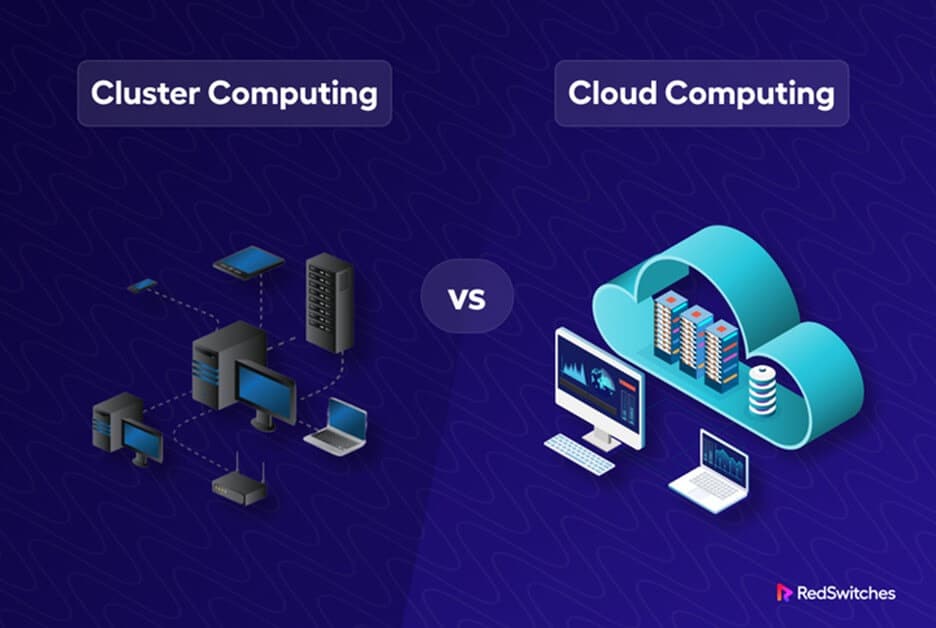
In today’s computing world, two prominent paradigms have revolutionized processing and storing data: Cluster Computing and Cloud Computing. Cluster Computing refers to a group of interconnected computers that work together to perform complex tasks in parallel. Cloud Computing refers to a network of remote servers that provide computing resources over the internet. In this article, we will discuss cluster computing vs. cloud computing in detail.
The differences between cluster computing and cloud computing lie in their architecture, deployment, and management. Cluster Computing is typically used for high-performance computing tasks that require a lot of processing power and memory, such as scientific simulations and data analysis. On the other hand, Cloud Computing is more flexible and can be used for various tasks, including web hosting, data storage, and software development.
Read on to explore the fundamental difference between cluster and cloud computing and their pros and cons. We will also discuss their use cases in modern computing environments for your quick and clear understanding.
Table of Content
- What is Cloud Computing?
- What is Cluster Computing?
- Difference Between Cluster Computing and Cloud Computing
- Key Takeaways
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is a paradigm for delivering computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, software, and applications, over the internet. It enables users to access these resources on-demand, anywhere, and anytime without needing physical infrastructure.
Cloud Computing has transformed how businesses and organizations manage their IT operations, providing greater agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It eliminates the need for businesses to purchase and maintain expensive hardware and software, reducing their upfront and ongoing costs. Instead, they can rent the computing resources they need from Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) on a pay-per-use basis.
Cloud Computing is based on virtualization technology, which allows multiple users to share the same physical resources without interfering with each other’s workloads. CSPs use sophisticated management and automation tools to ensure their cloud services’ availability, security, and performance.
Overall, Cloud Computing has become an essential component of modern computing infrastructure. Thus, enabling businesses of all sizes to innovate, compete, and grow in today’s digital economy.
Also Read: 6 Key Differences: Cloud vs On Premise Computing Revealed!
What is Cluster Computing?
Credit: iStock Photo
Cluster Computing is a computing architecture that connects multiple computers or servers to work together as a single system, whereas interconnected computers in cluster computing work parallelly. They divide the workload of a large task or job and distribute it across the cluster nodes. This allows the task to be completed faster than a single computer.
The main difference between Cluster Computing vs Cloud Computing is that Cluster Computing is typically used for high-performance computing (HPC) applications. These applications require a lot of processing power and memory, such as scientific simulations, data analysis, and complex modeling. Cluster Computing can be implemented using various technologies, including local area networks (LANs), high-speed interconnects, and specialized software such as Message Passing Interface (MPI).
Clusters can range in size from just a few computers to thousands of nodes and can be built using off-the-shelf hardware or customized components. Cluster Computing requires specialized knowledge and skills to design, deploy, and manage effectively. Therefore, making it more suitable for use by expert users and organizations with dedicated HPC teams.
Difference Between Cluster Computing and Cloud Computing
Here is a table showcasing the difference between cloud and cluster computing.
| Factors | Cluster Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Security | Each node in a Cluster Computing system has its security measures. | In Cloud Computing, security is managed by Cloud Service Providers (CSPs). |
| Cost | Cluster Computing requires dedicated hardware, resulting in high upfront costs. | Cloud Computing uses shared hardware resources, resulting in low, upfront costs with a pay-as-you-go model. |
| Resource Sharing | Resources in Cluster Computing are shared within the cluster, making it efficient. | Resources in Cloud Computing are shared across multiple users, making it more flexible. |
| Virtualization | Cluster Computing uses virtualization to partition workloads, which increases efficiency. | Cloud Computing uses virtualization to create multiple virtual machines, which is scalable. |
| Hardware | Cluster Computing requires dedicated hardware. | Cloud Computing uses shared hardware resources. |
| Maintenance | Cluster Computing requires skilled IT staff for maintenance. | In Cloud Computing, CSPs manage maintenance and updates, making it hassle-free. |
| Scalability | Cluster Computing has limited scalability, and adding nodes can be costly. | Cloud Computing is highly scalable and can add resources on demand. |
| Example | Cluster Computing is used for high-performance computing tasks such as scientific simulations, data analysis, and complex modeling. | Cloud Computing is used for various tasks such as web hosting, data storage, and software development, with examples including Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure. |
Key Takeaways
Here’s a quick summary of the entire Cluster vs. Cloud Computing scenario.
- Cluster Computing is a computing architecture that connects multiple computers to work together as a single system for high-performance computing tasks.
- On the other hand, Cloud Computing is a paradigm for delivering computing resources over the internet for various tasks, such as web hosting, data storage, and software development.
- Cluster Computing has high upfront costs and requires dedicated hardware, making it more suitable for expert users and organizations with dedicated HPC teams.
- Cloud Computing uses shared resources, is highly scalable, and has a pay-as-you-go model, making it more accessible and cost-effective for businesses of all sizes.
- Regarding security, each node in a Cluster Computing system has its security measures. Cloud Computing security is managed by Cloud Service Providers (CSPs).
- Resource sharing in Cluster Computing is limited to within the cluster. However, in Cloud Computing, resources are shared across multiple users, making it more efficient and flexible.
Cluster Computing vs. Cloud Computing is a never-ending debate since it all comes down to your needs and budget. However, if you’re looking for someone that can offer you the best of both worlds, we’d like to introduce you to RedSwitches!
RedSwitches is a leading dedicated server hosting and bare metal server provider with years of experience providing businesses with reliable and secure hosting solutions worldwide. Our team of experts is dedicated to delivering top-notch service and support to ensure your business runs smoothly.
To learn more about our services and cloud computing in general, visit our resources page. You’ll find a wealth of information on our offerings and how we can help your business thrive.