Key Takeaways
- Dedicated hosting is internet hosting where a client leases an entire server.
- Dedicated hosting offers tailored performance, absolute control, and dedicated support.
- Dedicated hosting comes with higher costs and maintenance responsibilities.
- Colocation server hosting is where businesses rent physical locations to hold their servers.
- Colocation hosting provides advanced security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Colocation server hosting features advanced security, network connectivity, redundant power supply, etc.
- Opt for dedicated hosted servers for high-traffic volumes, resource-intensive applications, increased security needs, etc.
- Consider colocation when you need geographical flexibility, custom hardware, etc.
Did you know that the global data center market revenue is predicted to show a growth rate (CAGR 2024-2028) of 6.56%? This will result in a market volume of $438.70bn by 2028. This growth shows the growing need for solutions like colocation and dedicated hosting.
Colocation and dedicated hosted servers are two hosting solutions that businesses constantly contemplate. This blog will discuss colocation vs dedicated server hosting, guiding you through the intricacies of each option. It will empower you to make informed decisions that align with your goals and operational requirements.
- Key Takeaways
- What is Hosting?
- What is Dedicated Server Hosting?
- Dedicated Hosted Server Features
- Pros and Cons of Dedicated Hosting
- What is Colocation Server Hosting?
- Colocation Server Hosting Features
- Pros and Cons of Colocation Server Hosting
- Choosing Between Colocation Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting
- Future Trends and Considerations
What is Hosting?
Credits: FreePik
Before we discuss colocation vs dedicated server hosting, it is important to understand what hosting is.
Hosting refers to offering storage space and access for websites on servers. It allows sites to be accessible on the World Wide Web. It’s like renting a space on a server where your website’s files, data, and content reside. Whenever users type in their web address or domain name, the hosting server sends these files to the user’s web browser, displaying your website.
Hosting services store and serve website content and often offer various related services. This includes website management, support, email hosting, domain registration, and more. The hosting choice can affect a website’s performance, security, and reliability. This makes it important for businesses and individuals looking to establish an online presence.
What is Dedicated Server Hosting?
Credits: FreePik
Dedicated server hosting is an internet hosting type where a client leases an entire server. The server is not shared with anyone else. This exclusive hosting environment offers complete control over the server. It includes the choice of hardware, operating system, and more. This setup provides clients with robust and dedicated resources. It ensures higher performance, security, and customization.
In this hosting model, the client benefits from the total computational power of the hardware. They don’t have to worry about competing for resources with other users, as is common in more shared environments. This exclusivity makes it ideal for websites with high traffic volumes, large-scale e-commerce platforms, and data-intensive applications requiring extensive processing power and memory.
Dedicated hosting also offers improved security, as the isolation from other users reduces the risk of cyber threats. Clients can put in place their security protocols to improve the protection of their digital assets.
One of the main benefits of this hosting solution is its customization level. Users can configure server settings, install specialized software, and adjust performance parameters. This flexibility is great for businesses with unique or evolving IT needs.
Dedicated Hosted Server Features
Understanding the key features of dedicated hosting will help you evaluate whether it fits your business needs well. Here are the key features of dedicated hosting:
Tailored Performance and Reliability
Exclusive hosting environments are synonymous with remarkable performance. Each server is an individual entity, providing users with the full spectrum of its resources. This means that RAM, storage, and CPU are at the sole disposal of one entity. It ensures that high-traffic sites, complex applications, and data-intensive workloads run smoothly and efficiently.
Absolute Control and Customization
One of the most celebrated features of dedicated hosting is its level of control and customization. Users can tailor every aspect of their environment to meet their specific requirements. This includes selecting the desired operating system or configuring software and security settings. This flexibility is invaluable for businesses with specialized needs. It is also ideal for businesses looking to optimize servers for peak performance.
Scalability for Future Growth
As businesses evolve, so do their digital demands. Exclusive hosting solutions excel in scalability. It allows for smooth upgrades to hardware and resources as needed. This adaptability ensures businesses can accommodate growth without migrating to a new server. It also saves them from dealing with a shared hosting environment.
Dedicated Support and Expertise
Server management can be a daunting task. That’s where exclusive hosting providers’ dedicated support and expertise come into play. Round-the-clock technical support, coupled with the knowledge and experience of seasoned professionals, provides businesses with the peace of mind that any issues will be promptly and effectively addressed.
Bandwidth and Connectivity
Exclusive hosting solutions come with dedicated bandwidth. It ensures consistent and high-speed connectivity for your online operations. This is crucial for maintaining optimal site performance, especially for sites with high traffic or that host multimedia content.
Redundancy and Uptime Guarantees
Reliability is a cornerstone of exclusive hosting environments. With built-in redundancy features, including backup power supplies and data storage solutions, these servers ensure maximum uptime and continuity of service. SLAs often back this reliability. It offers guarantees on uptime and compensates in the unlikely event of downtime.
Also Read: 5 Reasons You Need A Dedicated Hosted Server.
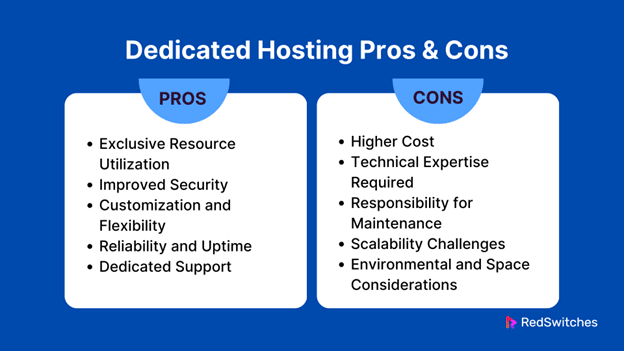
Pros and Cons of Dedicated Hosting
Before you decide between dedicated hosting and colocation hosting, weigh both options’ pros and cons to determine which is best for you. Below, we explore the pros and cons of opting for a dedicated hosting environment.
Dedicated Hosting Pros
Let’s discuss the pros of dedicated hosting.
Exclusive Resource Utilization
One of the top benefits of dedicated hosting is the sole access to server resources. This exclusivity ensures your website or application can leverage the server’s processing power and memory capacity. This leads to better performance and stability.
Improved Security
According to a forecast, cybercrime will cost the US over $452 billion in 2024. This is where the security feature offered by exclusive hosting solutions shines. With a dedicated environment, you completely control the security measures on your server. This autonomy allows for customized firewall configurations, security protocols, and software installations.
Customization and Flexibility
Dedicated hosting offers the freedom to customize server settings. You can conduct software installations and tailor operating systems to meet your requirements. This customization is beneficial for businesses with unique or resource-intensive applications.
Reliability and Uptime
The exclusive use of server resources in a dedicated environment minimizes server overload risk and ensures consistent uptime. This reliability is crucial for businesses where downtime can lead to revenue and reputation losses.
Dedicated Support
Due to the service’s high-value nature, dedicated hosting solutions providers often provide superior customer support. This can include 24/7 access to a team of experts, faster response times, and personalized assistance.
Dedicated Hosting Cons
Let’s discuss the cons of dedicated hosting.
Higher Cost
The most notable drawback of dedicated hosting is its cost. The exclusivity and high performance come with a higher price tag than shared or VPS hosting. This makes it less accessible for small businesses or individuals with limited budgets.
Technical Expertise Required
Managing a dedicated hosted server requires certain technical expertise. Users must be capable of configuring server settings, managing security protocols, and performing routine maintenance. This can be daunting for those without technical backgrounds.
Responsibility for Maintenance
With dedicated hosting, the server maintenance and troubleshooting responsibility lies primarily with the user. This can be time-consuming, and demands added resources for businesses without an in-house IT team.
Scalability Challenges
Dedicated hosted servers provide significant resources for hosting needs. However, scaling these resources to accommodate sudden spikes in traffic or growth can be more complex and slower than cloud or VPS solutions.
Environmental and Space Considerations
Dedicated hosted servers require physical space and environmental controls to ensure optimal performance. This necessitates a well-equipped data center. It can add to the overall cost and complexity of the hosting solution.
Have you decided to go with dedicated hosting? Learn how to Choose The Right Dedicated Hosted Server,’ for your needs.
What is Colocation Server Hosting?
Credits: FreePik
Colocation server hosting is where businesses or individuals rent physical locations to hold their servers and other computing hardware. This empowers clients to place their equipment in a professionally managed facility while keeping ownership and complete control.
These data centers offer vital infrastructure. This includes power, cooling, physical security, and connectivity to the computing equipment. Colocation benefits clients from a dedicated data center’s high-end infrastructure and bandwidth. Clients no longer have to worry about the cost of building and maintaining such facilities.
It’s an ideal solution for organizations that demand the physical presence of their servers but wish to avoid the challenges and costs that come with housing them on-premises.
This setup offers several other advantages. Those include improved security, reliable connectivity, and potential cost savings on bandwidth and infrastructure. This makes it a popular option for businesses with specific hosting needs.
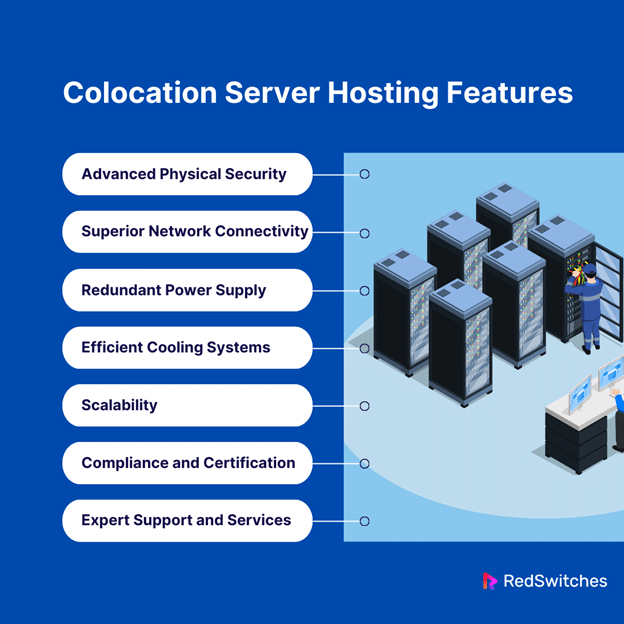
Colocation Server Hosting Features
Understanding the key features of colocation server hosting will help you determine whether it is right for your business. Here are the key features of colocation server hosting:
Advanced Physical Security
One of the most prominent features of colocation hosting is the level of physical security provided. Data centers feature multiple security measures. This includes surveillance cameras, security personnel, and intrusion detection systems. These measures help protect your hardware against unauthorized access, theft, and physical damage.
Superior Network Connectivity
Colocation facilities are created to offer superior network connectivity with numerous bandwidth options. These data centers are usually connected to multiple high-speed and major internet backbones. This ensures low latency and high throughput. This feature benefits businesses that require consistent, high-speed access to their data and applications. It ensures optimal performance and user experience.
Redundant Power Supply
Power redundancy is another critical feature of colocation hosting. Data centers are equipped with redundant power supplies. This includes UPS systems and backup generators to ensure continuous operation during a power outage. This level of power redundancy is often complex and costly for businesses to achieve on their own premises. Thankfully, it is a standard offering in colocation environments.
Efficient Cooling Systems
Maintaining the recommended temperature and humidity is important for the longevity of IT hardware. Colocation data centers have advanced cooling systems to manage the heat generated by high-density server racks. This ensures the hardware operates within safe temperature ranges. It also contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings on cooling.
Scalability
Colocation hosting allows businesses to scale their IT infrastructure as needed. You can easily add more servers or networking equipment as your business flourishes. You no longer have to worry about space constraints or upgrading power and cooling systems. This scalability feature allows for future growth while keeping capital and operational expenses in check.
Compliance and Certification
Many colocation facilities follow all compliance standards and hold certifications such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS. This is especially important for businesses in regulated industries or those handling sensitive data. It ensures that the colocation provider meets security and data protection standards.
Expert Support and Services
Colocation hosting often comes with access to expert support and additional managed services. This can include technical support, hardware installation, maintenance, advanced security, and network services. Access to such expertise can relieve the burden on your internal IT team and ensure your infrastructure runs optimally.
Are you still finding it difficult to understand colocation data centers? Read our blog. ‘Understanding Colocation Data Center: A Comprehensive Guide,’ for clarity.
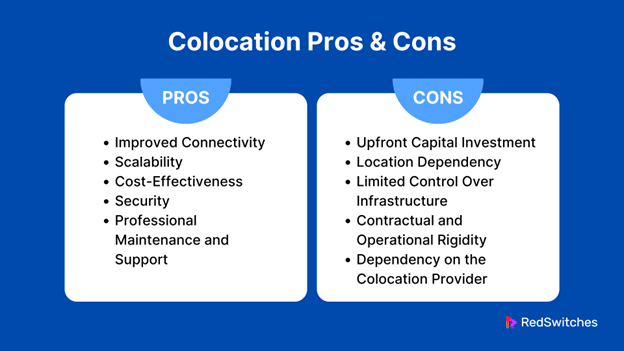
Pros and Cons of Colocation Server Hosting
Before you decide between dedicated hosting and colocation hosting, you must understand both options’ pros and cons to determine which best fits your needs and requirements. Below, we explore the pros and cons of Colocation server hosting:
Colocation Pros
First, let’s look at the pros of Colocation.
Improved Connectivity
Colocation facilities often provide superior network connectivity with multiple high-speed internet connections. They ensure optimal performance and minimal downtime. This is crucial for businesses that demand consistent online presence and swift data transactions.
Scalability
One of the key benefits of colocation is the scalability it offers. As your business grows, your IT infrastructure can expand without the need to move to a new location. You can add or upgrade existing servers within the same colocation facility. This makes it a flexible option for growing businesses.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in hardware and setup might be substantial, colocation can be more cost-effective in the long run. You avoid the high costs of building and maintaining your own data center. This includes cooling, power, and security, translating into savings over time.
Security
Colocation facilities often offer advanced security measures. This includes physical security guards, surveillance cameras, biometric access controls, and more. This level of security can be difficult and expensive to replicate in a private data center.
Professional Maintenance and Support
Most colocation centers offer professional maintenance and support services. This ensures that any power, cooling, or connectivity issues are swiftly addressed. This reduces the burden on your IT staff. It allows them to focus on core business activities.
Colocation Cons
Now, let’s look at the cons of Colocation.
Upfront Capital Investment
The initial cost of purchasing server hardware and setting up your infrastructure in a colocation facility can be high. This upfront investment can be a barrier for small businesses or startups with limited capital.
Location Dependency
Your physical proximity to the colocation facility can impact the ease of access to your hardware. If your business requires frequent physical server access, being far from the data center can be inconvenient.
Limited Control Over Infrastructure
While colocation allows for control over your hardware, you may have a limited say in the overall infrastructure of the data center. This includes the type of power backups, cooling systems, and network providers.
Contractual and Operational Rigidity
Entering into a colocation agreement often involves long-term contracts. These contracts may lack the flexibility some businesses need. Scaling down your operations if your business needs change can also be difficult.
Dependency on the Colocation Provider
Your operations may depend heavily on the colocation provider’s reliability and stability. Any downtime or issues on their part can directly affect your business. This makes due diligence in selecting a provider crucial.
Also Read: Understanding The Different Types Of Web Hosting Services.
Choosing Between Colocation Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting
Still confused about whether to go for colocation server hosting or dedicated server hosting? Here are a few scenarios where choosing colocation or dedicated hosting would be suitable for businesses.
When do You Choose Dedicated Hosted Servers
Choosing a dedicated environment is particularly beneficial in scenarios where:
- High Traffic Volumes
Your website or application experiences high traffic levels. It demands dedicated resources to ensure smooth and reliable performance.
- Resource-Intensive Applications
You run complex applications that require processing power, memory, and storage that cannot be shared with other users.
- Increased Security Needs
Your operations involve handling sensitive data. It demands stringent security measures best managed in a dedicated setting.
- Customization and Control
You need the ability to fully customize your server environment to meet specific software and configuration requirements. However, you don’t want to worry about dealing with the constraints of a shared infrastructure.
Dedicated environments suit businesses looking for turnkey solutions that provide robust performance, security, and ease of management. Such solutions allow businesses to focus on their core operations without the intricacies of hardware management.
When do You Choose Colocation Hosting
Colocation hosting might be the right choice under the following circumstances:
- Existing Hardware Investment
You have invested in server hardware and are looking for a cost-effective way to use professional data center facilities.
- Scalability with Control
You require the flexibility to scale your hardware. You also want direct control over the server specifications, hardware upgrades, and replacements.
- Custom Hardware Needs
Your operations require specialized hardware configurations not commonly offered by dedicated hosting providers, necessitating a custom approach.
- Geographical Flexibility
You need your server to be located in a specific region to reduce user latency or to comply with data sovereignty laws, offering more control over the physical location of your hardware.
Colocation balances the autonomy of managing your hardware and the benefits of a professional data center’s infrastructure. It suits businesses with specific hardware needs and desires physical server control.
Also Read: Host Vs Server: Highlighting The Major Differences.
Future Trends and Considerations
Credits: Freepik
The server hosting industry continues to change as we move into the decade. Technological advancements, environmental concerns, and regulatory changes shape these changes. Businesses contemplating colocation vs dedicated server hosting must consider the following factors to make informed, future-proof decisions.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Hosting Needs
Emerging technologies like the IoT, AI, ML, and 5G connectivity transform hosting needs. These technologies demand processing power, lower latency, and increased data storage capacities. For instance, AI and ML workloads require servers with specialized hardware. Examples include GPUs and TPUs (for handling complex computations).
Colocation facilities adapt by offering advanced infrastructure with high-density computing and high-speed networking. Dedicated hosted server providers are also adapting to the changing landscape. They are providing options for servers with the necessary hardware to support these advanced applications. This empowers businesses with the flexibility to scale up as their technological needs evolve.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations in Hosting
Environmental sustainability has become a major consideration for businesses worldwide. The digital sector is scrutinized for its substantial energy consumption and carbon footprint. This has caused a shift towards greener hosting solutions.
Colocation centers invest in renewable energy sources, energy-efficient cooling, and sustainable building designs to lower environmental impact. These facilities often boast certifications like LEED or ENERGY STAR. This provides businesses with a more sustainable hosting option.
Dedicated hosted server providers are also embracing green initiatives. They are optimizing their data centers for energy efficiency and partnering with renewable energy providers. This shift helps reduce the environmental impact. It also aligns with many businesses’ corporate social responsibility goals.
Data Sovereignty and Compliance in a Global Context
Data sovereignty and compliance have become complex due to data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA. These laws dictate how and where data can be stored, processed, and transferred. They directly impact server hosting decisions.
Colocation allows businesses to choose the geographical location of their servers. This makes it easier to comply with data sovereignty requirements. Businesses can ensure they follow all relevant regulations by selecting a colocation facility in a jurisdiction that aligns with their data compliance needs.
Dedicated hosted server providers are responding by offering more geographically diverse hosting options. This ensures their operations comply with strict data protection standards. It allows businesses to benefit from dedicated hosting without compromising compliance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solution between colocation vs dedicated server hosting demands understanding certain factors. This includes your business’s demands and the technical requirements of your digital operations.
Colocation offers the flexibility and scalability that businesses need. It also comes with the benefit of direct control over their hardware. Dedicated hosting environments present outstanding resource exclusivity, performance, and security. These benefits are tailored for those with intensive workloads and high-traffic online platforms.
RedSwitches offers countless hosting solutions catering to modern businesses’ diverse needs. We offer you access to state-of-the-art dedicated environments designed for peak performance.
So what are you waiting for? Contact us now to learn about our offerings and find the perfect fit for your hosting needs. Step into the future with a partner who understands your digital infrastructure’s value.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between hosting and collocation?
Hosting typically involves renting space on a server owned by a hosting provider to store your website or application. This server space can be on a shared, virtual, or exclusive server environment. Collocation involves renting physical space in a data center to house your server hardware.
2. What is the difference between dedicated web server and co located web server?
A dedicated web server is a hosting solution where a single client leases an entire server housed in the provider’s data center. A co-located web server is a server you own and physically house in a third-party data center. While both offer control and resource exclusivity, the key difference lies in ownership and management of the hardware.
3. What is colocation server hosting?
Colocation server hosting is where you rent space in a data center to install your own server hardware. The data center supports the necessary infrastructure. It allows you to enjoy a professional hosting environment with ownership and control over your physical server.
4. What is the difference between colocation and dedicated server hosting?
Colocation involves renting space in a data center to house your own server hardware. In contrast, a dedicated hosted server provides a server owned and managed by the hosting service provider.
5. What are the advantages of colocation over shared hosting?
Colocation allows you to have complete control over your hardware and software. It also offers better security and customization options compared to shared hosting.
6. How does server colocation work?
Server colocation involves you providing the server hardware. It is then placed in a data center where you can use the facilities offered. This includes rack space, power, cooling, and network infrastructure.
7. Is colocation or a dedicated hosted server the right choice for my business?
Choosing between colocation and a dedicated hosted server depends on your specific needs. Colocation is ideal if you want full control over your hardware. Dedicated hosting may be better if you prefer the hosting provider to manage the server.
8. What does colocation facilities offer?
Colocation facilities typically offer rack space, power, cooling, network connectivity, and security measures. They also sometimes offer additional services like remote hand support.
9. What is the main difference between colocation and existing server hosting options?
The difference between colocation vs exiting server hosting is that you own and manage the server hardware in colocation. With existing server hosting options, the hosting company provides the server for you.
10. How does colocation give you control over your server technology?
You are responsible for installing and maintaining the hardware and software in colocation. This gives you full control over the technology used.
11. How do colocation and dedicated hosted servers compare regarding control over hardware?
With colocation, you have full control over the hardware and software used in your server. In contrast, the dedicated hosted server offers limited control over the choice of hardware and software.
12. Which hosting option allows for more customization, colocation, or dedicated server hosting?
Colocation allows for greater customization as you can choose the hardware and software that best suits your needs.
13. How can I choose between colocation and dedicated server hosting for my business?
Consider the control you need over hardware to decide between dedicated hosting and colocation. You must also consider scalability needs and your budget.
14. What are some advantages of colocation services compared to dedicated server hosting?
Colocation services offer control over the hardware and network connectivity the server needs. It also offers the ability to refresh hardware as needed to keep up with technological advances.
15. In what scenarios would dedicated server hosting be better than colocation?
Dedicated hosted servers suit businesses that prefer managed hosting with technical support. It suits those looking for a more hands-off approach to server management.
16. Can you explain the difference between bare metal server and cloud hosting in the context of colocation and dedicated server hosting?
Colocation and dedicated server hosting typically involve bare metal servers. These servers provide physical hardware dedicated solely to your use. Cloud hosting is a virtualized environment that offers more flexibility and scalability.