Overview:
MTR, short for “My Traceroute,” is a network diagnostic tool that combines the functionalities of both traceroute and ping. It is a more advanced and user-friendly version of the traditional traceroute command.
Table Of Content
What is MTR?
MTR is commonly used to diagnose network connectivity and performance issues between a source and a destination, such as a client computer and a server.
Traceroute is a standard network tool that traces packets’ routes from a source to a destination, showing all the intermediate routers or hops the packets pass through. It also provides information about the time it takes for each hop, known as the Round-Trip Time (RTT).
MTR combines the capabilities of the traditional ping and traceroute utilities by continuously sending packets to the destination and displaying the results in real-time, providing a more comprehensive view of the network path and potential latency or packet loss issues.
As it runs, MTR continuously updates the information for each hop, allowing users to see any changes in the network path and pinpoint specific routers or links causing issues.
The MTR command should be executed on both the server and the client computer (for example, your home PC). If you do not know your PC’s IP address, go to www.whatismyip.com to get the information you need to run the MTR.
How to generate MTR?
We recommend setting the following options when running MTR for better results and analysis.
- Do not resolve names.
- Generate MTR with at least 100 packets.
Here’s how you can use the MTR utility on your preferred operating system.
- Windows
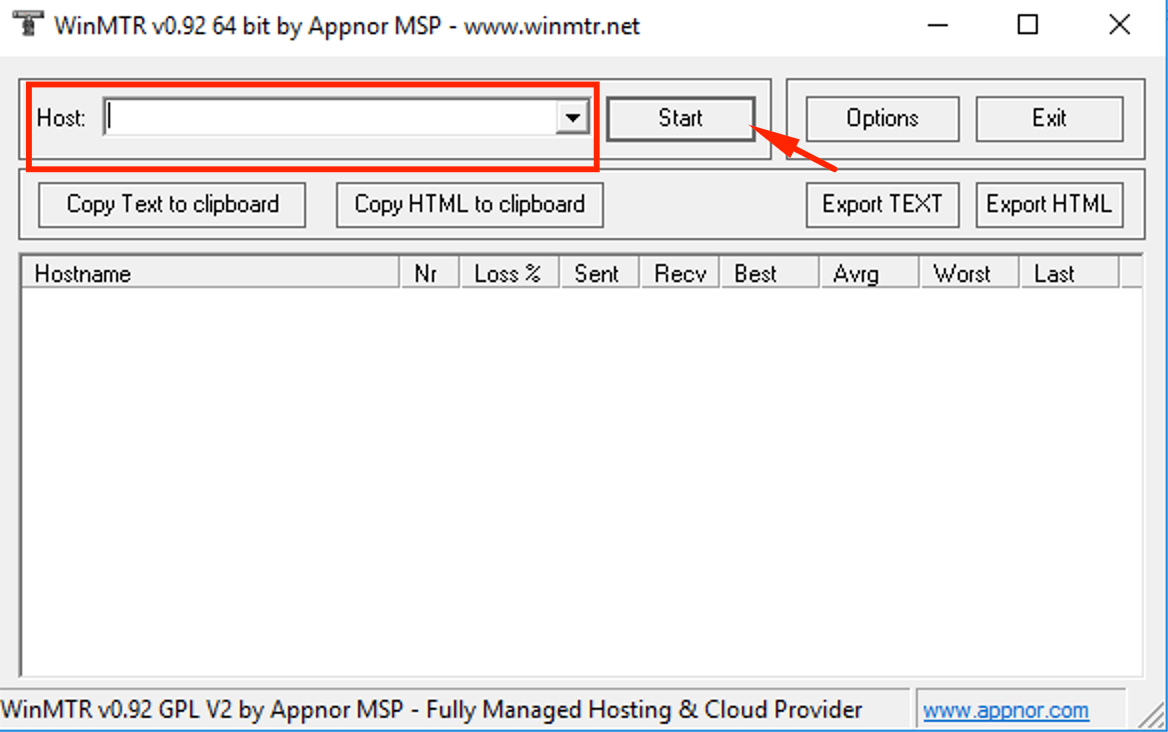
Download the WinMTR App to a Windows PC or server.With WinMTR, you may execute an MTR by entering the IP address you want to reach in the Host box and pressing the Start button.
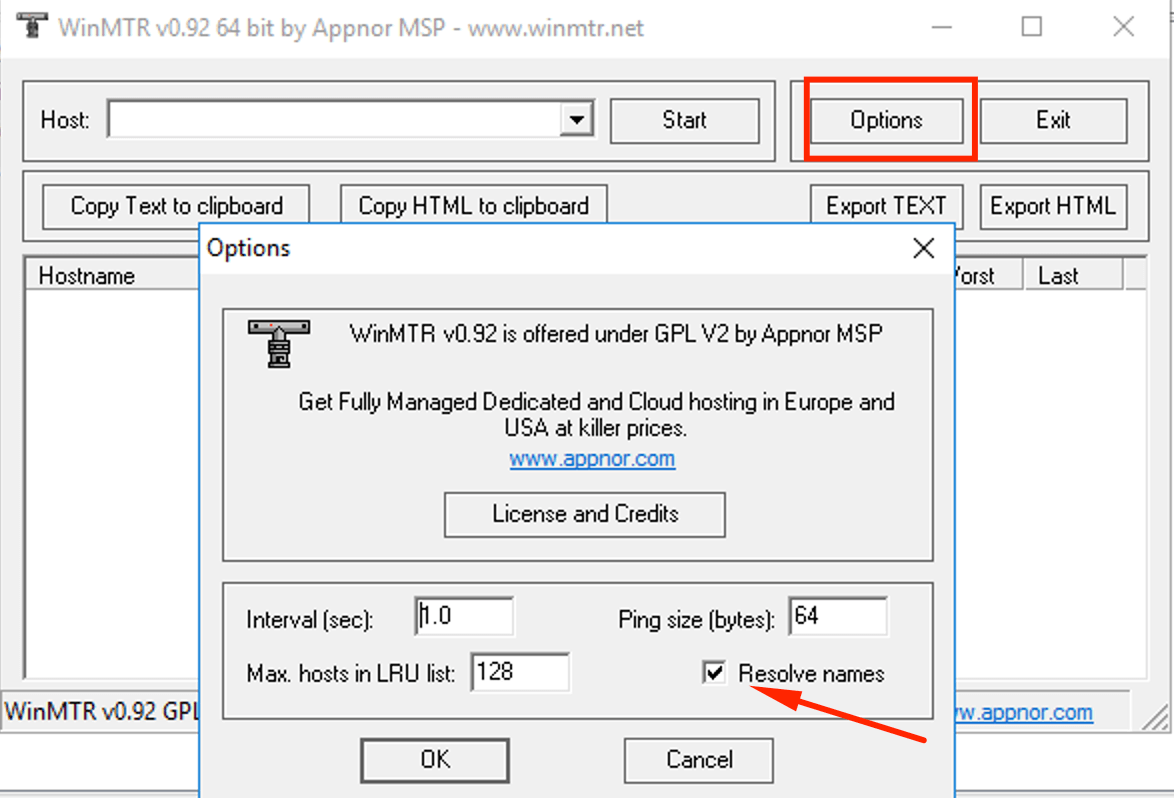
Note: At least 100 packets are necessary, and Resolve Names must be disabled in the Options menu, as seen in the second screenshot.
- Linux
MTR is usually not available on most Linux distributions by default.If that’s the case with your distribution, first install the required packages with the following commands:
For RHEL/CentOS-based distributions:
yum install mtr -yFor Debian/Ubuntu distributions:
apt-get install mtr -y
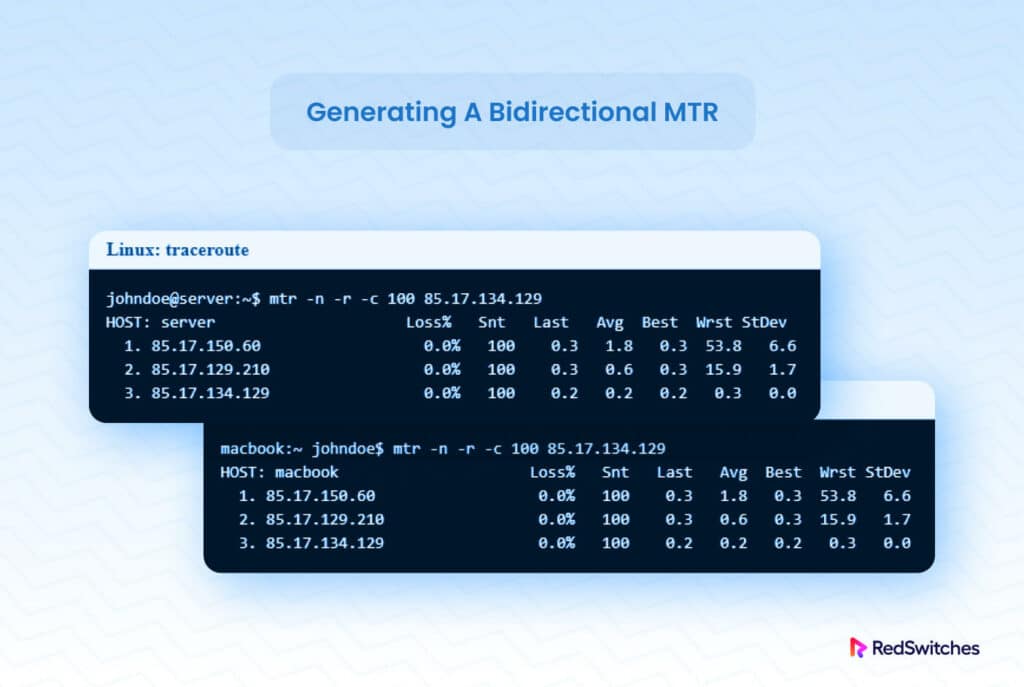
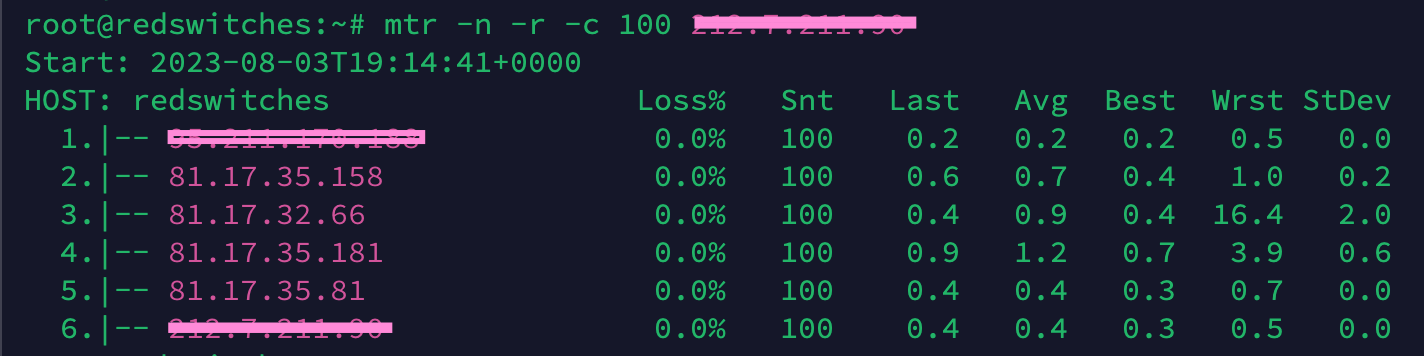
To get an MTR output, open a terminal and type “mtr -n x.x.x.x” (without quotes), or for a static output with 100 packets, type “mtr -n -r -c 100 x.x.x.x”.Please refer to the following screenshot for an example of the output of the following commands:
mtr -n x.x.x.x
mtr -n -r -c 100 x.x.x.x
Note: Replace x.x.x.x with your host IP address. - MAC
By default, MTR is not installed on macOS. So, before you can run an MTR on your Mac, you must first install it by following these steps:
- Homebrew. An installation guide is available here.
- MTR: If you have Homebrew installed, you may install MTR using the command:
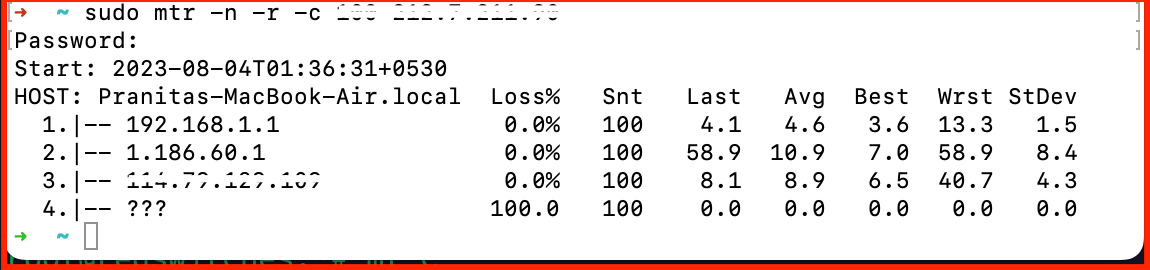
brew install mtrTo get an MTR output on MAC, open a terminal and type “mtr -n x.x.x.x” (without quotes), or for a static output with 100 packets, type “mtr -n -r -c 100 x.x.x.x”.
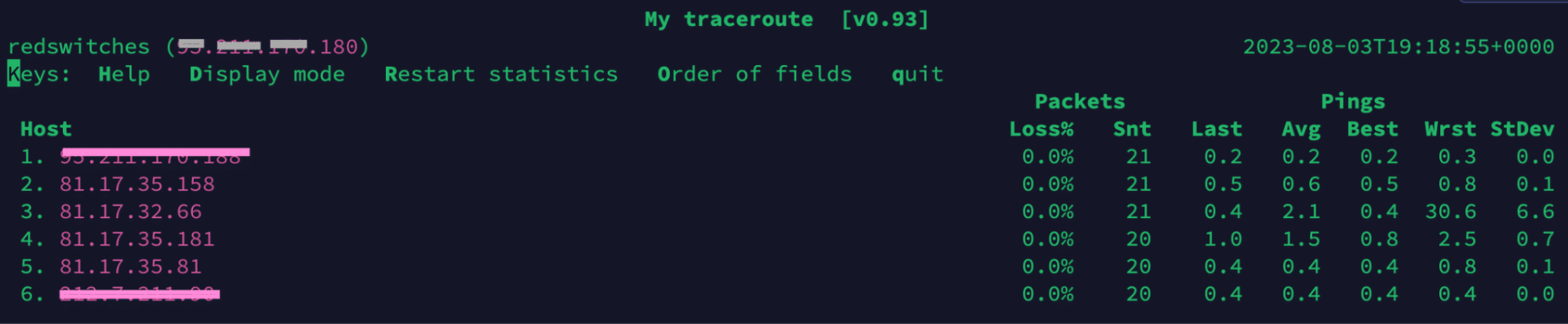
Packet Loss within the RedSwitches Network
You may see packet loss when you run a MTR on RedSwitches routers. This does not signify a loss of service because our routers have ping limiters that sometimes cause this behavior. This packet loss only affects packets sent to the router. As a result, packets passing via the router remain unaffected.
Check the next hop to discover if the loss you’re witnessing is real or caused by rate restriction. If the hop has a loss of 0.0%, it is due to ICMP rate restriction, not an actual loss.