The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a powerful suite of compilers for various programming languages, including C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, and Ada.
Many developers consider it an essential tool for their projects because of its excellent support for modern software production standards, efficient code output, and a comprehensive development environment.
Installing GCC on Ubuntu is often a prerequisite for compiling and running C and C++ code in a robust development environment. In addition to code compilation, GCC is a critical component of code production, debugging, and system administration tasks.
In this comprehensive tutorial, we will guide you through setting up the GCC on Ubuntu in four easy ways. We will also show how to access the GCC online documentation page.
Table Of Contents
4 Simple Ways to Install GCC on Ubuntu
Given its importance, it is no wonder that you can use several options to install GCC on Ubuntu. Let’s go through four of the methods in the following sections. Each method caters to different system requirements, from installing the default GCC version available in Ubuntu’s repositories to installing specific versions or even from the source.
But first, let’s take a look at the prerequisites.
The Prerequisites
Before Install GCC on Ubuntu, ensure you have the following:
- A system running Ubuntu 20.04 or 22.04.
- A user account with sudo or root permissions.
Method #1: The apt Package Manager
The apt Package Manager is the simplest approach to install GCC on Ubuntu.
We will discuss two scenarios where you can use apt to install GCC on Ubuntu.
Install the Available GCC Version
Ubuntu’s package repositories contain a recent stable GCC version.
We recommend the following steps where we used the apt install command to install this GCC’s default version.
Start by updating the current server package with the following command:
# sudo apt update
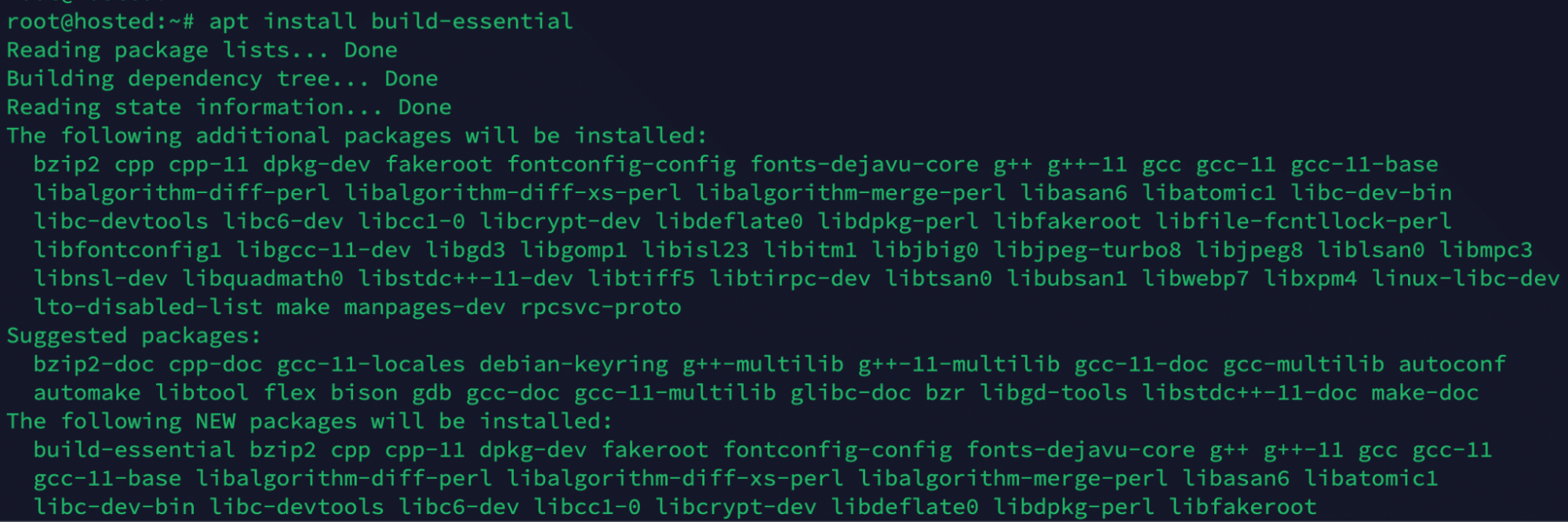
Install GCC by running the following command in the terminal:
# sudo apt install build-essential
The build-essential package includes the GCC compiler and many development and build tools necessary for compiling software.
Finally, verify the installation by printing out the GCC version information:
# gcc --version
Install a Specific Version of GCC
If you need a specific GCC version for your project, you can install it on your Ubuntu system via the apt. For this, simply specify the version and install it via the APT package manager.
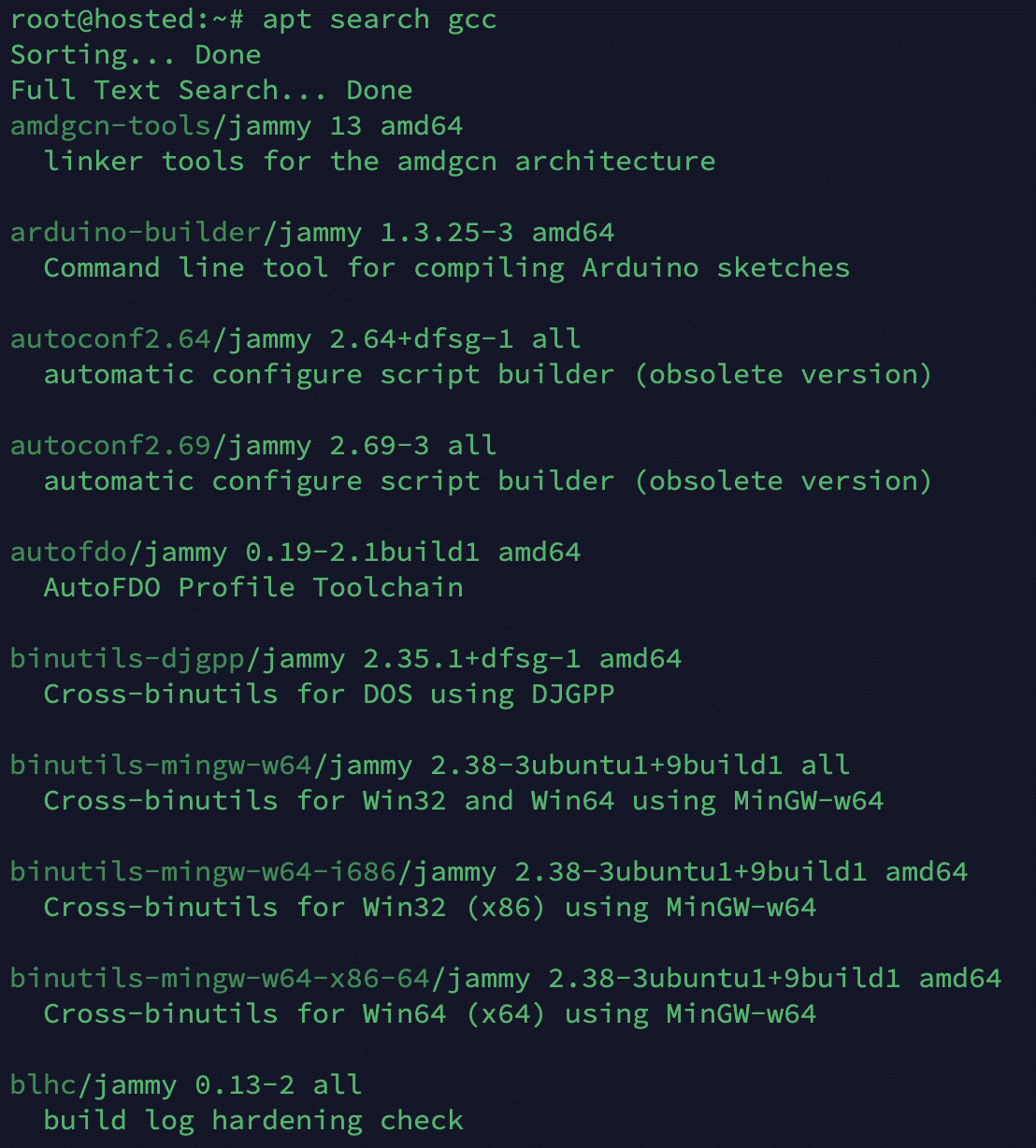
Start by searching for the available GCC versions with the following command:
# apt search gcc
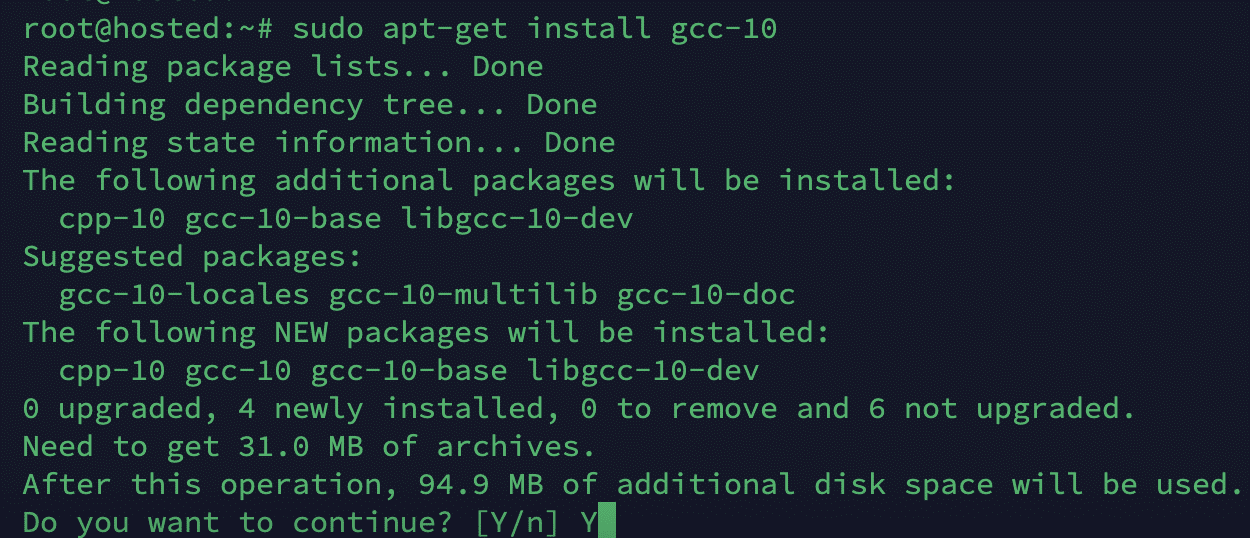
For this demonstration, we will install GCC version 10 on our test system with this command:
# sudo apt-get install gcc-10
Method #2: Use the Ubuntu Software Center
If you prefer the GUI approach, you can use the Ubuntu Software Center and install the currently available GCC version in three simple steps:
- Open the Software Center
- Search for GCC or the development tools
- Click the Install button next to the GCC package you wish to install.
Method #3: Install GCC from Source
If you are a power user and need the absolute latest version of GCC or a specific version of GCC not available in Ubuntu’s official repositories, you can compile and install it from the source.
While the process is more complex and time-consuming than previous methods, you get complete control over the installation process. The major steps in the process are:
- Downloading the GCC source code from the GNU website
- Configuring the build options,
- Compiling and installing the package(s)
Let’s dive into the details of this process.
Download GCC Source
Visit the official GNU GCC releases page (https://gcc.gnu.org/releases.html)
Download the source file for the desired GCC version. You can also use the following wget command to download it directly from the terminal:
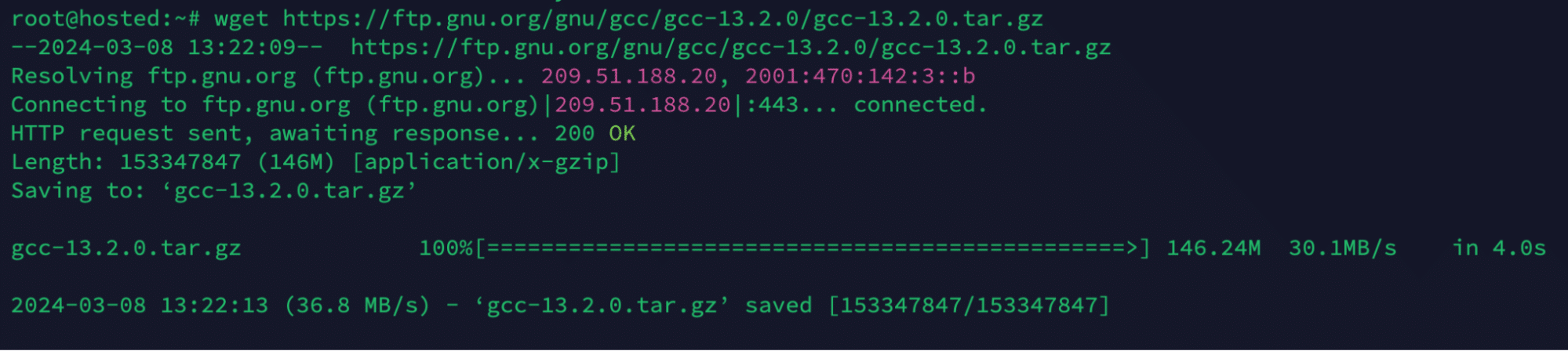
# wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-<version>/gcc-<version>.tar.gz
Replace <version> with the specific version number you want to download. For instance, consider the following command to download version 13.2.0:
# wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-13.2.0/gcc-13.2.0.tar.gz
Extract the Source
Extract the downloaded tarball using the tar command:
# tar -xf gcc-<version>.tar.gz
Change to the extracted directory with the following cd command:
# cd gcc-<version
Replace <version> with the version number you downloaded (version 13.2.0 in this case).
# cd gcc-13.2.0/
Configure
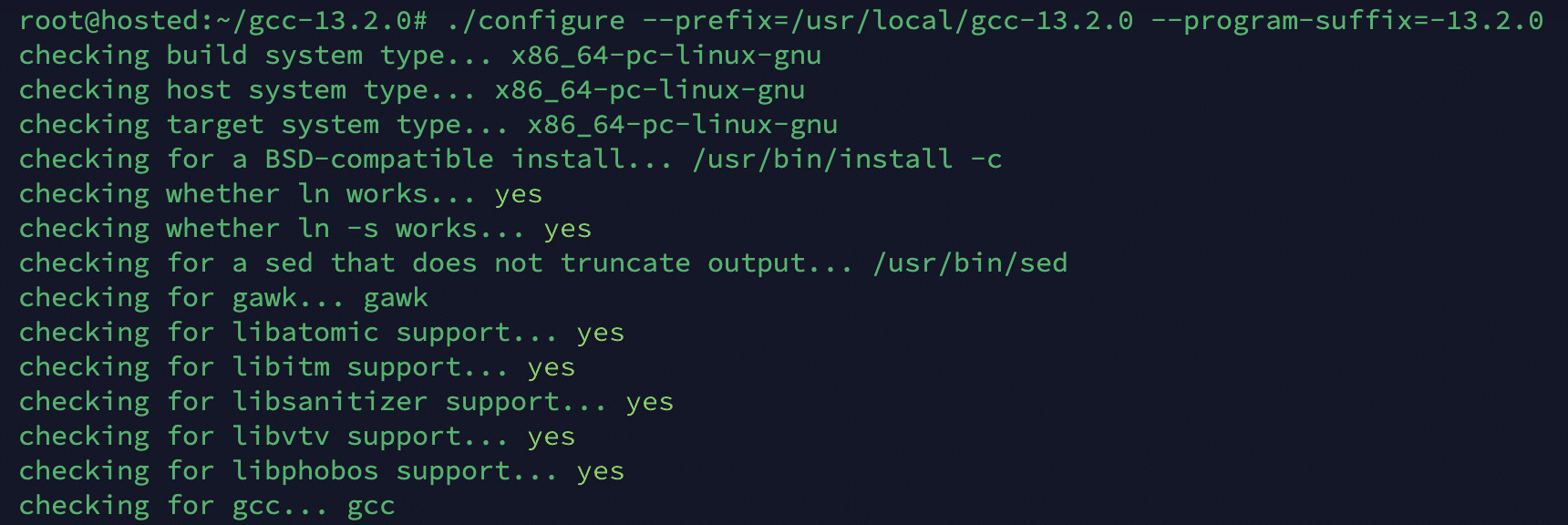
Run the configure script to prepare the build environment:
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/gcc-<version> --program-suffix=-<version>
Replace <version> with the version number you downloaded. So, the command on our test system looks like the following:
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/gcc-13.2.0 --program-suffix=-13.2.0
Build
Now, you can compile the source code using the make command. This may take a while, depending on your system’s resources:
# make -j$(nproc)
Install
Once the build process completes, you can install GCC to the specified prefix directory with the following command:
# sudo make install
Update the PATH Variable
Update your PATH environment variable to include the newly installed GCC binary files. For this, add the following line to your ~/.bashrc or ~/.profile file:
# export PATH=/usr/local/gcc-<version>/bin:$PATH
Next, reload the shell or run source ~/.bashrc to apply the changes.
Verify Installation
Verify the GCC installation by checking its version:
# gcc --version
Method #4: Use Third-party Repositories or PPAs
In some cases, you might need a specific version of GCC that’s not available in the official Ubuntu repositories. In this case, we recommend opting for third-party repositories, specifically Personal Package Archives (PPAs) and Ubuntu toolchain PPA.
However, it is important to be cautious when using third-party sources because of security concerns.
Here are the steps of the process:
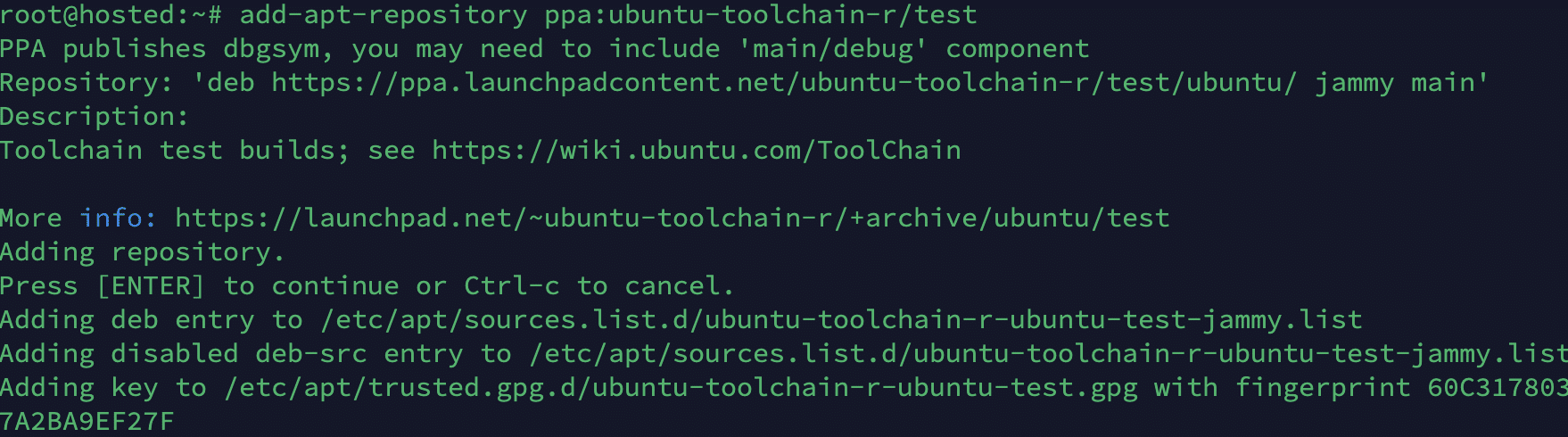
Add the PPA to the System
Launch the terminal and run the following command to add the PPA to the system:
# sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-toolchain-r/test
Press Enter when prompted to confirm adding the PPA.
Update Package List
After adding the PPA, update the package list to include the newly added repository
# sudo apt update
Install GCC
Once the PPA is added and the package list is updated, install GCC by running this command:
# sudo apt install gcc-<version> g++-<version>
Replace <version> with the desired version of GCC.
Verify Installation
Once the installation is complete, verify the version to check GCC installation:
# gcc --version
How to Access the GCC Documentation Page
Excellent documentation is one of the core benefits of using GCC. Developers and other users can access and utilize the documentation to resolve queries and discover specific features and options for your project.
When it comes to the documentation, you have the following options.
Online Documentation
Online GCC documentation comes in the following two flavors:
Official GNU GCC Website
The most comprehensive and up-to-date GCC documentation page is available on the GNU project’s official website. You can visit GCC’s documentation page to find manuals for the current and previous versions of GCC.
This documentation covers various aspects including user guides, installation instructions, and supported language standards.
Specific Version Documentation
If you’re looking for documentation for a specific version of GCC, you can find this directly through a web search or by navigating the GNU GCC website. Each version’s documentation is archived and available for reference.
Local (Offline) Documentation
If you don’t have access to the Internet, you can refer to the offline documentation that comes with Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
Man Pages
Once GCC is installed, you can access the manual pages in the terminal. You can view concise reference manuals for various GCC commands and functions.
To access the GCC man page, run this command:
# man gcc
Info Pages
GNU also provides info pages that offer more details than traditional man pages. If info pages are installed for GCC, you can access them through:
# info gcc
Local HTML or PDF Documentation
Certain installations of GCC, particularly those built from a source with the documentation option, might include HTML or PDF documentation. You can check the installation prefix ( /usr/local) for a share/doc or similar directory, which might contain this documentation.
Finally, we recommend the following command to get a summary of GCC command-line options:# gcc --help
Conclusion
Installing the GCC compiler is essential in setting up a development environment on Linux systems. As a standard compiler, GCC plays a pivotal role in the compilation process, providing developers with a powerful and indispensable tool for building software.
RedSwitches is your global dedicated hosting partner. We offer the best-dedicated server pricing and deliver instant dedicated servers, usually on the same day the order gets approved. Whether you need a dedicated server, a traffic-friendly 10Gbps dedicated server, or a powerful bare metal server, we are your trusted hosting partner.
FAQs
Q. What is GCC?
GCC, or the GNU Compiler Collection, is a suite of compilers for various programming languages, including C, C++, Objective-C, and Fortran. It is widely used in software development for compiling source code into executable files.
Q. How do I install GCC on my system?
GCC can be installed through the package manager of your Linux distribution. For example, on Ubuntu, you can use the command
#sudo apt install gcc.
Alternatively, you can download the source code and compile it yourself.
Q. Is GCC installed by default on Linux systems?
Some Linux distributions come with GCC pre-installed, while others may require you to install it manually. You can check if GCC is installed by running the command in the terminal
# gcc --version.
Q. Can I compile C programs without installing GCC?
No, you need a compiler to translate your C source code into an executable file. GCC is one of the most commonly used compilers for C programming.
Q. Where can I find the list of GCC developers?
The GCC project maintains a list of developers on its official website or through public archives. Information about contributors and maintainers can also be found in the project’s documentation.
Q. Does GCC installation include manpages?
The GCC package usually includes manpages that provide detailed information about compiler commands, options, and usage. You can access them using the man command,
For example,
# man gcc
Q. How do I compile a basic C program using GCC?
Write your C program in a text editor, save it with a .c extension, and compile it using the gcc command followed by the source file name.
For example,
# gcc my_program.c -o my_program.
Q. Can I customize GCC compiler options?
GCC provides many compiler options for optimizing code, specifying target architecture, enabling default language features, and more.
Q. How do I set GCC as the default system compiler?
On Linux systems, you can use the update-alternatives command to set GCC as the default compiler. Consult your distribution’s documentation for specific instructions on using update-alternatives.
Q. Is GCC only available for Linux?
GCC is a cross-platform compiler for various operating systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows. However, its usage and installation process may vary slightly depending on the platform.