In Windows, the hosts file is a powerful tool that allows you to modify how your machine resolves domain names.
Adding entries to this text document can alter the default DNS lookup process and direct your computer to specific IP addresses. This allows you to customize your surfing experience, improve security by blocking harmful websites, and even eliminate intrusive advertisements.
The local host file functions as a map, allowing you to explore the Internet and customize your experience to suit your tastes and needs.
Table of content
What is a Hosts File?
A host file is an essential text file used by operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux to map hostnames to IP addresses.
It functions as a local DNS (Domain Name System) resolver, allowing you to provide the IP address for a particular domain name rather than depending on third-party DNS servers.
When you enter a website URL into your web browser, it usually connects to a third-party DNS server to obtain the IP address associated with that domain name. With the local hosts file, this process is shortened, and the system uses this file to bypass the DNS lookup process and directly map a domain name and an IP address.
This allows you to customize the resolution of IP addresses for specified websites or domain names on your local workstation.
In a typical local hosts file, each line represents a mapping between an IP address and a domain name. For instance:
127.0.0.1 localhost
Here are a couple of pointers that explain the format of the lines in the hosts file
- The first part is the IP address to which a request will be made.
- The second part specifies the site we wish to be resolved against the IP address.
- The third part is an optional field that could contain a comment.
- A space or a tab separates these three parts.
Let’s consider another example:
{xx.xxx.xx7.x1} {Redswitches.com} {#Redswitches}
This entry associates the hostname (or domain name) Redswitches.com with the IP address xx.xxx.xx7.x1. If you wish to resolve this IP address to redswitches.com for your users, you need to add this line to the local host files of the workstations.
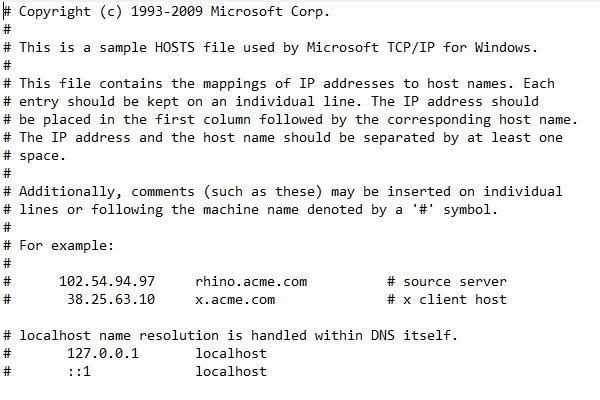
In Windows, the hosts file contains several primary entries by default. Here’s the text of a typical Windows hosts file:
Why is a Hosts File Useful?
Now that you know how the host file is structured, let’s discuss the benefits of having the host’s file on your computer.
Local Testing and Development
When testing websites or web apps on PCs, developers frequently use the hosts file to link domain names to local IP addresses. This enables them to replicate the behavior of a live website without changing DNS records or making the website publicly available.
Website Access Control
The hosts file can block or redirect access to specific websites. By mapping a website’s domain name to a non-existent IP address (such as 127.0.0.1), you can effectively prevent your computer from accessing that site. This can help block distracting or malicious websites.
Privacy and Security
Sometimes, you may wish to prevent your computer from connecting with particular ad servers, tracking domains, or known harmful websites. You may prohibit your computer from connecting to certain domains by mapping them to an incorrect IP address in the hosts file. This improves privacy and security.
Network Troubleshooting
The hosts file can be used to troubleshoot network problems. For example, suppose a website is unavailable due to DNS issues. In that case, you can temporarily map the domain name to a known functioning IP address in the hosts file to skip DNS resolution and determine whether the problem lies with the external DNS servers.
Speed Up Browsing Performance
You can increase the browsing speed for specific websites by mapping them to their associated IP addresses in the hosts file. When this happens, your computer may bypass the DNS query stage and connect directly to the IP address indicated in the hosts file. This minimizes the time required for rendering the website in the user’s browser.
Where is the Hosts File Located?
The location of the hosts file varies depending on the operating system:
- Windows: In Windows, the hosts file is typically found at C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.
- macOS: The hosts file is typically found at /private/etc/hosts
- Linux: The hosts file is commonly present in most Linux distributions at /etc/hosts.
How to Edit Hosts File in Windows?
You can edit the local host file in Windows to optimize and secure your browsing experience. Before editing, you should know you’ll need administrator privileges to modify the file.
Here’re the steps of the process:
- Right-click on the text editor icon and select “Run as administrator.” If you are prompted for permission, choose “Yes.”
- Open the file in the text editor by clicking “File” and then “Open.” Alternatively, you may open the file by using Ctrl + O.
- In the file selection dialog, navigate to the following location:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc - Optionally, you can modify the file type filter to show “All Files (.)” rather than “Text Documents (*.txt).”
- Select the “hosts” file and click “Open.”
- You can now make modifications to the hosts file. Remember that each entry usually starts with an IP address, then one or more hostnames separated by spaces or tabs.
- You can save the changes by selecting “File” and then “Save.” You may also use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + S.
- Finally, clear your DNS cache so your computer can identify changes to the file. For this, launch the command prompt and enter the following command and hit Enter.
C:\ipconfig /flushdns.
The local hosts’ file changes will take effect once you save the modifications. You may test the changes using a web browser or other apps to access the provided hostnames.
Conclusion
Modifying a hosts file offers several advantages that can substantially influence how you access websites. The local hosts file in Windows helps you better secure your system and speed up your browsing experience.
Suppose you encounter any problems when altering your hosts file. In that case, our Redswitches support team is staffed with Windows specialists and system administrators who understand how to set this file up to cater to your requirements. We are always accessible through email, chat, and tickets.
FAQs
Q. Is it safe to modify the Windows hosts file?
When done appropriately and thoroughly, being aware of the consequences, altering the Windows hosts file may be risk-free. We recommend backing up the file first. After modifying the file, if you see any unanticipated network connectivity issues or application behavior, simply restore the file from the backup.
Q. Is it necessary to restart Windows after modifying the hosts file?
Although restarting Windows is usually unnecessary after updating the hosts file, clearing the DNS cache may be required in some apps to enforce the new changes.
Q. What is the limit of the hosts file in Windows?
You should know that a line can be up to 256 characters long. All characters beyond that limit are trimmed off.
Q. What are the consequences of a hacked hosts file?
It is vital to examine and validate the local hosts file’s integrity regularly. Keep your system and security software up to date, use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, and be cautious when downloading files or clicking on links to limit the risk of your hosts file being hijacked.