Ubuntu is renowned for its ease of use and capable package management system. The Ubuntu Software Centre allows simple one-click access to popular apps.
However, there are instances when you need to install applications that are not available at the Software Center. In this situation, you need the .deb file (also known as a package) to install the application on your Ubuntu system.
Deb files (packages) are a popular way of packaging all the required assets in a single file used to install applications on Ubuntu and other Debian-based distributions.
This guide will walk you through installing deb files on Ubuntu systems. Let’s start with a short overview of the deb packages.
Table of Content
- What are Deb Packages?
- Benefits of Using Deb Packages
- Prerequisites to Installing Deb Packages on Ubuntu
- Use the GUI to Install Deb Files On Ubuntu
- Install Deb Files From the Terminal
- How to Uninstall Deb Packages
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Deb Packages?
Debian-based operating systems like Ubuntu and Linux Mint use software packages known as deb packages (short for Debian packages). These packages include all files (including executables, scripts, and configuration files) required to install and run software.
Deb packages can be installed using various tools, such as package managers (like APT) and the dpkg command.
Developers use these files to easily distribute and install a wide range of software on Debian-based systems. The structure of deb files ensures that all prerequisites are satisfied and configuration files are handled correctly.
Deb packages provide a dependable and effective way to manage software repository installations on your Ubuntu or Linux Mint operating system. In effect, these files simplify the process of downloading packages from external repositories and manually installing package files.
Benefits of Using Deb Packages
Deb files offer various benefits, such as:
Flawless Installation Experience
Deb packages offer an easy and efficient installation procedure, allowing users to quickly install applications by double-clicking the package file. Users no longer need to manually download and install new files for software updates.
Effective Package Management
Deb packages ensure a clean and properly organized system by ensuring automatic installation and removal of packages. Package managers like dpkg and APT on the Ubuntu systems handle this process.
These package managers resolve package dependencies, sparing users from the hassle of finding and installing necessary libraries or components manually.
Trusted Dependency Resolution
Package managers handle all underlying dependencies and ensure all necessary components are installed on the system. This prevents broken installation and similar dependency problems from affecting user experience.
Smooth Updates
Deb packages simplify the process of updating installed applications. The package managers fetch the most recent versions from the relevant package repository. Users can access the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches, ensuring their applications are up-to-date.
Due to these advantages, deb packages are commonly preferred for installing packages on Ubuntu and other Debian-based operating systems.
Prerequisites to Installing Deb Packages on Ubuntu
Before you install Deb packages on Ubuntu systems, you need to make sure that you have the following:
-
-
- A system running Ubuntu.
- Access to a terminal window.
- A root user or a user with sudo rights
-
Use the GUI to Install Deb Files On Ubuntu
The Ubuntu GUI greatly simplifies the process of installing deb packages. We’ll describe the two most popular methods of installing deb packages via the GUI.
Method #1: Use the Software Center
Follow these easy steps to install a deb package using Ubuntu Software’s default Software Center:
The first step is to locate the deb package. Usually, the system saves the downloaded files in the Downloads directory.
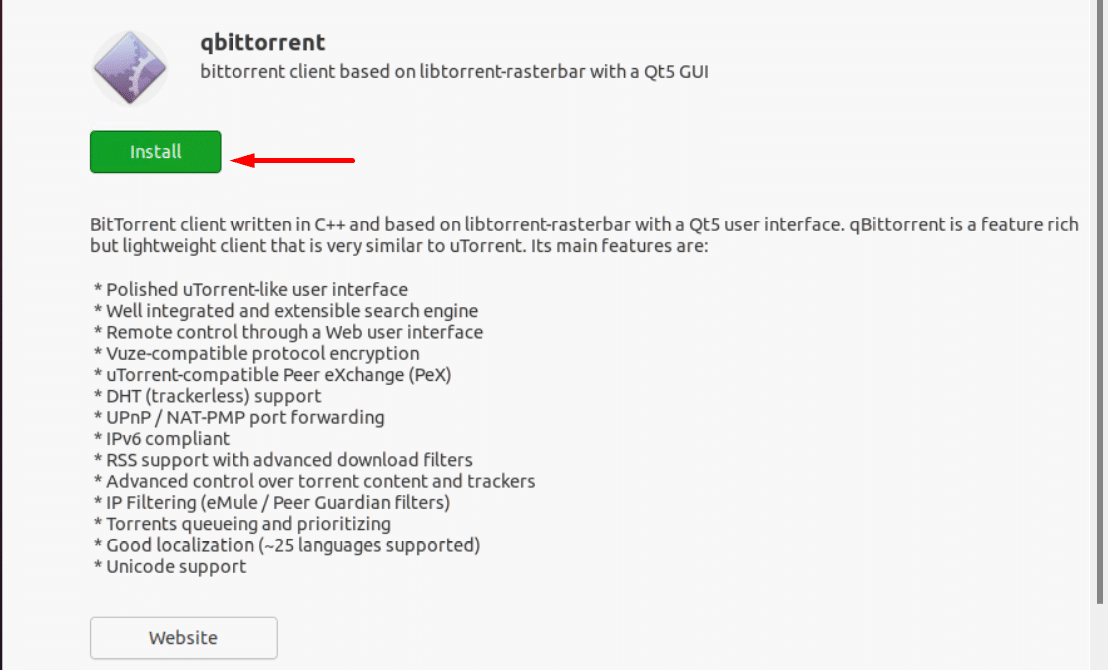
Right-click the deb file and select Open with Another Application from the context menu. Choose Software Install from the program list. To proceed, click the Install button.
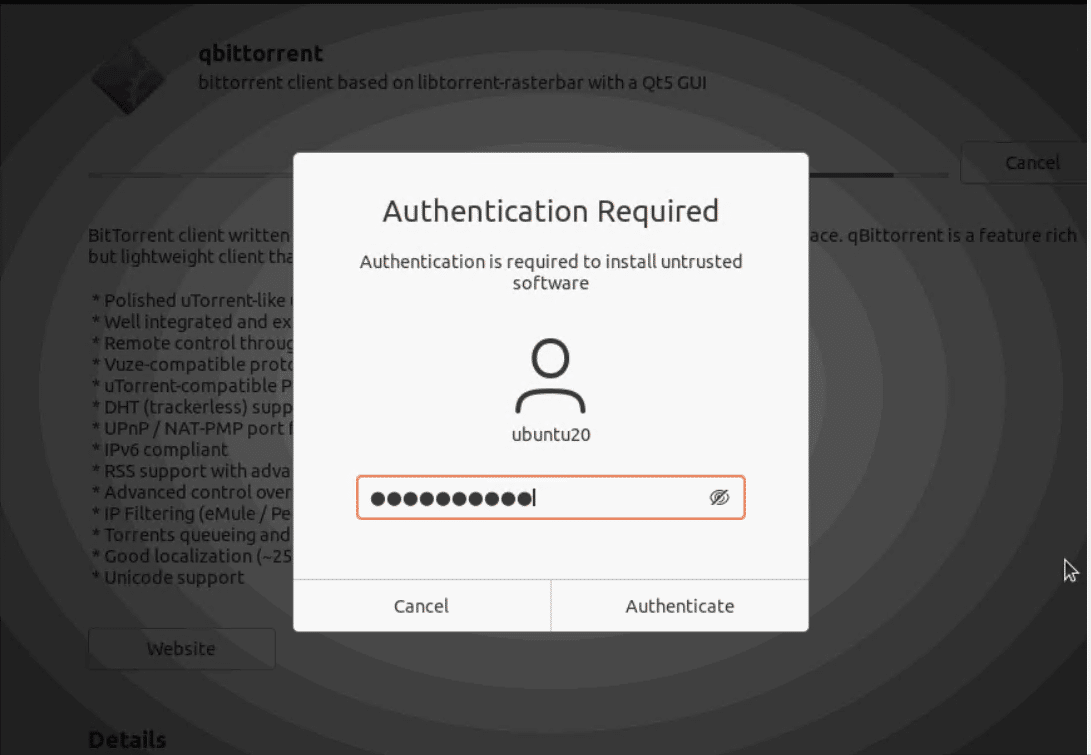
When requested, enter the password and click Authenticate.
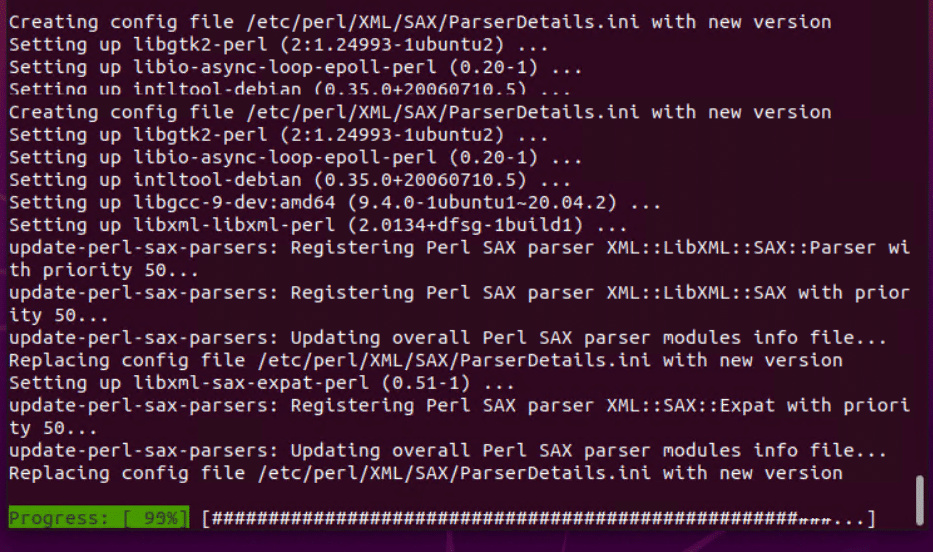
Wait for the installation to finish. When complete, the software is ready for usage.
Method #2: GDebi GUI
GDebi is a simple utility for installing local Debian packages. The utility also detects all essential dependencies and downloads and installs them automatically using the APT package manager. GDebi is accessible as a command-line and graphical interface user application.
Note that GDebi is not installed by default on Ubuntu systems. We recommend using the following command to install it:
# sudo apt-get install gdebi -y
Once the installation finishes, the utility is ready for deb file installation. Follow these steps to install a deb package using the GDebi GUI:
-
-
- Launch the file manager and browse to the deb file.
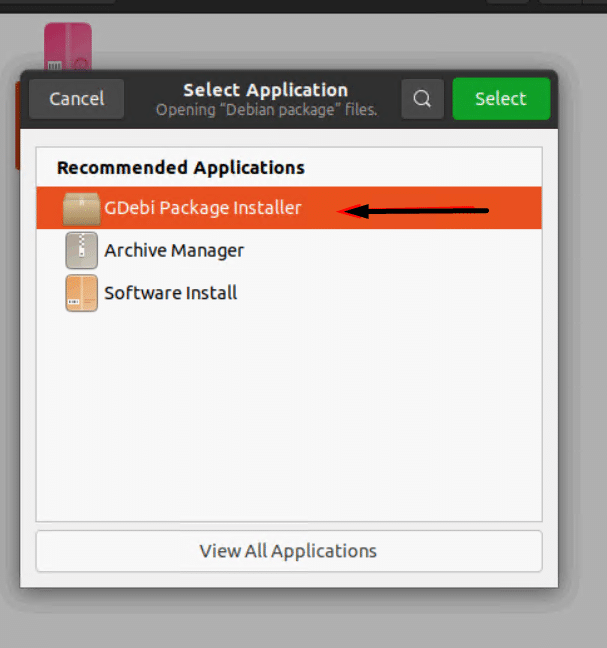
- Right-click and choose Open With Other Application from the context menu.
- Click GDebi Package Installer to select the option.
-
-
-
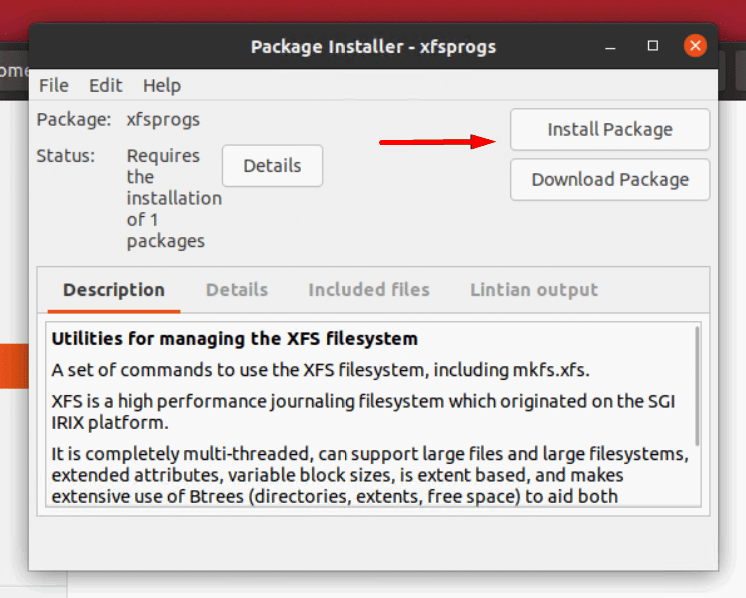
- The installer loads the deb package and displays a description of the software. Click Install Package to begin the installation process.
-
-
-
- When prompted, enter the password and hit Enter.
- Wait for the installation to finish. The software is now ready for use.
-
Install Deb Files From the Terminal
The Ubuntu terminal lets you install packages using various package managers and commands. You can use the following commands and utilities in the terminal to install deb packages on Ubuntu.
Method #1: Use The dpkg Utility
The dpkg command is the Debian package manager that allows you to install, remove, and build packages.
Run the following command to install a deb package with the dpkg utility:
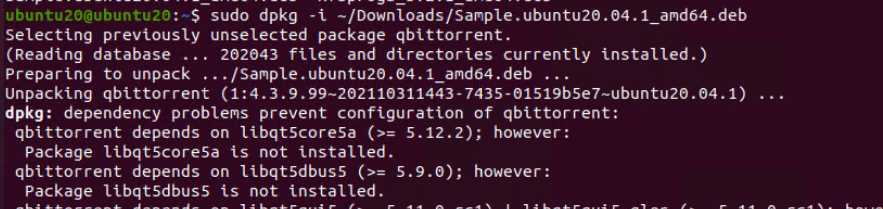
# sudo dpkg -i <package path> (Absolute path)
Enter the user’s password and wait for the installation to finish.
The dpkg utility returns an error if a package depends on unavailable dependencies. If you encounter this error, we recommend manually downloading the missing dependencies.
Method #2: Install Deb Files Through the APT Package Manager
The apt command launches Ubuntu’s APT package management utility.
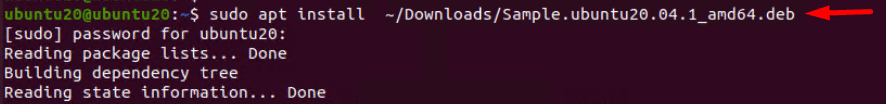
Run the following command to install a deb package with the apt utility:
# sudo apt install <package path>
If requested, enter the user’s password. The package manager will also automatically find and install any secondary dependencies.
Method #3: Use the GDebi Package Installer
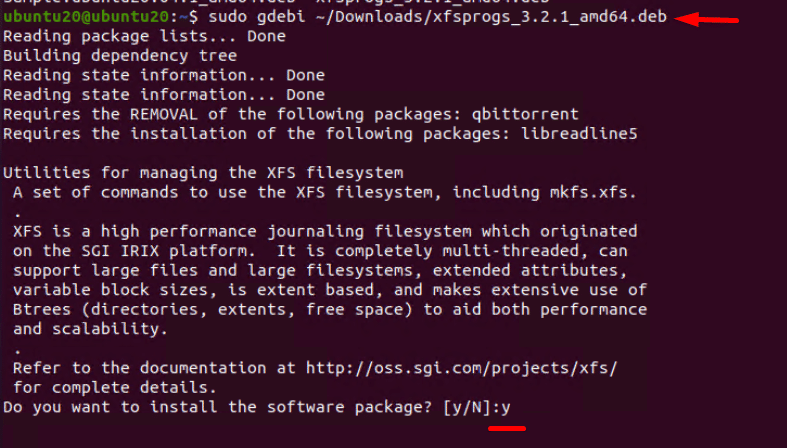
GDebi can also be used as a command-line tool to install packages. Run the following command in the terminal to install a deb package with GDebi:
# sudo gdebi <package path>
After downloading the required dependencies, the command will ask your permission to install the package. Press Y to give permission and enter the user’s password.
How to Uninstall Deb Packages
Ubuntu offers several methods for uninstalling a previously installed deb package. The process of removal is determined by how the package was previously installed.
The default options for removing deb packages from the system are shown below.
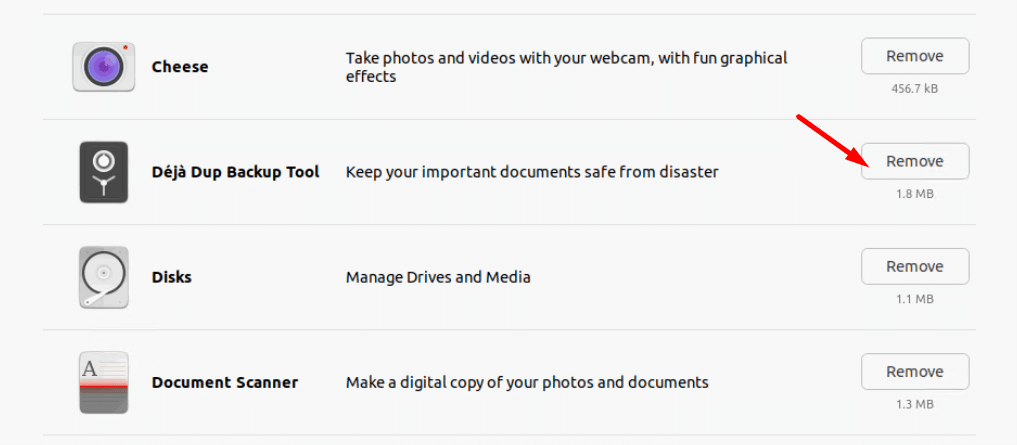
Method 1: Use the Software Center
To remove a deb package using the Ubuntu Software Center, perform the following steps:
1. Launch the Ubuntu Software.
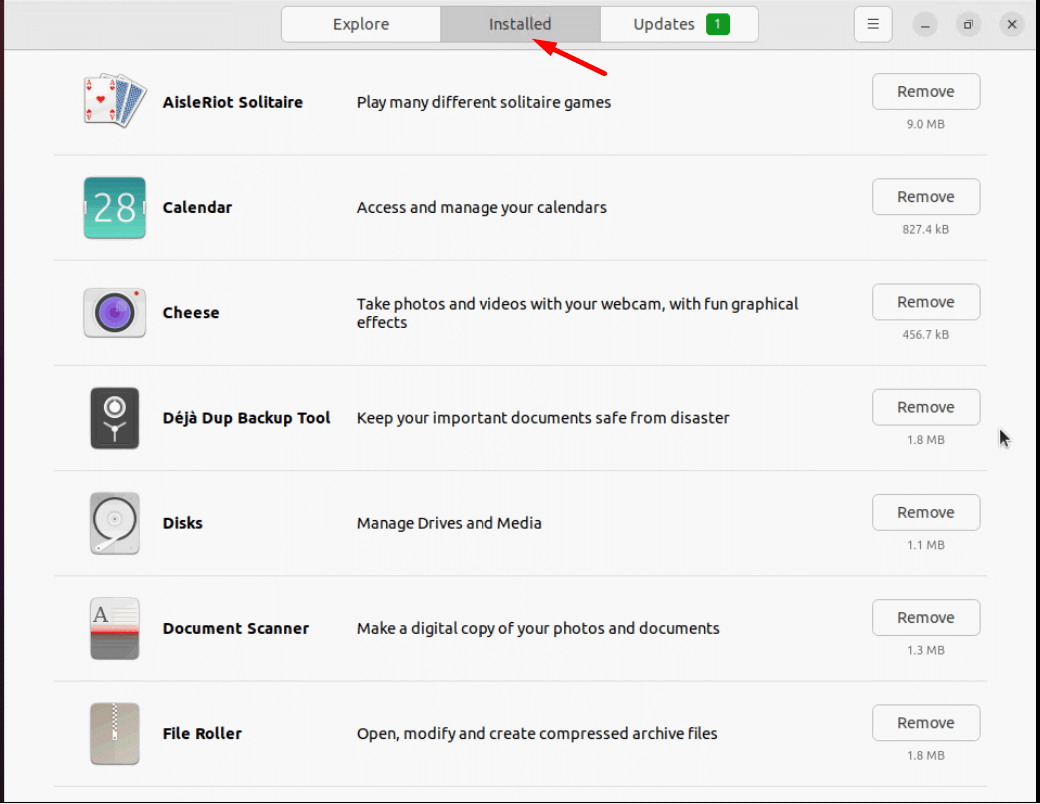
2. Go to the Installed tab.
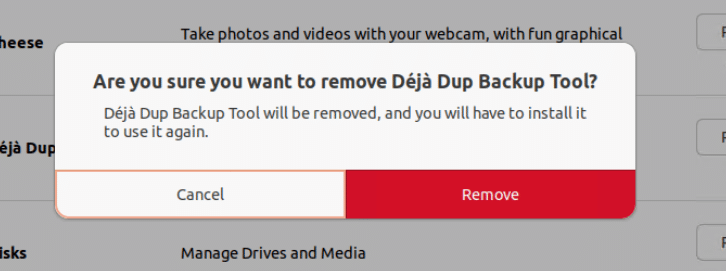
3. Find the software you wish to uninstall. To uninstall the application, select Remove.
4. Confirm the uninstallation and provide the user’s password to complete the software removal.
Method 2: Use the GDebi GUI
To uninstall software using Gdebi, follow these steps:
-
-
- Find the .deb package file on your system.
- Select Open With Other Application from the context menu.
- From the options, select GDebi Package Installer.
- To uninstall the software, click Remove Package.
-
-
-
- Enter the user’s password and wait for the uninstall to finish.
-
Method 3: Use the dpkg Command
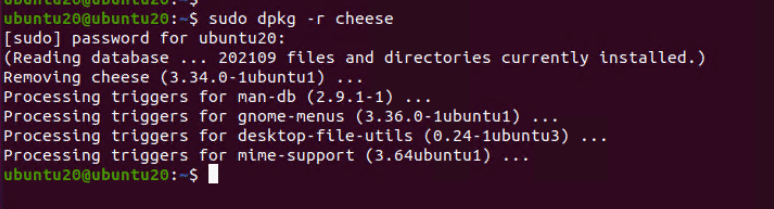
Use the following command in the terminal to uninstall packages installed with the dpkg utility:
# sudo dpkg -r <package name>
Important: Remember to use the official package name (not the .deb file name) in the command.
Method 4: Remove Packages with the APT Package Manager
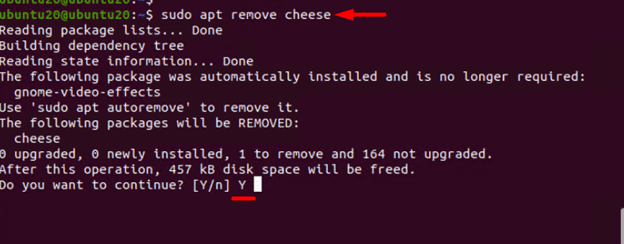
Run the following commands to uninstall a package using the apt command:
# sudo apt remove <package name>
To confirm the removal, press Y.
This method would work if you installed Ubuntu through the Ubuntu Software Center or the APT package manager.
Conclusion
This guide goes into the details of how to install deb files on Ubuntu. You need to be careful about the source of the package. While deb files provide flexibility, consider utilizing the Ubuntu Software Centre or APT for a simpler package management experience because they handle dependencies and updates effortlessly.
If you’re looking for a robust server for your Ubuntu projects, RedSwitches offers the best dedicated server pricing and delivers instant dedicated servers, usually on the same day the order gets approved. Whether you need a dedicated server, a traffic-friendly 10Gbps dedicated server, or a powerful bare metal server, we are your trusted hosting partner.
FAQs
Q. What does the .deb package file type refer to?
A .deb file represents a package format used by Debian and its derivatives, such as Ubuntu. This file type encapsulates the necessary files for a specific software program along with the package’s metadata.
Q. What is a .deb package file type?
A .deb file is a Debian software package used in Debian-based Linux distributions like Ubuntu. It contains all the files needed for a particular software application and metadata about the package.
Q. Why would I need to install .deb files on Ubuntu?
You might need to install .deb files on Ubuntu if certain software or applications are not available in the official Ubuntu repositories or through a Personal Package Archive (PPA). Additionally, any software downloaded from the internet in .deb format would require installation.
Q. How do I install a .deb package file on Ubuntu?
To install a .deb file on Ubuntu, you have two primary methods: using the dpkg or apt commands. Follow these steps:
For dpkg: Open your terminal and change to the directory where the .deb file is stored. Execute the command sudo dpkg -i filename.deb, substituting filename.deb with your specific .deb file’s name.
For apt: In the terminal, type sudo apt install ./filename.deb, ensuring to replace filename.deb with the name of your .deb file.
Q. What’s the difference between dpkg and APT when installing .deb files?
dpkg is a basic package manager that directly handles the installation and management of .deb files, but it does not automatically resolve dependencies. This makes it suitable for straightforward package installations. Conversely, APT is a more advanced tool that not only manages packages but also automatically resolves and installs any necessary dependencies and handles package repository configurations.
Q. How do I resolve dependencies when installing .deb files?
When installing a .deb file that encounters unmet dependencies, you can address this by using the apt command with the -f option to automatically find and install any required dependencies. Simply execute sudo apt -f install following your initial attempt to install the .deb file.
Q. Can I uninstall a .deb package later?
To uninstall a .deb package, you can utilize either the dpkg or apt commands. With dpkg, the command is sudo dpkg -r package-name, and with apt, you should use sudo apt remove package-name.
Q. What if I encounter a Dependency error during installation?
If you face dependency errors while installing, these are typically due to missing dependencies. Ensure that all dependencies are resolved beforehand. Should dependency issues persist, consider consulting Ubuntu forums or community support for assistance.
Q. Is it safe to install .deb files from untrusted sources?
It is risky to install .deb files from sources that are not verified, as these files could potentially contain malware or damage your system. It is advisable to download and install .deb packages only from the official Ubuntu repositories, trusted Personal Package Archives (PPAs), or other reputable sources.
Q. Can I upgrade .deb packages using apt?
If you have installed a .deb package with apt, it integrates into your system just like packages from a repository. To upgrade it, you can use the command sudo apt upgrade whenever updates become available.
Q. Where can I find .deb files for Ubuntu?
.deb files for Ubuntu can be sourced from the software providers’ official websites, third-party repositories, or by compiling them from source code using utilities such as checkinstall. Always ensure that the sources from which you obtain these files are trustworthy.