Key Takeaways
- Dedicated servers provide unmatched performance and stability due to exclusive access to resources.
- The isolation and ability to implement customized security measures on dedicated servers significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats.
- Dedicated servers offer significant scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to upgrade hardware or expand infrastructure to meet growing demands.
- While initially more expensive, dedicated servers offer a pay-as-you-grow model that becomes cost-efficient over time.
- Businesses have complete control over their server environment, allowing for tailored configurations that meet unique requirements.
- The evolution of server scalability is leaning towards hybrid/multi-cloud environments, automation, and AI.
Scalability is not just a phrase. It’s a need in today’s digital world. Your online presence must be fast and reliable. It may make or break your organization. Dedicated servers are at the front in this battle. They offer unmatched control and performance. But as your company expands, so does the difficulty of scaling these servers to accommodate growing demand without sacrificing performance or going over budget.
This article delves into dedicated server scalability. It removes the mystery and exposes the tactics. They can make the difference between your company’s survival and rapid expansion. It’s critical for both business strategists and tech experts.
You need to know how to scale your servers. This is essential to handle the huge surges in internet traffic. It’s also key to keep your data secure and your operations uninterrupted. Let’s explore this journey together to discover the keys to growing success.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What are Dedicated Servers?
- Key Characteristics of Dedicated Servers
- Scalability in the Context of Dedicated Servers
- Benefits of Scalable Servers
- Challenges in Scaling Dedicated Servers
- Best Practices for Server Scalability
- Future Trends in Server Scalability
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Dedicated Servers?
Credits: Freepik
These servers are independent physical servers used by only one client, company, or application. They are quite strong, and a server allocates all its resources to a single user. This is unlike shared hosting or virtual private servers (VPS), where CPU, RAM, and storage are shared among several users.
Dedicated hosting servers are the top choice for high-traffic websites, large commercial applications, and secure services. Their exclusivity gives them unmatched performance, security, and control.
Control and customization are two important benefits of dedicated hosting. With root or admin access, clients can install software and modify settings to boost their server’s performance.
Businesses have unique applications or specific server requirements. They cannot be met in a shared environment. They will find this level of control crucial.
Also, dedicated hosted servers can be upgraded when a client’s needs increase. They can get more memory, storage, or processing power. This offers a scalable solution that can adjust to changing business demands.
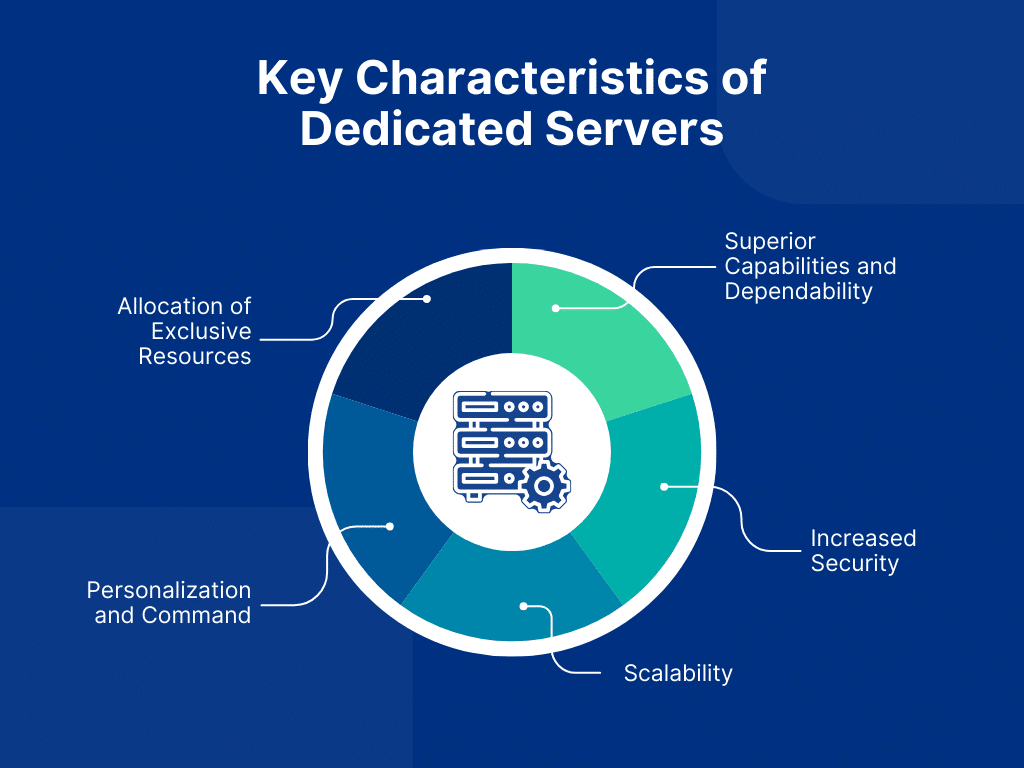
Key Characteristics of Dedicated Servers
Understanding the fundamental traits of dedicated servers is crucial for businesses seeking reliable and high-performance hosting solutions.
Let’s discuss the key characteristics of Servers.
Allocation of Exclusive Resources
The importance of exclusive resource allocation in servers cannot be overstated. It ensures that one client’s website or application will have exclusive access to the server’s processing power. This power includes its RAM, CPU cores, and server storage. This unique access will revolutionize businesses. It is for those who do complex, resource-hungry tasks. They also face changing traffic loads. It guarantees that resources will never be at risk of being throttled. This can’t happen because of demands from other users. And the resources will always be available when needed. In addition to improving performance, this separation from other users’ actions on the server greatly improves stability, making server performance more consistent and dependable—even under unforeseen high loads.
Superior Capabilities and Dependability
Dedicated servers are strong at delivering excellent performance. They are also reliable. Servers can process requests and handle data at speeds virtual environments share. The servers can do this due to their direct access to hardware resources. This is vital for busy websites and resource-heavy apps. These include enterprise-level databases, video streaming services, and massive eCommerce platforms. Servers are also vital, and are reliable and made to cut downtime. They ensure that users can always access your digital operations. This includes the network infrastructure that supports the server, built to maintain the highest uptime standards and the physical hardware robustness.
Increased Security
One crucial aspect of servers is their security advantages. Clients in isolated environments are not vulnerable to risks in shared hosting. These risks include damaging their reputation. It comes from shared IP addresses and nearby websites’ malware. Firms can adopt unique security measures. These include custom encryption algorithms, complex firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. They help firms meet industry standards and regulations.
Furthermore, servers with strict security protocols are often kept in data centers. These protocols include environmental safeguards, biometric access restrictions, and surveillance. Together, these measures offer a comprehensive security posture against digital and physical threats.
Scalability
In the context of servers, scalability provides a sophisticated expansion strategy. However, there is a set initial resource allocation. But, the infrastructure is meant to grow. Clients can scale up by improving the server’s hardware. For example, they can add more RAM for better data processing. They can upgrade the CPU for faster computation. Or, they can add more disk space for growing storage needs. This adaptability enables companies to customize the capabilities of their servers to meet changing needs, guaranteeing that they may grow quickly and successfully when demand rises without redesigning their infrastructure completely.
Personalization and Command
Credits: Freepik
Nothing compares to the degree of control and personalization offered by servers. With root or administrative access, clients have the most flexibility to customize the server’s operating system to their exact needs. This involves selecting an operating system, installing particular software, and configuring system preferences for peak performance. The customer is in charge of establishing particular database configurations, custom caching algorithms, or innovative security protocols. For companies with particular operating requirements or those aiming to obtain an ideal configuration that precisely matches their application requirements, this bespoke customization is crucial since it offers a customized hosting solution that regular hosting packages cannot match.
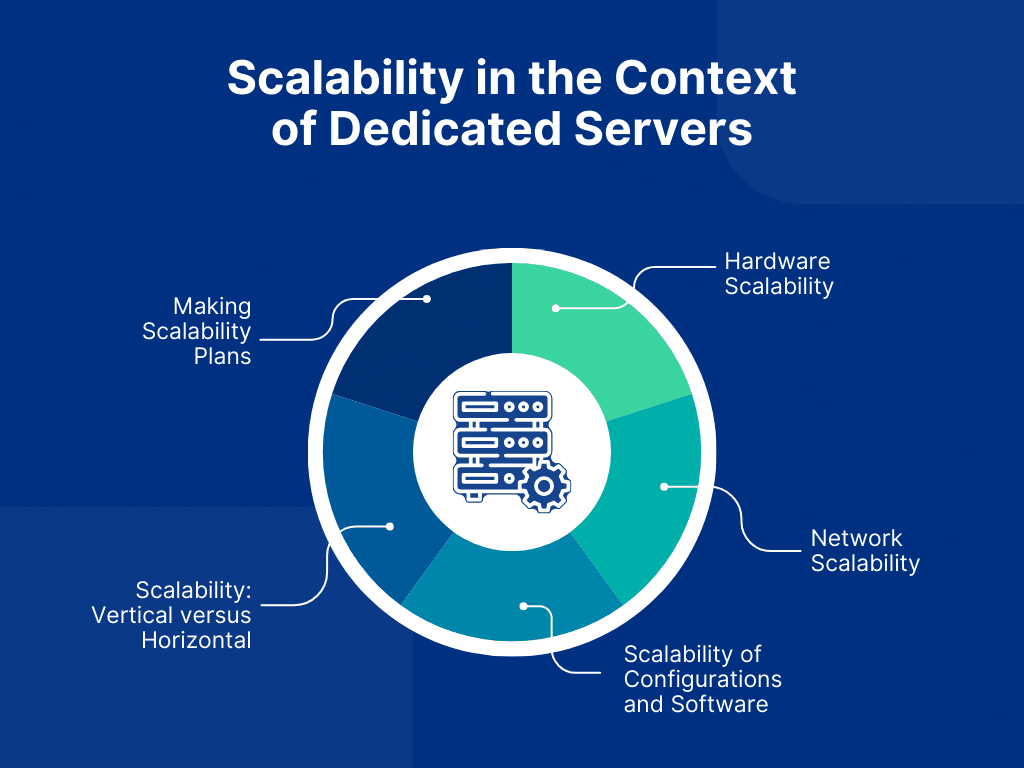
Scalability in the Context of Dedicated Servers
When discussing servers, scalability means increasing the server’s performance and resources to meet growing websites, apps, or service demands. This is essential for companies seeing increased user traffic, data volume, or computational demands.
Servers can scale in many ways, including software, hardware, and network changes. These factors are critical. They are key to maintaining performance, dependability, and user happiness over the long term.
Hardware Scalability
The simplest scalability method is to upgrade the server’s physical components. This can involve updating the CPU for more processing power. It can also mean increasing storage to hold more data. Or, adding more RAM to boost the server’s ability to do many things at once. Hardware can scale. It ensures that the server can keep up with growing databases or apps. It does so without needing to switch to a new one. It offers a clear path for expansion. It lets companies slowly increase their server’s abilities as their needs grow.
Network Scalability
We need scalability for the network. It supports servers, and demand for it is growing. This involves giving more bandwidth, if needed, to manage growing data transfers without causing bottlenecks or latency. Also, advanced networking, like load balancers, can spread incoming traffic among many servers or data centers, raising the infrastructure’s capacity to serve customers. Maintaining good availability and performance requires scalable networks. This is especially true for services that operate in global markets or face fluctuating traffic volumes.
Scalability of Configurations and Software
Scalability includes software and configuration optimizations and hardware and network modifications. This may involve tuning the server’s operating system, changing database settings to boost performance during peak traffic, or using scalable software designs like microservices, which can be spread over many servers or environments. Scaling software can greatly improve the server’s ability to handle high workloads. It does this by optimizing resources and processing requests efficiently.
Also Read 25 WordPress Speed Optimization Hacks
Scalability: Vertical versus Horizontal
Credits: Freepik
There are two types of scalability for servers: vertical and horizontal. Vertical scalability is often known as “scaling up.” It means increasing the current server’s hardware. This scaling is often the easiest. It doesn’t need major changes to the application’s structure. But, it could have financial or physical limits.
Adding servers to the current infrastructure allows for horizontal scalability, also called scaling out. This helps to divide the load more equally. This method clusters many servers. They function as a single system, providing nearly infinite scalability. However, it calls for more intricate setup and administration, in addition to software that can function in a distributed setting.
Making Scalability Plans
Anticipating future growth is key. So is making a server system that can handle it with the fewest disruptions. You must thoroughly understand the app’s traffic, performance goals, and resource use. Companies must also weigh the financial effects of scaling, balancing their demand for greater capacity and their financial limitations.
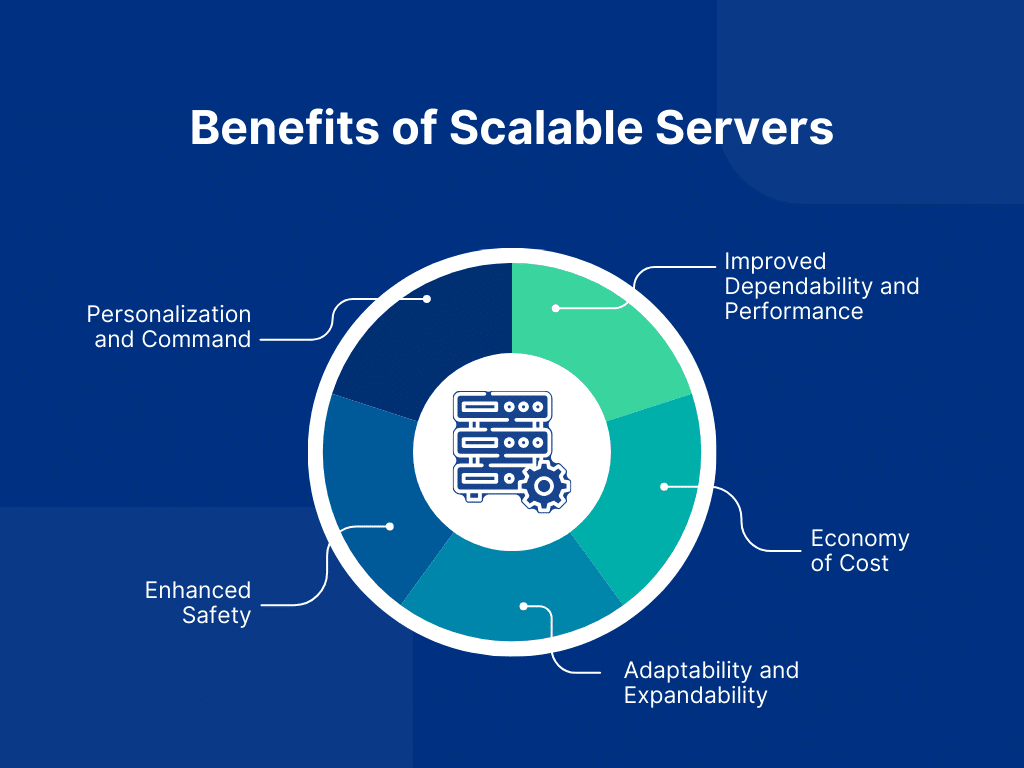
Benefits of Scalable Servers
Let’s discuss the benefits of Scalable servers in detail.
Improved Dependability and Performance
Scalable servers provide better performance. They are more reliable than managing more traffic and workloads. Applications like online gaming, financial transactions, and live streaming need real-time data processing and low latency. They can run on these servers with stability and consistency. Expanding resources guarantees that these high-demanding apps can run without interruptions.
Disruptions could erode customer satisfaction and confidence. SLAs (Service Level Agreements) provide a specific uptime guarantee. They are often included with servers. This inclusion further enhances the servers’ dependability and dedication to upholding high service levels regardless of demand.
Economy of Cost
Scalable servers offer a customized resource distribution and pricing method, redefining cost-effectiveness. Businesses can expand their server capacities as sales grow. They can do this thanks to the pay-as-you-grow approach. It ensures that IT costs are tied to business performance. With their typically tight budgets and uncertain growth paths, startups and SMEs stand to gain the most from this strategy. Also, avoiding spending on underused resources helps create a leaner, better operating model. It frees up funds that can be used to invest in other business divisions to promote innovation and growth.
Adaptability and Expandability
Flexibility and scalability are about more than handling growth or spikes in traffic. They are also about the ability to test new technologies, release updates, and add new services with little risk and disruption. Businesses can iterate quickly and keep an edge in competitive markets by using scalable servers. These servers facilitate agile development processes and continuous delivery models. Businesses can expand abroad and enter new markets by placing more servers in data centers near their customers. This move also lowers delays and improves service.
Enhanced Safety
Businesses face evolving dangers as the digital ecosystem changes. Scalable servers provide a strong base. It is for setting up a security approach that adapts to these threats. Scalability enables incorporating advanced threat intelligence and machine learning algorithms, which can anticipate and neutralize attacks before they affect the server, in addition to firewalls and intrusion detection systems. In the face of quickly spreading threats like denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults, the ability to swiftly scale security measures is essential to ensure that businesses can continue operating and protecting sensitive data in any situation.
Personalization and Command
Scalable servers offer a high degree of customization and control, enabling enterprises to precisely construct their IT infrastructure for the best performance. Every element of the server environment is customizable, including the network architecture, storage options, security protocols, and individual application configurations. Businesses in industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce must take compliance with industry rules and standards into account, and such granular control not only improves performance and security but also enables compliance with these requirements.
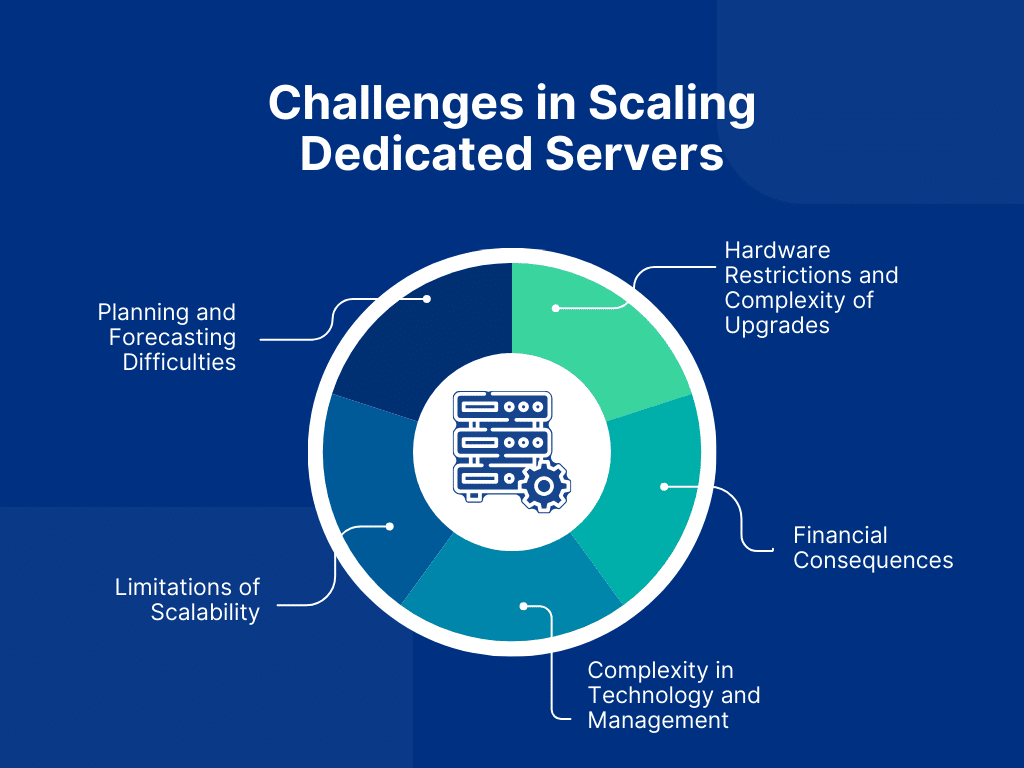
Challenges in Scaling Dedicated Servers
While scaling servers has many advantages, there are also some risks that companies must carefully consider. You must understand these obstacles. Then, you can make a scalable strategy. It will cut risks and ensure smooth operations.
The following are a few of the main obstacles to growing servers, along with an explanation:
Hardware Restrictions and Complexity of Upgrades
A primary obstacle to growing servers is the physical constraints of hardware and the intricacy of its upgrades. Unlike cloud or virtual servers, adding hardware to a server often means adding more RAM, boosting the CPU, or adding more disc space. This procedure may cause downtime due to the need to take the server offline for maintenance. Also, a server’s capacity for upgrades is limited. This may require deploying more servers and, as a result, more complex networks.
Financial Consequences
Significant financial consequences may arise from scaling servers. Servers cost more than shared or virtual ones. But they provide better performance and control. Suitable hardware is expensive at first. Also, the ongoing costs for power and cooling can add up soon. These expenses can rise a lot when firms scale their servers. This is especially true if they need more servers to handle growing traffic. You must do a cost analysis in any scalability planning. It ensures that the benefits of expanding are worth the costs.
Complexity in Technology and Management
Scaling servers adds more complexity to the administrative and technical aspects. Businesses confront a problem. They must manage a complex infrastructure. They add servers to handle greater loads. This includes building the network. It means balancing load, ensuring server data is consistent, and keeping up security. Every extra server adds to the burden for IT personnel, necessitating more effort and knowledge to handle efficiently. For businesses to handle this complexity, they need to be ready to invest in trained staff or outside assistance.
Limitations of Scalability
Servers have scalability limitations even though they can be scaled to some extent. As previously indicated, the amount of hardware that can be changed on a single server is limited. More servers will eventually need to be put online to manage increasing traffic or processing needs. Efficiently allocating workloads and managing network latency are two new difficulties. This comes with horizontal scaling. Also, a company may have practical limits on its ability to operate and afford a certain number of servers. These limits will eventually limit its potential for scalability.
Planning and Forecasting Difficulties
Credits: Freepik
You need precise planning and forecasting. They are necessary for effective scaling. They guarantee that resources are scaled up promptly to meet demand without overprovisioning. Predicting future needs is hard. This is especially true for companies in unstable markets or with erratic growth. While underestimating needs might result in downtime and performance bottlenecks, overestimating needs can result in needless expenses. Companies need to create scalable infrastructure plans that are economical and adaptable enough to change with demand.
Best Practices for Server Scalability
Credits: Freepik
Companies must follow best practices. These help them manage the challenges of growing servers well. These procedures provide scalability process optimization, high-performance assurance, cost management, and security maintenance.
Here’s a thorough look at some recommended methods. They are for making servers more scalable.
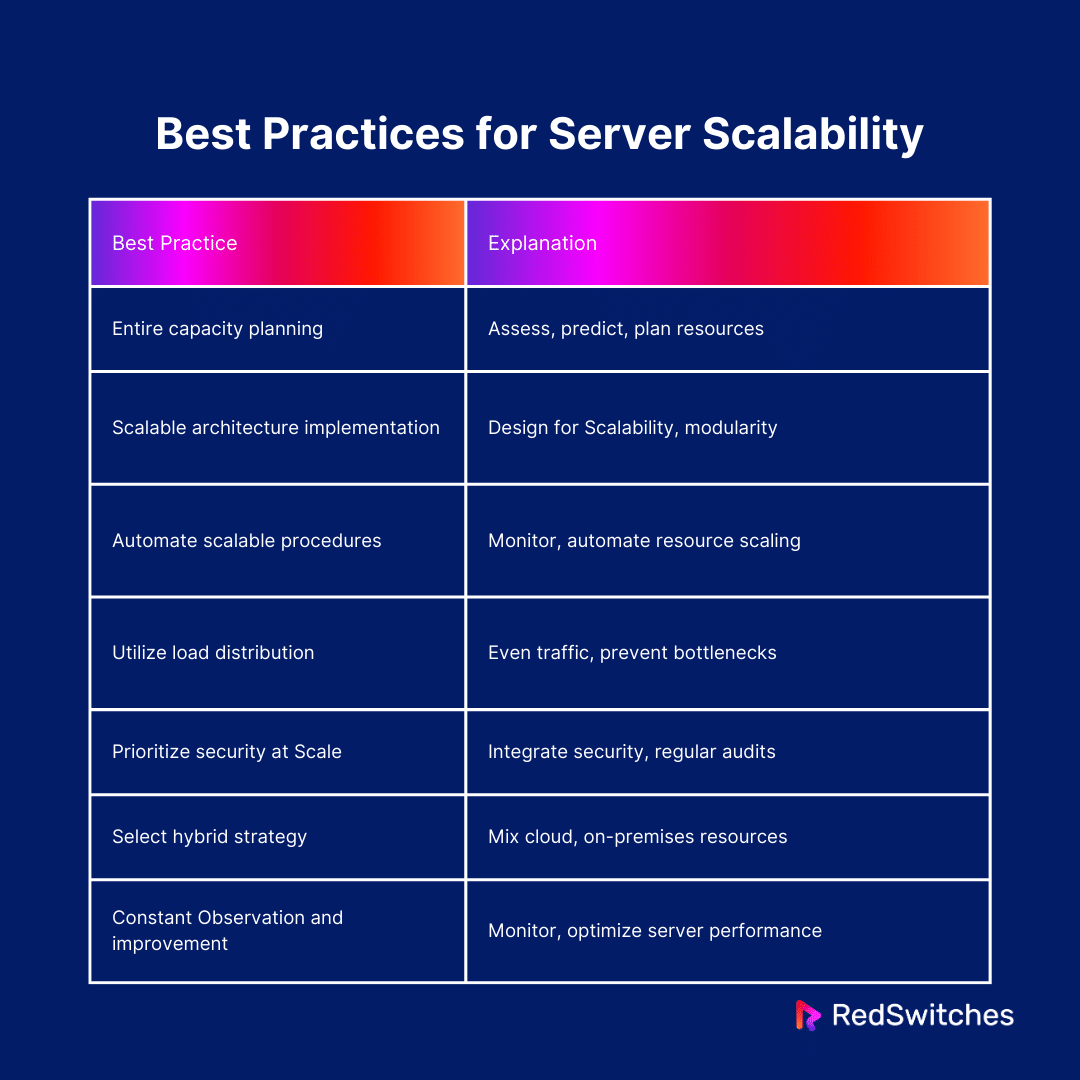
Entire Capacity Planning
Thorough capacity planning is the first step towards effective scaling. This involves assessing how resources are used now. It also involves understanding your apps’ needs. And it involves predicting future needs based on estimates of business growth. To scale, infrastructure must adapt to changing demands. It must do this without needing frequent overhauls. Capacity planning should consider short-term needs and medium- and long-term goals. You need to check that your servers still meet your business needs. You do this by periodically updating your capacity plan based on real growth and usage.
Start with Implementing a Scalable Architecture
It’s critical to consider scalability while designing your system from the beginning. The modular architecture provides precise control over resource allocation. It reduces the need for major system upgrades. This is because components can be scaled individually. You can make your server more scalable. To do this, use scalable technologies and architectures. These include cloud-native services, containerization, and microservices.
Automate Procedures for Scaling
An essential component of effectively managing scalability is automation. Automated monitors can track server performance and resource use in real-time. They scale the system when preset criteria are met. This proactive approach to scaling avoids manual intervention. It helps maintain ideal performance. It also lowers the risk of downtime or bottlenecks. Deployment procedures are also automated, guaranteeing that newly added resources are set up and smoothly incorporated into the current infrastructure.
Utilize Load Distribution
Load balancing is vital to prevent any one server from becoming a bottleneck and spread traffic evenly across your servers. Strong load-balancing techniques ensure that workloads are managed well. They work as you add servers, improving dependability and performance. In addition, load balancers can offer other advantages, including failover capabilities, which can reroute traffic in the case of a server failure and increase the robustness of your system.
Put Security First at Scale
The possible security threats will increase as your server infrastructure expands. Ensuring new resources adhere to your organization’s security policies and regulations requires integrating security considerations into your scaling planning. This entails maintaining data encryption throughout the enlarged infrastructure, expanding intrusion detection systems, and upgrading firewalls. As your environment changes, regular security audits and compliance checks can assist in identifying and reducing risks.
Select a Hybrid Strategy When It’s Required
The ideal scalability plan may entail a hybrid method that combines cloud resources and servers. This can provide the best of both worlds: cloud services’ scalability and flexibility for unpredictable workloads and the performance and control of servers for key functions when managing periods of high traffic. A hybrid strategy can be very useful since it allows organizations to adjust their resource levels on demand without investing in new physical infrastructure.
Constant Observation and Improvement
Maintaining the performance and efficiency of a scaled server environment requires constant monitoring and optimization. This entails monitoring traffic volumes and server health and evaluating performance data to find areas for optimization. Continuous optimization can involve changing software configurations, fine-tuning load-balancing techniques, and allocating resources accordingly to ensure that your infrastructure is always running as efficiently as possible.
Let’s summarize it in a tabular format.
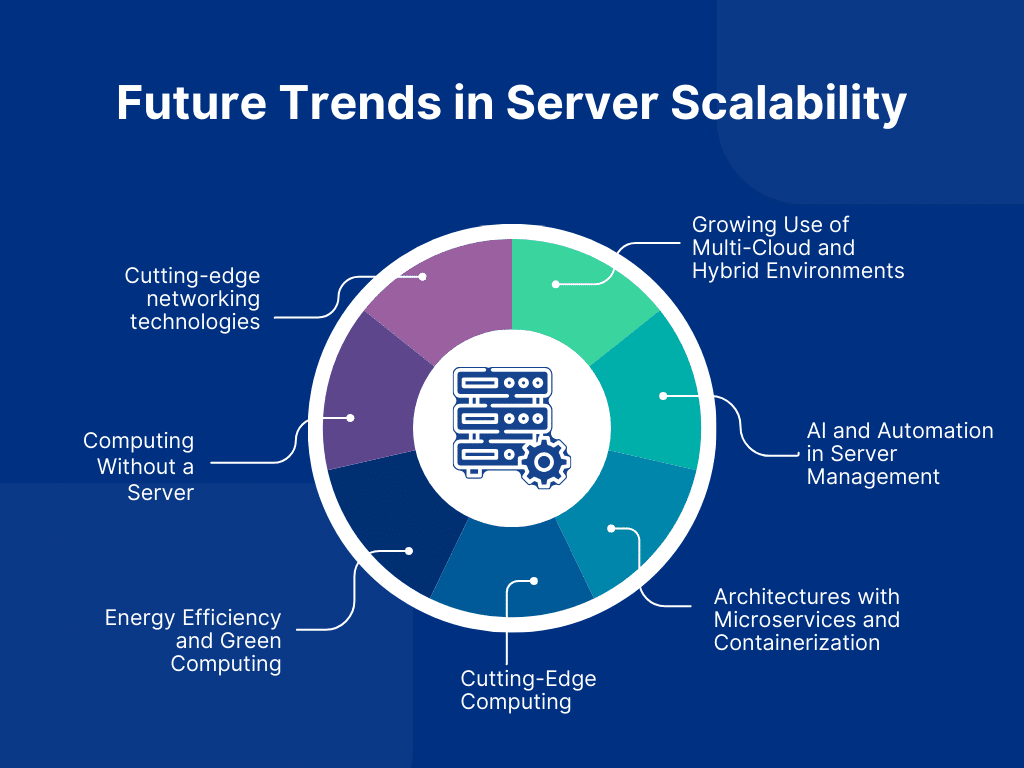
Future Trends in Server Scalability
Server scalability is a dynamic field. It changes because of better technology, shifting business needs, and the growing complexity of digital services. Several big trends are starting to emerge. They will fundamentally change how companies grow their server infrastructures. Understanding these trends is essential for organizations looking to stay ahead of the curve and make sure their infrastructures can accommodate growth and innovation. This is a thorough analysis of the upcoming developments in server scalability:
Growing Use of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Businesses are using hybrid and multi-cloud systems more. They do this to benefit from the advantages of different hosting providers. These environments offer the flexibility to extend server resources across several platforms by combining on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud resources. This method lets companies choose the best environment for each task. It keeps prices, performance, and security in check. Hybrid and multi-cloud methods will greatly impact server scalability. They do this because tech that enables smooth integration is improving.
Also read Private Cloud Security: 4 Things You Must Know
AI and Automation in Server Management
Scalability and server administration are about to change. This is thanks to automation and AI. Automation and AI-powered tech can predict demand spikes. They can also optimize resource use and scale servers ahead of time to meet demand. Take a proactive scalability strategy. It can greatly improve performance and efficiency. It can also reduce the need for manual intervention. AI may also help find chances to optimize. This ensures that servers are always at peak efficiency.
Architectures with Microservices and Containerization
Credits: Freepik
They are popular because they provide precise control over scalability. This control comes from containerization and microservices. Containers bundle applications and their dependencies into a single executable, simplifying deployment and scaling applications across different environments. Microservices architectures enhance containerization and allow more accurate scalability by dividing large applications into small, independently scalable services. Experts predict that microservices and containerization will be popular. They will give companies more efficiency and flexibility when growing their systems.
Cutting-Edge Computing
A big trend in server scalability is edge computing. This is especially true for apps that need real-time processing and low latency. Edge computing can lower latency. It boosts performance and lightens the strain on central servers. It does this by moving processing closer to the data source or end users. Businesses can now scale server infrastructures more easily. This is because of the decentralization of computing resources. It lets them manage applications with efficiency. These applications are sensitive to latency and use a lot of data.
Energy Efficiency and Green Computing
The emphasis on green computing and energy efficiency is growing. Sustainability is starting to play a big role in server scaling decisions. Companies seek solutions to grow their server infrastructures. They want to do so with the least energy and environmental impact. This means using renewable energy for data centers, optimizing software to use resources better, and using energy-efficient hardware. Sustainability will be key to server scalability because environmental issues are getting more attention.
Computing Without a Server
Serverless computing is becoming popular. It removes users from server maintenance and scaling choices. In serverless architectures, the cloud provider dynamically controls the distribution of computer resources. This model allows developers to create and manage services and apps. They can do this without worrying about the supporting infrastructure. Because users only pay for their resources and are precisely allocated based on demand, serverless computing can provide an affordable option for scalable applications.
Cutting-edge Networking Technologies
Networking technology must advance. It must handle more traffic and smoothly link dispersed resources. This is as server infrastructures grow. Advanced networking technologies like network function virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) provide more flexibility and control over network resources. These technologies make infrastructures better and faster. They improve data flow, cut latency, and boost security. This helps across scaled server environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, any company hoping to expand in the digital age must understand server scalability. To stay ahead of technology changes, the path toward scalable infrastructure involves recognizing obstacles, implementing best practices, and monitoring emerging trends. Businesses can ensure their server infrastructures are reliable, adaptable, and prepared to meet their growth goals by emphasizing security, adopting hybrid environments, turning automation into a valuable tool, and concentrating on capacity planning.
When starting or continuing your server scaling journey, think about collaborating with a provider knowledgeable about the subtleties and intricacies of scalable infrastructure. As a server supplier, RedSwitches distinguishes out by providing various scalable server options together with management and resource optimization knowledge for future expansion.
Contact RedSwitches today to discuss how it can support your scalability needs and drive your business forward!
FAQs
Q. Do servers run better?
Servers have exclusive access to resources. They frequently offer better performance, making them ideal for demanding applications and websites with heavy traffic.
Q. Why is a server more secure?
A dedicated server offers additional protection because it keeps your resources and data separate from those of other users. It can also be configured with security features specific to your requirements.
Q. How much bandwidth does a server use?
Depending on the application, a server’s bandwidth requirements might vary greatly. It can vary from a few Mbps for simple websites. The variation can go on to several Gbps for sites with significant traffic and data-intensive applications.
Q. What is dedicated server hosting?
Server hosting is a type of web hosting where the client leases an entire server exclusively for their use. Thus, providing greater control and resources compared to shared hosting.
Q. What are the benefits of using a server?
Some benefits of using a server include improved reliability, better security features, dedicated resources for your websites and applications. Additionally, they include faster load times, and the ability to handle large amounts of traffic and multiple users.
Q. How do I choose the right dedicated server for my needs?
To choose the right server, consider factors such as your specific needs, required server configuration, desired level of managed hosting, server hardware, security updates, and overall performance requirements.
Q. Why might someone need a server?
Someone might need a server if they have a web application or website that requires optimal performance, dedicated resources, and increased security. Or, if their current hosting plan is unable to meet their demands.
Q. What is a managed server?
A managed server is a hosting solution where the hosting provider takes care of server management tasks. These tasks include security updates, server maintenance, and technical support. They allow the client to focus on their business.
Q. What are the security features of a server?
Servers offer enhanced security features such as firewall protection, regular security updates, secure data centers, DDoS protection. Plus, the ability to implement specific security measures tailored to the client’s needs.
Q. How does using a server differ from a VPS or shared server?
Using a server provides you with exclusive access to the entire server’s resources, whereas VPS hosting involves virtual compartmentalization on a shared server. Shared hosting means sharing resources with multiple users, resulting in varying levels of performance and control.