Wherever a support engineer or sysadmin starts working on a CentOS-powered system, the first thing they check CentOS version of the operating system.
While it may appear a trivial detail compared to the actual troubleshooting, this simple piece of information determines the direction of the problem resolution.
How to check the CentOS version is crucial for ensuring compatibility with installed software packages, performing system updates, and reporting bugs.
In this tutorial, we will discuss several methods to check the CentOS version from the command line.
Table of Contents
- How to Check the CentOS Version Using the Command Line?
- The Prerequisites
- Method #1: Use the lsb Command for Revealing CentOS Linux Release Details
- Method #2: Check the CentOS Version Using the hostnamectl Command
- Method #3: Check CentOS Version via RPM
- Method #4: Inspect the CentOS Version via the Release File
- Method #5: View Full Release CentOS Version
- Method #6: Determine Linux Kernel Version in CentOS
- Conclusion
- FAQs
How to Check the CentOS Version Using the Command Line?
Let’s start with the prerequisites for checking the CentOS version on a system.
The Prerequisites
To effectively check the CentOS version, ensure you have:
- A system with CentOS.
- Access to a terminal window or command line interface (accessible via Ctrl-Alt-F2).
Method #1: Use the lsb Command for Revealing CentOS Linux Release Details
The Linux Standard Base (lsb) initiative, a collaboration among various Linux distributions, aims to unify the structure of software subsystems in the participating Linux distributions. Within this framework, the lsb_release command is a key option for revealing detailed information about the CentOS version installed on the system.
In many cases, lsb tools aren’t available by default. So, you must first install the necessary package before you can use the lsb commands to check the CentOS version.
Execute the following command to install the lsb core package:
# yum install redhat-lsb-core
Enter your root password when prompted to authenticate the installation process. Subsequently, press Y and Enter to approve and proceed with the installation.
Once installed, you can retrieve the CentOS version details by running the following command:
# lsb_release -d
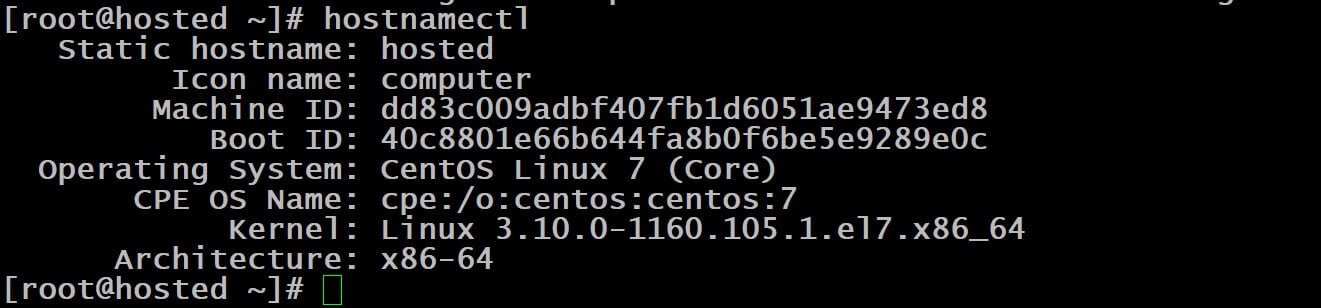
Method#2: Check the CentOS Version Using the hostnamectl Command
From version 7 onwards, CentOS supports the hostnamectl command. This command queries and modifies the system’s hostname and related settings. It retrieves information from files such as /etc/centos-release, including the output of the uname -a command.
This command displays the CentOS version information and the details of the Linux kernel currently in use on the system.
Simply execute the following command to access this information:
# hostnamectl
Method #3: Check CentOS Version via RPM
RPM is an open-source package management system. Originally developed for RHEL, it is now used by all current RHEL versions and derivatives. It’s a vital tool for managing software packages on distributions derived from RHEL.
You can use the rpm command to see the complete package name along with the release version of the CentOS active on your system.
Run the following command on your CentOS system:
# rpm -qa centos-release
Method #4: Inspect the CentOS Version via the Release File
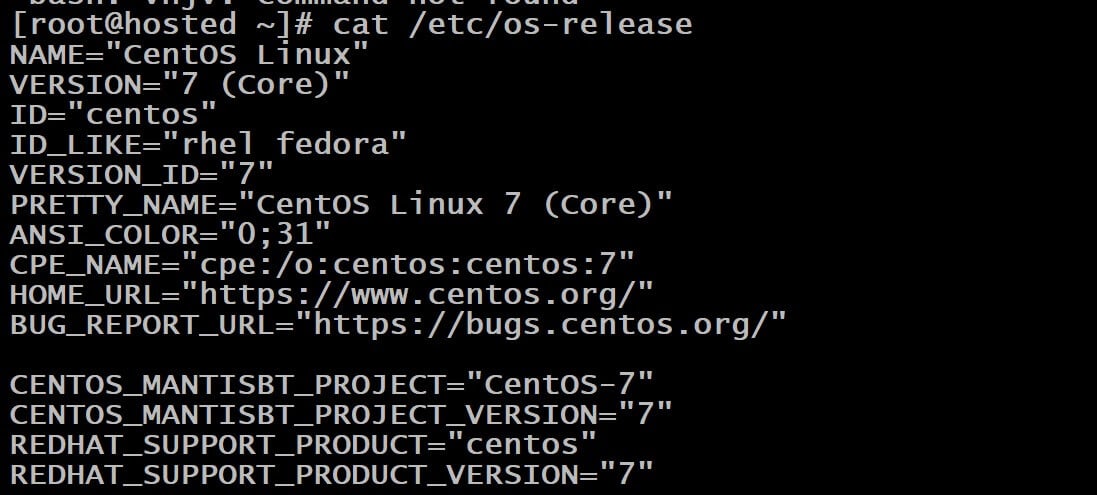
You can examine the release file to identify the specific Linux distribution and its major release version installed on your system. This is done through a simple command that reads the content of the file:
# cat /etc/os-release
Executing this cat command will display the details of the OS, including the CentOS version and other relevant information. The output provides a clear view of the major and minor CentOS versions on your system.
Method #5: View Full Release CentOS Version
CentOS maintains a dedicated file containing the version information about the currently installed operating system. You can use the cat command to print out the contents of the centos-release file in the terminal to see this information.
# cat /etc/centos-release
This output includes detailed information about the CentOS release version, such as:
- Major release number
- Minor release number
- Asynchronous release number
Method #6: Determine Linux Kernel Version in CentOS
Knowing the version of the Linux kernel your CentOS system is running can be just as essential as knowing the distro release version of the operating system. To discover the kernel release version, you can utilize the uname command:
Conclusion
Checking the default with CentOS versions from the command-line is a straightforward process. We outlined six command line methods of getting this information. We also suggest checking the system information in the GUI to get the CentOS version information.
RedSwitches helps customers by offering customizable bare metal servers. If you’re searching for a reliable server infrastructure for your projects, we provide competitive, dedicated server pricing and ensure swift delivery, typically on the same day of order approval. Whether you require a dedicated server, a traffic-friendly 10Gbps dedicated server, or a high-performance instant dedicated server, we are your trusted hosting partner!
FAQs
Q. What command should I use to check the CentOS version using the Linux Standard Base (LSB) method?
To check the CentOS version with LSB, use the command lsb_release -d.
Q. Can I find out my CentOS version using the hostnamectl command?
Yes, the hostnamectl command can find the CentOS version, especially in CentOS 7 and later.
Q. How do I check the CentOS version using RPM?
To check the CentOS version using RPM, execute rpm -qa centos-release.
Q. Can the CentOS version be viewed directly from a release file?
Yes, you can view the CentOS version from a release file by running
cat /etc/centos-release.
Q. How can I check the Linux kernel version on my CentOS system?
Use the command uname -r to check the Linux kernel version in CentOS.
Q. What details will the lsb_release -d command show about my CentOS system?
The lsb_release -d command will display the specific release information for your CentOS operating system.
Q. Does the hostnamectl command provide additional system information besides the CentOS version?
Yes, hostnamectl shows the CentOS version and other system details like the hostname and kernel version.
Q. What is the significance of checking the CentOS version with RPM?
Checking the CentOS version with RPM helps you understand the specific package version installed on your system.
Q. What information will it provide if I use cat /etc/centos-release?
The cat /etc/centos-release command will provide you with the full release version of your CentOS operating system, including primary and minor release numbers.
Q. Why is it important to know the Linux kernel version in CentOS?
Knowing the Linux kernel version in CentOS is essential for compatibility, security, and troubleshooting purposes.