Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage and store data. Two popular cloud computing models are single-tenant and multi-tenant. They may sound similar, but they offer different features and benefits depending on the business. You may ask, “What is a tenant in cloud computing?” They’re the user.
Understanding single and multi-tenant models’ differences is crucial in choosing one that meets your business’s computing requirements. Single-tenant offers a dedicated server for a single user, providing more control and customization. On the other hand, multi-tenant allows multiple users to share the same server resources, making it more cost-effective and scalable.
The choice between the two depends on the organization:
- Size,
- Workload,
- Level of security required.
This article will discuss tenancy in cloud computing, compare single and multi-tenant models, and weigh their benefits and drawbacks. Look at how RedSwitches’ bare metal servers provide better performance and security for both environments.
- What Is Single Tenant in Cloud Computing?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Single Tenant
- What Is Multi-Tenant in Cloud Computing?
- Types of Multi-Tenant Architecture in Cloud Computing
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Multi-Tenancy
- Multi-Tenant Examples
- Difference Between Single and Multi-Tenant
- Dedicated Hosting and Bare Metal Servers in Multi-Tenant Environments
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
What Is Single Tenant in Cloud Computing?
In cloud computing, a single-tenant refers to a deployment model where a single customer uses dedicated computing resources that are not shared with other customers.
It means the customer has exclusive access to the infrastructure, applications, and data and can customize and configure the resources according to their needs.
Organizations with high-security requirements often prefer using single-tenancy, as it provides better control over data privacy, security, and performance.
Understanding “what is a tenant in cloud computing” is crucial since it helps you know the types of tenants and their applications.
Characteristics of Single Tenant
The following are some characteristics of a single tenant in cloud computing:
- Resource allocation: The client has complete control over the server’s computing resources, which means they can allocate resources per their needs.
- Isolation: The environment provides high isolation levels as the client has exclusive access to the server’s resources.
- Security: The single-tenant architecture reduces the security risk and allows the client to implement security measures.
- Customization: It allows the client to customize the server’s configuration, including the operating system, software, and security settings.
- Scalability: The client can scale it vertically by adding more resources to the server as per their requirement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single Tenant
Pros
- Improved security due to the architecture’s singular client focus.
- High isolation levels make it suitable for applications that require dedicated resources.
- It allows the client to customize the server’s configuration, including the operating system, software, and security settings.
- It performs better as the client can access the server’s resources.
Cons
- It’s expensive as the entire server or a cluster of servers gets dedicated to a single client, meaning the client has to bear the entire server cost.
- It’s only scalable vertically by adding more resources to the server, but it is challenging to scale horizontally.
What Is Multi-Tenant in Cloud Computing?
A multi-tenant architecture in cloud computing refers to a deployment model where a single instance in cloud computing serves multiple customers or tenants. They share a common infrastructure, including virtual machines, storage, and networks. In this model, the system dynamically allocates and shares resources among multiple users while providing high isolation and security between the tenants.
Characteristics of Multi-Tenant
- Resource sharing: Resources get shared among multiple tenants, improving resource utilization and cost efficiency.
- Scalability: Dynamic provisioning and resource sharing among tenants handle usage spikes and increase the scalability of multi-tenant architectures in cloud computing.
- Customization: Multi-tenant architectures allow for the customization of applications and services to meet each tenant’s unique needs.
- Performance: Multi-tenant architectures in cloud computing can optimize and share resources efficiently among tenants, offering high performance.
- Centralized management: Centralizing management reduces administrative overhead and improves operational efficiency for multi-tenant architectures in cloud computing.
The Importance of Multi-Tenancy
- It enables better resource utilization and cost efficiency by sharing resources among multiple tenants.
- Multi-tenancy provides scalability to handle spikes in usage.
- It customizes applications and services to meet each tenant’s unique needs.
- It ensures high levels of isolation and security between tenants.
- Multi-tenancy centralized management reduces administrative overhead and improves operational efficiency.
Types of Multi-Tenant Architecture in Cloud Computing
There are three main types of cloud computing multi-tenant architecture:
1.Single Application, Single Database
In this architecture, a single application instance serves multiple tenants, but all tenants share a single database. The developers separate the data logically by adding a tenant identifier to all database records. This architecture is suitable for small to medium-sized applications with few tenants.
2.Single Application, Multiple Databases
In this architecture, each tenant has its database, but they all share a single instance of the application. This approach provides greater flexibility and scalability than the single application and database model but also requires more resources.
3.Multiple Applications, Multiple Databases
In this cloud computing multi-tenant architecture, each tenant has its instance of the application and its database. This approach provides tenants with the greatest level of isolation and customization but also requires the most resources and management overhead. This architecture is suitable for large-scale, complex applications that require a high degree of customization and scalability.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Multi-Tenancy
Pros
- It offers cost-efficient resource utilization.
- Cloud computing multi-tenant architecture has the scalability to handle spikes in usage.
- Users can customize applications and services.
- It offers centralized management.
- Users enjoy the flexibility to meet changing business needs.
Cons
- There are security risks if not implemented properly.
- Tenants have limited flexibility to make changes to the underlying infrastructure.
Multi-Tenant Examples
Multi-tenant architecture in cloud computing is typical in Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications that offer various services to multiple users. Some examples of SaaS multi-tenant applications that use different types of virtualization include:
- Dropbox: A cloud storage and file-sharing service that serves millions of customers from a shared infrastructure.
- Microsoft Office 365: It offers a suite of productivity tools and services shared among multiple customers from a single infrastructure.
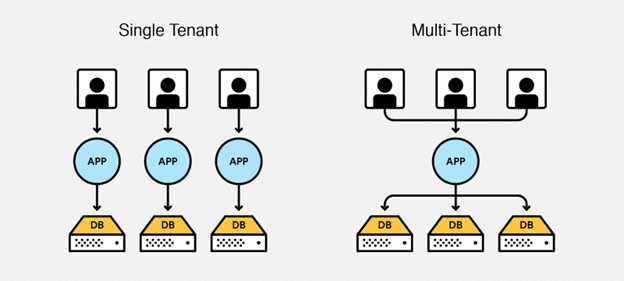
Difference Between Single and Multi-Tenant
Image Source: Igloo
As we dive deeper into server tenancy in cloud computing, here’s a table that compares single-tenant with multi-tenant models:
| Multi-Tenant | Single Tenant | |
| Tenant |
|
|
| Customization |
|
|
| Cost |
|
|
| Data Isolation |
|
|
| Maintenance |
|
|
| Security |
|
|
Although multi-tenant systems are more scalable and cost-effective overall, they may need additional layers of protection to prevent data breaches. Which one is better between two? Well, that depends on the program’s requirements and users.
Dedicated Hosting and Bare Metal Servers in Multi-Tenant Environments
Dedicated hosting and bare metal servers are two hosting alternatives to multi-tenant cloud infrastructures. Users in a multi-tenant cloud environment share infrastructure components like servers, storage, and networks. Bare metal servers and dedicated hosting, on the other hand, give their customers access to resources that aren’t shared with anybody else.
What Are Bare Metal Servers?
Bare metal servers are standalone physical servers housed in a data center and used exclusively by one client. They give users greater customization freedom by providing access to all hardware components. Applications that require high performance, low latency, and complete hardware control are ideal for this type of hosting.
What’s Dedicated Hosting?
When a customer hires a server from a hosting company, the server is set aside exclusively for that customer’s usage. Users can do whatever they choose with the server, including installing and configuring software. However, the host is responsible for handling hardware updates and repairs. Applications that need dedicated resources yet do not require root access to the hardware benefit most from this form of hosting.
How to Integrate Them With Multi-Tenant Environments
Users in a multi-tenant cloud environment share resources with other users, resulting in performance issues, security worries, and restricted customization possibilities. The good news is that users can build hybrid cloud systems by integrating bare metal servers and dedicated hosting with multi-tenant environments.
For example, one can use a bare metal server for a high-performance database application while using a multi-tenant architecture for web servers. Combining these two approaches allows the customer to maximize the cloud’s scalability and adaptability without sacrificing speed or expense.
The same user can employ dedicated hosting for mission-critical software that needs its resources, while other apps can run in a multi-tenant environment. The user can take advantage of a multi-tenant environment’s cost savings and scalability. Also, while still giving the dedicated server’s resources to the mission-critical application.
To summarize, bare metal servers and dedicated hosting users can access resources not shared with other customers. By merging these solutions, customers can build hybrid cloud environments that provide the best of both worlds.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing has two different models: single-tenant and multi-tenant.
- Users share the same server resources with multi-tenant, while in single-tenant, each user has their isolated server.
- Multi-tenant is more economical and scalable, whereas single-tenant provides more control, flexibility, and security.
- Multi-tenant is best for companies with fluctuating workloads and limited budgets, whereas single-tenant is ideal for companies with strict security or compliance regulations.
- The organization’s size, the workload’s nature, and the desired level of security are all considerations when settling on a model.
- Weigh the benefits and downsides of each model before making a final choice.
As a cloud services provider, RedSwitches understands that each business will have its requirements for using the cloud. That’s why we offer customized solutions for both single-tenant and multi-tenant environments. Our bare metal servers provide superior performance and security over virtualized environments, making them perfect for mission-critical applications.
Choosing RedSwitches means you get a reliable and efficient cloud computing experience with flexible pricing options and omnichannel support. Plus, our USPs separate us from our competition, and we ensure that our clients get the best value for their money. Take advantage of the opportunity for a high-performing and secure cloud computing environment for your business.
Check out our resources section to learn what is a tenant in cloud computing and our product offerings. When the best is available, don’t settle for less.
FAQs
Who Can Be Called a Tenant?
Tenants are customers who pay for cloud computing services from a cloud provider. One user, several individuals, or an entire business organization could fit this description.
What Is the Difference Between Tenant & Lessee?
The main difference is that with cloud computing, a tenant is any individual or business that has subscribed to and is making independent use of a cloud service. In a cloud computing setup, the responsibility for setting up and maintaining the tenant’s virtual resources falls on the tenant. A lessee is a person who has leased or rented physical property.
Is Domain a Tenant?
You can think of a domain as a tenant in some cloud computing platforms. A domain is a logical grouping of resources and people within the cloud environment that’s separated and dedicated to a specific client or company in these systems. In Microsoft Azure, for instance, a domain is a tenant in Azure Active Directory (AAD), the service Azure uses for cloud-based identity and access management.