Key Takeaways
- Colocation offers space in a data center for servers and hardware.
- Improved uptime, access to bandwidth, and support are some benefits of colocation.
- Initial setup costs, limited accessibility, and dependence on collocation providers are some disadvantages of colocation.
- There are five types of colocation facilities: Retail Colocation, Wholesale Colocation, Managed Colocation, Hyperscale Colocation, and Green Colocation.
- Location, reputation, scalability, security, connectivity, and cost are important factors in colocation decision-making.
The need for colocation in the current digital space cannot be understated. Businesses are using colocation services to meet their data management and infrastructure needs.
According to a recent industry report, the data center colocation market was valued at $63.65 billion in 2021. This value is expected to increase to $293.11 billion by 2030. This surge shows a growing recognition among companies of colocation services’ efficiency. Deciding to choose colocation involves considering several critical factors.
The decision to move to a colocation facility is multifaceted. It involves analyzing cost-benefit ratios and assessing scalability and security needs. This blog will help readers understand what is a colocation data center and the considerations in colocation decision-making. It will offer valuable insights for businesses contemplating a shift to colocation.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Colocation (Colo)?
- Colocation Features
- Advantages of Colocation
- Disadvantages of Colocation
- Types of Colocation Facilities
- Colocation Decision-Making: Factors to Consider
- Cloud Services vs Colocation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Colocation (Colo)?
Credits: FreePik
Colocation is a data center service model where individuals or businesses rent a location to hold their servers and other computing hardware. It is a professionally managed facility often labeled as a third-party data center. The appeal of colocation is that it offers the physical infrastructure needed for robust IT operations without the expenses and challenges of building and sustaining a private data center.
Clients are provided the rack space they need for their hardware in a colocation facility. These facilities also fulfill other requirements, like cooling, security, power, and internet access.
These data centers feature advanced infrastructure to ensure high uptime. This includes redundant power supplies, backup generators, cooling systems, and exhaustive security measures. Clients benefit from economies of scale, as the cost of maintaining these advanced facilities is shared among multiple parties.
Colocation offers greater bandwidth at a lower cost. It also comes with the reliability linked with a professionally managed data center. Clients are responsible for their hardware and software. This gives them control over their IT systems.
This setup is attractive to businesses that require a high degree of control over their data and infrastructure but don’t want to bear the total cost and responsibility of managing a data center environment.
Colocation also provides scalability. Businesses can expand their IT infrastructure as needed without much capital investment. It enables better connectivity options, as these facilities often have many ISPs and other service providers on-site. This ensures robust and redundant network connections.
Are you contemplating whether you should opt for colocation hosting? Read our blog, Colocation Hosting In 2024, for informed decision-making.
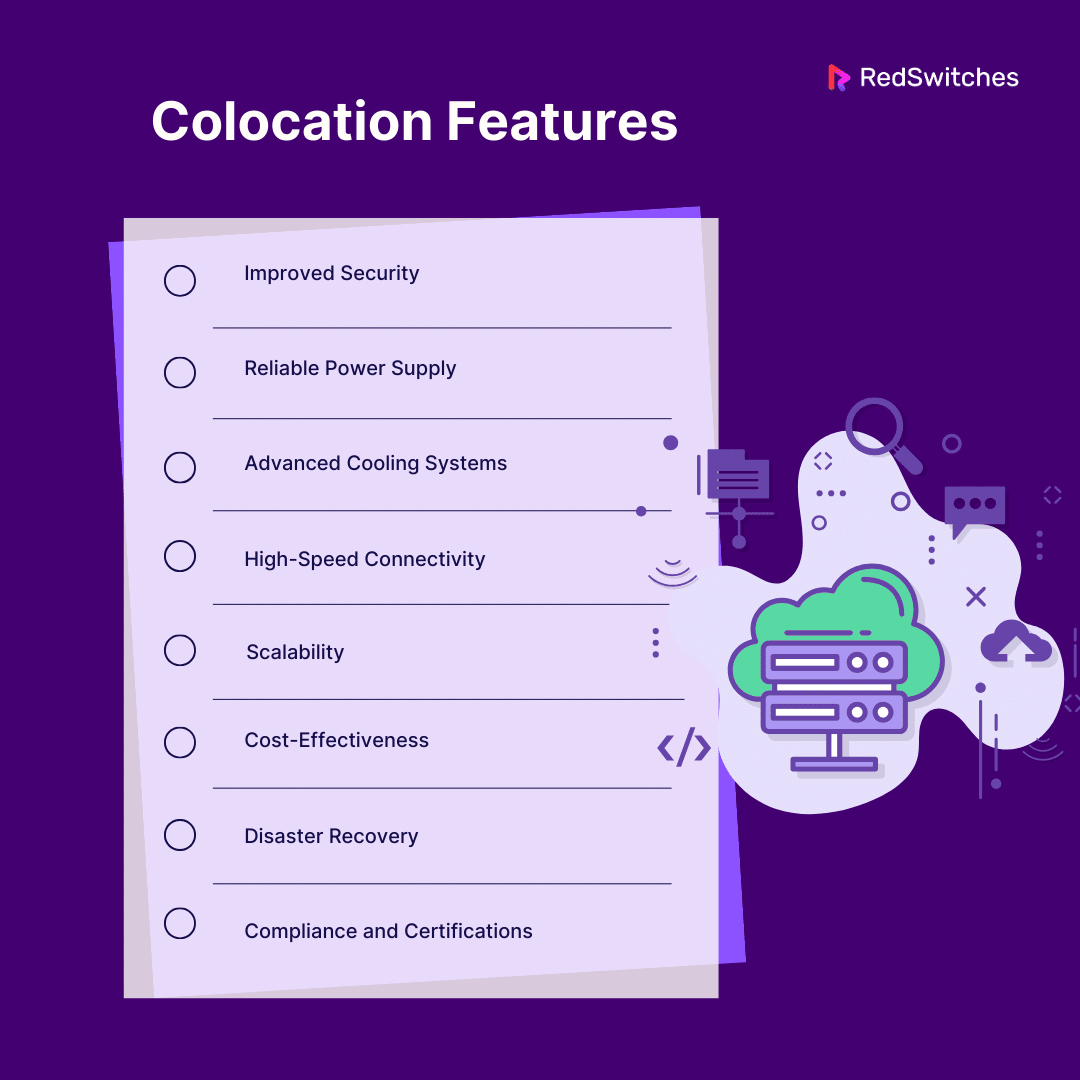
Colocation Features
Below are the top features of colocation facilities that make them an attractive option for businesses and individuals:
Improved Security
One of the main reasons why companies choose colocation is the improved security it offers. Servers can cost anywhere from $5,000 to over $25,000 or more. This makes them susceptible to robberies.
Colocation facilities have robust security measures, including CCTV surveillance and on-site security personnel. This level of security is often beyond what a business could affordably implement on its own. For those housing dedicated servers in these facilities, it means peace of mind knowing their critical data is protected against physical threats.
Reliable Power Supply
Reliability is the top property in server management. Colocation facilities excel in this regard. They come with redundant power supplies, like backup generators and UPS systems. This helps ensure your dedicated server remains operational even during a power outage. This is incredibly important for businesses that depend on continuous uptime.
Advanced Cooling Systems
Servers, like dedicated servers, generate significant heat. Every watt of power that a server uses is released into the air in the form of heat. If not properly managed, it can damage your system and negatively impact performance and lifespan.
The amount of heat output per server varies. It mainly depends on the server configuration. Colocation centers have advanced cooling and ventilation systems to maintain optimal temperature and humidity. This ensures that your dedicated server operates efficiently and remains in good health in the long run.
High-Speed Connectivity
Another key feature of colocation is its high-speed internet connectivity. Colocation facilities ensure your dedicated server has the fastest and most reliable internet connection.
They achieve this by offering multiple high-bandwidth options and direct connectivity to major ISPs. This is important for businesses that require high-speed data transfer and minimal latency for their applications.
Scalability
Scalability is a major concern for growing businesses. Colocation addresses this efficiently by offering the flexibility to scale your IT infrastructure up or down. You can easily add more dedicated servers or increase the space and resources allocated to your current setup as your needs expand without worrying about excessive capital investment.
Cost-Effectiveness
While owning and maintaining dedicated servers can be expensive, colocation offers a more cost-effective solution. It eliminates the need for building and maintaining your own data center. These factors can involve considerable capital and operational expenses. So, by opting for colocation, businesses benefit from economies of scale, sharing the cost of infrastructure, power, cooling, etc.
Disaster Recovery
Colocation facilities often serve as excellent disaster recovery sites. You ensure business continuity in case of disasters by housing your dedicated servers in a location separate from your leading operation site. Many colocation providers offer integrated disaster recovery and backup services. This increases the protection of your data.
Compliance and Certifications
Colocation centers often comply with various certifications and standards. This includes ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA. This is great for businesses in industries with strict regulatory requirements. It helps ensure that your dedicated servers are hosted in an environment that follows industry best practices and legal requirements. This can help you avoid non-compliance-related lawsuits.
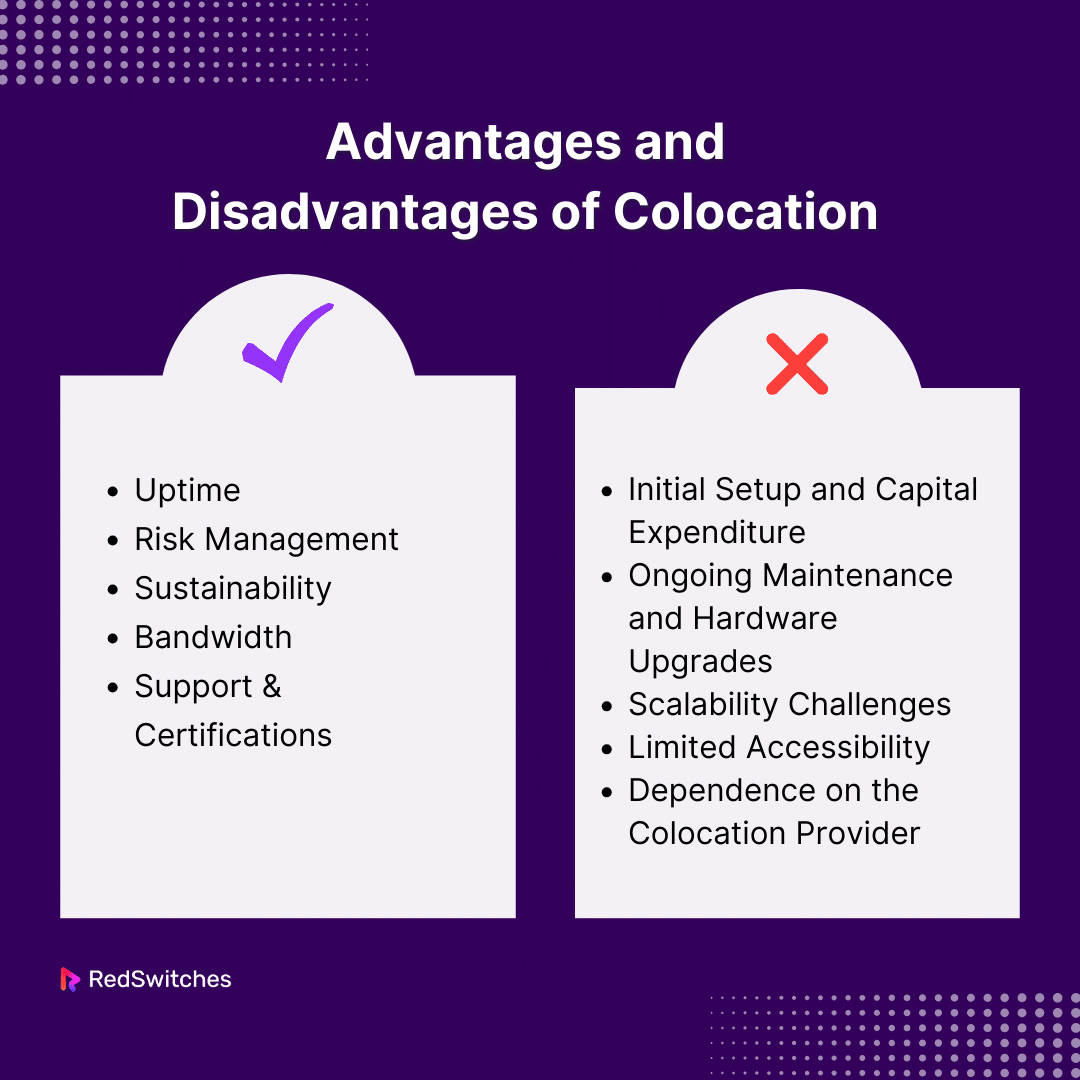
Advantages of Colocation
Colocation offers a notable list of benefits. This is why it has become a strategic move for businesses looking to boost their IT operations. Below are the top advantages that make colocation an attractive option.
Uptime
One of colocation’s most standout advantages is its improved uptime. Data centers are designed to provide high levels of redundancy in power and cooling systems. This ensures that your critical IT infrastructure remains operational despite any disruptions. This reliability can be a safety net for businesses where downtime means lost revenue and decreased customer trust.
Risk Management
Colocation facilities can serve as a major aspect of your risk management strategies. You’re effectively distributing risk by housing your infrastructure in a colocation facility. These facilities are built to withstand natural disasters and have disaster recovery capabilities. This geographical distribution of data and applications can be critical in maintaining operations during unexpected events.
Sustainability
Data centers focus on sustainable practices. This includes using renewable energy sources and implementing energy-efficient cooling systems. Businesses can reduce their carbon footprint by choosing a colocation provider prioritizing sustainability.
Today, approximately 81% of customers prefer to buy from sellers focusing on sustainability. Businesses can target environmentally-conscious customers by housing their servers in sustainable data centers.
Bandwidth
Another critical advantage of colocation is access to high bandwidth at a lower cost. Colocation facilities have numerous high-speed internet connections. This ensures businesses can access the necessary bandwidth without the high costs linked to private implementations. This connectivity is vital for businesses depending on high-speed data transfer and uninterrupted internet access.
Support & Certifications
Colocation providers offer both space and expert support. Their teams are equipped to handle various IT-related issues. This helps offer additional support to your business. These facilities also often hold various certifications that attest to their adherence to best practices in security and management. This level of compliance can be resource-intensive for businesses to achieve on their own.
It can be challenging to pick between managed hosting vs colocation. Read our piece, ‘Managed Hosting Vs Colocation’, to make an informed decision.
Disadvantages of Colocation
Before deciding to hold your equipment in a colocation facility, it is important to understand the disadvantages of colocation to ensure well-informed decision-making. Below are the disadvantages linked with colocation:
Initial Setup and Capital Expenditure
The top disadvantage of colocation is the initial capital investment required. Unlike cloud services, where the service provider offers the infrastructure, businesses must buy their own servers and networking equipment in colocation.
This initial outlay can be substantial, especially for small to medium-sized businesses with limited budgets. The costs extend beyond hardware. There are also software licenses, server transportation, and setup expenses.
Ongoing Maintenance and Hardware Upgrades
The maintenance and upgrading of hardware rests on the business that chooses colocation. This can be a big challenge, especially for companies that lack an in-house IT team with the ability to manage such tasks.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal server performance and longevity, which means additional ongoing costs. As technology advances, hardware upgrades might be needed, which could be a noteworthy recurring expense.
Scalability Challenges
While scalability is a colocation benefit, businesses can sometimes face scalability challenges. When a business grows, its data needs grow too, and scaling up in a colocation facility can be less flexible than cloud hosting solutions.
Increasing server capacity often means acquiring more physical hardware. This involves more capital expenditure and potential downtime during setup. There may also be limitations on the amount of physical space available in the data center. This can further complicate scalability.
Limited Accessibility
Another disadvantage is the physical distance between the business and its servers. Direct access to the hardware can be inconvenient if the data center is far from the business’s operational base. This geographical distance can bring challenges in managing and troubleshooting hardware issues.
Dependence on the Colocation Provider
Businesses using colocation services depend on their provider for several critical aspects. This includes cooling, physical security, power, and connectivity. Any shortcomings in these areas can directly impact the performance and availability of their servers. If the colocation provider experiences downtime, power outages, or security breaches, this can affect the customer’s operations.
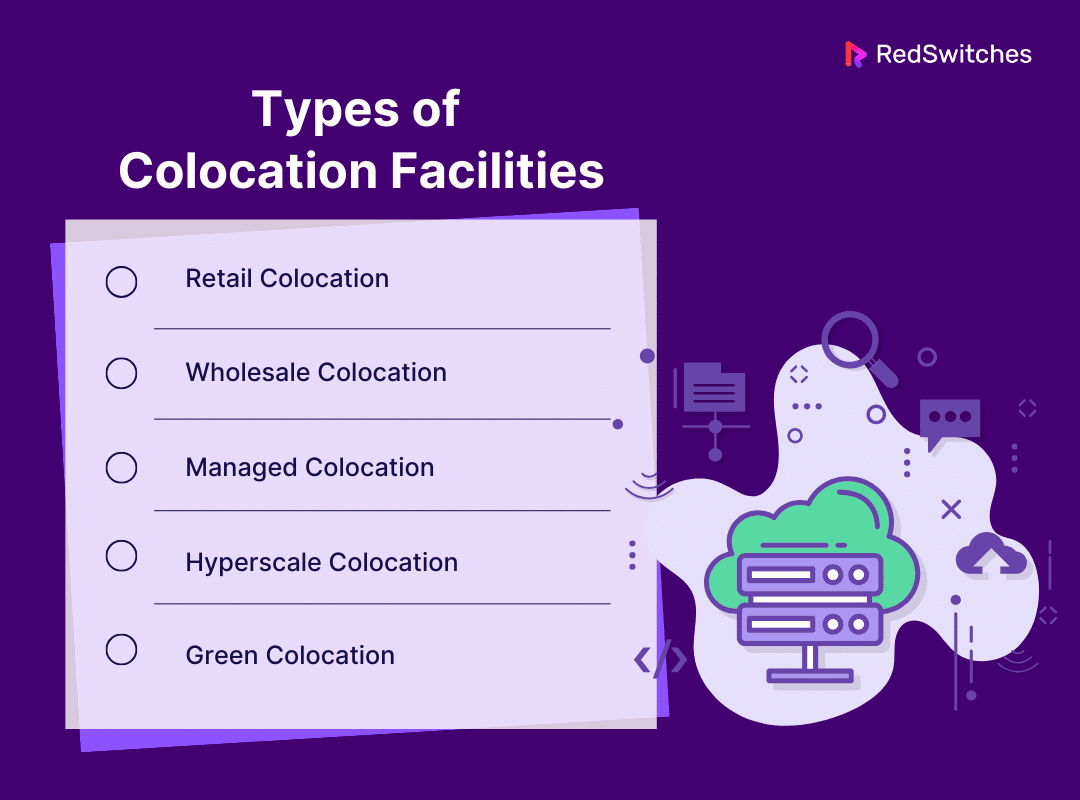
Types of Colocation Facilities
With several types of colocation facilities available, it is important to understand that not all are created equal. They vary in terms of size, services, and the specific needs they cater to. Below are the different types of colocation facilities:
Retail Colocation
Retail colocation facilities are one of the most common types of colocation facilities. They cater to small to medium business models and offer space in terms of racks or cabinets. Clients in retail colocation rent out a portion of a data center.
This portion could range from a single rack to a cage containing multiple racks. This type of colocation is ideal for businesses that do not need a large dedicated space but still want the benefits of a professional data center.
Also Read: Understanding The Different Types Of Web Hosting Services.
Key Features
Retail colocation is a service offered by data center providers where businesses can rent space for servers and other computing hardware. This service typically includes the physical space, power, cooling, and security necessary for the hardware’s operation. Here are some key features of retail colocation:
Customizable Space Options
Retail colocation facilities usually offer a range of space options. They have everything from single racks to lockable cages. This flexibility allows businesses to choose a space that fits their current needs and budgets while allowing them to expand as they grow.
Shared Infrastructure Costs
One main benefit that makes retail colocation popular is the shared infrastructure. Clients share the overall power, cooling, connectivity, and security costs. This makes it more affordable than maintaining an in-house data center. By holding their equipment in retail colocation facilities, businesses can save a large amount of money each month.
Community and Networking Opportunities
Since retail colocation facilities hold data servers and equipment for various businesses at a time, they can provide networking opportunities. This environment can foster collaborations and provide insights into industry best practices.
Wholesale Colocation
Wholesale colocation facilities cater to larger businesses with more substantial data management needs. In this model, clients lease a fully built data center space. These spaces usually come in the form of a large room or even an entire floor. This provides more control over the IT environment.
Enterprises with significant server and storage requirements often select wholesale colocation. These facilities serve as a more cost-effective solution for large-scale deployments.
Key Features
Wholesale colocation is a type of data center leasing where a large-scale space is rented out, usually to a single client. It differs from retail colocation, which typically involves smaller spaces leased to multiple clients. Here are some key features of wholesale colocation:
Large Dedicated Spaces
One of the defining characteristics of wholesale colocation is the provision of large, dedicated spaces for clients. This space is larger than typically offered in retail colocation. This feature benefits large enterprises requiring substantial space for their extensive server arrays, storage systems, and networking equipment.
Cost-Effectiveness for Large Deployments
Wholesale colocation is generally more cost-effective for large-scale deployments. Since clients lease larger spaces, the cost per unit (per rack or square foot) can be lower than retail colocation. This pricing structure makes wholesale colocation a suitable option for businesses that need considerable data center space.
Customizable Infrastructure
Clients in wholesale colocation often have the flexibility to customize their leased space to meet specific requirements. This includes tailoring power and cooling systems, arranging server racks and storage, and implementing specific security measures. Such customization is necessary for businesses with specialized IT infrastructure needs.
Managed Colocation
Managed colocation takes the standard offerings of a colocation facility a step further. It does so by adding managed services. Besides renting physical space, clients enjoy added services like maintenance and security management. This is perfect for businesses that want the benefits of colocation but prefer to focus their resources elsewhere.
Key Features
Here are some key features of managed colocation:
Large Dedicated Spaces
Managed colocation facilities often provide large dedicated spaces. These spaces usually cater to businesses with substantial hardware requirements. This large physical space is ideal for enterprises that need to hold many servers and networking equipment. Such large dedicated spaces empower businesses to customize the layout and setup to meet specific operational needs.
Suitable for Enterprises with Extensive IT Infrastructure
Managed colocation is well-suited for large enterprises with a comprehensive IT infrastructure. These organizations often need a setup with many server types, storage systems, and advanced hardware. These facilities offer an environment where large-scale IT systems can operate efficiently.
Greater Control Over the Environment and Infrastructure
A great benefit of managed colocation is the control it offers businesses over their IT environment and infrastructure. While the colocation provider maintains the physical space, the enterprise retains complete control over its hardware and software’s setup, configuration, and management.
This control is crucial for businesses with specific compliance requirements. It is also excellent for businesses that must maintain a certain level of customization and flexibility in their IT operations.
Also Read: 4 Different Server Types: A Detailed Analysis
Hyperscale Colocation
Hyperscale colocation is designed for large-scale operations run by large tech firms or cloud service providers. These facilities are built to support massive amounts of data storage and processing. Hyperscale colocation facilities are characterized by their vast floor space, high power capacity, and advanced cooling systems.
Key Features
The key features of hyperscale colocation include
Massive Scale Infrastructure for High-Density Computing
Hyperscale colocation centers are designed to handle massive amounts of servers and data storage systems. These data centers are designed for high-density computing. They can accommodate several servers in a comparatively small area. This maximizes processing power and space consumption through sophisticated rack designs and layout optimizations.
Tailored for Big Tech Companies and Cloud Service Providers
Hyperscale colocation is designed to meet the needs of large technology companies and cloud service providers. These entities require vast data processing and storage capacities to support their operations. Hyperscale colocation facilities provide the necessary infrastructure to support these intensive workloads.
Emphasis on Scalability and High Power Capacity
One of the defining features of hyperscale colocation is its scalability. These facilities can scale up resources quickly and efficiently. They are built with a focus on the future, accommodating rapid expansion in power and cooling capacities. This aspect is crucial for tech giants and cloud providers who experience fluctuating demands and continuous growth.
Green Colocation
Green colocation facilities focus on sustainability. They aim to reduce the environmental impact of data center operations. These facilities use renewable energy sources, energy-efficient cooling systems, and other green technologies. They are ideal for environmentally conscious businesses committed to reducing their carbon footprint.
Key Features
Here are some key features of Green colocation:
Use of Renewable Energy Sources
Green colocation facilities often rely on renewable energy sources. This includes solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. These data centers reduce their reliance on fossil fuels by using clean energy. As a result of this, they can lower greenhouse gas emissions. This commitment to renewable energy benefits the environment and resonates with environmentally conscious customers and stakeholders.
Energy-Efficient Systems and Design
Energy efficiency is at the core of green colocation facilities. They employ advanced technologies and design principles that reduce energy consumption. This includes using energy-efficient cooling systems, like free cooling techniques that use outside air or water sources. These facilities often feature highly efficient power distribution systems and LED lighting to reduce energy usage.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Green colocation facilities aim to reduce carbon footprint by focusing on renewable energy and energy efficiency. This is crucial in the fight against climate change, as data centers traditionally are major energy consumers and carbon emitters. Businesses can demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility by choosing green colocation.
Here’s an overview of the types of colocation facilities discussed above:
Also Read: Host Vs Server: Highlighting The Major Differences.
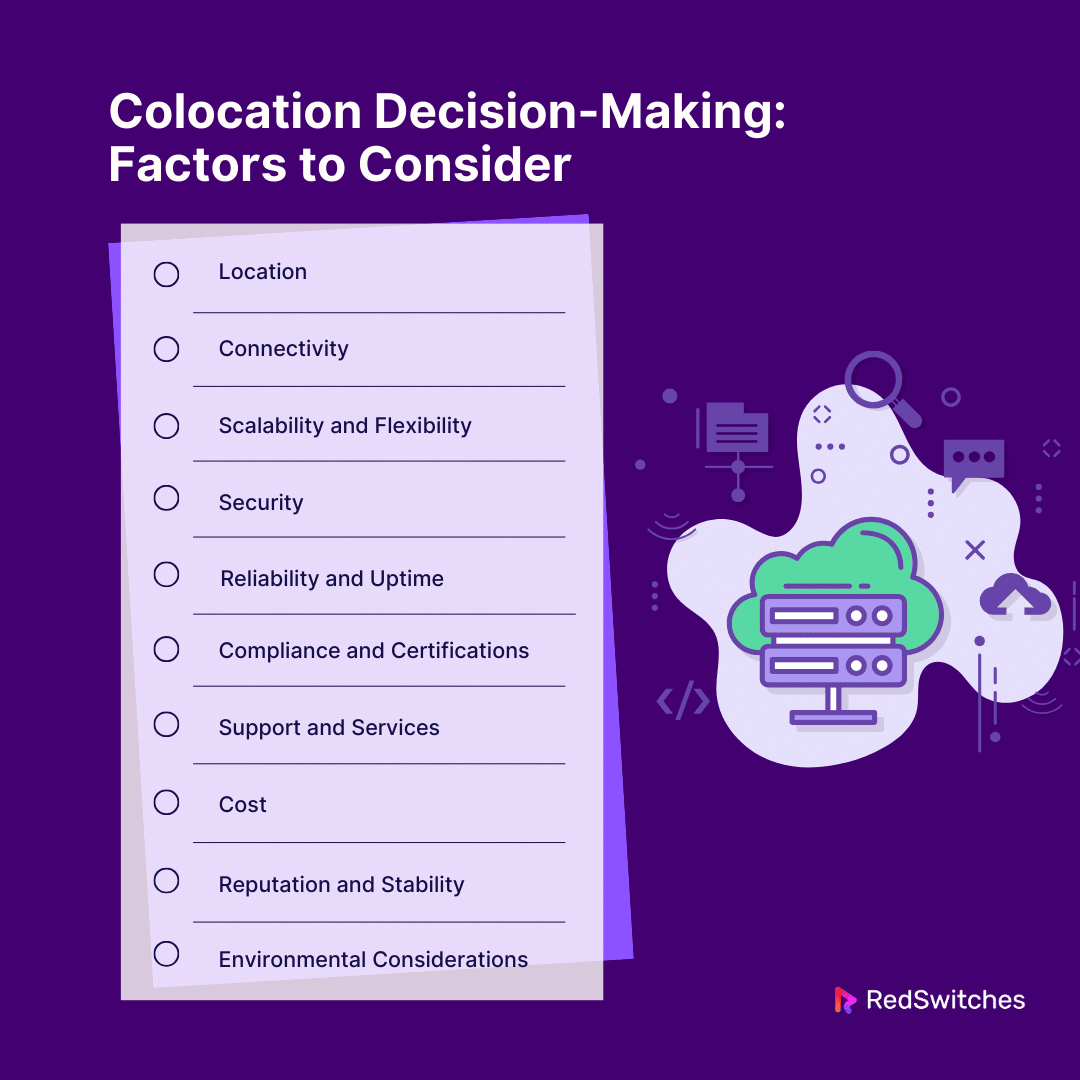
Colocation Decision-Making: Factors to Consider
Deciding on a colocation facility can be difficult, especially for businesses housing their equipment in a colocation facility for the first time. To make the decision-making process easier, we have compiled a list of the important considerations below. By considering these factors, you can easily pick the ideal colocation facility for your needs.
- Location
Credits: Freepik
The choice of location for a data center goes beyond just the risk of natural disasters. It’s also about connectivity to major network exchanges and access to a skilled workforce. Data centers near internet exchange points will likely offer better connectivity and lower latency. This is especially crucial for real-time applications.
Consider local climate conditions as they can impact cooling costs. A cooler climate can reduce the need for artificial cooling, lowering energy costs. The availability of a skilled technical workforce in the area can also be a deciding factor, ensuring quick and efficient handling of any onsite issues.
- Connectivity
Credits: Freepik
When evaluating connectivity, it’s essential to consider the data center’s peering arrangements and bandwidth capacity. Good peering relationships ensure faster and more reliable connections.
Check the data center’s redundancy in network connections to safeguard against single points of failure. This includes having multiple independent network paths that ensure continuous service if one path goes down. The data center should also be capable of supporting a variety of connectivity protocols and services. This includes IPv6, MPLS, and cloud direct connect services.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Credits: Freepik
Scalability should encompass the physical space and network, power, and cooling infrastructures. Check if the data center can provide high-density racks for future-proofing against more powerful hardware.
Flexibility is also crucial in contractual terms. Seek out data centers that offer customizable service agreements that can be adjusted as your business evolves. This flexibility should extend to pricing models, allowing you to pay for only what you use, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
- Security
Credits: Freepik
Besides physical and cyber security measures, it’s essential to consider the data center’s compliance with industry-specific regulations. You must also evaluate the data center’s track record in handling security breaches.
Go over the data center’s policies for incident response. Seeking information on the data center’s internal best practices, like employee security training and regular security audits, can also offer valuable insights.
- Reliability and Uptime
Credits: Freepik
A high uptime SLA is crucial, but understanding how it’s achieved is equally important. Investigate the data center’s infrastructure redundancies, not just in power and cooling but also in network hardware and service paths. It is also important to look into the data center’s disaster recovery capabilities.
This includes power backup systems like generators and their policies for handling outages. A thorough assessment of the data center’s performance data, maintenance routines, and upgrade plans can provide insight into its commitment to long-term reliability.
- Compliance and Certifications
Credits: Freepik
Beyond general compliance, it is also critical to explore the specifics of a data center’s certification standards. For instance, SSAE 18 SOC 1, 2, and 3 certifications are critical for data security and integrity.
Always look for data centers that follow international standards, like ISO 27001. These certifications are not only about meeting baseline requirements. They also reflect a data center’s commitment to maintaining high standards in every aspect of its operation.
- Support and Services
Credits: Freepik
Examine the range of value-added services a data center offers. This could include managed services like network monitoring, system updates, backup and recovery solutions, and cybersecurity services.
The availability of expert technical staff for consultation can also be a significant asset, providing insights and assistance for optimizing your infrastructure. Understand their SLA terms, especially concerning response times for various issues, which can be critical in minimizing downtime.
- Cost
Credits: Freepik
Assess the total cost of ownership when considering a data center. This includes the direct costs of space and power and ancillary costs like bandwidth, additional security features, and support services.
Compare pricing models among different providers. Some may offer a flat rate, while others might have a pay-as-you-go model. Ensure you understand what’s included in the base price and what would incur additional charges.
- Reputation and Stability
Credits: Freepik
Besides financial stability, look at customer reviews, case studies, and industry awards. These can provide insights into the data center’s performance and customer satisfaction.
Check for any data breaches or downtime history. These can indicate potential issues. A reputable data center should be transparent about such incidents and willing to discuss how they were resolved.
- Environmental Considerations
Credits: Freepik
Inquire about the data center’s initiatives in green computing. This includes using energy-efficient hardware, cooling technologies, and participation in carbon offset programs.
Some data centers are also exploring using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. This can help reduce environmental impact and ensure more stable long-term operating costs.
Also Read: The Future Of Data Centers In Cloud Computing.
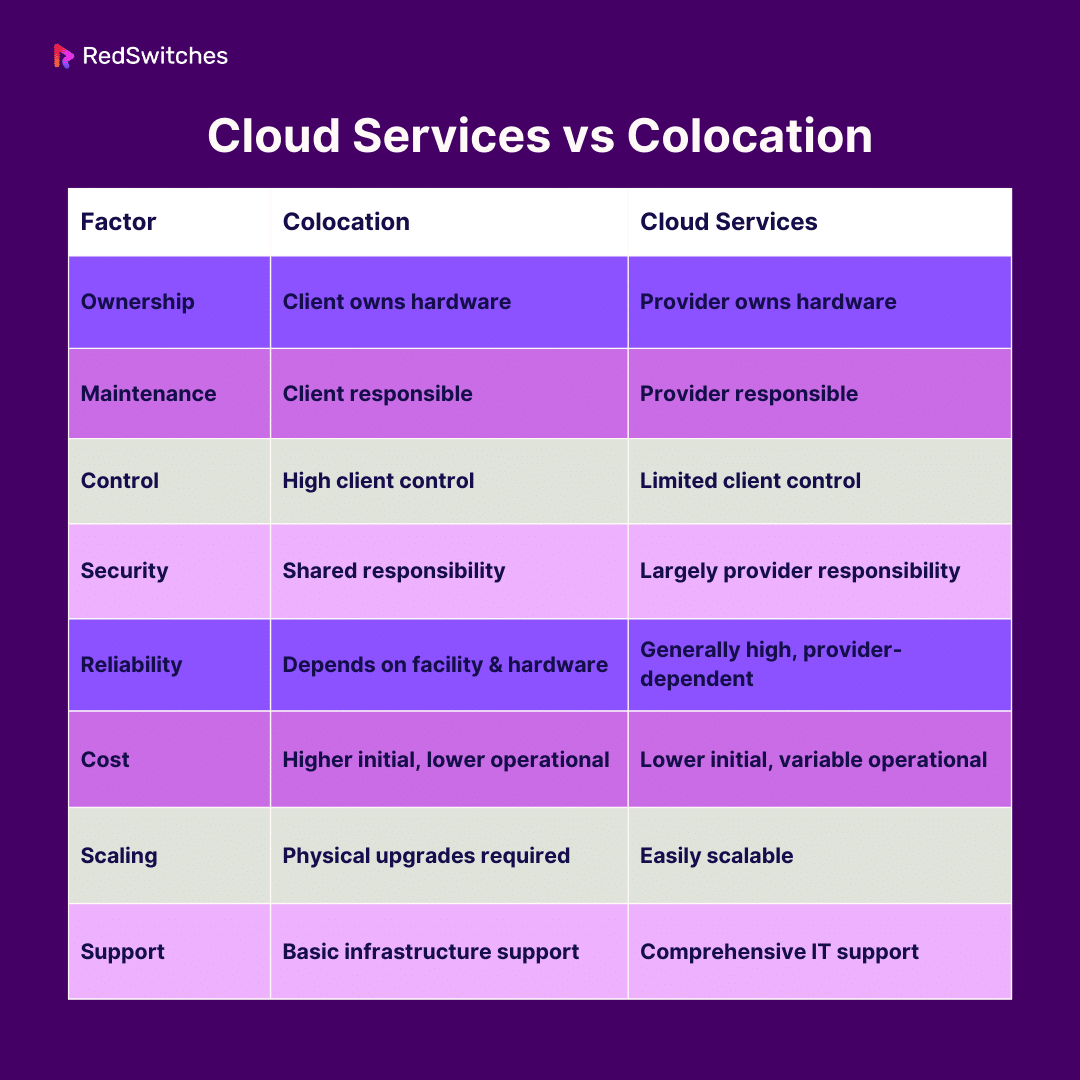
Cloud Services vs Colocation
Before we compare cloud services vs colocation, it is important to understand cloud services.
What is Cloud Services?
Cloud services mean storing and accessing your data and applications over the internet instead of your computer’s hard drive. Think of it like renting an apartment. You don’t own the building but use a part of it to live in. Similarly, in cloud services, you use a portion of a massive network of servers owned by a service provider.
Comparing the Differences
When it comes to managing your business’s IT infrastructure, two popular options are colocation and cloud services. Both have unique features. Understanding these differences can help you decide which is right for your business. Below, we compare colocation vs cloud services:
Ownership
Cloud services and colocation are two distinct approaches to managing IT infrastructure, and they differ significantly in terms of ownership and control:
-
Colocation
Think of colocation as having a land plot where you build your own house. You own the house (your servers and hardware) but rent the land (space in a data center). You have control over your hardware but also have to buy and manage it yourself.
-
Cloud Services
Using cloud services is like renting a furnished apartment. You don’t own the furniture (servers and hardware) or the apartment (space in the data center); you just use them. The cloud provider owns and manages all the hardware.
Maintenance
The maintenance responsibilities in cloud services and colocation differ significantly, reflecting the distinct nature of each model:
-
Colocation
Colocation demands you to maintain your servers. If something breaks, it’s up to you to fix it or hire someone to do it. If something in your house breaks, you’re responsible for the repairs. This is similar to how colocation works in terms of maintenance.
-
Cloud Services
The provider takes care of all the maintenance with cloud services. If there’s a problem with the hardware, they fix it, not you. We can compare it to living in a rented apartment where the landlord handles all the repairs.
Control
Control is a key differentiator between cloud services and colocation, impacting how businesses manage their IT infrastructure:
-
Colocation
Colocation offers total freedom with your setup. You pick the best hardware and software that suits your business. It’s comparable to customizing your workspace exactly how you like it.
-
Cloud Services
Cloud services are more about convenience. The cloud provider decides the technical details. You focus on using the service, not managing the tools. It’s similar to living in a fully serviced apartment. Everything is arranged for you.
Security
Security considerations in cloud services and colocation differ, largely due to the nature of infrastructure management and control in each model:
-
Colocation
Security is all in your hands when it comes to colocation. You can implement security measures that fit your specific needs. This could include firewalls, encryption protocols, or other security hardware and software. While the colocation facility provides general security, like surveillance, the security of your specific hardware is up to you. Some colocation providers may also offer managed colocation services.
-
Cloud Services
Cloud services offer professional-grade security without the hassle. Cloud providers usually have strong security measures, constantly updated by specialists. It’s like living in a gated community with professional security staff.
Cloud security teams monitor the network for suspicious activities and update security protocols. This includes patching vulnerabilities, applying the latest security software, and handling emerging threats.
Also Read: Learn About 4,3,2,1 Data Center Tiers Classifications.
Reliability
Reliability is a crucial aspect of cloud services and colocation. However, how it is achieved and managed can differ significantly between the two:
-
Colocation
Reliability is a joint effort. The data center provides the environment (like power and cooling), but the reliability of your equipment is up to you. It’s similar to renting a space to work. The building is good, but your work tools must also be reliable.
-
Cloud Services
Designed for high reliability. Cloud providers often have redundant systems, meaning if something goes wrong, they have backups in place. Imagine a hotel with a backup generator; the generator kicks in if the power goes out.
Cost
The cost structures of cloud services and colocation are distinct, each offering different financial implications and models:
-
Colocation
Colocation can be expensive to begin with. This is because you have to buy your servers and equipment. However, once you’ve made that investment, the ongoing costs can be lower than cloud services. This allows you to save money in the long run.
-
Cloud Services
Starting with cloud services usually costs less because you don’t have to buy hardware. You do, however, pay a regular fee for using the service. This can add up over time, mainly if you use many resources.
Scaling
Scaling capabilities differ significantly between cloud services and colocation, impacting how businesses can grow or adapt their IT infrastructure:
-
Colocation
Scaling up in colocation means buying more hardware and possibly needing more space in the data center. It’s like needing a bigger house as your family grows. It requires more investment.
-
Cloud Services
Scaling in the cloud is more accessible. Adjust your plan with the provider if you need more space or power. It’s like asking your landlord for a bigger apartment and paying more rent.
Support
The level and type of support offered in cloud services and colocation vary, reflecting the different models of IT infrastructure management:
-
Colocation
You’re on your own when it comes to support in colocation. This is why having a skilled IT team is crucial in a colocation setup. They handle everything from server maintenance to network configuration and deal with technical issues.
-
Cloud Services
Cloud providers usually offer support as part of their service. If you encounter a problem or have a question, you can usually contact the cloud provider’s support team via phone, email, or chat. They can assist with a wide range of issues related to their services.
Conclusion
Deciding to transition to a colocation facility is a major step for any business. It demands careful evaluation of various factors, including cost, scalability, security, and compliance. As we have explored, each element is important in ensuring that your colocation choice goes with your business’s needs and future growth plans.
If you are looking for a reliable colocation service, RedSwitches emerges as a standout option. We offer a range of colocation solutions tailored to meet diverse business requirements. Our colocation solutions emphasize space and infrastructure and provide robust security, uptime, and scalability.
Businesses can enjoy the benefits of a state-of-the-art colocation facility by choosing us. This allows them to focus on their core operations and ensure that data management needs are met professionally. Visit our website now to explore how our colocation services can align with and support your business’s unique demands.
FAQs
Q. What does colocation mean?
Colocation is a service where a business rents space in a data center to hold its servers and computing hardware. The data center supplies the hardware’s physical space, power, cooling, and security. The business retains control over the software and data stored on the servers.
Q. What is the meaning of Colocality?
Colocality refers to the state or condition of being located together or in the same place. It can relate to colocating resources, services, or activities in a single physical location for efficiency and convenience.
Q. What is the purpose of colocation?
The main purpose of colocation is to offer businesses a secure, reliable, and professionally managed space for their IT infrastructure. It offers benefits like cost savings on infrastructure, higher bandwidth, advanced security, and better reliability than hosting servers on-premises.
Q. What is a colocation data center?
A colocation data center is where businesses rent space for their servers and networking equipment. It provides the equipment’s physical space, power, cooling, and security. The businesses maintain full control over their own IT infrastructure.
Q. What are the benefits of using a colocation data center?
Colocation data centers offer benefits like reliability, security, and access to advanced infrastructure. They also allow businesses to focus on their core operations rather than managing the physical data center.
Q. How does colocation pricing work?
Colocation pricing is based on factors like power usage, space requirements, and added services. It is often more cost-effective than building and maintaining a private data center.
Q. What security measures are in place at a colocation data center?
Colocation data centers employ physical security measures like access control systems, surveillance cameras, and biometric authentication. They also have security personnel to ensure the safety and protection of the equipment and data.
Q. What is the difference between colocation and the public cloud?
Colocation involves housing and maintaining your own physical hardware in a data center. The public cloud offers virtualized resources and services on a pay-per-use basis. Colocation provides more control over hardware and data. The public cloud offers scalability and flexibility.
Q. What are the key factors when choosing a colocation provider’s data center?
Factors to consider when choosing a colocation provider include the location of the facility, power and cooling capabilities, and network connectivity options. One must also consider physical security measures, compliance certifications, service level agreements, and the provider’s reputation.
Q. How does colocation enable businesses to meet their IT infrastructure needs?
Colocation enables businesses to access advanced infrastructure and resources without investing in building and managing their own data center. It allows them to benefit from the expertise of a specialized colocation provider.
Q. What role does a colocation data center play in cloud migration?
Colocation data centers can be an ideal environment for businesses to migrate their on-premises infrastructure to the cloud. They provide the infrastructure, security, and connectivity for a smooth migration to the public cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
Q. What are remote hands in the context of colocation data centers?
Remote hands refer to the technical support and assistance the colocation provider’s on-site staff provides. This includes helping with equipment reboots, troubleshooting, hardware installations, and maintenance. It allows businesses to access skilled support without needing a physical presence.
Q. How does colocation benefit businesses in terms of network services?
Colocation data centers offer high-speed and redundant network connectivity options. This allows businesses to benefit from reliable and efficient networking infrastructure. This ensures optimal performance and smooth connectivity for their IT operations.