Key Takeaways
- Ensure backups are frequent and automated to reliably capture all essential data changes and configurations.
- Utilize geographically distributed storage solutions to enhance data safety and availability during regional disruptions.
- Encrypt backup data and implement strict access controls to protect against unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Regularly test backup integrity and the efficacy of recovery processes to guarantee reliability and operational readiness.
- Continuously adapt backup strategies to technological advancements and evolving cybersecurity threats to maintain effectiveness.
- Incorporate AI, blockchain, and cloud solutions to optimize backup procedures and enhance data security.
- Stay ahead by integrating quantum-resistant cryptography and considering regulatory and insurance aspects in backup and recovery planning.
Securing your digital assets is more critical than ever in the high-stakes world of bitcoin staking. As the risks grow, so does the need for ironclad backup and recovery strategies. This blog will guide you through essential steps to shield your assets and prepare you for any disaster—be it server crashes, cyberattacks, or unexpected data loss.
Dive into the world of advanced tools and techniques designed to protect and recover your precious investments. We’ll show you how to maintain security and continuity amid the digital dangers that lurk online. Join us as we equip you with the tools to implement rock-solid safeguards, ensuring your investments are secure and your mind is at ease.
Ready to fortify your virtual fortress? Let’s dive in!
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Staking?
- What is Staked Assets?
- Technologies For Staking
- Risks Associated With Staked Assets
- Importance of Backup and Recovery For Crypto Staking
- Developing Robust Backup Strategy For Staked Assets
- Effective Recovery Solutions
- Best Practices For Backup and Recovery for Staked Assets
- Future Trends in Backup and Recovery in Staking Assets
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Staking?
Credits: Freepik
Before discussing back and recovery, let’s first understand staking.
Staking is a crucial idea in cryptocurrencies, especially in blockchain networks that employ Proof of Stake (PoS) as a consensus method. It involves keeping money in a cryptocurrency wallet to keep a blockchain network secure and working. Staking is locking cryptocurrency to earn incentives and support the network.
In a Proof of Stake system, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the quantity of coins they possess. They are prepared to “stake” it as collateral. This is instead of the energy-intensive mining used in Proof of Work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin. Participants can join the network’s decision-making processes by staking their currencies. This is usually by creating blocks and verifying transactions. The likelihood that a node will be selected as a validator increases with the amount of bitcoin staked.
Staking makes it harder and costlier for attackers to hit the network. It also lets stakeholders benefit. These benefits are proportionate to the amount staked and the length of the staking period. They come from transaction fees and can be seen as passive income. Thus, funding staking encourages the upkeep of the network’s security.
What is Staked Assets?
Credits: Freepik
Bitcoin holdings are locked in blockchain technology to participate in network operations under the Proof of Stake (PoS) process. They are called staked assets. This idea is critical to modern blockchain systems. They use staking to prove transactions and secure the network. This is done without needing the costly energy of Proof of Work (PoW) systems, which rely on traditional mining.
Users deposit their tokens into a safe contract on the blockchain. They do this when they commit their cryptocurrency to the network through staking. These staked tokens function as a kind of security deposit; they are “at risk” in the sense that they could be entirely or partially forfeited as a penalty if the holder engages in evil behavior or neglects to carry out their obligations as a validator, such as approving fraudulent transactions.
On the other hand, individuals receive rewards, usually in the form of extra tokens, if they behave honorably and contribute to the network’s security.
Staked assets are essential to the functionality and security of proof-of-work (PoS) blockchains and to their underlying economic model. As token holders’ benefits are based on their performance and dependability as validators, staking incentivizes them financially to preserve the network’s integrity. Additionally, it democratizes participating in network governance by allowing anybody with sufficient tokens to stake and, subject to the blockchain’s specific rules, maybe become a validator.
Technologies For Staking
Credits: Freepik
Staking technologies include many tools and systems. They help store and manage cryptocurrency to protect blockchains and get rewards. Here is a quick rundown of the leading technologies used in staking:
Staking Wallets: Digital wallets made primarily to facilitate the staking procedure are known as staking wallets. They let users participate in network functions and safely keep their cryptocurrency holdings. Hardware-based staking wallets provide extra protection. They are better than software-based ones, which run on PCs or mobile devices.
Staking Pools: Staking pools are common since individual staking may need significant sums of money in order to become a validator. They combine the assets of many stakeholders. This lets them pool their resources and raise their chances of winning rewards. Pool operators oversee the technical aspects of managing staking pools. They do this in return for a small fee taken from the accrued prizes.
Blockchain Consensus using Proof of Stake (PoS) Consistency: Different blockchain protocols employ Proof of Stake (PoS) processes, each with distinct characteristics and guidelines. Notable examples include Tezos, Cardano, Ethereum 2.0, and Polkadot. These protocols allow stakeholders to participate directly. They help with the security and governance of the network. And they do so while still being energy-efficient.
Validator Nodes: Validator nodes are essential to staking. They are in charge of generating new blocks and handling transaction processing. Running a validator node needs technical skills and good infrastructure. They are needed to ensure ongoing network support and uptime.
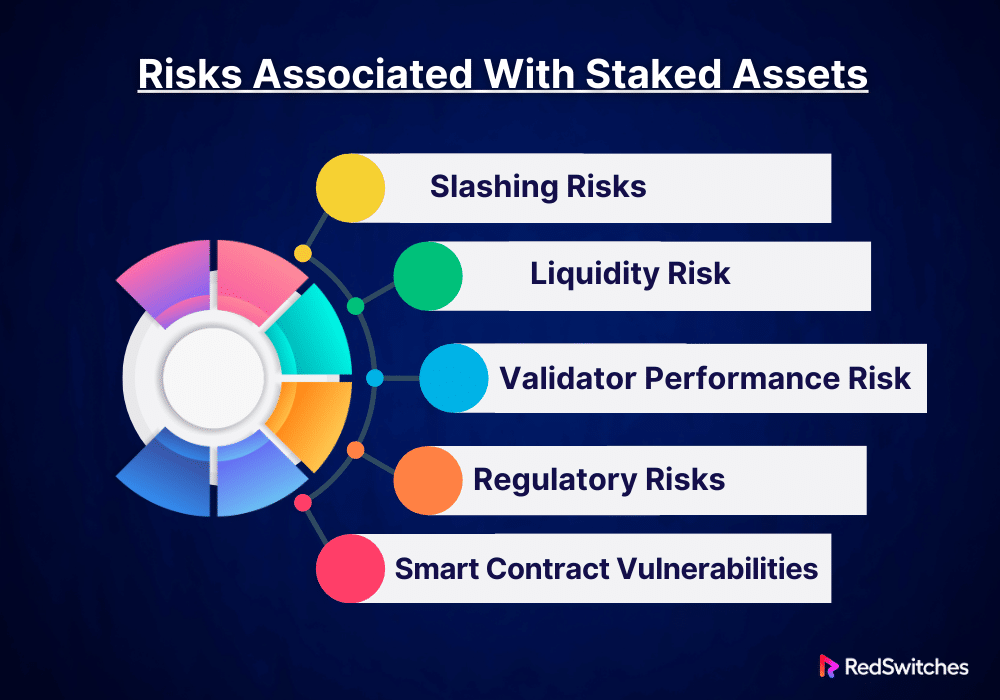
Risks Associated With Staked Assets
Staking cryptocurrency in Proof of Stake (PoS) networks has benefits. These include rewards and a role in blockchain governance. Stakeholders must take into account the inherent dangers that accompany it, though:
Slashing Risks
Validators are essential to preserving the network’s security and integrity in PoS systems. They will be subject to a disciplinary penalty called “slashing” if they neglect their duties with malice. This includes being inactive, validating transactions improperly, or trying to rig results.” With this approach, their staked assets may be forfeited in whole or part. Slashing is intended to penalize validators and discourage them from jeopardizing the network’s security. Stakeholders have a significant financial risk since, should the validators they support fail to follow protocol guidelines, their invested capital could vanish overnight.
Liquidity Risk
Staking usually entails locking up assets so they can’t be freely sold or traded for a predetermined amount of time. Liquidity is at risk during this lock-up period. This is especially true in a market where asset values might change a lot in the short term. Stakeholders won’t be able to use market opportunities. They also won’t be able to sell their holdings to meet their financial obligations. This danger underscores the significance of strategic financial preparation prior to allocating assets to a staking arrangement.
Validator Performance Risk
Credits: Freepik
The efficacy and dependability of validators directly impact the benefits the stakeholder receives. Reward payouts may be lowered or omitted if a validator’s node has outages, malfunctions, or performance problems. When relying on outside validators or staking pools, stakeholders need to consider the abilities of these entities. They must consider their technical and operational skills. Validators’ subpar performance can reduce returns and impact the staking investment’s long-term profitability.
Regulatory Risks
The rules for cryptocurrencies are always changing. This is due to increased government scrutiny of the industry worldwide. New laws may restrict staking policies. They may also reinterpret the tax consequences of staking rewards or, in some cases, abolish staking. Due to these rules, stakeholders must stay aware and follow local and international laws. These laws may impact the profits and legal standing of staking.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Many staking techniques use smart contracts, especially those that provide delegated staking or staking pools. Despite being automated and practical, these contracts are prone to security flaws and coding errors. An intelligent contract exploit may cause staked funds to be lost or stolen. Since blockchain transactions are irreversible, these contracts must undergo thorough security audits and ongoing monitoring to protect against flaws.
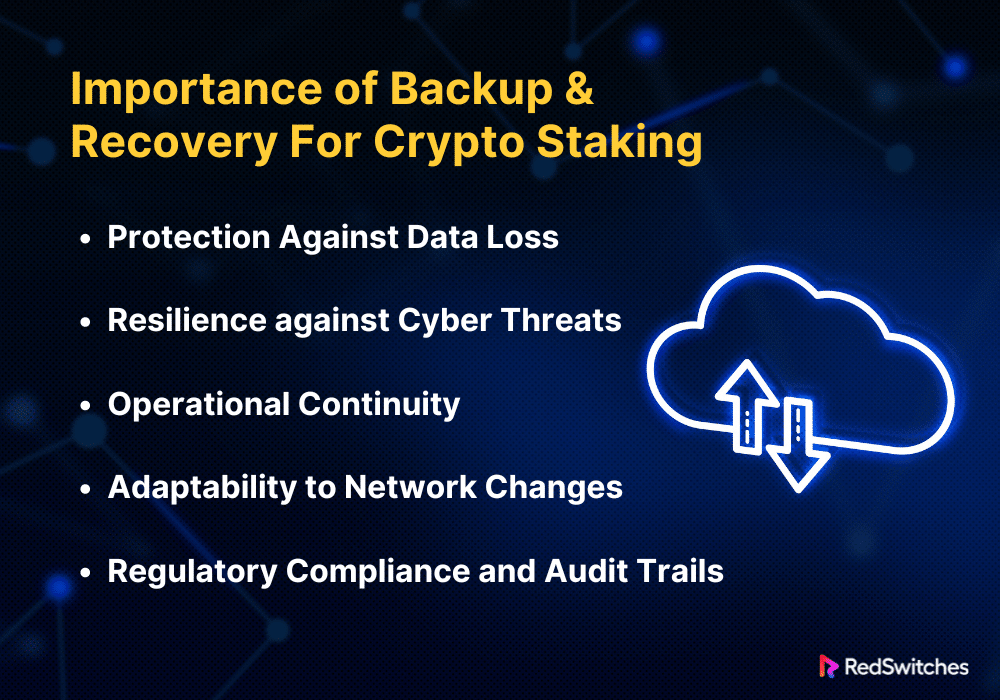
Importance of Backup and Recovery For Crypto Staking
The significance of backup and recovery in asset staking is enormous. This is especially true as digital assets and the platforms that hold them become more and more vital to finance. The following explains in detail why asset staking requires backup and recovery:
Protection Against Data Loss
In the digital age, many things can cause data loss. These include software bugs, hardware failures, and cyberattacks. For blockchain network users, losing important data—like private keys or wallet files—may mean they permanently lose access to their staked assets. Good backup plans ensure that important data is securely duplicated. It is kept in several places to guard against malicious or accidental data loss.
Resilience Against Cyber Threats
Credits: Freepik
Cybersecurity risks pose a serious threat to any online activity, including staking. Thus, it’s essential to be resilient against them. A ransomware attack, phishing attempt, or more advanced cyber espionage could risk the security of staking nodes. They also risk the assets the nodes oversee. In an attack, stakeholders can restore operations quickly and with low losses. This is thanks to regular backups and a strong recovery strategy. These ensure security and continuity.
Operational Continuity
People stake to maximize rewards and meet network obligations. Staking often involves running nodes or joining networks that require high uptime. Downtime from system failures might cause lost money. This could be from fines or missed staking rewards. Staking rewards are like slashing in PoS networks. After a breakdown, a well-thought-out recovery strategy enables the quick resumption of critical activities, reducing downtime and related expenses.
Adaptability to Network Changes
Blockchain protocols and technologies are regularly upgraded to add new functionality, boost security, or improve overall efficiency. Occasionally, these changes may result in unexpected faults or compatibility problems that interfere with staking activities. Frequent backups act as a safety net, enabling stakeholders or validators to roll back to earlier versions if an update goes wrong, guaranteeing their ability to continue uninterrupted network participation.
Regulatory Compliance and Audit Trails
Adherence to regulations is essential for institutional players and staking enterprises. This is frequently part of keeping thorough records of all transactions and asset holdings. Procedures for backup and recovery are essential for maintaining historical data and creating audit trails, both of which are useful in the event of a financial audit or legal investigation.
Developing Robust Backup Strategy For Staked Assets
Credits: Freepik
Creating a solid backup plan for IP assets is essential to maintaining their security and usability. The following five comprehensive solutions can be put into practice to build a complete backup system for staked assets:
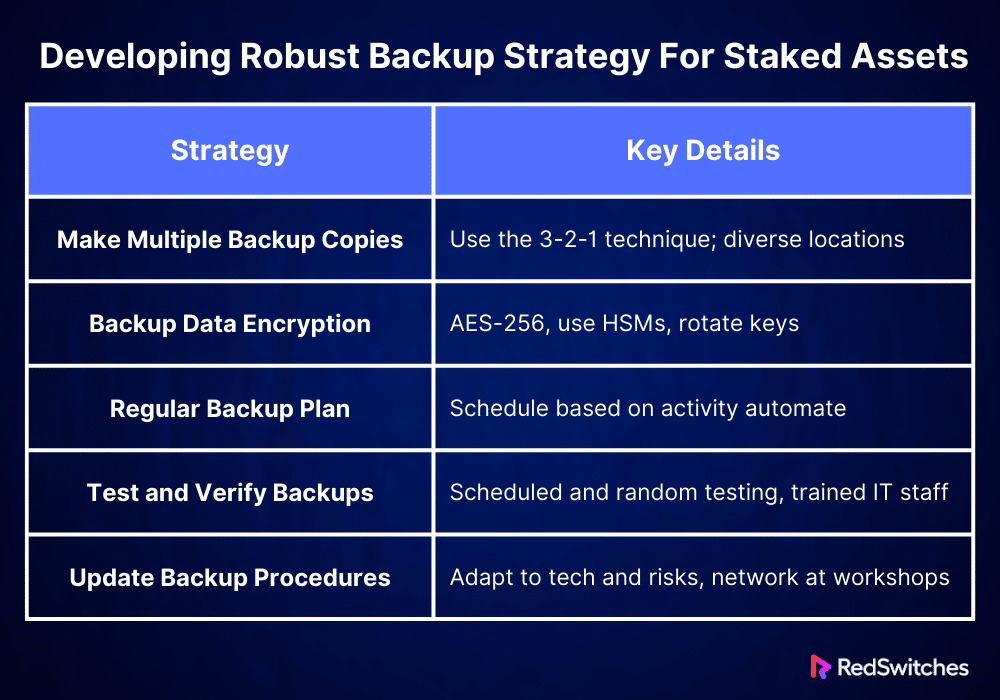
Make Multiple Backup Copies
Make many backups of essential information for staking. This includes wallet files, private keys, settings, and other crucial documents. Keep the backups in different places. This reduces the risk of two things. First, it prevents loss from fires, floods, or other disasters. Second, it prevents loss from hardware problems. Keep a mix of remote backups (in cloud storage services) and local backups (on actual hardware, like USB drives or external hard drives). This method is also known as the 3-2-1 backup technique. It involves keeping at least three copies of your data: one off-site copy and two local copies on separate devices.
Backup Data Encryption
Protecting the privacy and security of staked assets requires the encryption of backup data. Use cutting-edge encryption techniques, like AES-256, to protect backup files. This degree of encryption ensures the backup data is unreadable without the correct decryption keys, even if it is in the wrong hands. Moreover, keep the encryption keys safe from the data backups and handle them with the same diligence as the staked assets. To improve security more, consider using hardware security modules (HSMs). They are for key management. Rotate encryption keys regularly to reduce the chance of crucial compromise over time.
Regular Backup Plan
A well-defined backup plan is essential to guarantee data availability and integrity. Examining the transactional activity and staked asset value, ascertain the ideal backup frequency. In addition to daily complete backups, consider incremental backups that record changes as they happen for high-value or high-activity staking operations. To reduce the possibility of human error and guarantee regular and timely backups, use automated backup systems. For compliance and security audits, automation also aids in keeping an accurate and verifiable audit trail for all backup operations.
Test and Verify Backups
You must regularly test the backup’s integrity to keep confidence in the backup system. You must also test the recovery methods. Implement a systematic testing strategy incorporating scheduled and random testing to simulate unforeseen recovery circumstances. Make sure your IT staff knows about emergency response. They should know how to restart operations quickly. Use these tests to train them in this area. To ensure that the recovery process is continuously improved, record every test, any problems that arise, and the solutions you found. In addition to increasing trust in the backup systems, this proactive approach identifies areas that require improvement.
Update and Modify Your Backup Procedures
Your backup procedures should change along with the digital environment. Keep up with the most recent advancements in cybersecurity risks and technology. Regularly evaluate and update your backup and recovery procedures to take advantage of new technical developments and address growing security risks. Depending on changes in stakeholder activity or regulatory contexts, this can entail updating your backup schedules, incorporating new software tools, or implementing newer encryption technologies. Participate in professional workshops and industry forums to network with other industry members and gain insight from their best practices.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
Effective Recovery Solutions
If data is lost or the system breaks, fast recovery is essential. It lets us resume work and limit harm. The following are comprehensive methods for creating and executing successful staked asset recovery solutions:
Detailed Disaster Recovery Strategy
Create a thorough disaster recovery strategy. It should specify steps to take if data corrupts, hardware fails, or cyberattacks occur. In addition to providing step-by-step restoration instructions and communication protocols to notify users and stakeholders about the issue and anticipated recovery times, this strategy should outline roles and responsibilities for recovery operations. The disaster recovery plan can be kept current and valuable by testing and updating it often. This must happen as the business environment and technology change.
Quick Restoration Capabilities
Put in place procedures and technologies that allow staked assets to be recovered quickly. This involves enabling real-time or near-real-time data availability through redundant systems and data mirroring. Consider using cloud-based solutions. They offer scalable resources to fix broken systems and quickly recover data from backups. Automation in the recovery process can cut the chance of human error and speed up service restoration.
High Availability Systems
Use redundancy and fault tolerance in your system design to achieve high availability. Failover, load balancing, and clustering ensure that if a component fails, another can take over without disrupting service. This setup reduces downtime, which is especially crucial in blockchains. Uptime is vital for keeping network integrity and getting staking rewards.
Also Read Exploring High Availability vs Fault Tolerance
Frequent Backup Validation
Make sure that regular backup creation is accompanied by usability and integrity tests. This involves carrying out comprehensive simulated recoveries using the backups to confirm that data can be adequately restored and systems can be brought back to a working state. To take proactive corrective action before an actual crisis strikes, validation aids in locating possible problems in the backup procedure.
Awareness and Training
Hold frequent training sessions for the group in charge of recovery efforts. Ensure they understand the disaster recovery plans and feel at ease using the equipment and procedures needed in an emergency. This preparation includes drills and simulation exercises that imitate different crisis scenarios. Creating a readiness and awareness culture inside the company can significantly improve the efficiency of recovery operations.
Best Practices For Backup and Recovery for Staked Assets
Keeping blockchain activities profitable depends on the availability and security of staked assets. The following five practices are for backup and recovery. They are designed for places that handle staked assets.
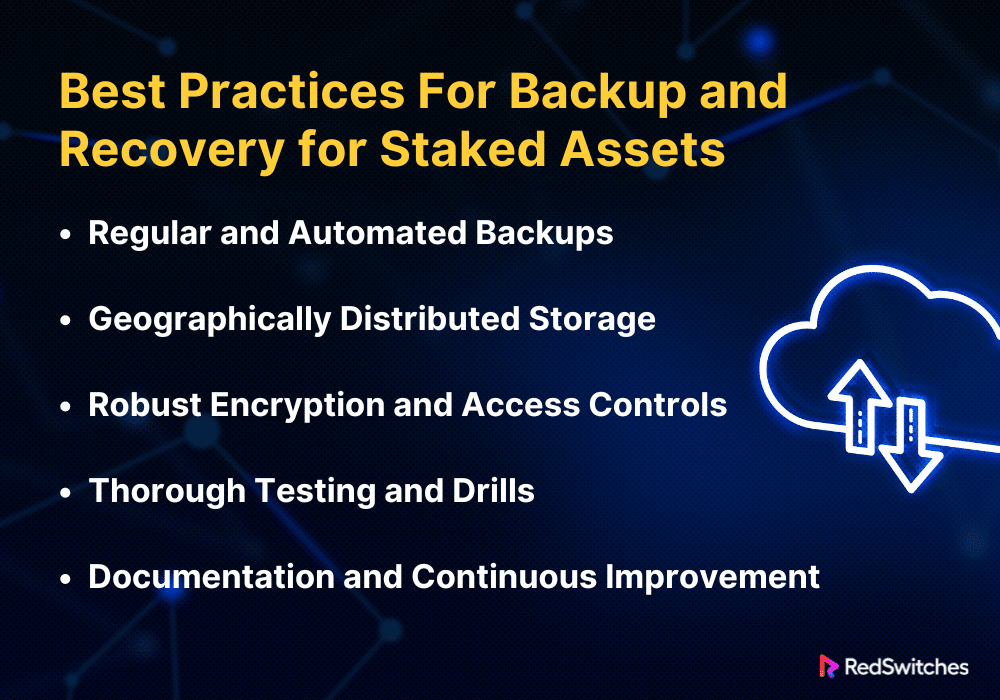
Regular and Automated Backups
Set up an automated backup system. It will periodically record the state of all essential information about staked assets. This contains transaction histories, configuration files, node software settings, and wallet data. Automation reduces the chance of human error. It also ensures that backups are done regularly and at the best times. To use less storage and enable more regular backups without slowing things, consider using incremental backups. They save changes made since the last complete backup.
Geographically Distributed Storage
Store backup copies in many different locations. This guards against disasters like natural disasters or power outages. These could damage local data centers. Cloud storage technologies can make this distribution easier, more scalable, and accessible. But be sure that any cloud providers you choose abide by the rules. They must meet the security needs for managing cryptographic assets.
Robust Encryption and Access Controls
To guard against unwanted access and possible data breaches, encrypt all backup data while it’s in transit and at rest. Employ robust, industry-accepted encryption techniques and safely store and handle encryption keys apart from the data they are used to encode. To further secure the sensitive data, impose stringent access restrictions and authentication procedures to guarantee that only authorised individuals can access backup and recovery systems.
Thorough Testing and Drills
Test them often using drills and real scenarios. This will ensure their efficiency and the team’s comfort with them. This testing should confirm both the recovery procedure’s operation and the backups’ integrity. Any problems found during these tests should be fixed immediately to keep the recovery plan improving.
Keep thorough records of the backup and recovery processes, including information on each employee’s duties. This documentation must be periodically reviewed and updated for technological advancements, operating procedure modifications, and insights gained from real-world catastrophes and recovery drills. Promote an environment of ongoing enhancement by integrating input from both authentic and test occurrences to augment the robustness and effectiveness of the backup and recovery procedures.
Future Trends in Backup and Recovery in Staking Assets
Technology is developing. The cryptocurrency industry is expanding. The backup and recovery scenario for staked assets is always changing. The following six themes will probably influence how backup and recovery plans for staking assets are developed in the future:
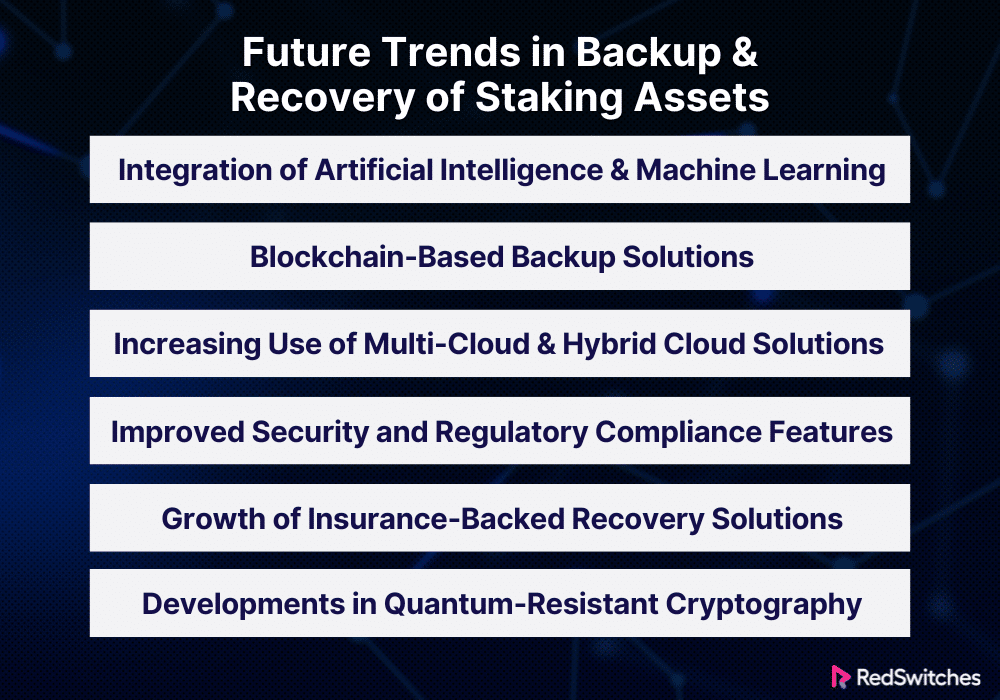
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are anticipated to be crucial in improving and automating backup and recovery procedures. These technologies can help predict and address possible issues by analyzing data access and usage patterns. AI may also improve backup plans and protocols based on current information and system performance, ensuring faster and better data protection.
Also read Machine Learning vs AI (Artificial Intelligence): Exploring the Best for 2024
Blockchain-Based Backup Solutions
An emerging trend is using blockchain technology to backup and recover digital assets. Blockchain technology can provide decentralized, unchangeable data storage options. They strengthen backup security against cyberattacks and corrupted data. Also, by speeding up recovery across systems, this strategy may let staking continue. It will also guarantee data integrity quickly.
Increasing Use of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Staking platforms will probably use multi-cloud and hybrid cloud backup. They will use these as they rely more on cloud solutions. These methods remove vendor lock-in. They cut costs and improve data protection and disaster recovery. Multi-cloud setups make solutions for data storage and recovery better. They are more resilient and adaptable. They work across several locations.
Improved Security and Regulatory Compliance Features
Governments worldwide are scrutinizing the rules and scrutiny around digital assets. Backup and recovery systems must adapt to remain compliant. They must do so while upholding high security. Future systems will need advanced, automated tech for continuous compliance. This is to ensure that all backups follow the latest data protection rules. These rules include the CCPA in California and the GDPR in Europe. Furthermore, stricter security procedures and encryption techniques would be adopted as standard. Solutions may also have features. For example, they may have real-time data masking and anonymization. These features protect sensitive data during backups.
Growth of Insurance-Backed Recovery Solutions
The link between cybersecurity and insurance will grow. This will happen as the financial stakes in Bitcoin rise. Insurance companies are expected to work more with tech companies. They will create policies that cover data breaches, system failures, and other issues. These issues can affect backup and recovery. They provide financial loss coverage after an event. They also help with quick recovery. This speed can be vital for keeping confidence and ensuring staking activities continue.
Developments in Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
Quantum computing may harm the security of both active digital transactions and backups. It challenges current cryptographic standards. Backup and recovery solutions will focus on future-proofing. They will develop and add quantum-resistant algorithms. This move will require upgrading the current infrastructure to enable these increasingly complicated cryptographic operations without sacrificing efficiency and implementing new algorithms resistant to quantum assaults. Organizations will probably also keep a close eye on ongoing research into cryptography and quantum computing so they can promptly modify their security protocols.
Conclusion
Protecting sensitive assets on servers requires putting strong backup and recovery procedures in place. We’ve looked at upcoming trends and best practices that will help you improve your staking operations’ security and dependability and ensure you’re ready for any eventualities, such as data loss or system breakdowns. Through their demonstration of dedication to operational integrity and resilience, these measures safeguard your investments and foster confidence with participants and stakeholders.
Collaborating with a reputable server supplier such as RedSwitches can significantly enhance backup and recovery systems. We provide high-performance dedicated servers with strong data protection capabilities and extensive security features that can be customized to match the particular requirements of blockchain applications. By taking advantage of their cutting-edge infrastructure, you can be sure that your staked assets are handled on safe and dependable platforms equipped to handle the difficulties of the evolving digital ecosystem.
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between data recovery and backup?
Data recovery is retrieving lost or corrupted data from backups or other storage, whereas backup is moving data to a safe location for protection.
Q. What are the three types of backups?
Full backup replicates all of the data; incremental backups preserve only changes made since the last backup; and differential backups store changes made since the last full backup. These are the three primary types of backups.
Q. What is data backup, and why is it important?
Data backup creates a copy of data to protect it from accidental deletion, corruption, or other data loss events. It is essential to have a data backup to ensure that valuable information is not lost and can be restored in emergencies.
Q. What are the different types of data that should be backed up?
Critical business data, an organization’s data protection data, and any other valuable information at risk of being lost or damaged should be backed up.
Q. What is a recovery plan, and why is it important?
A recovery plan is a documented strategy outlining the steps to recover data during a data loss event. It is essential to have a recovery plan in place to minimize downtime and data loss.
Q. How can cloud backup help in data protection?
Cloud backup allows data to be stored off-site in secure data centers, providing additional protection against loss due to local disasters or hardware failures.
Q. What are the risks of not having a data backup and recovery strategy?
The risks of needing a data backup and recovery strategy include potential data loss, data corruption, and disruption to business operations due to downtime while trying to recover lost data.