Key Takeaways
- P2P networks offer significant cost savings by distributing workload and resources among peers, eliminating the need for expensive server infrastructure.
- Servers provide superior performance and reliability, albeit at a higher cost, making them suitable for applications requiring high availability and throughput.
- P2P networks excel in scalability and flexibility, as they naturally expand with the addition of new peers, sharing resources efficiently.
- Servers, however, offer scalability through hardware upgrades but require careful planning and financial investment.
- The decentralized nature of P2P networks enhances resilience and reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
- Dedicated servers offer centralized control, simplifying management, security enforcement, and data integrity.
- P2P networks provide a degree of privacy and are challenging to monitor due to their decentralized structure.
- Servers offer a controlled environment where security measures can be uniformly applied.
P2P and dedicated server models are still contentious. This is in the fast-changing world of online gaming and networking. Every model has unique benefits and drawbacks that significantly influence end users’ experiences. P2P networks offer low-cost, decentralized alternatives, yet servers provide consumers with better speed and stability.
This article explores the key distinctions between these architectures. It explains how these distinctions affect security, scalability, and user experience. We hope our thorough examination will shed light on the subtleties of the P2P and server models and how these technologies affect the modern digital environment in which we live.
Join us as we explore the intricate world of online connectivity, offering a clear perspective on a complex subject.
- Key Takeaways
- What are Peer-to-Peer Servers?
- Advantages and Disadvantages Of P2P
- What are Dedicated Servers?
- Advantages and Disadvantages Of Servers
- Key Differences: P2P vs Dedicated Server
- Which is better: P2P or Dedicated Server?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Peer-to-Peer Servers?
Credits: Freepik
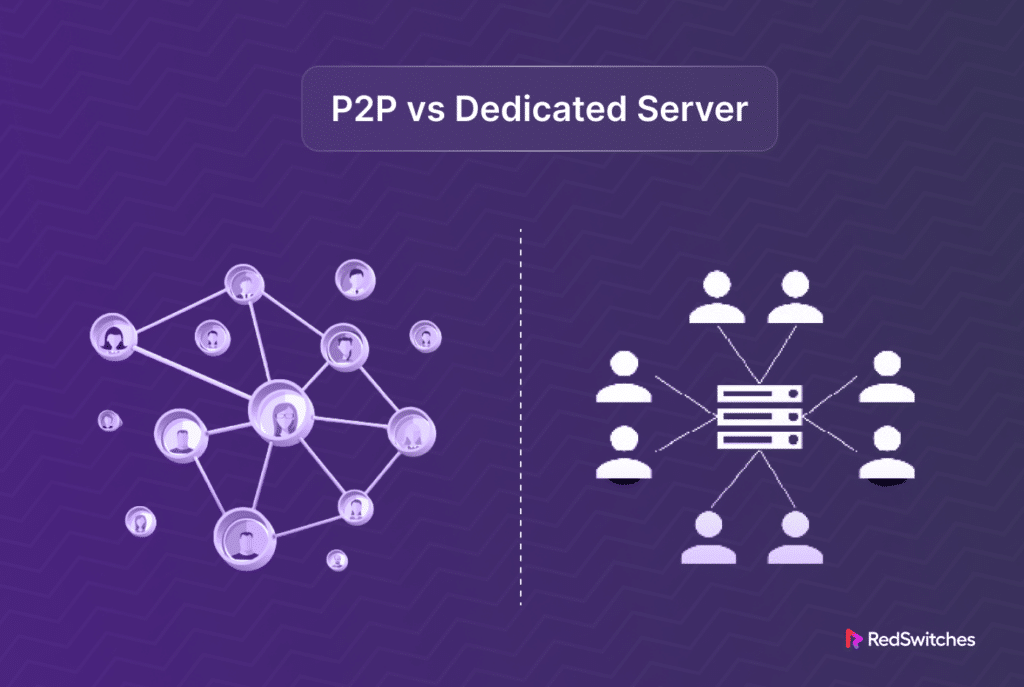
P2P servers use a decentralized network. They are different from the standard client-server model. Every member, or “peer,” in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network functions as both a client and a server and can send and receive data directly with other peers. This architecture divides the burden among many network nodes. It removes the need for a centralized dedicated hosted server. In a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, all peers are equal. They contribute resources like processing power, storage, and bandwidth. These resources are immediately available to others.
P2P technology is fundamentally distributed, which improves robustness and scalability. The system’s overall capacity grows as more peers join the network. This strengthens its ability to handle faults. P2P networks are resilient to server failure. Centralized systems depend on active peers to work. Due to the network’s ability to self-heal, there is no single point of failure, increasing reliability and uptime.
P2P networks are widely used. They are used in many contexts, such as blockchain technology, distributed computing, and file sharing. File-sharing programs like BitTorrent use P2P to distribute huge files quickly. It saves the original distributor a lot of money on bandwidth. Distributed computing projects like SETI@home use the idle processing power of millions of personal computers worldwide. They use it to analyze data.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of P2P
Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages of P2P networks:
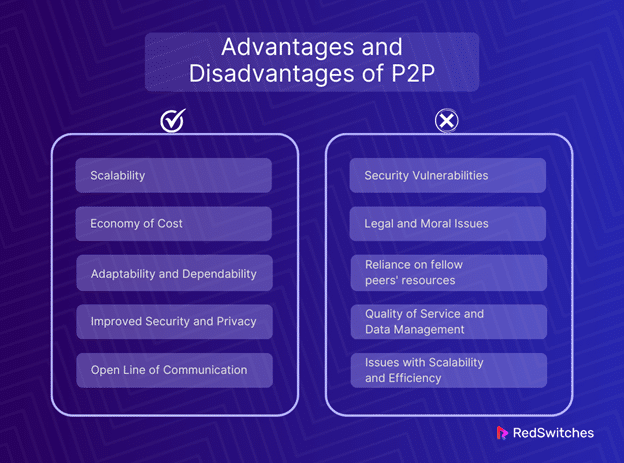
Advantages of P2P
Let’s discuss the Advantages of P2P in detail.
Scalability
P2P networks are scalable by nature. The network has resources like processing power, storage, and bandwidth. They increase as more peers join. This contrasts with traditional client-server models. They need investment in infrastructure and server capacity to scale up. When using a P2P arrangement, every additional user improves the network’s overall performance by dividing the workload more fairly and effectively among the users. P2P networks are well-suited to manage increasing volumes of data and users without centralized updates because of their dynamic scalability.
Economy of Cost
The cost-effectiveness of P2P networks is one of their strongest features. The costs of buying, maintaining, and updating server hardware and software are greatly decreased, if not eliminated, as a centralized server is not required to run the network. By sharing the cost of providing the network’s essential resources—like bandwidth and storage—peers lessen the financial strain on any one party. This model can result in significant savings for new businesses and smaller companies that might not have the funds to invest in pricey infrastructure.
Adaptability and Dependability
P2P networks’ decentralized design makes them extremely dependable and resilient. Since resources and data are dispersed among numerous nodes, the network can continue to operate even if some peers fail or become unavailable. Unlike client-server topologies, which allow a single point of failure to cause a complete service outage, this redundancy ensures that no single failure can destroy the network. P2P networks are especially useful for critical applications where uptime is crucial because of their capacity to self-heal by rerouting requests to peers that are accessible.
Improved Security and Privacy
P2P networks have improved security and privacy features. P2P networks are decentralized, which makes it more difficult for outside parties to monitor or regulate the flow of information. It gets harder to track and intercept data since data channels are dispersed and subject to frequent modification. Furthermore, many P2P networks use end-to-end encryption to ensure that peer-to-peer data transfers are safe and confidential. Remembering that the P2P network’s particular protocols and security mechanisms determine how secure and private a network is is crucial.
Also Read HTTP vs HTTPS
Open Line of Communication
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks allow direct communication without middle-man servers. Faster transfer speeds can result from this direct data exchange, particularly when transferring big files or streaming media. Applications that benefit from lower latency and better throughput, such as file sharing and multimedia streaming, are particularly good examples of direct transfers’ efficiency.
Disadvantages of P2P
Let us now discuss the Disadvantages of P2P in detail.
Security Vulnerabilities
This makes P2P networks less secure. They are more vulnerable than traditional client-server models. Malicious actors have multiple possible entry points to exploit because every peer in the network can function as both a client and a server. The decentralized structure increases resilience. But, adopting consistent security measures and procedures makes it harder. P2P networks are more likely to have problems. These problems include malware, attacks on peers, and software vulnerabilities. Each peer must rely on its defenses. There is no central authority to oversee security. This results in uneven security levels throughout the network.
Legal and Moral Issues
P2P networks are widely used in file-sharing apps. They enable copyright infringement. This has put them at the center of many legal and ethical disputes. Sharing copyrighted content without permission is easy. This puts P2P networks and their users at serious legal risk. Also, P2P networks are anonymous and not traceable. They might be used for crime, making it hard to enforce rules and laws.
Reliance on fellow peers’ resources
Peers who are online at any time and their willingness to share resources directly affect the availability and performance of resources. This occurs in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. Network performance may vary. Bottlenecks may happen if many users use resources without adding to the network. Free riders are users who gain from the network without contributing. They can hurt the P2P system’s effectiveness and fairness.
Quality of Service and Data Management
A centralized control mechanism in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network is needed to ensure data integrity and quality of service (QoS). Getting good information can be hard. The data is inconsistent and fragmented. It is stored and sent within the network. Also, the peers’ locations, bandwidth, and system performance all can greatly impact service quality. This includes data speed and availability. In contrast to centralized services, these factors lead to a less reliable and predictable user experience.
Issues with Scalability and Efficiency
P2P networks are theoretically scalable, but real-world issues may arise as they expand. Efficiency problems with large-scale P2P networks can include more overhead in connection management and data lookups. A large network might make finding and retrieving data difficult and time-consuming, which could offset some of the scaling advantages of P2P networks.
What are Dedicated Servers?
Credits: Freepik
These servers are a common and effective network architecture and hosting method. In it, a single server is set aside for one customer, business, or application. A server allows resources to a single customer. These resources include processing power, memory, storage, and bandwidth. This is different from shared hosting and virtual private servers (VPS). They distribute resources among several clients.
Because of dedicated server exclusivity, it offers excellent speed, stability, and control, making it the perfect option for busy websites, extensive apps, and vital corporate services.
Servers are superior from a security and compliance standpoint. Clients can entirely customize the server’s security. This includes firewalls, anti-malware programs, and encryption techniques. This makes it possible to have a customized security posture that can satisfy particular legal needs or industry norms. This is crucial for companies that handle sensitive data, such as financial records, medical records, or personal information. A server’s isolated environment greatly lowers the possibility of vulnerabilities and assaults, which are more frequent in shared systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Servers
Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages of servers:
Advantages of Servers
Let’s focus on the Merits of servers in detail.
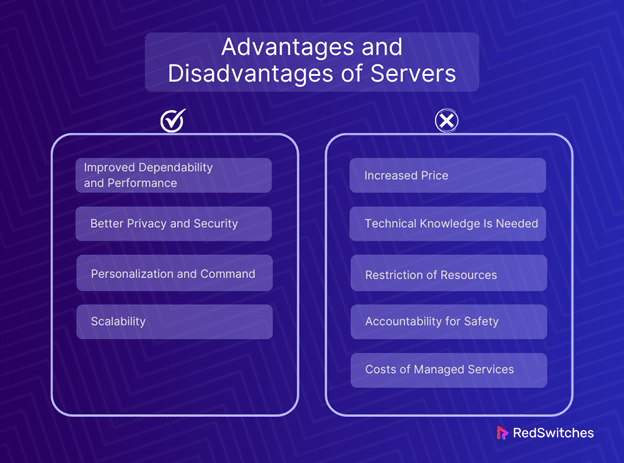
Improved Dependability and Performance
Servers’ outstanding performance and dependability is one of their biggest benefits. There are no problems with resource contention common in shared hosting setups because all of the server’s resources—CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth—are dedicated to a single client. This guarantees seamless program operation, reduced load times, and an enhanced user experience. A server can manage the strain for websites and applications with high traffic levels without experiencing performance hiccups that could happen on a shared server.
Better Privacy and Security
Regarding security and privacy, servers outperform VPS and shared hosting options. Clients have total control over the server environment, enabling them to install unique firewalls, security measures, and encryption methods suited to their requirements. This is especially crucial for companies that must abide by strict data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Cross-site contamination and other dangers related to shared resources are greatly diminished by the isolated environment of a server.
Personalization and Command
Complete administrative access to servers allows clients to customize and manage their hosting environment to the highest degree. This implies they can select the precise operating system, software combinations, and hardware specs that best meet their requirements. This kind of flexibility is priceless for unique workloads or applications that need particular conditions since it allows for the best possible functionality and performance. Moreover, this degree of control enables more effective resource utilization because customers can modify settings and configurations to suit their usage patterns and needs.
Scalability
Excellent alternatives for scaling are available with servers. The server can be upgraded to include more RAM, computing power, or storage as a firm expands or its demands change. Because of its scalability, companies can grow their online operations without running into the restrictions that come with shared hosting options. Maintaining excellent performance while keeping expenses under control is made easier by the flexibility to scale resources up or down as necessary.
Disadvantages
Let’s discuss the shortcomings of these servers in detail.
Increased Price
The price of servers is one of their biggest drawbacks. servers are significantly more expensive than virtual private servers (VPS) or shared hosting. This is because renting or buying a server requires exclusive usage of its hardware, bandwidth, and storage—all of which drive up costs. Extra electricity, cooling, and space costs can add up for those hosting on-site servers. They are for upkeep, security, and upgrades. The server’s cost is an important financial obstacle for startups and small businesses.
Technical Knowledge Is Needed
Requires a certain amount of technical know-how in managing a server. Server clients are in charge of these duties unless they pay extra for managed hosting. In that case, the hosting provider handles server security and maintenance. This is in contrast to shared hosting. This covers speed optimization, security fixes, troubleshooting, and software upgrades. This can be hard for businesses. They don’t have an IT staff with server management experience. It takes time and pulls resources from other crucial areas.
Restriction of Resources
Even while servers offer a lot of resources, these resources are restricted by the hardware requirements of the server. It can be disruptive and expensive to upgrade the hardware on a server or migrate to a more powerful server if a website or application grows suddenly beyond the server’s capability. Due to this scalability issue, we need thorough planning and forecasting. They ensure the server can handle expected growth. It does so without needing costly, frequent upgrades.
Accountability for Safety
The client is responsible for security while using a server. This entails safeguarding against DDoS assaults and hacking and ensuring that data is backed up and recoverable in the event of an error. Strong security measure implementation is expensive and takes experience, particularly for companies that comply with stringent regulatory requirements. Neglecting to safeguard a server sufficiently may result in significant data breaches and legal ramifications.
Costs of Managed Services
Managed services are an option for companies without the knowledge to maintain a server. However, these services are extra expensive, which raises the total cost of running a server. The cost-effectiveness of the server solution may be greatly impacted by managed services, even while they reduce the server security and maintenance load.
Also Read How To Prevent DDoS Attacks [8 Proven Tactics You Can Try Right Now!]
Key Differences: P2P vs Dedicated Server
We will now discuss the core part of our blog, i.e., P2P vs Server debate, in detail.
Architecture
Let’s discuss the comparison between P2P vs dedicated hosted servers regarding their architecture:
P2P
The decentralized network concept, peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture, differs greatly from conventional client-server configurations. Every node, or “peer,” in a P2P network serves as a client and a server. This implies there is no need for a central server since any peer in the network can share and access resources directly with other peers. Peers share resources and data and communicate directly with one another. Because of this architecture, nodes can be added and removed dynamically without significantly affecting the functionality of the network as a whole. P2P networks’ decentralized architecture improves resilience because there isn’t a single point of failure and allows for easier scalability as the network’s capacity increases with each additional peer.
Server
On the other hand, a server design is based on a centralized paradigm in which clients connect to a single server containing the services, apps, or data to access the resources. One client or organization is given exclusive use of the server, which gives them complete control over its resources, including CPU, memory, storage, and bandwidth. Because no client shares the server’s resources, good performance and dependability are guaranteed by this centralization. However, it also introduces a single point of failure; all services and applications hosted on the server become unavailable in the event of a server failure.
Scalability
Let’s examine how P2P networks contrast with dedicated hosting servers in terms of their Scalability differences.
P2P
P2P networks are very scalable because of their decentralized architecture. The system’s total capacity, whether in terms of bandwidth, storage, or processing power, inevitably rises as additional peers join the network. This is such that there is no need for centralized infrastructure improvements because every new peer adds its resources to the network, increasing its overall capability. P2P networks may effectively manage growing user numbers and data volumes by dividing the load across multiple nodes.
Server
In a server environment, on the other hand, scalability is more linear and contingent upon the hardware restrictions of the server. Adding more CPUs, memory, or storage space to a server might help it handle higher loads, but doing so can be expensive and require downtime for setup and installation. Although users of servers benefit from better speed and control, scaling them up to handle expansion requires careful planning and financial commitment.
Cost
Consider exploring the Cost distinctions between P2P networks and dedicated hosted servers.
P2P
One of the best things about Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networks is their affordability. Because each peer provides resources like bandwidth, storage, and computing power, the total infrastructure costs in a P2P architecture are shared by all users. As a result, a lot less costly centralized hardware and maintenance are required. The decentralized model does away with the need for one organization to pay for all server acquisition, operation, and maintenance aspects.
Server
On the other hand, servers are more expensive, mostly because they require specific hardware, upkeep, and the physical infrastructure needed to house and operate the server. These servers offer one client exclusive resources, guaranteeing excellent performance and dependability but at a cost.
In addition to the initial cost of buying or leasing the server gear, costs include recurring charges for electricity, cooling, bandwidth, and physical security. The operational costs of servers may also rise if they need a managed service for security, upgrades, and maintenance.
Performance
Let’s analyze the Performance variations between dedicated hosted servers and P2P networks
P2P
P2P networks are intrinsically dispersed. Their performance depends on all involved peers’ combined bandwidth, storage, and computing. Depending on the number of peers, how they are distributed geographically, and the resources each peer gives, this might result in a high degree of performance fluctuation. P2P networks can work quickly and efficiently. This happens when many peers have high-capacity resources. This is especially true for file sharing and data delivery.
Servers
Conversely, dedicated servers provide reliable and superior performance. There is no bandwidth, CPU, or memory rivalry on a dedicated server since all resources are allotted to a single customer. This guarantees high availability and quick loading times for apps. Dedicated servers are good for websites and apps. They need lots of processing power and bandwidth. This is because the servers offer a dependable and stable environment.
Security
Let’s take a closer look at how dedicated hosted servers and P2P networks vary in Security.
P2P
P2P networks are decentralized, and security in them is intrinsically complicated. Every peer is responsible for their security without a central authority to supervise and enforce security regulations. P2P networks are more at risk to many kinds of attacks. These include virus distribution, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The risk comes from inconsistent security levels across the network. Also, P2P networks are anonymous. This anonymity can be used for crime. It makes it hard to keep a network safe and legal.
Server
The administrative staff of a server can put in place extensive security policies and procedures, and dedicated servers provide a more controlled security environment. Administrators can detect and neutralize threats using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and routine security audits when they have complete control over the server.
Management
Now, let’s compare the Management aspects of P2P networks against those of dedicated hosted servers
P2P
Taking charge of a P2P network entails managing a decentralized system in which every node performs the functions of both a server and a client. This arrangement makes centralized management challenging because there isn’t a single control point. Instead, the peers share management duties. This can make tasks like updating software, enforcing security rules, and ensuring data integrity across the network more difficult.
Server
On the other hand, servers are operated by a single organization or team using a centralized management strategy. This makes software upgrades, security patching, performance monitoring, and backup procedures more simply and uniformly possible.
Data Integrity
Let’s explore the Data Integrity distinctions between P2P networks and dedicated hosted servers.
P2P
Since data in P2P networks is dispersed among many nodes, centralizing control over data integrity is difficult. Because data can be kept on numerous nodes, P2P can recover lost data from other nodes even if some peers go offline or experience data loss. Although ensuring data consistency becomes more difficult with this distributed strategy, resilience against data loss is improved.
Server
Servers provide a centralized solution for data integrity. Having all data housed on one server (or a centralized cluster of servers) makes establishing and enforcing uniform backup, recovery, and data validation processes simpler. Implementing strong security measures, such as frequent audits, access limits, and encryption to guard against unauthorized data change and breaches, is made possible by administrative control over the server environment.
Availability
Let’s explore the Availability distinctions between P2P networks and dedicated hosted servers.
P2P
P2P networks’ decentralized structure makes them excellent at delivering high availability. The network’s overall functionality remains relatively unaffected by the failure of a single or more peer, as data and resources are dispersed among various nodes. Because of its built-in redundancy, services and data are guaranteed to continue functioning even in the event of hardware malfunctions, network problems, or isolated disruptions.
Server
Servers can be more susceptible to single points of failure even though they provide a centralized point of management and control. The services offered by the server hosting the data or application may stop working until the problem is fixed if it suffers a hardware malfunction, a software fault, or a connectivity issue.
Control
Let’s discuss how the Control of P2P networks differs from that of dedicated hosted servers.
P2P
Control in P2P networks is dispersed among all users and is decentralized. Thanks to this structure’s high degree of autonomy, individual nodes can join or exit the network, share resources, and access data without centralized control. This can improve privacy and resilience to censorship and centralized failure, making enforcing consistent network-wide regulations and standards more difficult.
Server
Organizations have total control over their server environment with servers. The precise tuning of hardware, software, and network parameters to satisfy particular operating requirements is made possible by this centralized control. Administrators can oversee access restrictions, impose stringent security guidelines, and guarantee that data processing meets legal requirements.
Which is better: P2P or Dedicated Server?
Let’s discuss whom to choose and when.
Select P2P If
You want cost savings. P2P can achieve them by sharing the workload across active peers. This can sharply cut the need for costly server hardware and maintenance if cutting infrastructure costs is a top goal.
Scalability is key: P2P networks can scale more naturally and economically by using the resources of new peers. This is especially true for projects. They expect sudden or changing increases in usage or data volume.
Decentralization and resilience are crucial. P2P networks are decentralized. They have built-in benefits if your application needs high availability. They also provide resilience to censorship or centralized control.
Decentralization and resilience are crucial. P2P networks are decentralized. Their structure has built-in benefits if your application needs high availability. They also help with resilience to censorship or centralized control.
Select Dedicated Hosted Server If
Performance and reliability are crucial. A server provides the control and resources needed for an application that demands low latency, great performance, or the ability to manage large traffic volumes consistently.
Priorities are compliance and security: A server give companies that handle sensitive data or must adhere to tight regulations the capacity to administer and execute thorough security protocols and guarantee compliance.
You Must Have Complete Control Over the Setting: A server is the best option if you need complete control over your server environment, including hardware specs, software setups, and operational factors.
Also Read: Choosing Between Dedicated Servers vs AWS for Your Business
Conclusion
Choosing between dedicated servers and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks depends on understanding your project’s needs. These include factors like cost, scalability, performance, and security. servers offer unmatched control. They also offer dependability and performance. They are for applications needing high security and regulatory compliance. At the same time, P2P networks provide a decentralized, economical option perfect for scalable content distribution and robust communication.
You need an experienced and reputable hosting company. You need them as you choose the best architecture for your online projects. RedSwitches is a notable partner in this regard. We offer a broad array of server solutions. We are made to satisfy the needs of companies wishing to use server technology.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between P2P and server?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks divide work and responsibilities among peers, whereas client-server designs centralize server control and resources.
2. Are P2P servers good for gaming?
P2P servers may be advantageous for gaming because they can withstand server outages, but they may also have issues with latency.
3. Is P2P faster than client-server?
Direct file sharing between users may benefit from P2P. However, client-server systems may offer more reliable and consistent speeds for various services.
4. What is the difference between Dedicated hosted Servers and P2P Hosting?
Dedicated hosted Servers are physical servers solely dedicated to hosting a single client’s data and resources, whereas P2P hosting relies on a network of peers to distribute resources and information.
5. How do Servers enhance the gaming experience compared to P2P hosting?
Servers offer better performance and stability for multiplayer games, providing a centralized location for hosting the game and managing player connections.
6. What is Peer-to-Peer gaming and how does it differ from Dedicated Gaming Servers?
Peer-to-peer gaming refers to multiplayer games where one of the players’ machines acts as the server, distributing the game data among all the players. On the other hand, dedicated gaming servers offer a centralized and more reliable hosting solution.
7. When should game developers consider using a Server over Peer-to-Peer hosting?
Game developers should opt for servers to provide a more stable and seamless gaming experience for their players, especially in multiplayer games with larger player bases.
8. What are the advantages of Server Hosting for multiplayer games?
Using a server for hosting multiplayer games ensures better performance, reduced lag, improved security, and scalability for accommodating more players as the game grows in popularity.
9. Are Servers better than P2P hosting for hosting online multiplayer games?
Yes, servers are preferred for online multiplayer games due to their superior performance, reliability, and management capabilities compared to P2P hosting.
10. How does P2P hosting impact the gaming experience for console gamers?
P2P hosting can lead to inconsistent gaming experiences for console gamers, as it relies on each player’s system’s network connections and capabilities, which may affect gameplay quality.
11. What role does a Master Server play in Peer-to-Peer gaming?
In Peer-to-Peer gaming, a Master Server acts as a central point for coordinating player connections and game sessions, providing a level of organization and control in an otherwise decentralized network.