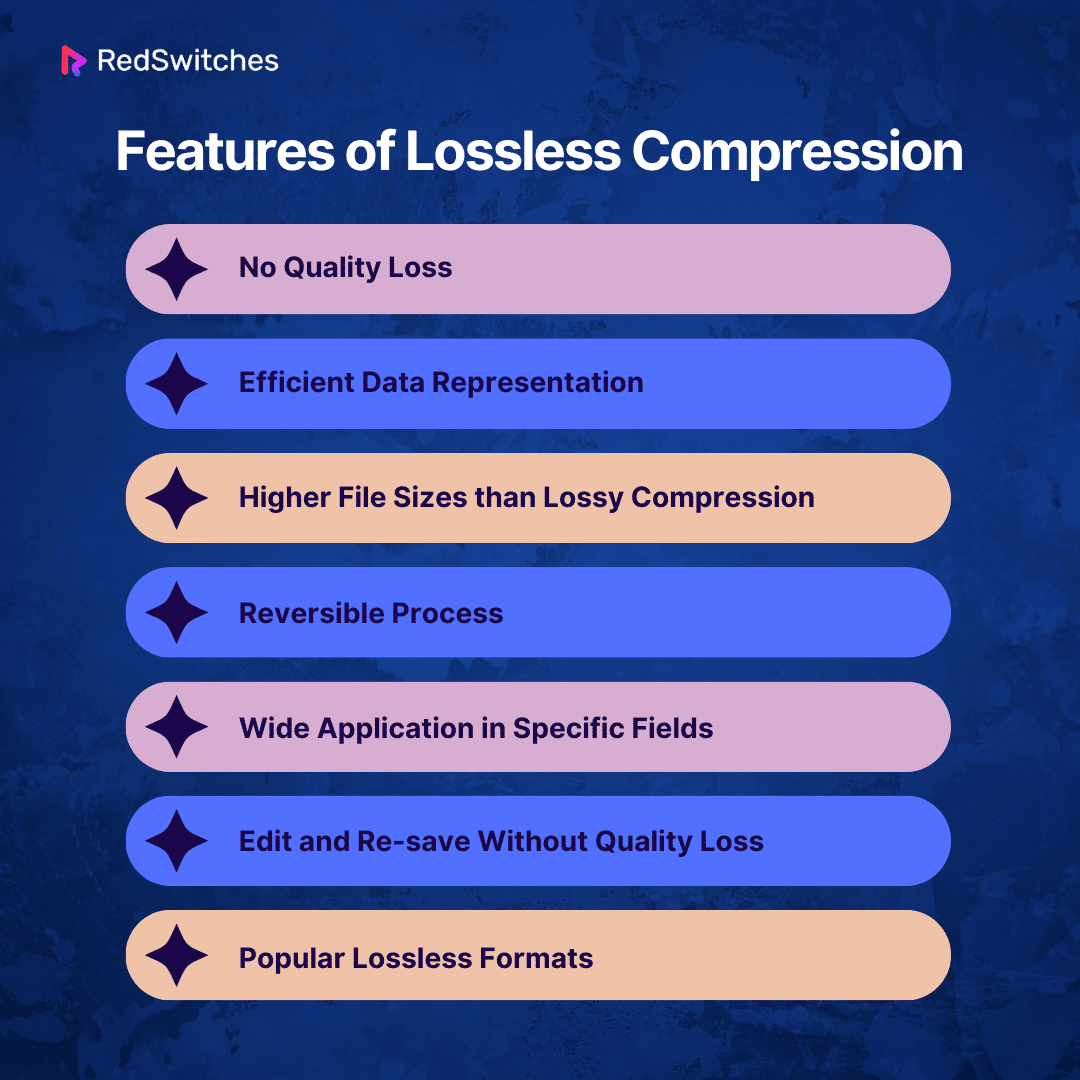
When we talk about “lossy vs. lossless” compression, lossless compression stands out for keeping data intact. Here’s what makes it special:
- No Quality Loss:
You can return your original data perfectly with lossless compression. It’s key when you can’t afford to lose any details. - Efficient Data Representation:
This method finds and cuts out repeat data, making storage smarter without dropping any content. It uses clever techniques like Huffman coding or LZW compression. - Higher File Sizes than Lossy Compression:
Though it shrinks data sizes from the original, lossless files are still bigger than lossy ones. They keep everything from the original data. - Reversible Process:
Unlike lossy compression, lossless compression is reversible. The original data can be perfectly and completely restored from the compressed file. - Wide Application in Specific Fields:
In areas where every detail matters, like medical images, science research, and keeping records safe, lossless is vital. - Edit and Re-save Without Quality Loss:
You can change and save files repeatedly without harming the quality, unlike with lossy compression. - Popular Lossless Formats:
Common lossless formats include PNG and TIFF for images, FLAC and ALAC for audio, and ZIP for file archives.
Knowing these points helps choose the right compression method. Your choice between lossy and lossless depends on what you need: keeping every detail or saving space.
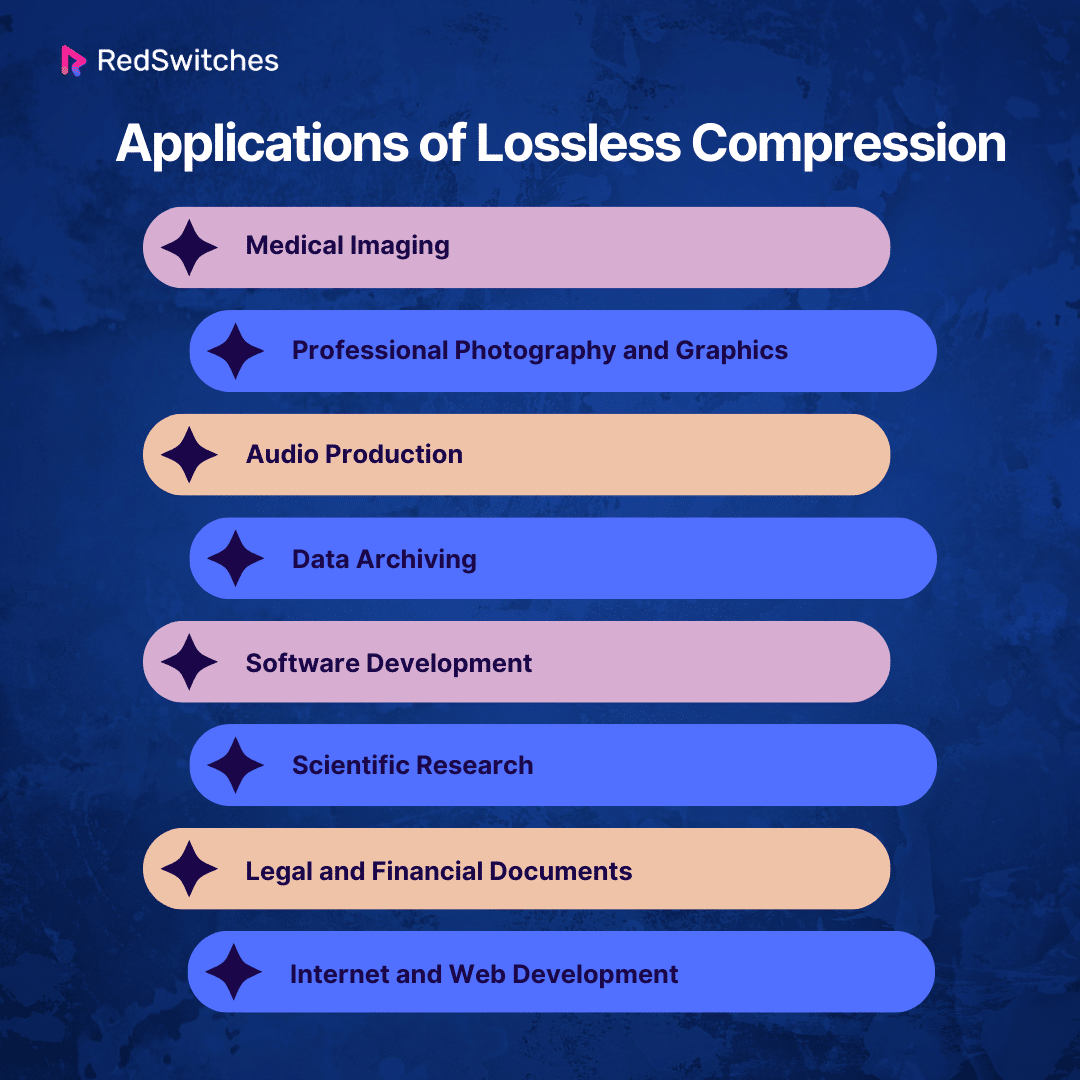
Applications of Lossless Compression
In the “lossy vs. lossless” debate, lossless compression is key when you need to keep all the original details. Here’s where it really matters:
Medical Imaging:
Doctors need every detail in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans for correct diagnoses. Lossless compression makes sure no detail is lost.
Professional Photography and Graphics:
Photographers and designers use formats like TIFF or PNG. These keep pictures sharp for editing, printing, and saving.
Audio Production:
For clear sound, professionals and music lovers choose lossless formats like FLAC and ALAC. This keeps recordings crisp and clean.
Data Archiving:
Libraries and research centers must save documents and data without losing anything. Lossless compression helps keep these records intact.
Software Development:
Coders compress their code and files with lossless methods to keep them working right. ZIP is a popular choice.
Scientific Research:
Scientists in many fields, like space or earth science, use lossless compression. It ensures their hard-earned data stays accurate for analysis.
Legal and Financial Documents:
Accuracy is key in legal and finance documents. Lossless compression keeps these documents complete and unchanged.
Internet and Web Development:
Websites often need clear graphics, like logos. Lossless PNG is great for this, keeping images sharp
Lossless compression is a must in these areas, where losing any detail isn’t an option. Using it often comes down to needing quality and detail over saving space.
Also, Read SCP Command in Linux [13 Examples Inside!]
Pros and Cons of Lossless Compression
In the discussion of “lossy vs lossless” compression, it’s essential to understand the advantages and drawbacks of lossless compression. These factors determine its suitability for various applications.
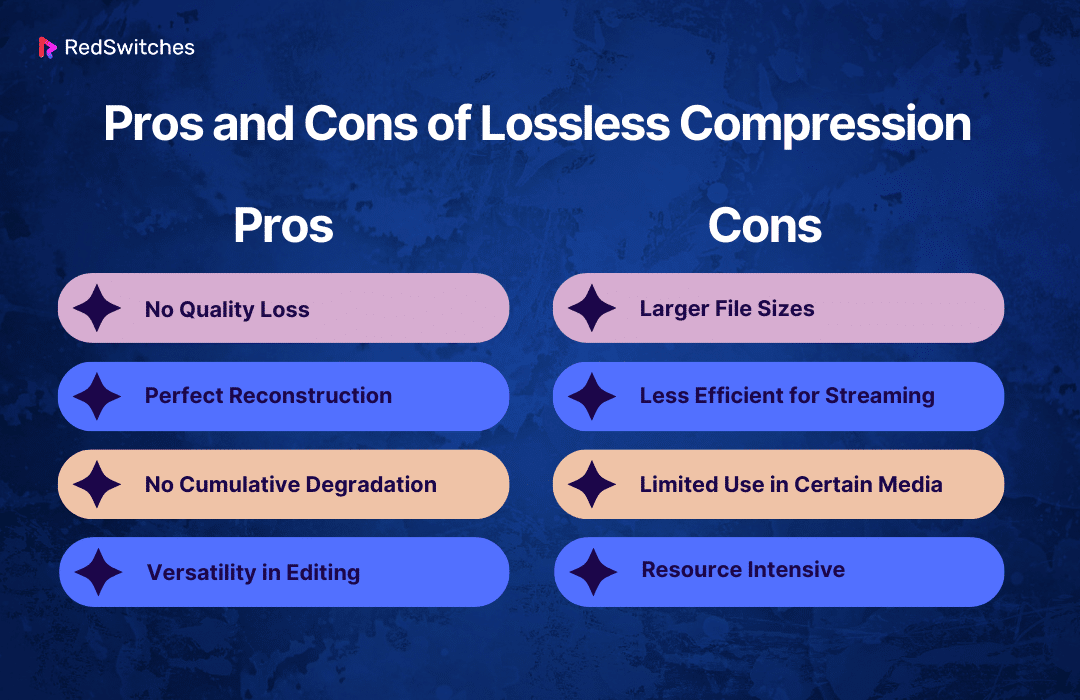
Pros of Lossless Compression:
- No Quality Loss: The primary advantage of lossless compression is preserving the original data’s quality. All information is retained, which is crucial in applications where accuracy and detail are paramount.
- Perfect Reconstruction: Lossless compression allows for the exact original data to be reconstructed from the compressed file. This is essential for archival purposes and applications where data integrity is critical.
- No Cumulative Degradation: Unlike lossy compression, editing and re-saving files in a lossless format do not degrade their quality, even over multiple iterations.
- Versatility in Editing: Lossless formats are ideal for files needing to be frequently edited and saved, as they prevent quality degradation with each modification.
Cons of Lossless Compression:
- Larger File Sizes: Lossless compression results in larger file sizes than lossy compression. This can be a significant drawback when dealing with limited storage space or bandwidth.
- Less Efficient for Streaming: The larger file sizes of losslessly compressed data make it less suitable for streaming applications, especially where bandwidth is a concern.
- Limited Use in Certain Medi For some media types, especially where high resolution is not a priority, lossy compression’s efficient storage and transmission benefits often outweigh the need for the perfect quality of lossless compression.
- Resource Intensive: Lossless compression and decompression can require more processing power and time, which might be a limitation for some users or devices.
Understanding these pros and cons helps make an informed decision about using lossless compression. The choice often depends on the specific requirements of the task, balancing the need for preserving data quality with considerations of file size and processing efficiency.
What’s the Difference Between Lossy and Lossless Compression?
Credits: Vector from Freepik.
Diving into the digital realm, one frequently encounters “lossy” and “lossless,” especially when dealing with media files like images, audio, and video. But what exactly sets these two apart? At a glance, they both serve the same purpose – to make files smaller and more manageable.
However, the way they achieve this and the implications of their methods mark the critical differences that can significantly impact both the quality of media and its usability. In the “lossy vs lossless” compression debate, understanding these differences is key to making the right choice for your digital needs.
Quality Preservation: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
One of the most crucial aspects in the “lossy vs lossless” comparison is how each method handles quality preservation.
Lossy Compression and Quality:
- Quality Loss: Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently removing certain data. This inevitably leads to a loss of quality.
- Perceptual Considerations: It often leverages human perceptual limitations, removing parts of the data less likely to be noticed, such as subtle sound frequencies or minor color variations.
- Application Sensitivity: The degree of quality loss can be acceptable in many applications, like online streaming or casual photography, but problematic in professional settings requiring high fidelity.
Lossless Compression and Quality:
- Integrity of Data: Lossless compression maintains the original quality of the data, enabling perfect reconstruction of the original file from the compressed version.
- Importance in Precision-Required Fields: This is critical in areas where data integrity is paramount, such as medical imaging, scientific data, and archival preservation.
- Consistency in Quality: Unlike lossy compression, lossless does not suffer from quality degradation with repeated editing and saving.
In essence, finding out what is lossless and lossy compression in terms of quality preservation depends mainly on the requirements of the task at hand and the acceptable level of quality loss.
File Size: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
Another critical difference between lossy and lossless compression is the impact each has on file size.
Lossy Compression and File Size:
- Significant Reduction: Lossy compression is known for drastically reducing file sizes. This is achieved by removing parts of the data that are deemed less critical.
- Ideal for Limited Storage/Bandwidth: The smaller file sizes are particularly advantageous for online streaming, email attachments, and storing large quantities of data where space is a constraint.
Lossless Compression and File Size:
- Moderate Reduction: Lossless compression reduces file sizes compared to the original uncompressed state, but the reduction is not as substantial as with lossy compression.
- Balancing Size with Fidelity: The larger file sizes resulting from lossless compression are a trade-off for maintaining data integrity. This makes it less suitable for limited bandwidth and storage but ideal for scenarios requiring complete data preservation.
The decision between lossy and lossless compression in file size management balances the need for compact file storage and preserving original data quality.
Also Read The Best WordPress Cache Plugins of 2023
Usage in Professional Fields: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
The choice between lossy and lossless compression often hinges on professional requirements and industry standards.
Lossy Compression in Professional Fields:
- Media and Entertainment: In industries like film and music, lossy compression is often used for final distribution due to its balance of quality and file size, which is essential for streaming services and digital downloads.
- Web Development: Lossy compressed images are prevalent in web design, optimizing loading speeds while maintaining acceptable visual quality.
- Journalism and Blogging: For online articles and blogs, lossy compression helps load images and videos quickly, essential for maintaining user engagement.
Lossless Compression in Professional Fields:
- Medical Imaging: Lossless compression is crucial in medical fields to ensure diagnostic images retain all their detail and accuracy.
- Archival and Libraries: Lossless compression is preferred to ensure data integrity over time for preserving historical documents and digital archiving.
- Scientific Research: Lossless is critical in scientific research, where every bit of data can be vital for analysis and conclusions.
The use of lossy or lossless compression in professional fields largely depends on the industry’s specific needs, balancing factors like file size efficiency and the necessity for high-quality, unaltered data.
Recompression Impact: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
Understanding the impact of recompression is vital when choosing between lossy and lossless compression.
Recompression with Lossy Formats:
- Cumulative Quality Degradation: Each time a lossy compressed file is edited and re-saved, it undergoes further quality degradation, known as generation loss. This can be problematic over time, especially for files that require frequent edits.
- Not Ideal for Editing Purposes: Due to this cumulative degradation, lossy formats are not recommended for files that need regular updating or editing.
Recompression with Lossless Formats:
- Consistent Quality Maintenance: Lossless compression allows files to be edited and re-saved without any loss of quality. The data remains intact, regardless of how often the file is re-compressed.
- Preferred for Edit-Intensive Tasks: Lossless compression is ideal for tasks involving frequent modifications, such as graphic design or audio editing projects.
The impact of recompression is a critical factor to consider, especially in fields where files are subject to frequent edits and updates. While efficient in size reduction, Lossy compression can compromise quality over time, whereas lossless maintains quality consistency.
Data Retrieval: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
The efficiency of data retrieval is another crucial aspect in the “lossy vs lossless” comparison, especially when considering the time and resources needed to access and use the compressed data.
Data Retrieval with Lossy Compression:
- Faster Retrieval Times: Due to smaller file sizes, lossy compressed files can be accessed and transmitted more quickly. This is beneficial in scenarios where speed is a priority.
- Potential Quality Compromise: While the retrieval process is efficient, the data quality may not be suitable for all purposes, especially where fine details are essential.
Data Retrieval with Lossless Compression:
- High-Quality Retrieval: Lossless compression ensures the retrieved data maintains its original quality, which is vital in fields where precision is non-negotiable.
- Slower Retrieval Times: The larger file sizes can result in slower retrieval times, especially in environments with limited bandwidth or processing power.
Data retrieval efficiency varies significantly between lossy and lossless compression, with trade-offs between speed and data quality playing a pivotal role in determining the appropriate method for specific applications.
Bandwidth and Storage Requirements: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
Bandwidth and storage constraints are critical factors in deciding between lossy and lossless compression.
Bandwidth with Lossy Compression:
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: The smaller file sizes of lossy compressed files consume less bandwidth, making them ideal for streaming and online use where bandwidth may be limited.
- Efficient for High-Volume Transmission: This efficiency is crucial for platforms that handle high data transmission volumes, like social media and video streaming services.
Bandwidth with Lossless Compression:
- Higher Bandwidth Demand: Lossless compression, with its larger file sizes, requires more bandwidth for transmission, which can be a limiting factor in bandwidth-constrained environments.
- Selective Use in High-Bandwidth Scenarios: Its use is often reserved for scenarios with high bandwidth, and data quality is a primary concern.
Storage Requirements:
- Lossy Compression: The significantly smaller size of lossy compressed files makes them more storage-efficient, a key consideration in environments with limited storage capacity.
- Lossless Compression: The larger size of losslessly compressed files demands more storage space, making it less suitable for environments where storage capacity is a constraint but ideal for applications where data preservation is critical.
In summary, bandwidth and storage requirements significantly influence the choice between lossy and lossless compression. While lossy compression is more efficient regarding bandwidth and storage space, lossless compression is indispensable when data integrity and quality cannot be compromised.
Also Read What is Website Bandwidth & How Much Do I Need For My Site?
Examples of File Formats: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
Understanding the examples of file formats used in lossy and lossless compression helps recognize their applications and limitations.
Lossy Compression Formats:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Widely used for digital photography and online images, JPEG is known for its efficient compression and flexibility in balancing quality and file size.
- MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III): A standard for audio compression, MP3 is ubiquitous in digital music due to its ability to reduce file sizes significantly while retaining a quality acceptable for most listeners.
- MPEG-4: Common in video streaming, MPEG-4 compresses video files efficiently, making it suitable for online distribution and playback.
Lossless Compression Formats:
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): Images requiring high detail and transparency, like logos and graphics, are ideal. PNG provides lossless compression, ensuring no quality loss.
- FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec): Preferred for high-fidelity audio storage, FLAC compresses without losing audio quality, making it popular among audiophiles and professionals.
- ZIP: Used for archiving and transmitting files and folders, ZIP allows for lossless compression of various data types, ensuring the integrity of the compressed content.
These formats illustrate the diverse applications of lossy and lossless compression in digital media, highlighting their respective strengths and suitability for different types of content.
Editability and Archiving: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
Editability and suitability for archiving are essential considerations in the “lossy vs lossless” comparison.
Editability:
- Lossy Compression: Not ideal for files that require frequent editing. Repeated editing and saving can lead to cumulative quality degradation (generation loss).
- Lossless Compression: Preferred for files that undergo regular edits. Lossless formats allow for editing and saving without any loss of quality, maintaining the integrity of the original data.
Archiving:
- Lossy Compression: While it saves space, it’s not typically recommended for long-term archiving due to quality loss, which can be significant over time or generational degradation.
- Lossless Compression: The go-to choice for archiving, ensuring that files are preserved in their original state. This is essential for historical records, legal documents, and any data where preservation of original quality is crucial.
The choice between lossy and lossless compression for editing and archiving hinges on the balance between storage efficiency and maintaining data quality and integrity.
Real-time Streaming and Loading: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
In digital media, real-time streaming and loading efficiency is a critical factor influenced by the choice between lossy and lossless compression.
Real-time Streaming with Lossy Compression:
- Optimized for Speed: Lossy compression’s smaller file sizes are ideal for real-time audio and video streaming. This efficiency is crucial for platforms like Netflix and Spotify, where quick buffering and smooth playback are essential.
- Wide Usage in Online Medi Most online streaming services use lossy compression to deliver content efficiently, balancing quality with internet bandwidth constraints.
Loading Efficiency with Lossless Compression:
- Potential for Slower Loading: Due to larger file sizes, lossless compressed files can take longer to load, which might not be suitable for real-time streaming applications.
- Selective Use in High-Quality Streams: Lossless compression is used when the highest quality is necessary and bandwidth is not limiting, such as in professional music streaming or high-definition video platforms.
The real-time streaming and loading efficiency significantly influences the user experience, choosing between lossy and lossless compression pivotal in these applications.
Complexity and Processing Power: Lossy vs Lossless
Credits: Freepik
The complexity of the compression algorithm and the required processing power are essential considerations in the “lossy vs lossless” decision.
Complexity in Lossy Compression:
- Less Processing Intensive: Generally, lossy compression algorithms are less complex and require less processing power. This makes them suitable for devices with limited computational capabilities.
- Faster Compression and Decompression: The relative simplicity allows for quicker compression and decompression, which is beneficial for real-time applications like video conferencing and online streaming.
Processing Power with Lossless Compression:
- Higher Computational Demand: Lossless compression algorithms are often more complex and require more processing power. This can be a consideration for devices with limited resources.
- Balanced Use in High-Capacity Systems: Lossless compression is more common in systems where computational power is not a constraint, such as servers or high-end workstations.
Also read CyberPanel vs cPanel: Which Is The Top Hosting Control Panel?
The complexity of compression algorithms and the associated processing power requirements play a significant role in determining the suitability of lossy and lossless compression for different technological environments and applications.
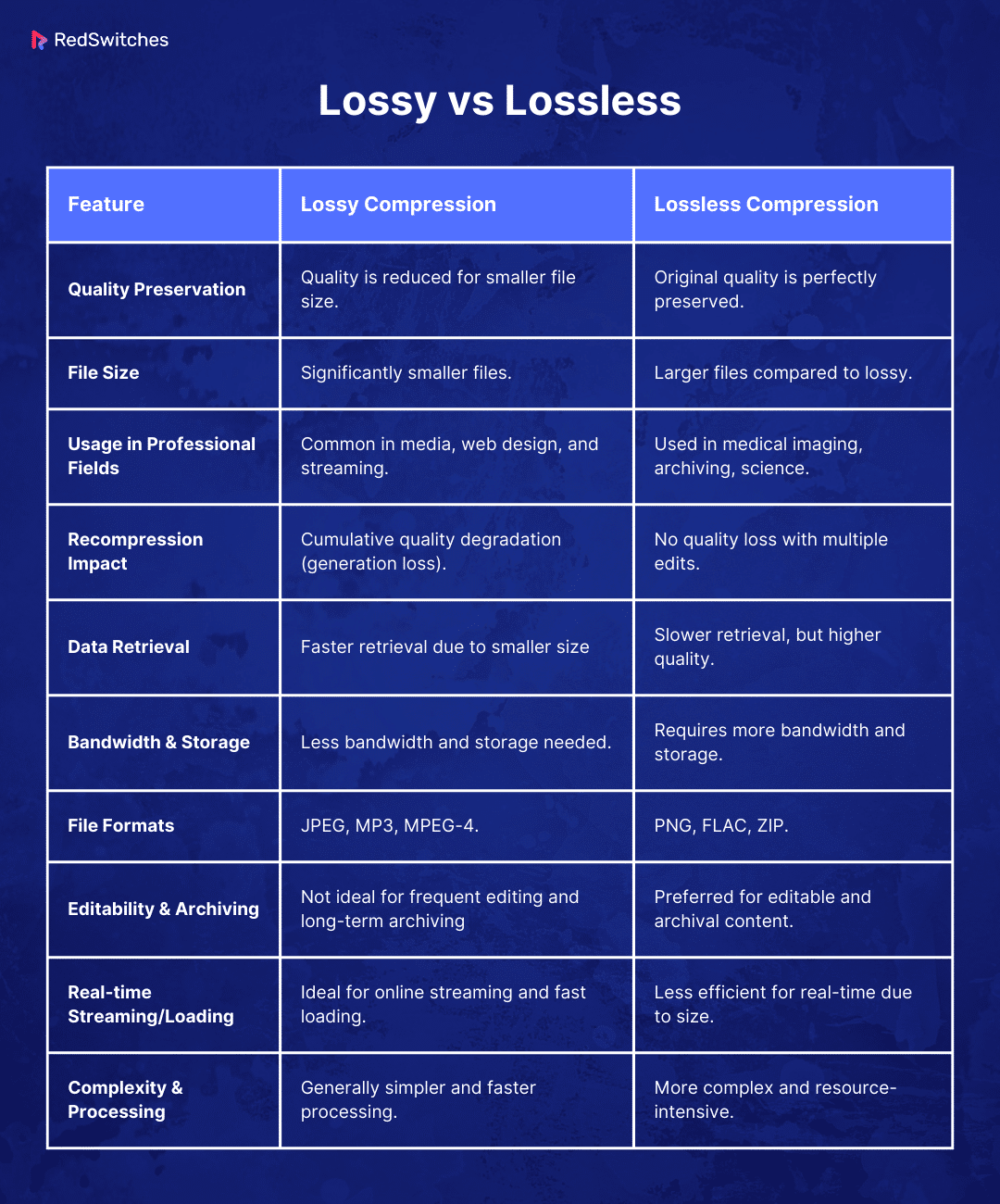
Here is the Comparison Summary Table: Lossy vs Lossless Compression
Lossy vs Lossless: Which One Is Better?
Deciding whether lossy or lossless compression is “better” depends largely on the specific requirements and constraints of the situation. The “lossy vs lossless” debate is not about finding a one-size-fits-all answer but rather understanding which method best aligns best with the needs of the task.
Considerations for Choosing Lossy Compression:
- When Speed and Efficiency Are Key: Choose lossy compression for scenarios where file size and quick transmission are crucial, such as in online streaming, web imaging, or bandwidth limitations.
- Acceptable Quality Trade-Off: If quality reduction is acceptable for the end-use, lossy compression can provide the necessary efficiency.
Considerations for Choosing Lossless Compression:
- When Quality Cannot Be Compromised: Opt for lossless compression in professional or technical fields where every detail matters, such as medical imaging, archival data, or high-quality audio production.
- Requirement for Editing and Archiving: Lossless is the choice for data that will be frequently edited or needs to be archived in its original state.
Balancing Factors:
- Resource Availability: Consider the available storage and bandwidth. Lossy compression offers practicality in limited-resource scenarios, whereas lossless compression is ideal when resources are abundant.
- Purpose and Audience: The intended use and audience also play a role. General consumer applications might lean towards lossy compression for its efficiency, while professional or specialized audiences might require the fidelity of lossless compression.
Neither lossy nor the lossless compression is inherently “better” than the other. Each has its strengths and appropriate contexts for use. The key is to assess the specific needs of your project or application – considering factors like required quality, available resources, and intended use – to determine which type of compression is the most suitable.
Conclusion
As digital media keeps changing, it’s important to know when to use “lossy” or “lossless” compression. This matters whether you’re watching your favorite show, saving important medical images, or creating a cool new website. Getting the hang of these compression methods is key to making your online stuff better.
Choosing between lossy and lossless is about finding the right balance. You need to pick the best option for what you’re doing, making sure your work looks great and fits your needs.
Want to make your online projects even better? Check out RedSwitches. They offer top-notch hosting that can handle all your internet needs, big or small. Whether you’re starting a business, making content, or just love tech, RedSwitches has what you need to boost your digital projects. Head over to RedSwitches to find out how they can help you with fast, reliable, and flexible hosting made just for you.
Embrace the future confidently. Choose wisely, compress efficiently, and let RedSwitches be the backbone of your digital success!
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between lossy and lossless?
Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently removing specific data, resulting in some quality loss. It’s used in JPEG images, MP3 audio, etc. On the other hand, lossless compression reduces file size without losing any data, allowing the original file to be perfectly reconstructed. It’s seen in PNG images, FLAC audio, etc.
Q. Is MP3 lossy or lossless?
MP3 is a lossy compression format. It reduces the size of audio files by eliminating parts of the sound that are less audible to human ears, leading to a smaller file size but with some loss in sound quality.
Q. Is a PNG lossy or lossless?
PNG is a lossless compression format. It compresses graphical data without any loss of quality, allowing images to retain their original visual details, making it ideal for graphics with text, transparent backgrounds, or detailed artwork.
Q. What is the difference between lossless and lossy WebP?
WebP is a modern image format that offers both lossy and lossless compression. Lossy WebP provides higher compression rates similar to JPEG but with better quality at smaller file sizes. Lossless WebP, like PNG, compresses images without any quality loss but with better compression efficiency, resulting in smaller file sizes than PNG.
Q. What is the difference between lossy and lossless compression?
Lossy compression reduces file size by removing unnecessary data, decreasing image quality. On the other hand, lossless compression retains all original data without any loss in quality.
Q. How does lossless compression work in image compression?
Lossless compression algorithms reduce the file size of an image without sacrificing quality by identifying and eliminating redundant information in the data.
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using lossy compression?
The main advantage of lossy compression is a significant reduction in file size, but the major drawback is a decrease in image quality due to data loss during compression.
Q. When should I choose between lossy and lossless compression for image optimization?
Choose lossy compression when file size is a priority, and slight loss in image quality is acceptable. Opt for lossless compression when preserving image quality is essential.
Q. How does lossless compression preserve image quality?
Lossless compression techniques maintain all original data in an image file, ensuring no data loss occurs during the compression process.
Q. What common compression algorithms are used for lossy and lossless image compression?
Examples of lossy compression algorithms include JPEG, while lossless compression algorithms include PNG and GIF.
Q. What is the significance of choosing the right compression method for images?
Selecting the appropriate compression technique ensures optimal reduction in file size while retaining desired image quality and details.
Q. Can you provide an example of lossy compression in image optimization?
An example of lossy compression is reducing the file size of an image by discarding certain color information or fine details, resulting in a smaller image with some loss in quality.