In today’s world, IT architecture plays a crucial role in the success of businesses.
But what exactly is IT architecture?
How does it impact an organization’s operations, and what strategies should you implement for sustained support for critical operations?
Whether you’re an IT professional or simply curious about the topic, this article will offer a comprehensive overview of IT architecture, including its definition, various types, and strategies for implementation.
Let’s start with a brief overview of the topic.
Table Of Content
Introducing the Idea of IT Infrastructure
With rapid technological advancements, organizations increasingly rely on multiple technical systems to support their operations.
IT architecture is the foundation for these systems, providing a blueprint that guides IT asset design, deployment, and management. It encompasses the structure, components, and interrelationships of an organization’s technology infrastructure, applications, data, and interfaces.
Understanding IT architecture is essential as it enables businesses to align their IT capabilities with their objectives, optimize efficiency, ensure scalability, and enhance overall performance.
That’s why managers and decision-makers must understand the IT architecture’s definition, types, and strategies. This way, all stakeholders can gain valuable insights to make informed decisions and leverage technology for competitive advantage.
A Brief History of IT Architecture
In technical terms, the IT architecture of an organization is the detailed design of an organization’s information technology infrastructure, including hardware, software, networks, and data storage.
It encompasses the principles, guidelines, and best practices that ensure efficient and effective IT management and operation.
The 1950s: The Hardware-based Beginnings
The history of IT architecture can be traced back to the 1950s when computers were first introduced for commercial purposes. At that time, the primary focus was structuring and designing the hardware architectures based on these early computers. It involved the physical arrangement of components and the organization of data processing systems. The goal was to optimize performance and reliability.
The 1970s: Focus on Resource Optimization
IT architecture underwent a significant transformation as technology advanced in the 1960s and 1970s.
With the advent of mainframe computers, businesses started understanding the importance of diversification and function compartmentalization.
Organizations began to separate different functions and applications into distinct departments to improve efficiency and facilitate scalability. This approach allowed for better resource allocation and ensured the independent operation of various systems.
The 1990s: Leveraging the PC Revolution
The 1980s and 1990s marked a period of competitive positioning in IT architecture.
With the rise of personal computers and the introduction of client-server systems, organizations now have to consider how IT architecture could support their competitive advantage. The focus shifted towards aligning IT strategies with business goals, providing flexibility and agility to stay ahead in the market.
During this era, the concept of modular architecture emerged, enabling organizations to adapt their IT infrastructure quickly and easily to meet changing business needs.
At this point, the focus was on breaking down complex systems into smaller, reusable components, promoting interoperability and scalability. This approach facilitated cost-effective IT management and fostered innovation.
2000s: The Modern Take on IT Infrastructure
The 21st century brought further advancements in IT architecture with the rise of cloud computing, virtualization, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
IT architecture now encompasses hybrid, multi-cloud environments and the integration of various technologies to create synergies and enhance digital capabilities.
State of IT Architecture Today
Today’s IT architecture focuses on providing a seamless and secure user experience while maintaining agility and scalability. It embraces concepts such as microservices, containers, and serverless computing, empowering organizations to leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain.
Understanding the Three Types of IT Architecture
The idea of IT architecture has been implemented in several ways.
Over time, three types have become popular because of their high compatibility with business outcomes.
Let’s discuss these three types in more detail.
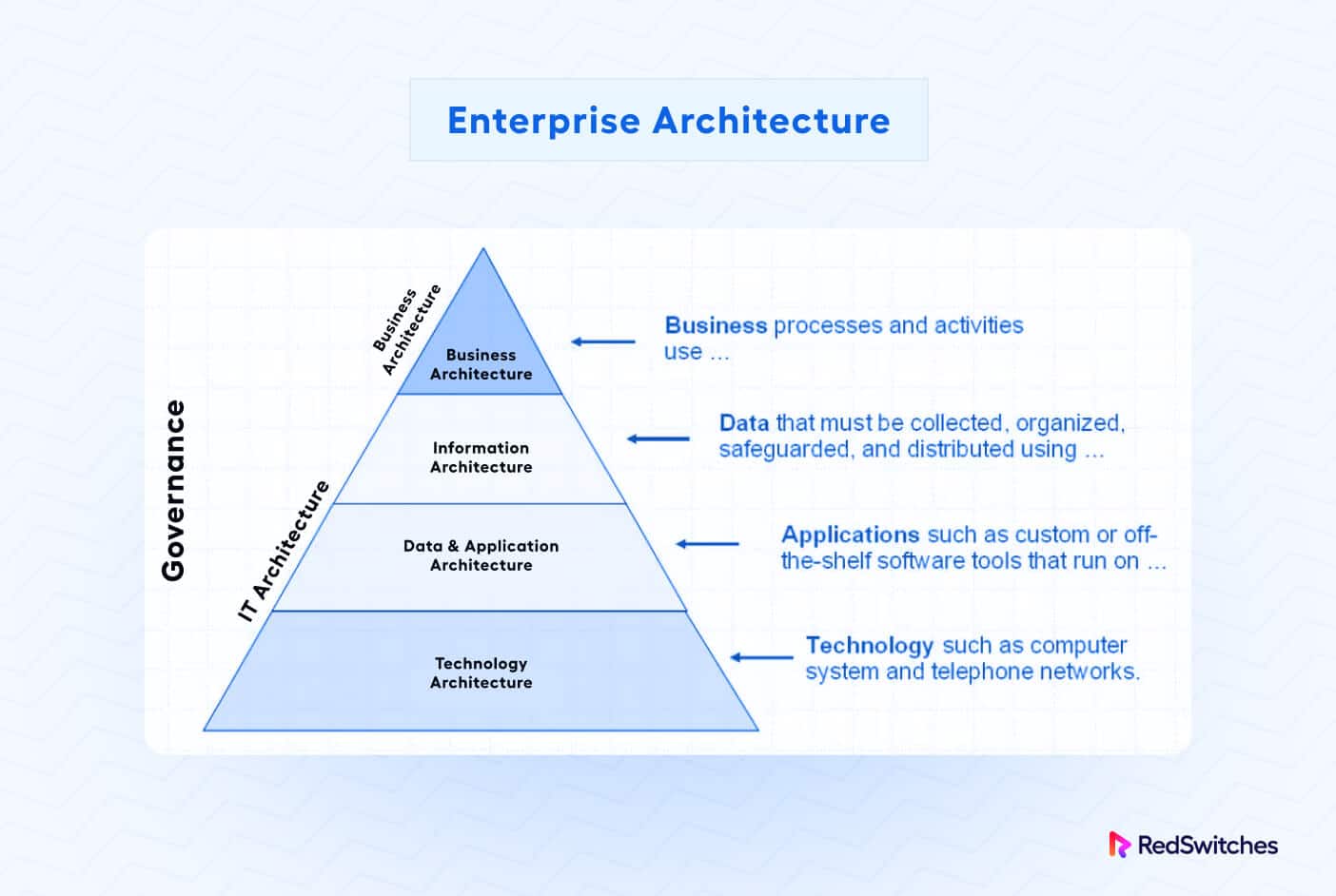
Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise architecture is a comprehensive and strategic approach to IT architecture that focuses on aligning an organization’s IT capabilities with its business objectives and processes.
This idea provides a high-level view of the organization and its various business units, systems, and technologies.
EA aims to optimize the use of IT resources, improve interoperability between systems, and ensure that IT investments are aligned with business goals.
A common implementation of this idea starts with analyzing the current state of the organization’s IT infrastructure and then designing a target state that supports future growth and innovation.
During this process, EA architects work closely with business leaders, IT teams, and stakeholders to create a cohesive IT strategy that spans the entire enterprise.
Solution Architecture (SA)
Solution architecture, also known as application architecture, zooms in on specific organizational projects or initiatives.
It focuses on designing and implementing IT solutions that address specific business problems or requirements.
SA architects work closely with project managers, development teams, and stakeholders to define a solution’s technical requirements and specifications. They consider system integrations, data flows, security, scalability, and performance factors.
Solution architecture ensures that the final deployed solution is aligned with the organization’s overall IT strategy and enterprise architecture principles. This type of architecture is crucial for successful project delivery and ensuring that the implemented solutions meet the expected outcomes.
Technology Architecture
Technology architecture, sometimes called infrastructure architecture, deals with designing and implementing the underlying technology components and infrastructure that support an organization’s IT systems.
This architecture type focuses on hardware, networks, servers, databases, operating systems, and other foundational elements.
Technology architects evaluate and select the most suitable technologies that align with the organization’s overall IT strategy and solution architecture. They ensure that the technology components are scalable, secure, and can support the required levels of performance and availability.
Technology architecture is crucial for building a robust and reliable IT infrastructure that can meet the organization’s current and future needs.
The EA Model for Developing the Best IT Architecture Strategy
A robust IT architecture strategy is crucial for businesses of all sizes. It ensures that a company’s technological aspects are aligned with its overall goals and objectives.
The EA (Enterprise Architecture) model is a practical framework for developing and implementing this strategy.
This model is successful because of the four key components of this model and how they contribute to the development of a sustainable and scalable IT architecture strategy.
Business Architecture
The first step in developing an IT architecture strategy is understanding the business’s objectives and requirements. This involves analyzing the organization’s core functions, processes, and activities. The business architecture defines the organization’s structure, business models, goals, and strategies.
This process helps determine how technology can support and enable the business objectives, ensuring that the IT architecture aligns with the company’s overall direction.
Data Architecture
Data is a valuable asset for any business, and a well-defined data architecture is essential for effective IT management.
Creating and maintaining data architecture involves identifying and organizing data assets, defining data storage and retrieval methods, and ensuring integrity and security protocols.
This component of the EA model helps establish data standards, governance policies, and data integration methods. A solid data architecture enables businesses to manage and utilize their data assets effectively, leading to better decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Application Architecture
The application architecture focuses on designing and implementing software applications that support business functions and processes.
This component includes identifying and selecting the right applications, defining integration requirements, and ensuring interoperability with existing systems.
Application architecture also considers scalability, performance, security, and user experience. By aligning the applications with the business requirements, organizations can optimize their processes, enhance productivity, and deliver value to their customers.
Technology and Infrastructure Architecture
The final component of the EA model is technology and infrastructure architecture. This involves selecting and implementing the appropriate hardware, software, and network infrastructure to support the organization’s IT needs.
Critical considerations include server architecture, network design, cloud computing, security measures, and disaster recovery plans.
A well-designed technology and infrastructure architecture ensures that the IT systems are reliable, scalable, and secure, enabling smooth operations and reducing downtime.
By following the EA model and focusing on these four components, businesses can develop a comprehensive IT architecture strategy that aligns with their goals and objectives. This systematic approach ensures that the organization’s technology investments are optimized for effective resource utilization and enhanced competitiveness.
The Three Best IT Architecture Strategies
Now that you understand the makeup of the Enterprise Architecture strategy, we’ll now discuss the three best IT architecture strategies that businesses can apply to get expected outcomes.
Reconsider Enterprise Architecture Principles
Enterprise Architecture (EA) principles are the fundamental guidelines that govern an organization’s IT architecture.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, it is crucial to reassess and update these principles regularly.
Traditional EA principles often focus on stability, standardization, and control, which may hinder agility and innovation. By reconsidering and modernizing these principles, organizations can embrace flexibility, adaptability, and scalability.
One approach is to adopt a modular architecture, where different components or services are loosely coupled and can be easily replaced or upgraded. This allows organizations to quickly respond to changing business requirements and adopt new technologies without disrupting the system.
Additionally, leveraging cloud computing and virtualization technologies can provide scalability and cost-effectiveness in managing IT infrastructure.
Emphasize User Experience
In today’s digitalized world, user experience (UX) has become critical for organizations to differentiate their products and services from competitors.
The business’s IT architecture should focus on technical aspects and prioritize delivering an exceptional user experience. In practical terms, this means designing systems and applications that are intuitive, user-friendly, and accessible across different devices and platforms.
Organizations can adopt a user-centric approach to ensure their IT architecture aligns with user needs and expectations. UX design principles, such as usability testing, prototyping, and continuous feedback loops, should be integrated into the IT architecture process. This approach enhances customer satisfaction and improves employee productivity and engagement.
Develop a Design-Driven Architecture
A design-driven architecture emphasizes the importance of design thinking in creating IT solutions. It involves understanding user needs, brainstorming creative ideas, and prototyping solutions before implementation. This approach promotes innovation and ensures that IT architecture continues to align with business goals.
Organizations should foster a culture of collaboration and cross-functional teamwork to develop a design-driven architecture.
IT architects should work closely with business stakeholders, designers, and developers to co-create solutions that meet user requirements and solve real-world problems. This collaborative approach fosters creativity and ensures that IT architecture is functional, aesthetically pleasing, and engaging.
Conclusion
IT architecture is a crucial aspect of business success. It involves designing, deploying, and managing IT systems and assets.
Understanding IT architecture allows organizations to align their IT capabilities with objectives and optimize efficiency.
Today, IT architecture aims to provide a seamless and secure user experience.
Set Up Your Modern Cloud IT Architecture With RedSwitches
Opting for a modern cloud IT architecture with RedSwitches bare metal servers offers numerous advantages and flexibility for businesses.
With RedSwitches, businesses have complete control over their infrastructure, including hardware and networking. You can opt for a customized IT architecture policy that optimizes your IT environment.
Our bare metal servers offer high-performance computing power, low latency, and high scalability. Additionally, we offer various customization options, ensuring businesses can tailor their cloud architecture to meet their specific needs.
Contact us now to learn more.
FAQs
Q1. What is IT architecture and design?
IT architecture and design is the process of planning, designing, and constructing the IT systems and infrastructure needed to support an organization’s goals. It involves analyzing user requirements, developing system designs, developing software programs, and implementing solutions that meet those requirements. The goal is to create a reliable, secure, scalable, efficient, and cost-effective system while meeting users’ needs. It also ensures the system aligns with an organization’s strategy and business objectives.
Q2. What is the role of technology architecture?
Technology architecture provides the IT systems and infrastructure that enable organizations to achieve their business goals. It is a critical component of the overall architecture of an organization, providing the foundation for applications and data services. The role of technology architecture involves understanding user requirements, designing IT solutions, developing and deploying software programs, and ensuring that all elements are in line with an organization’s strategy.
Q3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of IT architecture?
The advantages of IT architecture include increased efficiency, improved scalability, better security and reliability, cost savings, and greater flexibility. The IT architecture enables businesses to achieve their goals by providing the necessary systems and infrastructure to support their operations. It also helps organizations stay competitive by enabling them to adapt to changing conditions in the marketplace quickly. On the other hand, IT architecture can be complex and expensive and requires a considerable amount of time and effort to implement correctly. It also requires ongoing maintenance and support to remain current with the latest technology trends.