During a day’s business, organizations create, use, and save a surprisingly massive volume of data. This data is generated and collected from diverse sources, including social media, online transactions, and IoT sensors.
Given this increasing data generation and collection trend, many businesses feel that traditional database administration technologies are no longer adequate to manage and analyze this massive volume of data.
This is why organizations are using Big Data databases.
Big Data databases are designed to meet the challenges presented by growing data volumes.
These databases can gather, store, manage, and analyze massive amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. The database platforms allow users to extract significant insights and make informed decisions based on these insights.
Big Data databases come with the latest data management and analytics capabilities that allow businesses to take full benefit of their extensive data store. These platforms can handle and use data with attributes such as high volume, variety, high velocity, and multiple relationships between data items.
In this article, we’ll discuss the concept of Big Data databases, their distinguishing characteristics, and the benefits they offer. But, before we discuss these databases in more detail, it is essential to understand what is data and Big Data.
Table of Contents
- What is Data and Big Data?
- Types Of Big Data
- Characteristics Of Big Data Databases
- What Are Big Data Databases Used For?
- How to Choose the Right Big Data Database?
- Advantages Of Big Data Processing
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Data and Big Data?
Data is a collection of raw and unorganized facts, statistics, or information, generally expressed in multiple forms, such as numbers, text, sensor inputs, and graphics.
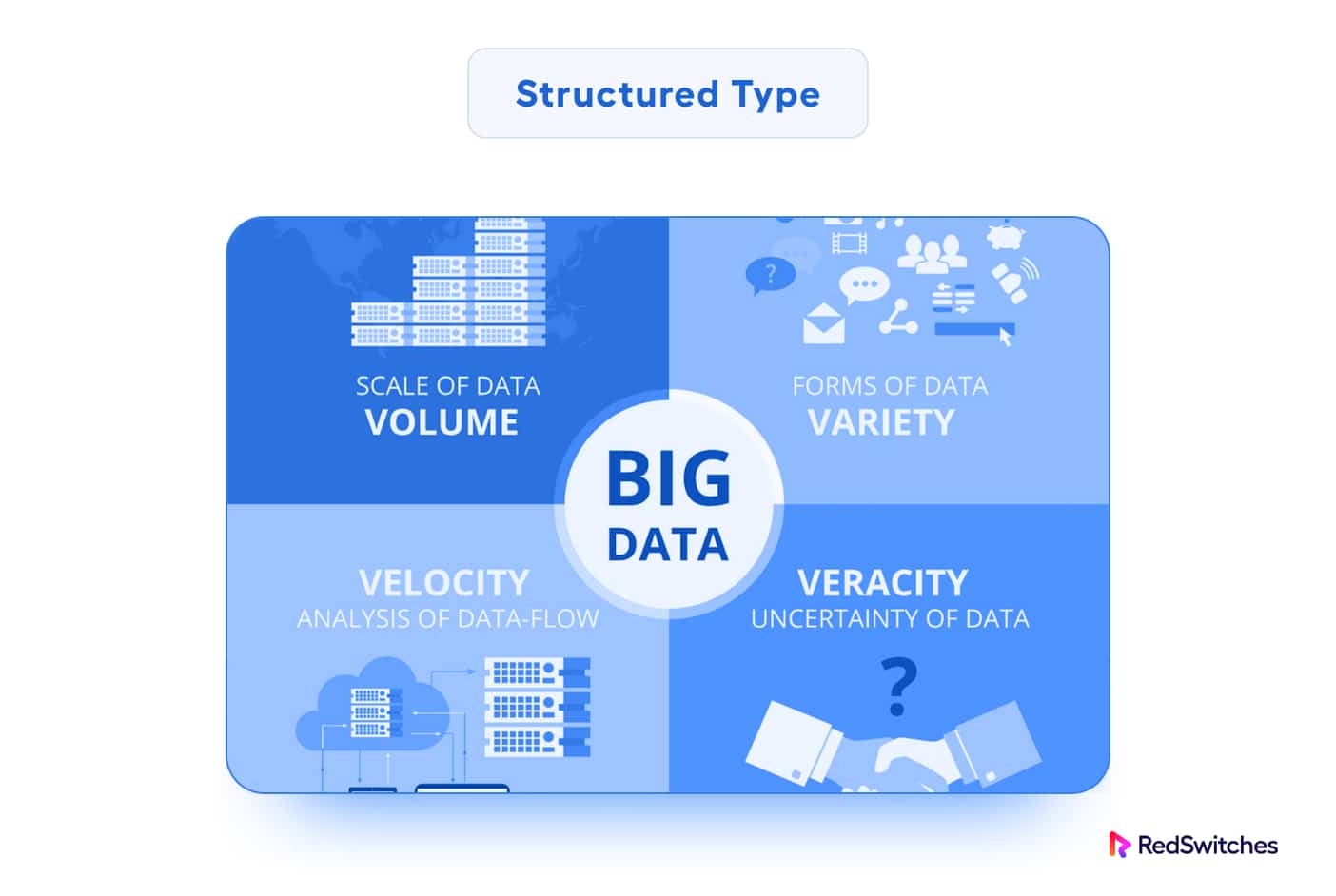
Big Data, on the other hand, refers to extraordinarily vast and complicated data collections. In contrast to traditional data, Big Data has high Volume, Diversity (multiple types and formats of data items), and Velocity (the speed at which data items are created and processed). In addition, Big Data has complex relationships at several levels.
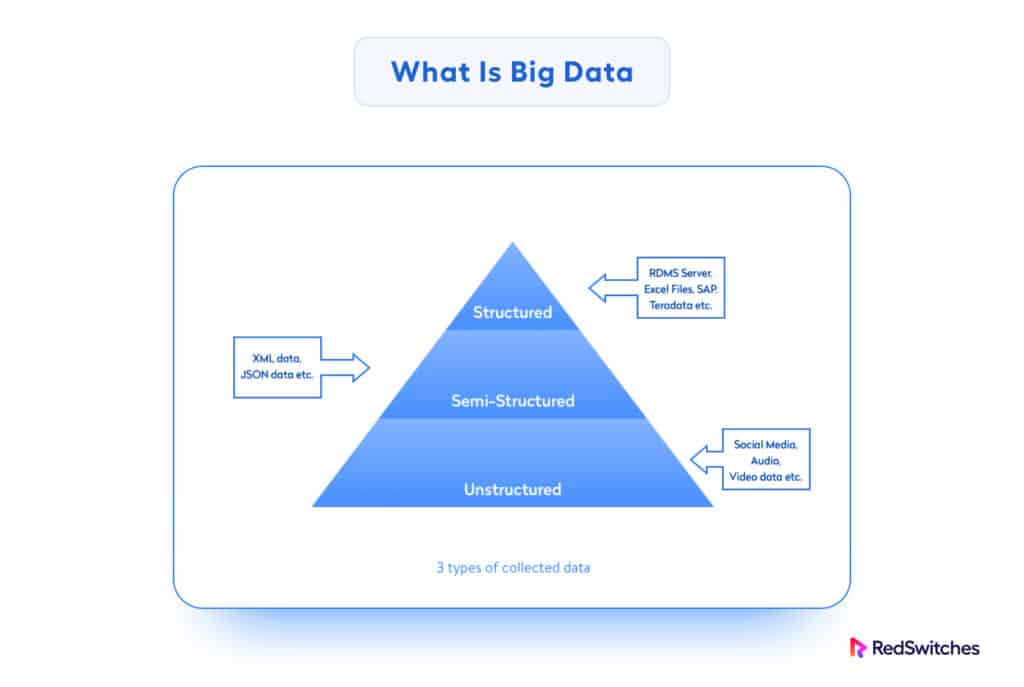
Types Of Big Data
An important characteristic of Big Data is the huge flexibility in what is considered Big Data, based on the three main types of sources and makeup of data items.
Let’s discuss the specifics of Big Data types:
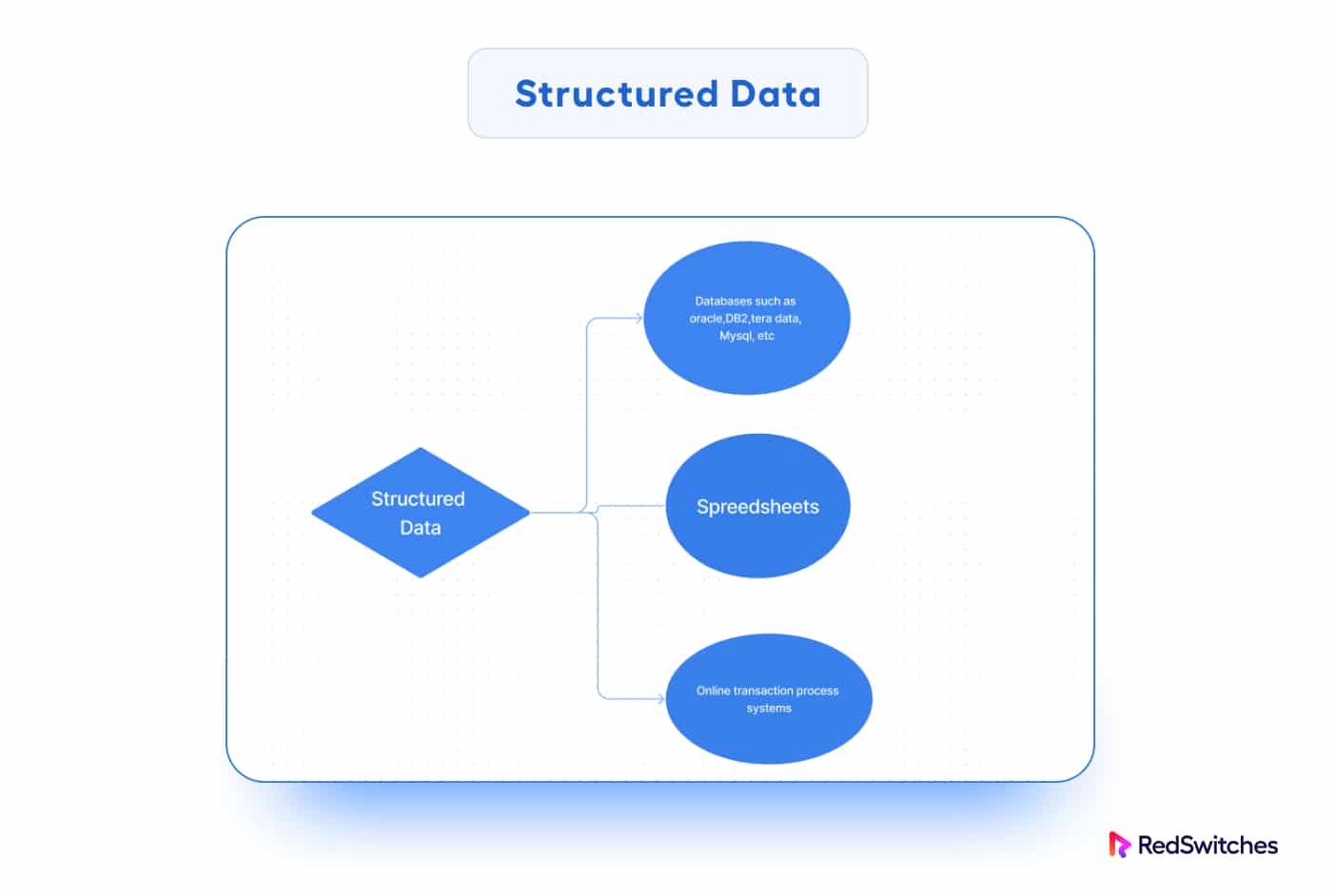
Structured Data
Structured data refers to well-organized data that follow a predefined format. This makes it easy to store and query in traditional relational databases. In most cases, this data type is properly organized into rows and columns with fixed data types.
Structured data is also called relational data. When storing it in a relational database, you can divide it into numerous tables to improve data integrity by establishing a single record representing an object.
Table constraints are used to enforce relationships between data items.
The commercial value of structured data is determined by how well an organization can analyze it using its existing systems and procedures.
Data in relational databases, spreadsheets, and structured text files are examples of structured data.
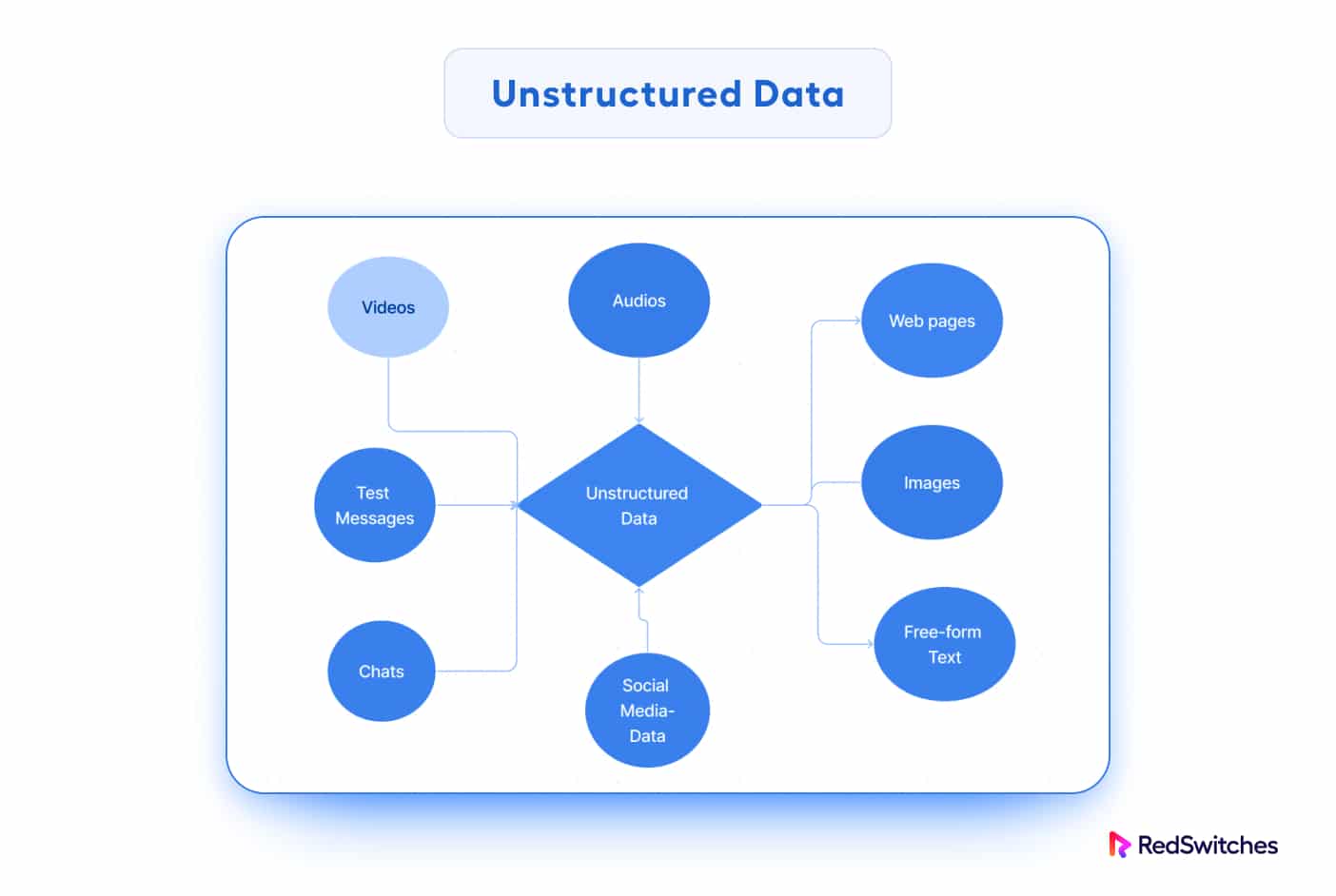
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data lacks a set format and does not fit appropriately into the typical relational database architecture. This data type is more challenging to process and analyze since it doesn’t follow a strict schema.
Unstructured data does not adhere to any particular schema or set of data design principles. In all cases, its layout is chaotic, and database designers find it challenging to fit it into a predefined data classification scheme.
Text documents, emails, social media postings, photos, audio files, video files, and sensor data from IoT devices are all examples of unstructured data. As you can guess, even when the information about a picture or video is semi-structured, the actual data in the file or record is unstructured.
In some cases, unstructured data is called “dark data” because applications often cannot analyze it without appropriate software tools.
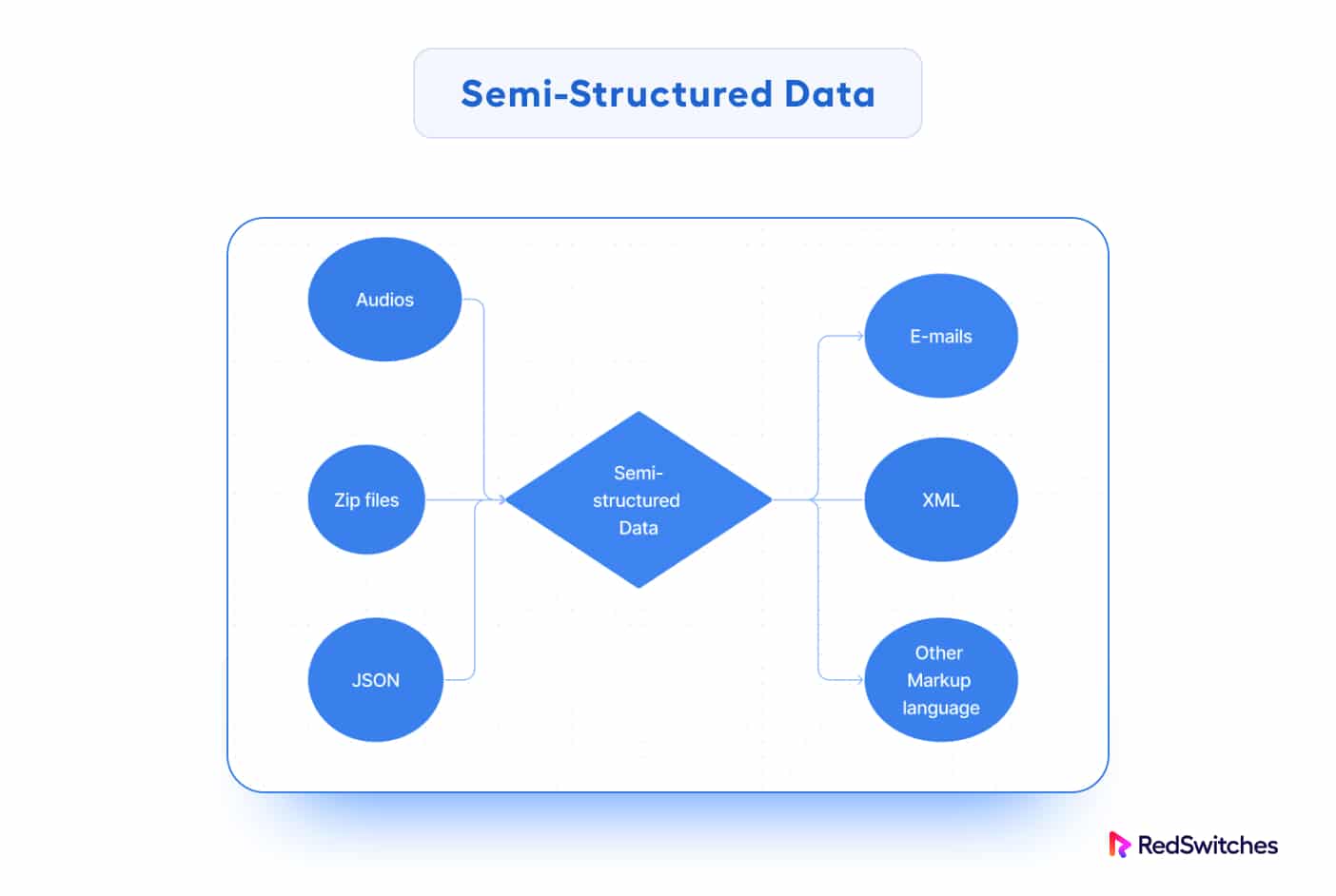
Semi-Structured Data
Semi-structured data exists between structured and unstructured data. It has some level of organization but does not conform to the rigidity of structured data.
The data is neither in relational format nor properly organized into rows and columns as in a spreadsheet. However, properties like key-value pairs distinguish it from unstructured data entities.
Semi-structured data is also known as NoSQL data because it does not require a structured query language for data processing and manipulation.
Semi-structured data is frequently expressed as JSON, XML, or key-value pairs.
It’s important to note that Big Data often involves a combination of these data types, referred to as “variety” in the three Vs of Big Data (Volume, Velocity, Variety). The variety of data types poses challenges in storing, processing, and analyzing Big Data, leading to the adoption of specialized data storage capabilities and NoSQL databases capable of handling diverse data structures.
Characteristics Of Big Data Databases
Big Data databases have several characteristics that distinguish them from traditional relational databases. The following characteristics are essential for handling Big Data’s massive volumes, variety, velocity, and complexity.
Scalability
Big Data databases can scale horizontally to handle additional data. Similarly, they handle high-velocity data streams by distributing data across multiple servers or nodes.
Distributed Architecture
These databases have a distributed architecture for faster parallel processing, enhancing overall performance and significantly reducing response time.
NoSQL Data Models
Big Data databases use NoSQL models for flexibility in handling diverse data formats and unstructured data.
High Availability
Big data databases prioritize high availability to ensure data and services are accessible despite hardware failures or network issues.
Fault Tolerance
Big data databases are designed with fault-tolerant mechanisms to ensure service delivery during system failures and data inconsistencies.
Real-Time Processing
Applications depending upon Big Data databases rely on their near real-time processing to deliver immediate data insights and responses.
Cost-Effectiveness
Big Data databases deliver a higher value for the investments in hardware and open-source tech used to save and handle large data volumes.
Complex Query Support
Big Data databases are optimized for complex queries and analysis, allowing users to view and explore data in various combinations and derive meaningful insights.
Data Replication and Backup
Big Data databases implement data replication and backup strategies to ensure data redundancy and prevent loss.
Security and Access Control
Big Data databases prioritize data security with strict protection and access control measures.
What Are Big Data Databases Used For?
Big Data databases are used in scenarios requiring unique capabilities to handle and process large and diverse datasets. The following are some of Big Data databases’ key applications and use cases.
Data Storage and Management
Big Data databases are generally used for storing and handling massive volumes of data, which can be organized, semi-structured, or unstructured. They provide effective data storage and retrieval techniques to deal with the large amounts of data created by multiple applications and systems.
Real-time Analytics
Big Data databases often have real-time data processing and analytical capabilities businesses use to get rapid insights from data streams. This capability makes these databases a great fit for scenarios such as real-time fraud detection, sensor monitoring systems, and personalized suggestions.
Business Intelligence and Reporting
Big Data databases are often the primary resources for BI and reporting systems. Analysts and decision-makers use these applications as database interfaces to access, query, and analyze large datasets to derive valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Social Media Analytics
Big Data databases are used to store and analyze social media data, allowing organizations to understand customer attitudes, track brand mentions, and obtain insights into social media trends.
Log and Event Data Management
Many business applications such as web servers, mobile apps, and network devices generate large volumes of log and event data that are usually stored in Big Data databases. ICT and security teams use these databases to store and analyze data for debugging, performance monitoring, and security investigations.
Scientific Research and Exploration
Big Data databases facilitate large-scale data processing, common in scientific research, such as genetics, climate studies, particle physics, and high-level mathematical modeling.
How to Choose the Right Big Data Database?
Choosing the right Big Data database depends on factors such as your specific use case, data volume, performance requirements, scalability, data structure, and budget.
Fortunately, you can find several popular Big Data databases, each with their unique strengths and drawbacks. Here are a few examples:
Apache Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS stores Big Data across multiple nodes and is often paired with Apache Hadoop to take advantage of the MapReduce framework for building Big Data apps.
Apache Cassandra
Cassandra is a high-performance NoSQL database with low latency capabilities for handling write-heavy workloads.
Apache HBase
HBase is a real-time NoSQL database for big datasets, commonly used for applications that require quick read/write operations.
Apache Hive
Hive is a data warehousing and SQL-like query language tool built on top of Hadoop. Analysts and data scientists can use its capabilities to perform ad-hoc queries and analyses on Big Data.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database that offers high performance, scalability, and flexible data models. It is a popular choice for Big Data applications that collect and process huge data volumes.
Apache Spark
Spark is a distributed computing engine for iterative processing and machine learning tasks that works with various data sources, including HDFS and Apache HBase.
Amazon DynamoDB
DynamoDB by AWS is a great choice for a fully managed NoSQL database in the cloud. It scales automatically and offers low-latency access to large datasets.
Google Bigtable
Bigtable is Google’s NoSQL database service for big workloads and applications that require fast data access.
Apache CouchDB
CouchDB is a distributed NoSQL database that supports replication and offline access. It is suitable for applications that use a decentralized data model.
Apache Druid
Druid is an open-source OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) database for fast data aggregation and interactive analytics on large datasets.
When selecting an extensive data database, you should carefully consider data consistency requirements, average query complexity, real-time processing demands, and the technical skills necessary for database maintenance and operations.
Assessing the integration capabilities with your existing data flow and analytical tools is also critical.
If you have the resources and the time, consider benchmarking and performance testing using sample data relevant to your use case before making the final selection.
Advantages Of Big Data Processing
Big Data processing offers several advantages that can revolutionize how organizations handle and utilize data. Here are some key benefits of Big Data processing:
Scalability
Big Data tech scales horizontally, handling massive data by adding more servers or nodes. Organizations may now store and analyze petabytes of data without any noticeable performance drops.
Real-time Data Analysis
Real-time data processing frameworks such as Apache Spark and Apache Flink enable organizations to analyze and respond to data as it is collected and loaded into data processing features.
Data Variety
Big Data processing systems can handle various forms of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This flexibility is essential in today’s data landscape, where data comes from multiple sources like social media, sensors, logs, and other databases.
Cost-Effectiveness
With the advent of cloud computing and distributed processing frameworks, the cost of storing and processing large amounts of data has decreased significantly.
Easy Access to Advanced Analytics
Processing large amounts of data enables businesses to leverage emerging advanced analytical options and techniques such as machine learning, natural language processing, pattern identification, and predictive analytics. These methods assist organizations in gaining essential insights, identifying patterns, and making data-driven choices.
Data Integration
Big Data processing technologies may interface with existing data infrastructure, such as relational databases, data warehouses, and data lakes. This integration enables businesses to use their existing data investments while adding new data sources and technologies.
Improved Customer Insights
Big Data processing allows businesses to analyze massive volumes of historical and real-time customer data. This results in a more comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior, preferences, and requirements, allowing for more focused marketing tactics and personalized customer experiences.
Better Competitive Advantage
Companies that use Big Data processing acquire a competitive advantage. They can make quicker and more informed judgments, adjust to changing market conditions more rapidly, and uncover new business prospects before rivals.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Big Data processing allows organizations to make decisions based on evidence and data rather than intuition or gut reactions. This data-driven technique increases the precision and reliability of decision-making.
Faster Innovation and Research
Big Data processing encourages innovation by allowing data-driven research, the investigation of new data sets, and finding hidden patterns and connections. It is instrumental in scientific research, healthcare, and other fields requiring large-scale data analysis.
Simply put, Big Data processing enables organizations to extract important insights, promote innovation, and make data-driven choices that enhance business results by unlocking the potential of huge and diverse data sets.
Conclusion
Big Data databases are now the foundation of modern data management, allowing organizations to extract critical insights, drive innovation, and make data-driven decisions that lead to improved business results.
Big Data databases will remain crucial tools for organizations looking to realize the intrinsic value of their data by building applications that use data complexity and volume as critical features.
If you’re looking for a robust server infrastructure for your Big Data projects, RedSwitches offers the best dedicated server pricing and delivers instant dedicated servers, usually on the same day the order gets approved. Whether you need a dedicated server, a traffic-friendly 10Gbps dedicated server, or a powerful bare metal server, we are your trusted hosting partner.
FAQs
Q. What is the scalability of Big Data databases?
Scalability in Big Data databases is achieved via distributed architectures that allow data to be stored and processed across several nodes or servers. As data volumes expand, this horizontal scaling strategy allows for smooth expansion.
Q. What are the benefits of using Big Data databases?
Businesses generally opt for Big Data databases because of their capacity to manage massive volumes of data, help with real-time data analysis, support varied data types, cost-effectiveness, sophisticated analytics capabilities, and improved data-driven decision-making.
Q. How do Big Data databases offer real-time data processing?
Big Data databases use distributed processing frameworks and in-memory computing for real-time data processing. These technologies enable real-time data analysis as it is collected and loaded into the database.