Both Linux and macOS are two of the most renowned operating systems. Each boasts a dedicated following and unique features. According to statistics, approximately 96.3% of the top one million web servers rely on Linux, whereas around 15.6% of desktop computers utilize macOS operating systems.
It is important to understand that while Linux may be more popular, macOS may be more suitable for certain users. Whether you’re a developer, an individual user, or an entrepreneur, choosing between Linux and Mac can significantly impact your computing experience.
In this blog, we will explore the key factors to consider when deciding between Linux vs Mac. By examining these factors, we aim to provide the insights you need to make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and preferences.
Table Of Contents
- What is an Operating System?
- What is macOS?
- What is Linux?
- macOS vs Linux: Factors to Consider
- Linux vs Mac: Which Operating System to Choose?
- Conclusion – Linux vs Mac
- FAQs
What is an Operating System?
Credits: FreePik
An operating system is an integral software component serving as an intermediary between a computer’s hardware and its software applications. It is crucial system software that manages and coordinates all hardware resources and provides essential services to enable the execution of software programs. The main functions of an operating system include managing memory, file systems, input and output devices, and controlling the execution of processes or tasks.
It also offers a user interface through which users can interact with the computer, whether through a graphical user interface (GUI) or a command-line interface (CLI). An operating system is critical in ensuring a computer system’s secure and efficient operation. It serves as the foundation upon which all other software and applications rely.
What is macOS?
Credits: Apple Website
macOS is an operating system designed by Apple Inc. exclusively for their Macintosh line of computers. It is known for its sleek, user-friendly interface and integration with Apple’s hardware and software ecosystem. macOS offers robust features, including a graphical user interface with a menu bar for system and application controls, a Finder for file management, and a Dock for launching applications.
It also includes several pre-installed productivity, multimedia, and creativity applications, like Photos, GarageBand, Safari, and Mail. macOS supports multi-touch gestures on trackpads and has a reputation for stability and security, thanks partly to its Unix-based foundation.
Also Read: A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Environment Variables in Linux.
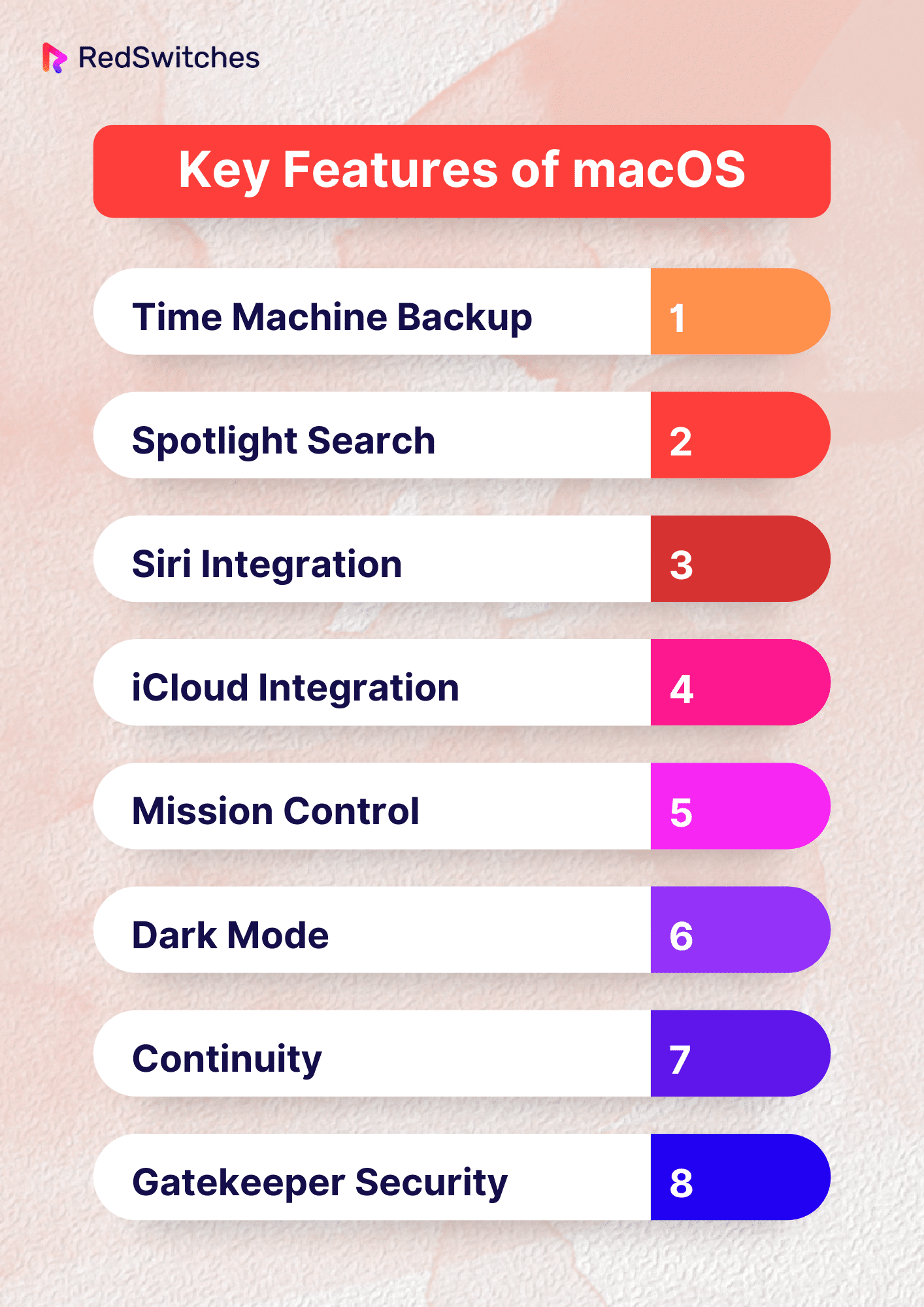
Key Features of macOS
When contemplating between Linux vs macOS, exploring the features of each OS can help streamline the decision-making process. Below are the key features of macOS:
Time Machine Backup
macOS offers an effortless backup solution through Time Machine. It automatically backs up your entire system. This feature lets you easily recover files or restore your entire Mac to a previous state, providing peace of mind and data security.
Spotlight Search
Spotlight is a powerful search tool that helps you find files, applications, emails, and more with lightning speed. It even provides suggestions and previews, making it a handy tool for quickly accessing the information on your Mac.
Siri Integration
Siri on macOS allows you to use voice commands to perform tasks, search the web, send messages, set reminders, and control system settings. This hands-free approach streamlines multitasking and adds convenience to your daily workflow.
iCloud Integration
Seamless integration with iCloud ensures that your documents, photos, and other data are available on all your Apple devices. It syncs your data across devices, making it easy to access and edit your content from anywhere.
Mission Control
Mission Control provides a bird’s-eye view of your open applications, virtual desktops (Spaces), and full-screen apps. It simplifies multitasking by efficiently organizing and switching between various tasks and workspaces.
Dark Mode
Introduced in macOS Mojave, Dark Mode offers a visually appealing and comfortable alternative to the traditional light user interface. It reduces eye strain in low-light environments while giving your Mac a modern, sleek appearance.
Continuity
macOS offers Continuity features like Handoff, allowing you to seamlessly transition between your Mac and iOS devices. You can start a task on one device and pick up where you left off on another, enhancing productivity and workflow efficiency.
Gatekeeper Security
Gatekeeper ensures the safety of your Mac by verifying the authenticity of downloaded apps, preventing the installation of malicious software. It offers three security settings: App Store-only, App Store and identified developers, and Anywhere, giving you control over app installation sources.
Are you looking to learn how to install pip on macOS? Read our informative blog, ‘How to Install pip on Mac.’
Pros and Cons of Using macOS
Weighing the pros and cons of each operating system when deciding between Linux vs Mac can offer valuable information on the better option for you. Below are the pros and cons of using macOS:
Pros
- User-Friendly Interface: macOS is known for its intuitive and user-friendly interface. Its clean design and well-organized menus make it easy for new and experienced users to navigate the system and find what they need quickly.
- Stability and Reliability: Apple controls hardware and software for seamless integration. This results in fewer crashes and system errors than other operating systems.
- Exceptional Hardware Integration: Apple’s tight integration between macOS and its hardware is a significant advantage. The Mac ecosystem offers a seamless experience, with features like Continuity (allowing you to transition tasks between Mac and iOS devices) and optimized performance for Mac hardware.
- App Ecosystem: The Mac App Store provides a vast selection of high-quality applications, many of which are optimized for macOS. Users can easily find and install applications, making it convenient to expand their software library.
- Security and Privacy: macOS is renowned for its robust security features. Features like Gatekeeper, FileVault, and regular security updates protect users from malware and security threats. Apple also strongly emphasizes user privacy, ensuring that personal data is kept secure.
Cons
- Price Tag: One of the most significant drawbacks of macOS is the high cost associated with Apple hardware. Mac computers tend to be more expensive compared to similarly configured PCs. This makes them less accessible to budget-conscious users.
- Limited Customization: macOS offers less customization than other operating systems. Apple’s design philosophy emphasizes a consistent user experience, meaning users have fewer options to tailor the system to their preferences.
- Compatibility Constraints: While macOS provides a smooth experience within the Apple ecosystem, it may face challenges regarding compatibility with non-Apple devices and software. Users who rely heavily on Windows-exclusive applications or peripherals may encounter compatibility issues.
What is Linux?
Credits: Linux Website
Linux is an open-source, Unix-like operating system kernel. It is the core component of many popular Linux distributions. Developed by Linus Torvalds and released in 1991, Linux is renowned for its stability, security, and versatility. It provides the essential functionality for managing hardware resources, scheduling tasks, and facilitating communication between software and hardware components.
Linux has gained widespread adoption and popularity across various computing platforms, including servers, desktop computers, mobile devices, and embedded systems. Its open-source nature allows developers and communities to collaborate, contributing to the continuous improvement and customization of Linux-based operating systems to meet diverse user needs.
Also Read: What is Curl Command and How to Use it in Linux.
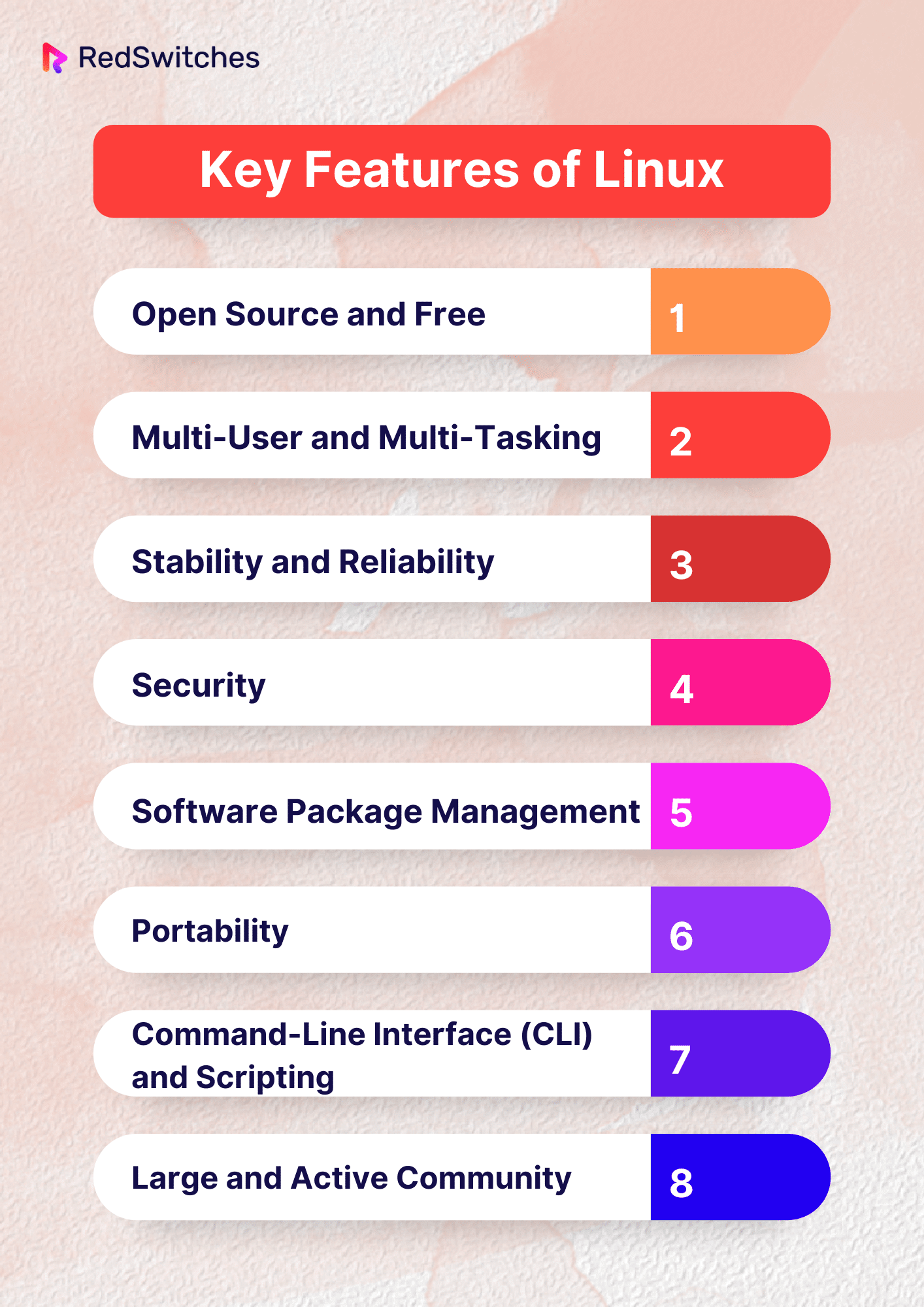
Key Features of Linux
Exploring the key features of Linux when comparing Linux vs Mac can help you pinpoint the operating system that best suits your preferences and needs. Below are the key features of Linux:
Open Source and Free
One of the fundamental characteristics of Linux is its open-source nature. Linux is distributed under various open-source licenses, such as the GNU General Public License (GPL). Anyone can view, modify, and distribute the source code without licensing fees. This openness fosters a collaborative community of developers continually improving and enhancing the operating system.
Multi-User and Multi-Tasking
Linux is inherently designed to support multiple users and tasks simultaneously. Users can log in to a Linux system and perform their tasks independently while the operating system efficiently manages system resources. This feature is crucial in server environments and advantageous on personal computers with multiple users.
Stability and Reliability
Linux is renowned for its stability and reliability. It can run for extended periods without reboot, making it an ideal choice for mission-critical systems. This robustness is attributed to the open-source community’s separation of user and kernel space and extensive testing and debugging.
Security
Linux provides robust security features, including access control mechanisms, file permissions, and user privilege management. It also benefits from quick security patching and updates, reducing the risk of exploiting vulnerabilities. Linux is widely used in security-sensitive applications, including servers and embedded systems.
Software Package Management
Linux offers efficient package management systems like APT (Advanced Package Tool) and YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) that simplify software installation, updates, and removal. Users can easily search for, install, and update software packages from vast repositories, ensuring a seamless and organized software experience.
Portability
Linux is highly portable and can run on various hardware architectures, from embedded systems to supercomputers. This versatility allows developers to adapt Linux to various platforms, making it a valuable choice for embedded systems, mobile devices, and cloud computing.
Command-Line Interface (CLI) and Scripting
Linux provides a powerful command-line interface that allows users to interact with the system efficiently. The availability of scripting languages like Perl, Python, and Bash makes it easy to automate tasks, create custom scripts, and develop complex workflows, enhancing productivity and flexibility.
Large and Active Community
Linux enjoys the support of a large and vibrant community of users, developers, and enthusiasts. This community actively contributes to the operating system’s development, creates extensive documentation, and offers support through forums and mailing lists. Users can easily find solutions to problems, receive assistance, and stay updated with the latest developments.
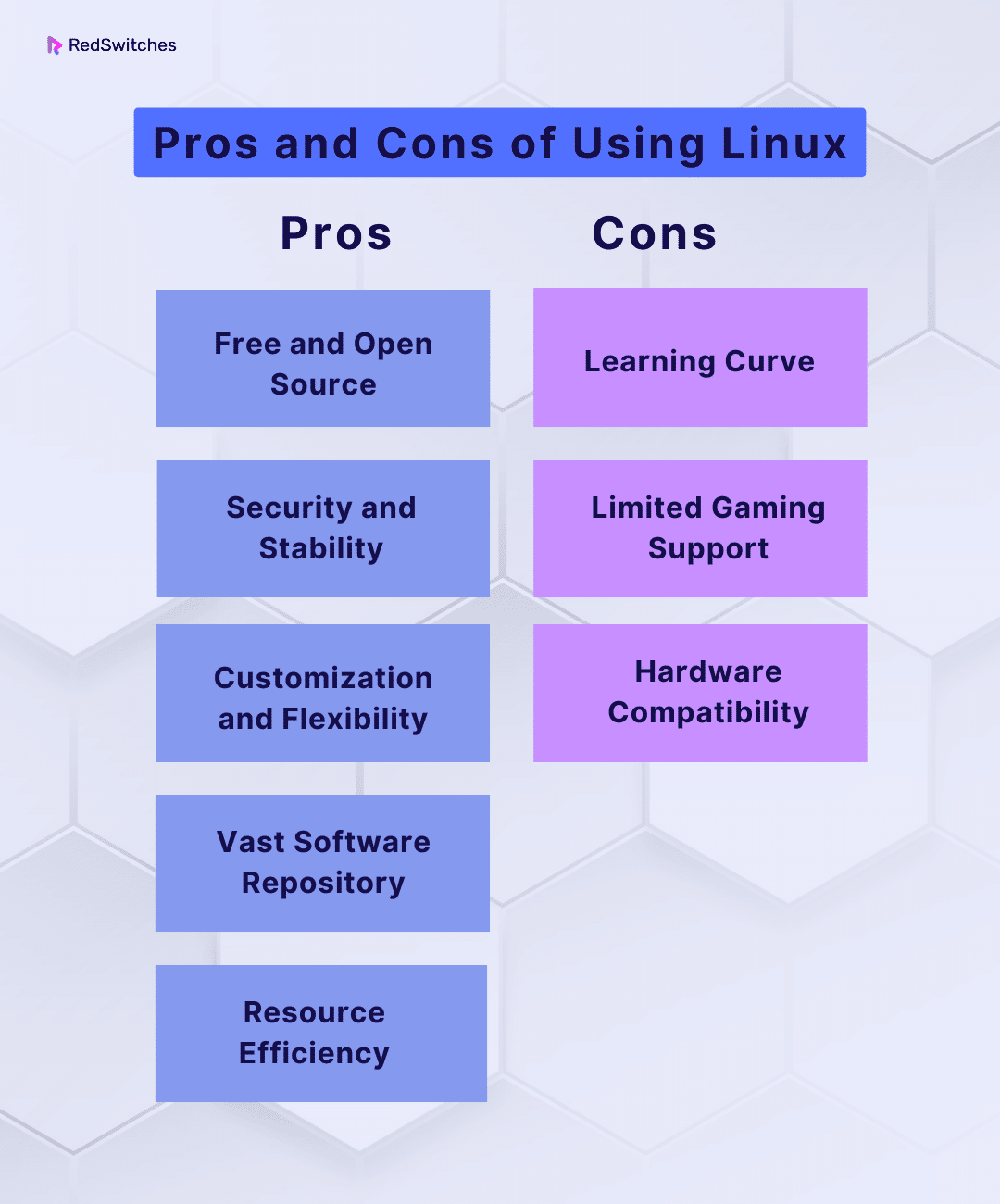
Pros and Cons of Using Linux
Weighing the pros and cons of Linux can offer valuable insight into which Operating system, between Mac OS X vs Linux, offers the most pros for you. Below are the pros and cons of Linux:
Pros
- Free and Open Source: One of the most significant advantages of Linux is its cost – it’s completely free. It’s open source, which means anyone can access, modify, and distribute the source code. This fosters a vibrant community of developers and enthusiasts who continuously improve the system.
- Security and Stability: Linux is renowned for its security and stability. With a strong user-based security model and regular security updates, Linux is less vulnerable to viruses and malware than other operating systems. Linux servers are also widely used in critical applications due to their reliability.
- Customization and Flexibility: Linux provides unparalleled customization options. Users can choose from various desktop environments, tweak system settings, and install software tailored to their needs. This flexibility empowers users to create a personalized computing environment.
- Vast Software Repository: Linux distributions come with access to extensive software repositories, making it easy to find and install a wide range of applications and tools. Package managers like APT and YUM simplify software installation and updates.
- Resource Efficiency: Linux is known for its efficient resource usage. It can run on older hardware, making it an excellent choice for reviving older machines or reducing hardware costs in server environments.
Cons
- Learning Curve: While Linux is user-friendly, it does have a steeper learning curve, especially for those accustomed to Windows or macOS. Commands are often used in the terminal, and users may need to learn new terminology and concepts.
- Limited Gaming Support: Although Linux gaming has improved significantly in recent years, it still lags behind Windows regarding game availability and compatibility. Popular game titles are often developed primarily for Windows.
- Hardware Compatibility: Linux may face challenges with specific hardware components, particularly those lacking official Linux drivers. Although Linux developers actively work on driver support, some peripherals may not work smoothly.
Now that we have discussed the definitions, features, and pros and cons of Linux vs Mac, let’s explore some factors or differences to consider when deciding between the two operating systems.
Also Read: A Comparison of Rocky Linux vs Ubuntu: Choosing the Ideal Linux Distribution.
macOS vs Linux: Factors to Consider
When Comparing Linux vs Mac, considering the following factors can help simplify the decision-making:
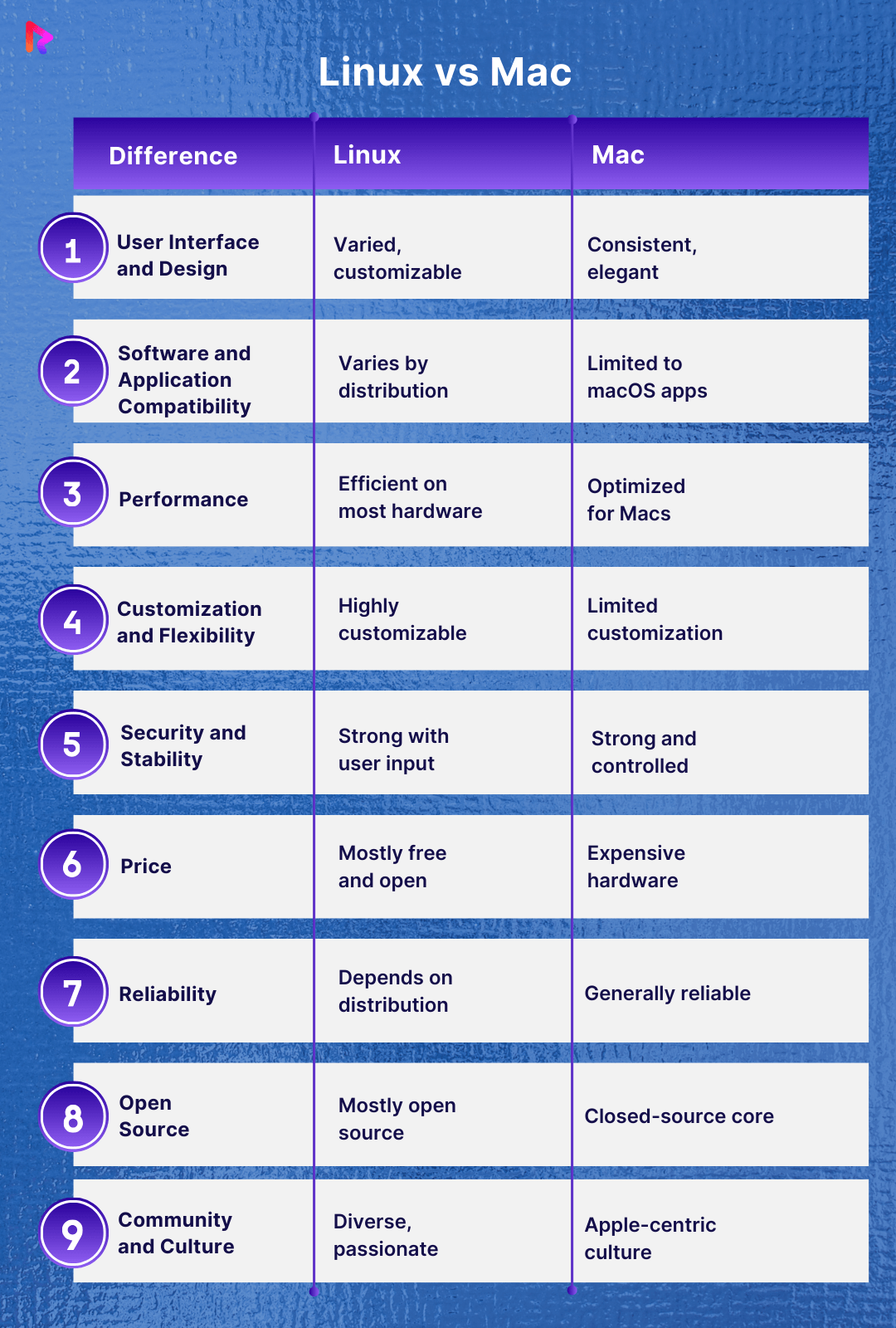
User Interface and Design
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of user interface and design:
macOS
One of macOS’s standout features is its sleek and polished user interface (UI). Apple is renowned for its design aesthetics, and macOS reflects this commitment to visual excellence. The interface is intuitive, user-friendly, and consistent across all Apple devices, offering a unified experience for Mac users.
Linux
Linux offers diverse desktop environments, each with its design philosophy and appearance. Popular Linux desktop environments like KDE Plasma, GNOME, and Cinnamon provide customizable and visually appealing UIs. The degree of consistency and refinement can vary depending on the chosen desktop environment and distribution.
Software and Application Compatibility
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of software and application compatibility:
macOS
macOS boasts a rich ecosystem of software and applications, thanks to the Apple App Store and its extensive third-party software library. It offers compatibility with popular productivity tools, creative software like Adobe Creative Cloud, and various commercial applications. It may lack some specialized software commonly available on Linux.
Linux
Linux provides a diverse range of software through its package management systems and software repositories. While it may not have the same quantity of commercial software as macOS, it excels in open-source software availability.
Linux is an excellent choice for developers, with a vast array of development tools and libraries. Compatibility issues can arise with proprietary software designed exclusively for macOS or Windows.
Linux vs macOS: Performance
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of performance:
macOS
macOS is known for optimizing Apple hardware, offering a smooth and consistent user experience. Apple controls the hardware and software aspects, allowing for efficient resource management and enhanced performance. macOS may not be as resource-efficient on non-Apple hardware.
Linux
Linux’s performance varies depending on the distribution, desktop environment, and hardware. It is highly customizable and can be optimized for various use cases, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices and high-performance servers. It also excels in performance on a wide range of hardware, offering users the flexibility to tailor their system for optimal efficiency.
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of customization and flexibility:
macOS
macOS is known for its sleek and user-friendly interface. While macOS provides a visually consistent and polished experience, it may not offer the same customization and flexibility as Linux. macOS is designed with a focus on providing a streamlined and controlled environment. While you can personalize aspects such as wallpaper, icons, and themes, you have limited control over system-level modifications.
Linux
Linux is renowned for its unparalleled customization and flexibility. Linux distributions (distros) come in various flavors, each offering a unique desktop environment, like GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and more.
Users can tailor their Linux environment to their preferences, from choosing the desktop interface to customizing every aspect of the user interface and system behavior. This level of customization allows Linux users to create a highly personalized computing experience.
Security and Stability
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of security and stability:
macOS
Apple invests heavily in security measures like Gatekeeper, XProtect, and FileVault, which help protect your system from malware and unauthorized access. macOS also benefits from regular updates and patches, addressing security vulnerabilities promptly.
macOS also boasts stability, thanks to its closed ecosystem and tightly controlled hardware and software integration. This control over the entire stack provides a stable and reliable computing experience.
Linux
Linux is renowned for its security, primarily due to its open-source nature. The Linux community actively monitors and addresses security issues, making it a secure choice for users who prioritize security. Linux’s security also depends on user practices and system configurations, so keeping your system updated and following best security practices is essential.
Linux distributions can vary in terms of stability. Some distributions, like Debian and CentOS, prioritize stability and offer long-term support (LTS) releases. Others, like Arch Linux, provide cutting-edge software but may require more frequent updates and maintenance. The level of stability can be customized based on your choice of Linux distro and software sources.
Price
Credits: Pexels
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of price:
macOS
macOS is exclusively available on Apple hardware, like MacBooks, iMacs, and Mac Pros. These devices tend to come with a premium price tag, making macOS less accessible to budget-conscious users. While macOS updates are typically free, the cost of entry can be a significant consideration.
Linux
Linux is open-source and freely available for anyone to use and distribute. This makes Linux a cost-effective choice, especially for users who want to repurpose older hardware or build custom systems. Linux distributions come in various flavors, which are entirely free to download and use.
Reliability
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of reliability:
macOS
macOS is known for its robust reliability. Apple tightly controls its ecosystem’s hardware and software aspects, resulting in a stable and consistent user experience. macOS updates are rigorously tested to ensure compatibility and minimize the risk of system crashes. This level of control and integration often leads to fewer system issues for users.
Linux
Linux, as an open-source operating system, can vary in terms of reliability depending on the distribution and hardware you use. Some Linux distributions, like Ubuntu and Debian, are well-known for their stability and reliability.
Factors like hardware compatibility, software selection, and system configuration can influence the reliability of Linux. Linux offers a high degree of reliability when configured and maintained properly, but it may require more technical expertise to achieve this.
Open Source
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of open source:
macOS
macOS is not open source. It is a proprietary operating system developed by Apple, and its source code is not freely available for inspection or modification by the general public. This means users have limited control over the inner workings of the OS.
Linux
Linux is renowned for its open-source nature. The source code of the Linux kernel and most software packages is freely accessible and modifiable by anyone. This open-source philosophy promotes transparency, encourages collaboration, and empowers users to customize their operating system to their liking. It also means numerous Linux distributions are tailored to different needs and preferences.
Community and Culture
Below is a comparison of Linux vs Mac in terms of community and culture:
macOS
macOS has a strong and dedicated user base, often associated with Apple’s ecosystem of products and services. The macOS community tends to be smaller than the Linux community but is known for its passionate user base and active support forums. Users benefit from Apple’s customer support and official documentation.
Linux
Linux boasts a diverse and passionate community of users and developers. It thrives on open source, collaboration, and user empowerment principles. Countless online forums, wikis, and user communities are dedicated to Linux. This makes finding help, tutorials, and solutions to common issues relatively easy. Linux’s community-driven nature encourages sharing knowledge and helping others.
Are you seeking information on creating and removing symbolic links in Linux? Read our beginner’s guide: How to Create and Remove Symbolic Links in Linux – A Beginner’s Guide.
Linux vs Mac: Which Operating System to Choose?
Credits: FreePik
Although considering the above factors can help simplify the decision-making between Linux vs Mac, it can still be difficult for newcomers to pick between the two. Below is a simplified comparison between both operating systems to help you make an informed decision:
Cost
- Linux: Choose Linux if you are seeking an operating system on a budget. You can download and install it without any licensing costs.
- Mac: macOS is only officially available on Apple hardware, so you’ll need to purchase a Mac computer, which can be relatively expensive compared to some Linux-compatible hardware.
Use Case
- Linux: Choose Linux if you value flexibility, customization, and a wide range of software choices.
- macOS: Choose macOS if you prioritize a polished user interface, integration with other Apple devices, and specific macOS-only software.
Software Availability
- Linux: Linux has a vast open-source software repository available through package managers like APT and YUM. While many popular applications have Linux versions, some proprietary or specialized software may not be natively available.
- Mac: macOS has a robust software ecosystem, including various commercial and open-source applications. Most popular software, like Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Cloud, and professional software tools, are available for Mac.
Compatibility
- Linux: Linux is highly customizable but may require more technical knowledge to configure and maintain. Some hardware drivers and software may not be readily available for all distributions.
- Mac: Choose macOS if you use other Apple devices. macOS offers seamless integration through iCloud and Continuity features.
Security
- Linux: Linux is known for its security features, frequent updates, and robust permission system. The level of security can vary depending on the distribution and user practices.
- Mac: macOS is considered relatively secure, thanks to features like Gatekeeper and the App Store’s curated software selection. Apple also regularly releases security updates.
Development and Terminal
- Linux: Linux is a go-to choice for developers due to its command-line tools, programming libraries, and development environments. It’s often used for server management and software development.
- Mac: macOS, being Unix-based, also offers a powerful command-line interface and development tools. It’s a favored platform for iOS and macOS app development.
Privacy
- Linux: Linux distributions prioritize user privacy and transparency. You have more control over telemetry and data collection.
- Mac: Apple has faced criticism for its data collection practices, but it has tried improving user privacy with recent macOS updates.
Conclusion – Linux vs Mac
When contemplating between Linux vs Mac, It’s important to weigh the factors that matter most to you to select the ideal operating system for your computing needs. Whether it’s the sleek, user-friendly interface and application compatibility of macOS or the customization, security, and open-source nature of Linux, each operating system has its strengths and weaknesses.
At RedSwitches, we understand that your choice of operating system is crucial for your web hosting needs. Our hosting services are designed to support both Linux and macOS environments, ensuring you can choose the platform that suits your requirements.
Whether you’re hosting a website, running applications, or managing a server, our hosting solutions are ready to accommodate your preferences. Explore our hosting options today and experience smooth performance with the operating system of your choice.
FAQs
Q. Which is safer, Mac or Linux?
When comparing Linux vs. Mac in terms of security, both have strong foundations. Linux is often considered more secure due to its open-source nature, allowing for quick security updates and community scrutiny. Mac benefits from Apple’s stringent control over hardware and software, making it less prone to malware but not entirely immune.
Q. Is it better to code on Mac or Linux?
The choice between coding on Linux vs Mac depends on personal preference and specific development needs. Both platforms offer robust development environments. Linux is favored for its open-source tools and extensive programming libraries, while Mac appeals to those who prefer a sleeker user interface and access to popular commercial development software.
Q. Why do people use Mac instead of Linux?
People opt for Mac over Linux for several reasons, including its user-friendly interface, seamless integration with other Apple devices, wide commercial software availability, and a strong focus on design and aesthetics. Mac also provides a polished and well-supported ecosystem for creative professionals.
Q. Why Linux is better than Windows and Mac?
Linux offers advantages over Windows and Mac, like greater customization and flexibility, robust security features, and being open source. Linux is also more resource-efficient, making it suitable for older hardware and server environments.
Q. What is the difference between macOS and Linux?
macOS is the operating system developed by Apple exclusively for their Mac devices, whereas Linux is an open-source operating system available for a wide range of devices.
Q. Which one is better, Linux or macOS?
The superiority of Linux or macOS depends on individual preferences and requirements. Linux is preferred by many due to its customization options and open-source community support, while macOS is known for its reliability and seamless integration with other Apple products.
Q. Can I run Linux on a Mac device?
Yes, it is possible to run Linux on a Mac device through dual-booting or using virtualization software, allowing users to experience both operating systems on the same hardware.
Q. What are the key differences between macOS and Linux?
Some key differences include the desktop environment (macOS uses the Mac desktop environment while Linux has various desktop environments), the availability of applications and software tailored for each OS, and the underlying kernel (macOS uses the XNU kernel, while Linux uses the Linux kernel).
Q. Is gaming on Linux as good as on macOS?
Gaming on Linux has significantly improved over the years with more game titles becoming compatible with the platform. However, macOS still offers a smoother gaming experience due to its optimized integration with hardware and software developed by Apple.
Q. What are the security features of Linux compared to macOS?
Linux is known for its robust security features due to its open-source nature, extensive community support, and strict user permission controls. While macOS also provides strong security measures, its closed-source ecosystem may limit community-driven security enhancements.
Q. Can I use Mac OS-specific applications on Linux?
Mac OS-specific applications are designed to run exclusively on the macOS environment and may not be directly compatible with Linux. However, some software alternatives or emulation tools may offer partial functionality for certain Mac OS applications on Linux.
Q. Are there any similarities between macOS and Linux?
Both macOS and Linux share some similarities, such as being based on Unix-like systems, offering terminal access for advanced users, and providing a stable and efficient environment for development and programming tasks.
Q. Which is better for enterprise use, Linux or macOS?
The choice between Linux and macOS for enterprise use depends on the specific requirements and existing infrastructure. Linux, especially distributions like Red Hat Enterprise Linux, is widely favored for its robustness and scalability in enterprise environments. macOS, on the other hand, is preferred in organizations with a strong Apple ecosystem and development focus.
Q. Can I compare macOS, Linux, and Windows in terms of their usability?
Each operating system – macOS, Linux, and Windows – offers distinct usability features catering to different user preferences and needs. While macOS is known for its user-friendly interface and seamless integration with Apple products, Linux and Windows provide diverse customization options and compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software.